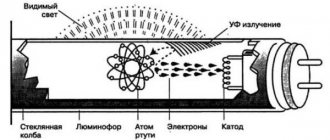
What is a filament lamp
In simple words, a filament lamp is a combination of two types of light bulbs: LED and incandescent. The principle of operation is taken from the first, and the design features from the second.
Inside the glass bulb there is an LED strip connected, which is why the lamp got its name. The word "filament" is translated from English as "thread".
In terms of glow, a filament light source is almost no different from an incandescent lamp (it has a yellowish tint), but in design and functionality it is ahead of its competitor.
Heat dissipation and heating
In addition to the usual transparent flask, you can sometimes find models with a special coating. It creates softer and warmer lighting.
Since LEDs get very hot during operation, it is necessary to quickly remove heat from them. In old LED light bulbs, this is done through massive radiators, which significantly increase the dimensions of the product.
And in the filament ones, an inert gas based on helium is pumped inside the flask. This is the one that, when inhaled, makes you talk like a small child for a while.
It promotes the rapid transfer of heat from the crystals to the glass walls and further into the surrounding space.
That is, there is no vacuum inside the light bulb at all.
Without gas and glass, the rods themselves heat up quite noticeably.
But rapid heat removal and a large area of glass walls, compared to the area of the LEDs themselves, allow the filament light source not to heat up more than 50-60 degrees.
At the same time, try touching an incandescent light bulb that is on. Some craftsmen even make infrared heaters from them.
And quite successfully.
Design, design features of the Tomich filament lamp
Structurally, the emitter of such a lamp consists of three elements:
- Glass or sapphire base.
- Blue/red LEDs in the amount of 28 pieces.
- Phosphor coating providing white light with a special color temperature.
If we consider the design as a whole, the filament light source consists of the following elements:
- Base for E14 or E27.
- Transparent bulb with high light transmittance.
- Glass leg with elements that provide voltage supply to the LED strip.
- Filament parts.
- Driver (electronics) located in the base casing.
The driver takes up minimal dimensions and easily fits on the board. The latter, in turn, is mounted in the base of the light bulb.
This design allows the use of high-quality circuits with varying levels of complexity to reduce ripple.
Experimental part
So, for the experiments, three lamps from different manufacturers were taken: a cheap Chinese lamp from Ebay from the company CroLED (in fact, the price is equivalent to Eglo), another lamp from Eglo from the local Leroy Merlin and the respected and well-known Phillips. Yes, it is worth noting that the light bulb on Ebay may NOT have anything to do with CroLED.
CroLED: Chinese Ebay quality
Let's start with a filament lamp from the Middle Kingdom. The light bulb arrived from China in a simple cardboard box with a minimum of information on it (temperature, power and supply voltage. To be honest, the expectations were different, but the reality turned out to be much harsher. The ripple coefficient was 67% (!), it seems to me that this is a record In fact, the light went out and came on again with a frequency of 10 ms.The color temperature was less than what was indicated in the seller's store on Ebay.
NB: All lamps presented in this article have a glass bulb. And although it can withstand being dropped on the floor, be careful when handling them!
Analysis of the light bulb revealed one interesting design feature - namely the driver. More precisely, its complete absence: the light bulb is powered through a banal MB10F diode bridge with a pair of resistors and a huge solid-state capacitor. But it’s compact!
The LEDs are located on a matte (!) substrate in the amount of 18 pieces. Each LED chip is made of a sapphire textured star-type substrate. The chips are absolutely small - smaller than a human hair.
Why is it profitable for manufacturers to make ultra-small LEDs?
What about the temperature? - the reader will ask. Yes, the temperature on the flask reaches approximately 40 degrees in 5-7 minutes and remains so for half an hour.
But let's now look under the bulb of our lamp. After removing the glass and measuring the temperature, it turned out that the threads very quickly (literally in 1 minute) heat up to almost 90 degrees, and in some places, apparently where the LEDs are located, the temperature reaches more than 100 degrees.
Eglo: ordinary lamp with ordinary characteristics
The next lamp from the Eglo company, which, by the way, has a representative office in the Russian Federation, generally pleased with its characteristics. Ripple at a frequency of 100 Hz was about 6%, while the color temperature and CRI fully corresponded to the declared characteristics.
