Modern fluorescent lamps (FL) do an excellent job of lighting large residential, work and technical premises and can reduce overall electricity consumption by 50-83%, thus reducing utility bills.
In this article, we will consider the operating characteristics of LLs, their design, and analyze the main advantages and disadvantages in comparison with other types of lighting devices. In addition, we will provide thematic photos and diagrams, as well as videos about the operating principle of fluorescent light bulbs and the features of their application.
Operating principle and device of LL
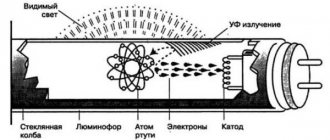
A luminescent device is a gas-charged light source, where an electrical discharge in mercury vapor creates intense ultraviolet radiation.
Compact fluorescent-type modules have a standard base, which makes them a convenient replacement for bright, but more energy-consuming incandescent lamps.
How does a fluorescent light bulb work?
It is transformed into light visible to the human eye by a special composition called phosphor, consisting of calcium halophosphate mixed with additional elements.
After connecting a fluorescent lamp to the central power supply, a so-called glow discharge must be maintained inside the glass bulb.
It makes it possible to ensure the glow of the phosphor layer in constant mode and even during a short-term outage of the central power supply.
Previously, a classic fluorescent lamp looked like a tube sealed on both sides, inside of which there were mercury vapor. Devices are now available in a wider variety of shapes and configurations.
Design features of the device
The traditional fluorescent type lamp is a glass cylinder with an outer diameter of 12, 16, 26 and 38 mm, usually represented as:
- straight extended tube;
- curved U-shaped module;
- ring;
- complex figure.
The legs are hermetically sealed into the end edges. On their inner side there are tungsten electrodes, which are structurally reminiscent of the spiral filament bodies built into Ilyich light bulbs.
Some types of fluorescent lamps use more advanced tri-spirals, which are a twisted bi-spiral. Devices equipped with them have an increased level of efficiency and a lower heat loss threshold, which significantly increases the overall efficiency of light flow
From the outside, the electrode elements are soldered to the metal pins of the metal base, which are supplied with operating voltage.
U-shaped and straight devices are usually equipped with G5 and G13 bases, where the letter coding indicates the pin type of the base element, and the number indicates how far apart the working elements are located.
The electrically conductive medium located inside the glass bulb has negative resistance. When a current increase occurs between two opposing electrodes that requires limiting, it manifests itself and reduces the operating voltage.
The circuit diagram for switching on a conventional fluorescent light bulb includes a choke or ballast. It is responsible for creating the high-level pulse voltage necessary to correctly activate the lamp.
The figure shows the internal arrangement of a fluorescent type lamp and clearly explains the basic operating principle of its main components
In addition to this part, the electronic ballast is equipped with a starter. It is a glow discharge element, inside of which there are two electrodes surrounded by an inert gas environment.
One of them consists of a bimetallic plate. In sleep mode, both electrodes are open.
What are fluorescent lamps and their characteristics
A fluorescent lamp is a fairly common phenomenon in our lives.
Surely each of us has visited some public institutions and noticed the specifics of lighting in these buildings. However, few people know what exactly this product is.
Fluorescent lamps are gas-charging devices that base their operation on the physical impact of an electric discharge in gases.
Such a device contains mercury, which provides ultraviolet radiation, which is converted into light in the lamp itself.
This process occurs with the help of a very important element - phosphor.
The phosphor can be a mixture of any chemical elements, for example, calcium halophosphate with something else.
By selecting any type of phosphor, you can achieve the most interesting effects, for example, changing the color scheme of the lamp light. When choosing a product, you should pay attention to one of the most important indicators - the overall color rendering index. It is designated by a combination of the letters Ra, and the higher the value indicated in the accompanying documentation for the lamp, the better it will perform its job.
Thanks to this lighting system, the fluorescent lamp has become a clear leader over the same incandescent lamps.
And if we take into account that its operational characteristics provide a much longer period of use, then there is no need to think about the correct choice in favor of a fluorescent lamp.
Common types of such light bulbs
The primary classification of fluorescent-based products is based on the level of base pressure. High pressure devices are used for high power lighting installations and outdoor street lighting.
Low pressure lamps are used in everyday life to supply light to industrial, technical and residential premises for various purposes.
