The modern Russian lighting market is diverse. Manufacturers predetermine the optimal characteristics for each element at the design stage of lighting devices. Light sources (lamps) are no exception. Choosing the appropriate bulb shape, base type or lamp power for a particular lamp is not difficult. It is much more difficult for the consumer to decide on the type of light source: energy-saving or LED.
This issue can be resolved both by comparing the advantages of the common structural elements of energy-saving and LED lamps, and by determining the pros and cons of their additional operational parameters.
Design Features
The only structural element that unites all types of lamps is the base. Otherwise, the design differences between energy-saving devices and LED devices are significant.
All such devices are divided into three types:
- Incandescent. Base: tungsten filament; vacuum flask, usually containing an inert gas composition.
- Gas discharge.
- LED.
Only gas-discharge and LED light sources are considered energy-saving.
The glow of gas-discharge lamps is realized through an electric discharge in metal or gas vapor. Gas dischargers can be divided into:
- High pressure lamps. There are sodium, mercury and metal halide. This type is optimal for outdoor lighting.
- Low pressure lamps. This type includes fluorescent light sources. The main structural element is an electrode tube, which is filled with argon and mercury gas vapors. The inside is coated with phosphor. For it to glow, a short-term high-voltage discharge must hit the spiral. If there is low voltage in the electrical network at home, the lamps may light up problematically (not immediately and dimly or not light at all). They are used for both internal and external lighting of a house or apartment.
When you need to choose which light bulbs are better for your home: LED or energy-saving ones, the latter means fluorescent devices.
A modern alternative to the types of lamps described above are LED devices. Such lighting elements, due to their design, are characterized as:
- energy saving;
- environmentally friendly;
- durable, resistant to mains voltage surges.
A minor drawback is the cost of LED lamps. The technology for their production is new, not yet modernized, and therefore quite expensive. The return on one-time costs for their acquisition is almost 100%, due to their durability and cost-effectiveness.
Design features of LED sources:
- The principle of using light flux. The light emitter is an LED or a group of them. Such a diode element converts electric current into light by flowing current through a special crystal (semiconductor).
- The light-emitting element of the diode family converts electrical current into light by passing it through a semiconductor crystal. A significant advantage is that current is passed only in the required direction.
- The light emitter can be either in an open design or placed in a special flask.
Such light emitters are much more resistant to mechanical stress, in contrast to a similar element of fluorescent lamps (an electrode tube with mercury and gas vapor).
Differences in the design of CFL (compact fluorescent lamp) and LED light bulbs are one of the main parameters of technical and operational characteristics, allowing you to determine how they differ. Their cost-effectiveness is also important.
Low pressure sodium lamps (LPNS)
These are the brightest light sources, with a luminous efficiency of 200 Lm/W. The principle of operation of the device: sodium vapor, passing an electric current through itself, begins to glow yellow-orange. The internal flask of the NLND is made of borosilicate glass, resistant to aggressive environments.
Positive traits:
- high light output;
- long service life reaching 28,000 hours;
- comfort of color radiation;
- wide range of operating temperatures, from – 60 to + 40 degrees Celsius;
Negative qualities:
- presence of mercury;
- Explosion hazard; contact with air may cause fire;
- inertia when turned on;
- complexity of connection and maintenance;
- low level of color rendering;
- increased pulsation of light flux in the network 50 Hz;
- high ignition voltage and even higher when restarting;
- increase in power consumption during operation.
Despite the fact that low-pressure sodium lamps can shine brighter than others, and in terms of efficiency they are in first place, they are used only in places where people temporarily stay, illuminating:
- open spaces, streets, highways,
- tunnels, sports facilities, squares,
- architectural structures, airports.
NLND is used in automobile fog lights to improve visibility on roads, in warehouses and in other places where high color rendering is not necessary.
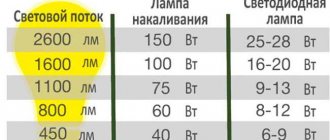
Luminous flux: which lamps are more economical
Most consumers are guided by this very criterion when choosing fluorescent or LED lamps. The difference in economics and electrical efficiency of these two types can be determined by comparing them in terms of energy consumption and operational efficiency with traditional incandescent lamps.
The most important indicator, without which it is impossible to make such a comparison, is the luminous flux. This parameter determines how light it will be in the room of the house or apartment. Measured in Lm (lumens; lm). The higher the luminous flux of a lamp, the brighter the room will be during its operation. Over time, this value may decrease.