A lyrical digression on the question of flickering
Inside the lamp there are also four threads of LEDs, just like in the Chinese lamp. A driver based on a capacitor ballast is hidden inside. The LEDs are slightly larger - 113 by 57 microns - than in the previous case. However, they are extremely poorly fixed to the matte substrate.
As for the temperature, the light bulb quickly (in the same 5-7 minutes) warms up to a temperature of about 50 degrees. And the threads again show a temperature of ~90 degrees. Just like some kind of curse on the design of an incandescent lamp!
Phillips: quality comes first
The last Phillips bulb tested. Surprisingly, this bulb in an E14 housing demonstrates excellent compliance with the declared characteristics and has extremely low ripple levels.
What is the reason for this, since the E14 base is much smaller than E27? - you ask yourself a question. The genius is simple: Phillips has good, very good engineers who are able to create an ultra-compact driver (flyback converter) so that it fits into an E14 cartridge, while the driver provides extremely low ripple levels (<1%).
The lamp itself has only two LED filaments, as it consumes only 2.3 W. The LED chips are placed on a transparent substrate and are similar in size to those used in Eglo lamps, but with a different substrate texture - “shield”. As noted above, you cannot argue against the laws of thermophysics.
In about 10 minutes, the lamp bulb warms up to ~45 degrees (two filaments “warm up” the entire lamp more slowly). However, the temperature of the filaments without a glass bulb was still 95 degrees, in some places - we repeat, most likely at the place where the LED chips are attached to the substrate - reaching values of 110-120 degrees.
In order not to be unfounded when making a verdict regarding filament lamps, we will add a few photographs of already familiar IKEA lamps and powerful smart Prestigio lamps, which we will talk about next time. The body of an IKEA lamp warms up to 75 degrees within half an hour, and a smart Prestigio lamp to 58. At the same time, the SMD LEDs of Prestigio lamps, for example, at maximum power only heat up to the “safe” temperature indicated at the very beginning of the article, 60-70 degrees.
What power does it produce?
The average filament power is about 1 W, and the voltage is 60 V. In general, the light bulb consumes from four to eight W and has the following parameters:
- luminous efficiency: 120 - 140 Lm/W;
- light temperature: up to 4500 K depending on the level of performance;
- service life 30,000 hours;
- ratio of output power with incandescent lamp, filament/LC: 2 – 25 W, 4 – 40 W, 6 – 60 W, 8 – 75 W.
For comparison, incandescent, LED and fluorescent lamps have power in the ranges: 10 - 500 W, 3 - 30 and 15 - 80 watts, respectively.
Conventional light sources show the lowest light temperature - 2700 K with a service life of 1000 hours.
As for fluorescent and LED lamps, they show the best characteristics: light temperature up to 6500 or 6400 K, and service life - 40 and 50 thousand hours, respectively.
Are high wattage light bulbs a myth?
Unfortunately, the power of all filament lamps is limited by the volume of the bulb. Of course, theoretically you can stuff 20-30 rods there, but they will only glow for a few seconds.
A small space and a small volume of gas in it simply do not have time to quickly remove the generated heat and the LEDs will instantly overheat. You will need flasks of completely different shapes and sizes.
Therefore, filament light bulbs of the usual A60 dimensions try not to make a lot of power. Savings have nothing to do with it.
It's all about the technical component and restrictions on overheating.
Secret No. 4
Remember, filament lamps in candle or ball format cannot meet their declared characteristics if their power exceeds 9 W.
Real figures will be two times less than indicated on the packaging.
In terms of lumens and lighting level, 11-watt models will not replace the full 80-100 W that simple incandescent lamps provide.
They will correspond to a maximum of 60W. The same applies to the CRI color rendering index.
At best, it will exceed 80, but not CRI>90.
Here is a table of the most common types of lamps, their maximum power and the luminous flux they are capable of producing.
The data was obtained by a well-known specialist in the field of lighting technology, Alexey Nadezhin, as a result of independent tests and laboratory measurements.
Every time you see a light bulb in a store with values exceeding these measurements written on its packaging, know that you are being fooled. This is pure marketing and a race for producers.
If you write 7W on your product, and next to it there will be a competitor with the inscription 9W, and for the same money, then 9 out of 10 will buy his product, not yours. 99% of consumers simply do not have the appropriate measuring and testing instruments.