Type #1 - high pressure modules
High-pressure devices produce a rich light flux of good density. The inner surface of the bulb element has a special phosphor coating made of fluorogermanate or magnesium arsenate.
The operating power of such fluorescent lamps ranges from 50-2000 W.
High-pressure mercury modules require a 220-watt nominal mains voltage to operate correctly. Their pulsation coefficient is usually from 61 to 74%
Full ignition of the lighting module occurs within 3 seconds. The service life of 80-125-watt products is about 6,000 hours, and lamps from 400 W or more can work up to 15,000 hours if the operating rules established by the manufacturer are strictly followed.
Type #2 - low pressure products
Low pressure LL is used to provide light flow to residential, technical and industrial premises.
Structurally, the device is a tube made of durable glass containing argon inside at a pressure of 400 Pa and a small amount of mercury or amalgam. It is offered on the market in a wide variety of modifications and is equipped with two electrode elements.
The lowest temperature that low pressure LLs can tolerate is -15 °C. Therefore, these light sources are considered irrelevant for use in open areas.
A glass flask can have a wide variety of diameters. The level of light output varies depending on the power of the device itself. For its correct operation, a throttle-type starter is required. Average service life is 10,000 hours.
Network connection
Gas-discharge lamps cannot be directly connected to the electrical network, this is due to the high resistance in the cold state and negative differential resistance.
These problems can be corrected by using ballasts. The most common are EMPA (electromagnetic ballast) and electronic ballast (electronic).
The electronic ballast is an electromagnetic choke that is connected in series with the lamp. A starter is connected in series with the filament coils, which is a neon lamp with bimetallic electrodes and a capacitor. Advantages: simplicity of design, reliability, durability. Disadvantages: long startup time, large amount of electricity required, hum during operation, flickering, large size.
Electronic ballasts supply the light bulb with high-frequency voltage, which eliminates flickering. Uses two options for starting lamps:
- Cold. The lamp turns on immediately after voltage is applied.
- Hot. The electrodes warm up and the source lights up after 0.5-1 second.
The advantages include long service life, lower energy consumption, dimming on some models, and quietness.
Features of compact LLs
Compact-type LLs are hybrid products that combine some of the specific distinctive features of incandescent lamps and the characteristics of fluorescent lamps.
Thanks to advanced technologies and expanded innovative capabilities, they have the small diameter and medium-sized dimensions characteristic of Ilyich light bulbs, as well as a high level of energy efficiency characteristic of the LL line of devices.
Compact-type LLs are produced for traditional sockets E27, E14, E40 and are actively displacing classic incandescent lamps from the market by providing high-quality light with significantly lower power consumption
CFLs are in most cases equipped with an electronic choke and can be used in specific types of lighting fixtures. They are also used to replace simple and conventional incandescent lamps in new and rare lamps.
Despite all the advantages, compact modules have such specific disadvantages as:
- stroboscopic effect or flickering - the main contraindications here concern epileptics and people with various eye diseases;
- pronounced noise effect - during prolonged use, an acoustic background appears that can cause some discomfort in a person in the room;
- odor – in some cases, products emit pungent, unpleasant odors that irritate the sense of smell.
The last position is more often observed in nameless crafts of Chinese origin, and even branded devices made in accordance with all the rules and modern requirements often suffer from the first two. We have given the rating of the best CFL manufacturers in this article.
Application area
Nowadays, the economy is quite developed, which forces us to use energy-saving resources. Thus, fluorescent lamps began to be used almost everywhere, be it your own apartment, a summer cottage, or any industrial premises, or just an office. At the same time, gas-discharge production is also used in plasma TVs.
The most appropriate use of gas-discharge lighting is in large spaces (stadium, swimming pool, school grounds, on city streets and suburban areas). Where high output from lighting elements is required, switching on occurs quite rarely.
Basic range of color temperatures
The color of the glow is one of the most important parameters, directly dependent on the composition of the phosphor that converts ultraviolet radiation into light.
Today, the most common are 7 definitions of the shades of flux produced by fluorescent lamps:
- LEB – natural white with a noticeable cool tint;
- LDC – natural daylight with improved color rendering quality;
- LTB – warm white;
- LD – traditional day white;
- LB – classic white;
- LEC – natural with the highest quality rendition of shades;
- LCB – simple cool white.