Almost all manufacturers of energy-saving and LED light bulbs indicate on their packaging that the main operating parameters of their lamps correspond to the same characteristics of incandescent lamps.
Based on the average values of similar performance characteristics of most common lamp models and manufacturers, an analysis was made of the efficiency and economy of electricity consumption in relation to the luminous flux value. The results of such a comparison are shown in the table.
Based on the tabular data, you can easily determine that LED light bulbs are much more economical and have better quality of operation compared to similar energy-saving ones.
Which light bulbs are best for home use?
Experts advise using LED lamps for all types of lighting at home, with the exception of task and diffused general light. It is better to buy high-quality light bulbs from well-known manufacturers to avoid possible damage to vision.
Even at an expensive price, it is better to choose LED bulbs due to their excellent payback and long service life. Their quality depends on the developer.
LED light bulbs. Photo by AliExpress
Usually they are not thrown away because they can be easily repaired, unlike ESL (a burnt-out LED can simply be short-circuited or another one installed), which will not affect the functioning of the lamp. This feature is another advantage of LED lamps.
LED lamps are superior to energy-saving lamps in all respects:
- pear-shaped bulb with a matte shade;
- the price in the basement segment is comparable to ESL;
- light output is twice that of fluorescent lamps and 10 times higher than that of incandescent lamps;
- service life 30-50 thousand hours;
- environmentally friendly;
- do not heat up;
- The diffuser is made of plastic, not glass.
All technical parameters confirm the advantages of LED. However, the choice remains with the consumer, because Not everyone has the opportunity to immediately pay for a diode source.
In conclusion, watch the video about which light bulbs to choose for your home:
LED lights
What are some ways to save energy in a private home?
What is it: economy windows? Greater energy savings occur when they are facing which way?
Efficiency
The efficiency of the light bulb is also indicated by the ratio of the luminous flux to the operating power of the lighting element. This value isolates a certain set of indicators and is called efficiency (efficiency factor) or “luminous efficiency”. Measured in lm/W. The higher the indicator, the more economical the lamp operates.
For an incandescent lamp this value is very low - less than 10 lm/W, therefore, it has a very low luminous efficiency. This is its most significant drawback. For comparison: the average efficiency of an ice lamp is 90%; for most energy-saving ones it is below 90%.
To make it easier to make a choice, it is worth considering how else these types of lamps differ.
Energy-saving lamps
The boom for these products passed several years ago. Energy-saving lamps are available in three shades of light:
- cold (blue);
- warm (yellow);
- day.
However, the light is significantly different from daylight, so they very soon began to attract a lot of criticism. Given the stated proportions that a 25 watt lamp will produce 150 watts of light, at best one could expect a brightness of 120 watts. Many noted the dimness of the light, which cannot but be called a disadvantage of this option. If you choose energy-saving products of good quality, for example, from the well-known company Philips, it is worth considering that such light bulbs are quite expensive.
Energy-saving lamps are more economical, which allows them to be used for a longer period. If a regular incandescent lamp burns for 1,000 hours, energy-saving products can last five times longer. The specific service life depends on the manufacturer.
Comparing popular light sources
Comparison of quality indicators of light sources
The fundamental differences in the main parameters of such characteristics should be summarized by highlighting the most basic criteria. Namely:
- Brightness. This parameter is also called luminous intensity. Measured in cd (cd). Information about this indicator is found on the packaging of lamps intended for non-home use. This is an important criterion when choosing an artificial source for the “running lights” of cars.
- Colorful temperature. Also called color rendering index, color temperature. It is measured in K (kelvins). The base is an indicator of the hue of the source color, which can be divided into:
- warm color. It is indicated on the packaging by numbers from 2700 K to 3300 K. This shade is comparable to the diffused color of the sky at sunset;
- daytime or natural color. Designated 4000 K; 4200 K. Compare with the shade of a dim sky;
- cold. The packaging indicates 5000 K.
To determine the priority in this choice, it is also worth considering the difference in the sizes and shapes of the lamps.
Energy-saving lamps
They are also called “compact fluorescent”. That’s how it is: the principle of operation is the same, but the dimensions are smaller. Miniaturization was possible due to the fact that a long lamp was twisted into a spiral or folded several times.
The rest remains unchanged: the tube inside is coated with a phosphor, filled with gas, and at the ends there are two electrodes that are heated during startup. Inside the base there is a control circuit and elements of its power supply.