The main thing for them is that the product lasts longer.
Secret No. 5
Some manufacturers, so as not to be accused of lying, deliberately write on the packaging - not 10 W power, but 10 W MODEL!
Pay attention to this.
Tomich filament light bulb driver
Using the LED principle requires installing a driver located inside the base. The purpose of the device is to reduce the current from the network to a value that is safe for LED elements.
The driver consists of the following elements:
- Fuse.
- Diode bridge rectifier.
- Smoothing capacitors.
- Pulse current regulator microcircuit with additional components. The circuit includes a diode, a choke, and an RF resistance capacitor.
The driver circuit deserves special interest. A fuse F1 is installed in the phase wire, instead of which you can put a resistance of up to 20 Ohms up to 1 W of power.
The elements of the scheme also include:
- diode bridge for rectifying current to a voltage of 400 - 1000 V, DB1;
- capacitor for smoothing ripples at the output DB1, E2;
- additional capacitance for supplying voltage to the circuit, E1;
- device driver, thanks to which the entire circuit works, SM7315P;
- capacity for filtering ripples at the output, E3;
- current sensor for adjusting the current in the light source circuit, R1 (the higher the resistance, the lower the current);
- resistance to reduce the current on the converter, R2;
- diode ensuring the operation of the converter, D1;
- storage inductance for voltage conversion, L
In fact, elements D1, L1 and a transistor switch form a typical pulse converter circuit.
How the scheme works
The principle of operation of the circuit is simple. The voltage supplied to the input is rectified using a diode bridge. Further, thanks to the action of the capacitance and capacitor, the current is smoothed.
On approaching the microcircuit, the current is converted into RF pulses, smoothed using a capacitor. Subsequently, power is supplied to the filament LED and returned to the network.
As for the driver, it includes a PWM controller and additional devices (comparators, multiplexers, etc.). They compare the real and nominal currents, and then send a signal to the PWM controller to make changes to the pulse duty cycle.
Cooling
There is a false misconception that LEDs do not get hot. On the contrary, they get very hot, and some microcircuits do not work for even several minutes without cooling.
For small LEDs housed in SMD-type housings, heat is transferred to the contact pads installed through them.
We already know that one filament consumes an average of 1 W. For comparison, SMD diodes for 1 W of power are designed to provide about 25-30 kW. see cooling device. And here the question arises about cooling the lamps.
Please note the following:
- The filament is a matrix.
- Structurally, diodes are soldered behind the matrix part, which emit a small amount of heat due to low power. For example, if you divide 1 Watt by 28 light bulbs, you get an average of 0.036 Watts per LED.
Helium or a special gas is used to remove heat, providing minimal heating to 55-60 degrees Celsius. This allows them to be used in luminaires with fabric, paper and plastic lamps. In this case, the filament lamp thread heats up to 100 degrees Celsius.
What is it used for?
Experts predict that in a few years filament lamps will become as popular as LED lamps, used in everyday life to save energy. But thanks to a number of advantages, filament diodes have a chance of even greater demand. For example, a transparent bulb that provides a dispersion angle of 300°.
Lamps as a decorative element in the interior
This type of LED light bulbs is often combined with the design of a room where a standard LED device does not fit in appearance due to the white bulb. For example, if you screw filament lamps in the form of burning candles into an electric candlestick, they will look more advantageous.
Advantages and disadvantages of filament lamps
Before switching to filament light sources, it is necessary to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages:
- Economical.
- Uniform glow in all directions, an excellent solution for lighting a summer house.
- Stylish appearance, which allows them to be used in open lamps.
- Wear resistance.
- Long service life.
- Versatility of use and the possibility of installation in many models of lighting devices.
- Excellent color rendition.
- Minimal heating due to gas pumped inside.
- High degree of brightness.
- Easy to dispose of as household waste.
Disadvantages of filament products:
- High price.
- A fragile flask that requires careful handling.
- When the voltage is unstable, flickering appears and the quality of light deteriorates.
- Impossibility of repair.
- Designed only for 220-volt networks.
- The presence of two types of socles - on E14 and E27.
- Variation in quality.
- Complaints about short service life.
- The presence of a dead zone under the light source when the bulb is positioned vertically (details below).