For living spaces where people spend a lot of time, warm shades or natural daylight lamps with a high level of color rendering are suitable.
White and daytime tones are usually present in office, work, industrial spaces, classrooms and classrooms. They promote concentration, increase brain activity and improve overall learning and productivity.
The coolest shades are used in medical institutions, laboratories, hospitals and technical rooms. They give objects additional clarity and enhance visual acuity.
Luminescents for meat displays in grocery stores are distinguished by a specially selected pink emission spectrum. It emphasizes the natural shades of products, making them more attractive in the eyes of buyers.
Color components added to the phosphor make it possible to obtain pink, blue, green and other unusual lamp shades.
Such devices are used for design, advertising and commercial purposes. With their help, they create an original glow that is necessary in a specific individual case.
We wrote more information about the color temperature of light, the peculiarities of human color perception and the nuances of choice in the next article.
Marking
Basic information about a specific fluorescent lamp is indicated on its packaging. Some information in the form of markings is applied directly to the product, including the length. This includes the manufacturer, power of the light source, type of base, shade of light, service life, etc.
The first letter - L - stands for fluorescent lamps, followed by types. The following symbol indicates the shade of the emitted color: B - white, D - daylight, HB - cold white, etc. To indicate design features, there is the following marking: U - U-shaped configuration; K – ring; R – reflex type; B – quick-start products.
Luminescence indicators measured in Kelvin (K), also known as color temperature, are indicated separately. For example, 2700 K is equivalent to the light emitted by a conventional incandescent lamp, 6500 K corresponds to a snow-white cool tone. Power is indicated in watts (W), and the indicator itself is indicated by numbers from 18 to 80.
The diameter of the glass tube is designated by the letter T8, T12, etc. The number 8 corresponds to 8/8 inches and is 26 mm, 12 corresponds to 12/8 inches and will be narrower than 38 mm. Others are marked in the same way. Threaded sockets are marked with the letter E, the numbers indicate the diameter of the thread, pin sockets are designated with the symbol G, and the number corresponds to the distance between the pins (for example, E27, G24).
Strengths and weaknesses of devices
Like any technical devices designed to illuminate domestic and work spaces, fluorescent lamps have their strengths and weaknesses.
Based on this information, you can determine where it is wiser to use them, and in which cases it is worth giving preference to light sources of a different type.
Positive aspects of lamps
The main advantage of luminescent products is considered to be increased light output and a good level of efficiency. They provide the room with lighting that is not irritating to the eyes, and demonstrate normal endurance even under intensive use.
The module is approximately 5 times the base power of a conventional Ilyich light bulb. A 20-watt fluorescent lamp produces a luminous flux equal to that provided by a 100-watt incandescent lamp
Various temperatures of light shades, close in gamut to natural sunlight, allow you to select the appropriate lighting device for various purposes and for rooms of any purpose.
The light flow produced by the module is not directed, but scattered. A calm, pleasant-to-the-eye glow comes not only from the tungsten filament located inside, but also from the entire outer surface of the flask.
This allows the use of luminescent sources both to create general background lighting and to organize zonal light.
For use in places where lighting turns on automatically, according to signals from motion sensors, fluorescents are not suitable. They are limited in the permissible number of activations over a certain time period and can fail if activated too frequently.
The service life of luminescent products varies depending on the model and reaches up to 20,000 hours or up to 5 years.
However, the buyer should know that the lamp produces this resource only if the following conditions are met:
- availability of a sufficient volume of high-quality power supply without surges and drops;
- high-quality ballast;
- a certain number of activations, usually no more than 2000 for the first 2 years of use, which is only 5 activations per day.
Violation of these basic conditions will significantly degrade the efficiency of the lighting fixture and significantly shorten its lifespan.
The modules can be used to illuminate greenhouses. They provide natural light, as close as possible to sunlight, do not consume a lot of power and show good resistance to voltage surges typical of suburban power supply networks.
The energy consumption level of luminescent lamps is almost 5 times lower than that of traditional products, so they can be classified as energy-saving light sources.
With their help, it will be possible to effectively illuminate a large room without spending a lot of money on utility bills.