Advantages of energy-saving lamps
With the same luminous flux, energy-saving bulbs consume less power than incandescent bulbs, but LED bulbs are even better in this regard. The service life of a high-quality energy-saving lamp, under equal conditions, exceeds the service life of an incandescent lamp. Selecting the shade of light output:
- warm white
- corresponds to light from an incandescent lamp (color temperature - 2700 K); - white
- almost never used at home (3300-3500 K); - cool white
- has a faint blue tint (4000-4200 K); - daytime
- corresponds to the glow of powerful fluorescent lamps (6000-6500 K).
Typically, warm light is used for the home, and cool light for the office. The price of energy-saving light bulbs is lower than LED ones.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=XaDwd_kDHBI
Disadvantages of energy-saving lamps
Energy-saving lamps do not like frequent switching. In this regard, they are not recommended for use in places where lights are often turned on for a short time. For a home, this is a corridor, a bathroom, a toilet. Optimal operating mode: turn on the light for at least 5-10 minutes, with breaks of more than 5-6 minutes. They do not immediately show the full brightness of the glow; for some time they shine dimmer. There are models that turn on with a slight delay. Energy-saving light bulbs require ventilation. Inside hermetically sealed lamps, their service life is sharply reduced; this is also facilitated by changes in temperature and air humidity. They don't light well in the cold. Like fluorescent ones, they need to be disposed of, but collection points are very difficult to find. The lamps contain mercury, which, if damaged in the premises of a residential building, must be neutralized. Not all models meet the requirements for the luminous flux pulsation coefficient. Depending on the control scheme, it varies widely and for some models can reach up to 60%. These flickers are not visible, but have a detrimental effect on the human body, causing fatigue and decreased performance. It is impossible to measure the ripple factor at home. As the phosphor wears out, infrared and ultraviolet radiation appears in the emission spectrum. It is impossible to adjust the brightness of the light with a dimmer. Dimmable versions are available, but adjusting their brightness is not effective.
Appearance: base type
The perception of interior design largely depends on the quality of lighting in the room. A correctly selected lighting option will highlight the advantages of the interior and hide the shortcomings. An important aspect, without which it will not be possible to implement such a design move, is the choice of a suitable shape and pleasant appearance of lamps for modern lighting fixtures.
Having decided on the type of light bulb, a person pays attention to the type of base. They are:
- Standard or screw. The most common in everyday life are E14 (minion) and E27. The number indicates the diameter of the base. There are no installation features provided. Light bulbs with sockets of type E40, E27 or E14 are allowed to be mounted in standard incandescent lamp sockets. The E27 base has a thread of 27 millimeters, and the E14 has a reduced thread of 14 millimeters.
- Pin. In everyday life they are not used as often as screw ones. Pin contacts are more often used in luminaires of modern lighting options. The marking of the cartridge is very important.
The number that follows the letter marking of this type of base is the distance between the pins, indicated in millimeters (GU4 or GU5.3, etc.).
After selecting the base, the type and size of the lighting electrical elements is selected. LED and halogen lamps have a more original shape (candle, ball) and beautiful design. Luminescent ones can only have the shape of a spiral or tube.
The best price/quality LED light bulbs for the home
OSRAM Led Star Classic 827 FR, E27, A60, 9.5 W
Many are still convinced that the products of world leaders (OSRAM, Philips) are very expensive. Today this is not entirely true: look, for example, at the Star Classic lamp series from OSRAM. You can buy one for less than 100 rubles, with a power of 9.5 W and a service life of up to 15,000 hours. Warm white light is suitable for both the bedroom and rooms such as a corridor or office.
ERA B0020629, E27, P45, 6 W
An inexpensive LED light bulb from ERA can last 25,000 hours. Its power is only 6 W, which corresponds to 40 W of an incandescent lamp. For the most part, it is convenient for installation in the toilet, since, for example, when visiting this room at night, it does not hurt the eyes too much. It can also be screwed in to illuminate closets, closets and other rooms where people are relatively rare.
Its average price in stores is 50 - 60 rubles. Over a long service life, it will pay for its price in full. It fits a regular cartridge, which “accepts” bases with a diameter of 27 mm.
Lightstar E27 G95 13W 4200K
The 13-watt balloon-shaped LED bulb is suitable for illuminating a room in a house up to 20 m2. The lamp is made in Italy, which the manufacturer claims, speaking about its high quality. The frosted bulb has a pleasant warm light (as close as possible to daylight). One of its main advantages is the ability to connect a dimmer. A dimmer is a regulator of the power of a light bulb in a home lighting system, which allows you to change the brightness to suit your needs.
Lightstar products appear from time to time in television programs such as “Housing Question” and “Repair School”. The lamp life is 20,000 hours - not the longest for LED models, but it pays for its cost.