Experiments with filamentary LED assemblies (Filament COB LED)
I’m afraid to seem unoriginal, but still, what if there are those here who haven’t read the article “Coproeconomics or the cycle of shit in nature.” When “there wasn’t enough for everyone” © they lived poorly, but interestingly. Now there’s just no sh*t! Everyone has everything they need for life. Nowadays, everyone’s life lacks only non-essential items, the absence of which has virtually no effect on the quality of life.
Well, for example, I don’t have, say, a DVR in my car - what? As I used to travel without it, I continue to travel. But I’m not going to buy it due to the lack of enough free money. Yes, I'm not particularly smart with money. That's why I don't spend much of it on semi-useless things. This means that my actions are slowing down the economy. After all, the one who produces a semi-useless thing cannot sell it to me, which means that he, in turn, does not receive income and also begins to squeeze in his purchases. Thus, the economy gradually fades away.
There are several ways to restore the economy to its former pace. One of them is the discovery of some new physical phenomenon and its implementation for the benefit of humanity. Development of some new technology. Well, for example, in the 80s, such a dope was the emergence of the topic of “personal computers”. This spurred the development of the software industry and many other related matters. It’s not that “movement” has begun, but the world economy has noticeably increased its momentum. People have a need to have a computer.
After 10-15 years, people began to need a mobile phone - another incentive for production.
But after the 2008 crisis, there were no such noticeable breakthroughs in science or technology. Therefore, it somehow became unclear how you can sell to the consumer what he already has. And really, why do I need three TVs, five refrigerators, four vacuum cleaners, half a dozen different types of computers and tablets - what am I going to do with this horde?
It’s no secret that an excessive abundance of things sucks out a person’s karma and makes him unhappy. You need to take care of things, keep an eye on them - well, a normal owner’s approach! And if you have three cars in your family, then somehow it becomes tiresome to wash them, repair them, change tires for the winter, and so on. When I had one car, I did all this with joy. Now I have two of them. And this circumstance, to be honest, stresses me out.
It's like having two wives, two families. It’s good at first, but then, after a certain time, you realize that a wife/family/children is not a way to have fun. This is first and foremost a responsibility. This is not a small load. Do you need it?
There is another way to make the economy work again - switch to producing inexpensive, low-quality products - a la Made in China. (I’ll make a reservation right away: China is a huge country that produces products in a very wide range of quality - from bloody crap to very high-quality world-class products. But (for me personally) in the 90s, China is remembered for the production of extremely low-quality products. )
Low-quality products will not last long, so the economy will maintain a constant demand for them. (Coproeconomy!)
Another way to improve the economy is to mandate the production of certain products. Moreover, order to do this with strict adherence to the release plan. A kind of return to planned management, as opposed to the wild, greedy economy of capitalism. This is probably the most loyal way to make the world healthier.
Another way to make the economy work is war. Well, this is already an extremely radical medicine. Although there are individual comrades (as they are now commonly called - “partners”) who press precisely this “button”.
Well, in general, one way or another, the problem is what products to produce and how to sell them to those who have little money. Nowadays, with extremely high automation of production, it is almost impossible to enter the market with your own small-scale products. More precisely, it’s possible to get out, of course, but it will be impossible to sell it (the product).
Well, firstly, in order to sell something (not one-time sales, but a constant flow of sales. Even if it’s a small, but constant “trickle” or trickle), you need to have a noticeably low price for the product. Question - how to make a low price for a small-scale product?
You can go the other way - “stick” to the feeding trough. You don't have to have anything unique to do this. This requires “connections” and the ability to “share”. No, how could it be otherwise!
In general, it turned out to be complete garbage - everyone already has everything they need, but there is no money to buy what is not particularly necessary. In other words, the bulk of the money was concentrated in the hands of a small group of people. That's why the whole economy is in shambles.
I don't pretend to be right. I just expressed my point of view. I admit that in some places I am wrong, and in others I am completely mistaken. I am not an economist or a politician. I'm just an electronics engineer, a developer. And I don’t know what I’m doing wrong or wrong. On the one hand, I develop quite good, even competitive devices, but on the other hand, for some reason my start-up does not take off. Maybe you just need to stop being a purist and accept the unspoken rules of the game?
What is a meter zone
When a filament lamp glows, if the bulb is positioned strictly vertically, a so-called zone of less illumination is formed under it, which can be called “dead”. The lighting level in it is two times less than in the main lighting zone.