The operating temperature on the surface of the flask does not exceed 50 degrees. This makes it possible to operate the lamp in rooms where increased fire safety requirements are imposed.
Main disadvantages of modules
The first big disadvantage of the products is excessive sensitivity to temperature changes. They react strongly to the movement of the mercury column and may stop working when the temperature drops below -20 °C.
Heat exceeding +50 °C does not have the best effect on the functioning and seriously limits the range of use of these light sources.
Moisture susceptibility is also not an advantage and does not allow the products to be widely used in bathrooms and sanitary facilities.
Over time, the phosphor in lamp bulbs degrades and the emission spectrum changes. At the same time, the level of light output of the device decreases and the efficiency decreases noticeably
Sometimes the light flow itself is considered a disadvantage, as it has a lined, uneven spectrum that distorts the natural shades of objects in the room.
Not everyone feels this visually, but for those who perceive this minus too clearly, lamps are sold with a phosphor that is close to a solid, more natural spectral color. True, their light output is significantly less.
There are situations when luminescent lights flicker at twice the frequency of the supply network. This problem can be solved by some improvement of the device, in particular, by using electronic ballasts with a suitable level of capacitance for the rectified current smoothing capacitor at the inverter input.
But the fact that manufacturers are trying to save money and do not equip devices with capacitors of the required capacity is somewhat upsetting.
Household LL modules perform best when the ambient temperature is in the range from +5 to +35 ˚С. When the thermometer shows lower readings, starting the device becomes significantly more difficult, and the operating time is noticeably reduced
The need for an additional starting device also slightly reduces the popularity of lamps. They definitely require either an overly noisy and rather bulky throttle with a starter of low reliability or a more advanced electronic ballast that has a power adjustment function, but at the same time costs a lot of money.
Another weak point of luminescents is their high sensitivity to switching on. During direct activation of the lamp, a special composition burns out and crumbles on the electrodes, which ensures discharge stability and protects the internal tungsten filament from overheating.
Constant switching on significantly reduces the service life of the device. In addition, a visible, irritating flicker appears, and the edges of the lamp bulb darken and lose their aesthetics.
Chemical health hazard
One of the main disadvantages of fluorescent light sources is the chemical hazard. The lamp bulb contains highly toxic mercury, and its amount ranges from 1 to 70 mg.
The vapors of this substance can harm the health of people who are constantly in rooms illuminated by LL-type devices.
The integrity of the spent lamp must not be compromised, otherwise toxic mercury will be released into the external environment. There is a fine for unauthorized disposal, so it is better to transfer the product to a center that processes elements hazardous to nature and humans
When a module fails, under no circumstances should it be broken or thrown into an ordinary trash bin. It must be disposed of in accordance with the rules and regulations clearly described in current legislation.
For example, transported to landfills where toxic materials are accepted from the population for their correct destruction or recycling.
Technical features of CFL
This type of lamp is divided into three categories:
- With a U-shaped or H-shaped tube , a starter inside and external ballasts. (1)
- With a curved tube , built-in starter and ballast microcircuit. (2)
- With a ring-shaped tube , built-in starter and ballasts. (3)
These types of compact lamps have the following features:
- Voltage: 5-35 W.
- Light flow:
- 400-900 lm (1),
- 425-1200 Lm (2),
- 700-1450 Lm (2).
- Color rendering index: 60-98 Ra.
- Color temperature: 3000-6000K
- Base:
- G23 (1),
- E27 (2) and (3)
- Dimensions:
- 27 x 13 x 135-235 (1);
- 85 x 150-180 (2);
- 165-216 x 100 (3).
Comparison with other light sources
LL-type products differ significantly from both aging incandescent lamps and progressive LED lamps.
Compared to the first ones, they consume 5 times less electricity, while providing the same level of light flux saturation. But they are somewhat inferior to LED devices in terms of power combined with energy consumption.
The table clearly shows in numbers how much more profitable it is to use more modern sources of high-quality lighting instead of traditional Edison light bulbs
True, an incandescent lamp burns with the same intensity throughout its entire operating period, while fluorescent lamps lose some of their saturation due to the burnout of the inner layer that reflects ultraviolet light.
LED products become somewhat dim during operation due to degradation of the working diodes. And in some models it is possible to adjust the brightness of the lighting using a dimmer.