REV 32421 8, E27, 50W
A powerful German-made LED lamp of 50 W (equivalent to an incandescent lamp of 400 W) is intended for lighting repair boxes or a small home workshop. Fits standard cartridge. The bulb produces a cool, rich white light.
The light bulb can serve its owner up to 30,000 hours - three and a half years of continuous operation (and if you take into account that it does not work all the time, the service life doubles). The cost of the lamp is, of course, considerable, but you have to pay for German quality.
- 6 dangerous mistakes when working with an angle grinder that you should not make
- Three-phase power supply in the house: does it make sense?
Comparison of shapes and sizes
For the modern consumer, it is important not only how economical the operation of one type of lamp will be compared to another, but also the priority of their appearance.
By choosing the optimal size, you can eliminate the situation when a lamp that is not suitable in size and shape sticks out of a regular lamp.
Energy-saving lighting elements can often be found in the form of a complex spiral tube with a phosphor deposited inside . They are as compact as possible - they can be mounted in a medium-sized lampshade.
LED devices have a much more varied interpretation of shapes and sizes. Of these, the two most common are:
- Mini size. The diameter of the crystal circumference is 1.5–3 cm. A source with this size of LED will turn out to be very small - less than three centimeters. Very often, such a light bulb is installed in furniture and suspended ceilings.
- Standard format. It all depends on the size of the flask. Its presence is not required. The diode does not require a specific environment. Bulbless LED lamps (called “corn” for their characteristic appearance) are increasingly being used.
As a result, when choosing which type of lighting sources is better, you can see that LED lamps have more advantages - many different shapes and sizes.
Which lamp is the best energy saving or LED?
A comparison of energy-saving and LED ones showed that the second option is the best. After all, it has the fewest disadvantages and the most positive characteristics. The main disadvantage of LED lamps is their high cost. Although the first option is quite popular among buyers. An economical lamp is more affordable and helps save light. Only it can only be used in a room where there is no humidity. And it is not recommended to turn it on (off) often.
In the near future, LED products will become more affordable. After all, their popularity is increasing every day.
Read more
Advantages of LEDs compared to fluorescent analogues
Of course, if you have the opportunity to choose, it is better to buy ice lamps to illuminate your home or apartment. To justify such a decision, it is enough to highlight the advantages of this type of light bulbs and compare them with an analogue, based on the above material, namely:
- Increased operational efficiency. The average luminous efficiency level in relation to operating power is 130–160 lm/W. For comparison: most energy-saving light bulbs have a maximum of 100 lm/W.
- Immunity to temperature. This means that this type of light source is capable of operating at different ambient temperatures, both at –60 °C and at +40 °C.
- The presence of different directions of light flux. An important advantage, especially when installing table or wall lighting devices. The ice bulbs mounted in them will provide a uniform luminous flux for a specific narrowly focused device.
- Quality of luminous flux. The design of this type of lamp is made with a different number of LEDs. Due to their significant concentration, the quality of light output will be as high as possible.
- Some modern devices with ice technology are designed with the ability to adjust the brightness level.
- Durability. The structural elements of ice light sources are impervious to most external factors and do not have burnout elements (as in old lamps - tungsten filament). The service life of an average energy-saving light bulb, according to manufacturers, is about 10,000 hours of operation, for an LED light bulb - from thirty to sixty thousand.
It all depends on the manufacturer, the price-quality ratio. Preference should be given to global brands: OSRAM; Philips or domestic - “Era”; "Space". These companies are stable in terms of selling high-quality products.
In addition to the technical and operational advantages of LED sources, it is also worth dwelling on a comparison of the impact on the user’s health.
Temperature and service life
LED crystals are small, but emit a fairly intense luminous flux. In this case, part of the energy goes into heat. Its removal is carried out through aluminum radiators. If the product is handmade, this will significantly reduce its service life. The same effect is created by the lack of the required amount of thermal paste. Note that at low temperatures these features do not manifest themselves.
Fluorescent tubes are less resistant to frost. At temperatures closer to zero, they have to spend quite a lot of time reaching operating temperature. Without this, the device cannot reach the nominal brightness level. Under conditions of high humidity, a film forms on the fluorescent tube, reducing the surface resistance. This in turn affects the ignition voltage of the device.
In general, if you value durability, then replacing fluorescent lamps with LED lamps will be relevant for you. The service life of the latter ranges from fifty to one hundred thousand hours. Note that energy-saving light bulbs have a safety margin that is almost 5–10 times less.