At a distance of one and a half meters, the spot reaches a size of 50 cm. Accordingly, it increases as it moves away from the light source.
The shape of this spot, depending on the model of the llama, the number and location of the spirals, is different.
Light output and dead zone
In addition to low heating, filaments have another advantage - high light output. It reaches up to 120 Lm/W.
In this case, the scattering angle of the light bulbs reaches 360 degrees. While in conventional LEDs it does not exceed 120-270 degrees.
Secret No. 6
Speaking about large angles of illumination, for some reason many people are silent, or maybe they don’t know, about the so-called “dead zone”.
When a filament light bulb hangs upside down, a spot appears in its center that is two times darker than the entire illuminated perimeter. The diameter of the spot reaches 50 cm at a distance of 1.5 meters from the light bulb itself.
The shape of the spot is a quatrefoil, which is formed from the threads of LEDs coming together at the top.
The wider it is, the larger the spot.
In addition to straight threads, models with arcuate and spiral shapes are available.
They are more expensive and are most often used as decorative lighting for the New Year.
Filament lamps are ideal for crystal lamps and chandeliers. What is important in them is the thread-like light source, which, when reflected, will play on the edges of the crystal.
Matte housekeepers in such chandeliers look ridiculous. The light turns out “dead”, and the pendants do not shine.
Check pulsation when purchasing
When purchasing a filament lamp, it is important to check the ripple. Ignoring this requirement may lead to disappointment when using the device as the main lighting in a bedroom, living room or other room.
According to the laws of the Russian Federation (PP No. 1356 of October 10, 2017 “On approval of requirements for lighting devices”), the sale of light sources with a pulsation of more than 10% and a CRI of less than 80 is prohibited.
The driver is responsible for pulsation and in high-quality products this figure does not exceed 1%.
And you need to remember that inside even light bulbs of the same shape there can be two different drivers. One with normal pulsation and high-quality parts, and the second one made using cheap elements.
Beautiful LED lamps for a restaurant
In addition to the usual transparent flask, you can sometimes find models with a special coating. It creates softer and warmer lighting.
In addition to straight threads, models with arcuate and spiral shapes are available. They are more expensive and are most often used as decorative lighting for the New Year.
Filament lamps are ideal for crystal lamps and chandeliers. What is important in them is the thread-like light source, which, when reflected, will play on the edges of the crystal. Matte housekeepers in such chandeliers look ridiculous. The light turns out “dead”, and the pendants do not shine.
Today we can say for sure that the future development of the lighting industry is not behind filaments. Yes, they resemble the familiar Ilyich light bulbs, they look nice in the interior, but still, such an imitation of incandescent lamps is, first of all, a big, big compromise.
Determining the temperature of the glow
Few people know that the glow temperature can be easily determined by the shade of the phosphor even without screwing the lamp into the socket.
Here it stands out:
- Lemon shade - 4500 K (neutral white).
- Yellow - 3000 K (warm white).
- Orange - 2500 K (with an even warmer tint).
One glance is enough to determine the oriented temperature.
Varieties
Filament LEDs differ in the design of the “threads,” the base, and the shape of the bulb.
Sources with direct “filaments” are used in offices and residential buildings to illuminate large areas. Products with a spiral and arc are used in decorative lighting, as they emit muted, soft light.
Screw sockets are used, most often E 14 and E 27. U 27 is suitable for almost all standard lamps, E 14 are intended for small decorative chandeliers and sconces.
Flask shape:
- standard A60;
- A95 – ball, sphere.
More recently, filament products with matte bulbs and dimmable ones have appeared.
This is interesting! The quality of lighting depends on the number and length of the “filaments” - the higher the indicators, the brighter the light bulb shines. The color temperature can be determined by the color of the threads. Daylight is provided by elements with a lemon tint, warm yellow - with orange or yellow.
Results
Filament lamps are an alternative to LED products that offer better performance and a stylish look. Such models are characterized by versatility, high light output, a huge selection and the absence of a dead zone around the perimeter.
Thanks to their long service life, the devices quickly pay for themselves and provide high-quality lighting.
We must not forget about the shortcomings that prevent such products from “exploiting”.
Today this is the fragility of the flask, high price and pulsations with low quality of the product and electricity.