Incandescent or fluorescent lamps do not provide this function. But this convenient mode in LED devices is not free and you will have to pay an additional amount for it.
In terms of the level of structural fragility, incandescent lamps and fluorescent lamps are similar, since they have a glass bulb. In this regard, ice modules are more resistant to shock and mechanical damage. And the absence of any harmful or toxic elements inside makes them much more attractive for use at home.
The highest costs for the entire operating period are incurred by the use of incandescent lamps. Luminescents consume energy within reasonable limits, and LEDs make it possible to reduce costs to the very minimum.
As for the financial side, initially an incandescent light bulb costs less than others. However, given its working life of only 1,000 hours, this can hardly be considered a pronounced advantage.
The basic price of fluorescents is higher, however, and they last much longer. As reputable manufacturers say, they last for 10,000-15,000 hours if the number of daily activations does not exceed 5-6 times.
LED modules can boast even better performance, but you will also have to pay much more for this pleasure, and this is not advisable in all cases. Although the tendency to replace some light sources with others can be seen everywhere. We wrote about the need to replace fluorescent light bulbs with LED ones and the procedure for performing this work here.
How to properly light a house
Visitors to our site often ask the question of how many fluorescent lamps are needed to illuminate a particular room, and how to correctly position the light sources.
Combination of natural and artificial lighting
Despite the fact that there are clear regulations on this issue, the answer is not so simple. The reason is that we all perceive light differently and must largely rely on our own sensations.
State standards only establish minimum values. They are measured in Lux, the number of which is shown in the following table.
Lighting standards for different types of rooms
1 Lux is 1 Lumen per 1 m2. That is, to get standard lighting in a living room of 15 m2, you need to make the following calculation: 15*150=2250 Lumens. This is the total amount of light that the lamps in the room should produce.
Calculation of lighting level
A 10 W fluorescent lamp produces about 400 Lumens, which means that such a room requires at least 6 such lamps. The instructions are simple, but the calculation is approximate, since you need to additionally take into account the distance from the floor to the lamps and other factors, but it works and is applicable for living rooms.
We recommend increasing the table indicators by at least 1.5 times.
In conclusion, we suggest watching a video story from a famous TV show about fluorescent lamps. Perhaps someone will find additional interesting information for themselves.
What are the types of lamps?
There are several versions that differ in the emission spectrum. There are only three types:
- standard;
- special;
- fluorescent lamps with improved light transmission.
The radiation of the first option is characterized by various shades of white. This is due to the fact that the design provides for a single-layer phosphor coating. As a result, the scope of application of such light sources is somewhat narrowed. They are usually used in organizing lighting systems for industrial, administrative and public facilities (offices, shops, etc.).
Various execution forms
Special type versions are characterized by a different emission spectrum. Their main task is to provide the most natural conditions for staying in various rooms. For example, there are fluorescent fluorescent lamps, as well as design options designed for installation in aquariums specifically for plants or animals.
There are also versions that are used in premises where birds are bred. In addition, there are light sources for decorative purposes. Their main difference from other options is the multi-colored glow.
Lamps with improved light transmission have one main advantage over other types; the name of such light sources speaks volumes about it - better color reproduction. This is achieved by applying a multilayer coating (3-5 layers of phosphor) to the inner surface of the bulb/tube.
Classification by type of base
The classification of this type of lighting device is also carried out on the basis of differences in designs:
- Linear executions.
- Compact fluorescent lamps.
The first option is also called tubular. And, in addition, this variety comes in straight and U-shaped designs. Linear light sources are also divided into groups based on differences in size (length and diameter). Moreover, there is a direct relationship between the dimensions of the product and its power: the longer the lamp, the higher the value of this parameter. The diameter of the flask is also different: T4, T5, T8, T10, T12. From the designation you can find out the size of the product in inches. The base type for such light sources is G13.
Divided into versions according to the design of the flask
Compact fluorescent lamps are divided into versions according to the design of the bulb (it can be curved in different ways) and base: E14, E27, E40, as well as 2D, G23, G27, G24, G53 and several subtypes (G24Q1, G24Q2, G24Q3). The first three of the above structural elements make it possible to install a lighting device instead of versions with an incandescent filament.