Of course, when we talk about service life, we mean high-quality products from branded manufacturers that provide an appropriate guarantee. Cheap fakes from unknown manufacturers, both LED and fluorescent, will last a year or two at most.
Effect on the human body: comparison of fluorescent and ice lamps
This criterion can most easily be determined by highlighting the following main points of impact:
- Radiation. LED light bulbs are completely coherent. This means that the LED itself acts as an emitter of light in the working spectrum. Compared to energy-saving ones, it does not have a noticeable effect on human vision. Fluorescent lamps are the opposite. The principle of producing light is based on the interaction of a discharge and a phosphor, which is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the discharge. This creates lighting. Moreover, such a discharge also creates an additional luminous flux - ultraviolet radiation. The effect on vision is minor, but negative.
- Flicker. This performance characteristic is not typical for an ice lamp; there is practically no flickering, due to the fact that a constant voltage is required for the operating power of the LED. And the flickering frequency of fluorescent lamps is about fifty hertz.
- Mercury. Fluorescent lamps contain mercury vapor. If the flask breaks, the body is poisoned by certain doses of these fumes. LED sources do not contain any harmful substances.
Choosing an LED or energy-saving lamp to illuminate your home is a very pressing issue. It’s quite easy to decide by assessing the advantages and disadvantages of each type: both operational and structural. After such a comparison, the user will understand how to distinguish an ice lamp from an energy-saving lamp not only in appearance, but also to find differences in their functionality. Then you will be able to select the optimal light source for a specific lighting design solution and for the individual operational features of the room.
So should you choose LED lamps or energy-saving ones?
Obviously, LED lighting has fewer disadvantages than energy-saving lamps. Does this mean LEDs are better? There is no need to rush to conclusions. When choosing which lamps are better to buy, LED or energy-saving, you need to take into account additional nuances. Unfortunately, in addition to high-quality lighting devices, the market is flooded with products of dubious quality. When purchasing an expensive product, the buyer invests money, hoping over time to receive economic benefits in the form of energy savings. In fact, he is often disappointed: the light bulb fails after not having served the period stated in the passport. The reason does not necessarily lie in the quality of the purchased product. To extend the service life, you need to take into account the operating features described above in order to understand which LED or energy-saving lamps can be installed in luminaires in specific places. Not everyone has the opportunity to spend a lot of money on LED lamps, but they can afford energy-saving ones. In some places, the use of incandescent lamps is still quite justified. What kind of lighting devices to install in the lamps is decided on the spot. Another disappointment is related to the different susceptibility of the color shades of the glow of the lamps in different people. Some people feel better in the cold white light of an energy-saving lamp, while others feel uncomfortable from it. Therefore, saving is good, but it is better to put health and comfort first. Unfortunately, choosing a lighting device “for yourself” is only possible through trial and error. Thus, you just need to choose the right energy-saving or LED lamps for your home, taking into account their advantages and disadvantages.
Colorful temperature
We perceive light from different types of light bulbs differently, feeling it as warm or cold. This impression is created due to the different emission spectrum of the lighting device. To distinguish lighting devices based on these characteristics, the concept of color temperature was introduced, which is measured in Kelvin (K). The higher this parameter, the more blue light rays in the emitted spectrum, and the colder the light is perceived. Among the options under consideration, it is LEDs that have the maximum color temperature, while energy-saving ones are closer to the comfortable characteristics of daylight.
How to choose analogues
Choosing a suitable LED lamp instead of an energy-saving one is not difficult. To do this, it is necessary to select an analogue of lower power, which has approximately the same luminous flux. You can do it simpler - divide the power of the luminescent source by 2–2.5 and get the required power of the LED .
For example, when choosing LED lamps instead of 18W fluorescent lamps, you need to select products with a power rating from 7 to 9W. Such LEDs will create the same level of illumination. If you need LED lamps instead of 36 W fluorescent lamps, you need to choose products with a power consumption of 14 to 18 W.
Comparison by other factors
The fluorescent energy-saving lamp turns on within 1 second, which is due to the operation of its electronic circuit.
At low temperatures, due to a drop in gas pressure inside the flask, the brightness decreases significantly. This is due to the fact that mercury loses its volatility and is forced to heat up over a longer period of time. High humidity also negatively affects the operation of a fluorescent light bulb. It causes a film to form on the surface of the flask, which is an interfering factor for its stable operation and rapid heating. LEDs start working instantly and have an impressive temperature range for stable operation. Another important comparison criterion is the warranty period. For LEDs it averages 3 years, while for energy-saving light sources it is 1-2.