When selecting circuit breakers that can protect electric motors from damage as a result of short circuits or excessively high loads, it is necessary to take into account the large value of the starting current, often 5-7 times higher than the nominal value. Asynchronous power units with a squirrel-cage rotor are subject to the most powerful starting overloads. Since this equipment is widely used for work in industrial and domestic conditions, the issue of protecting both the device itself and the power cable is very relevant. This article will discuss how to correctly calculate and select a motor protection circuit breaker.
Tasks of devices for protecting electric motors
Household electrical equipment is usually protected from large inrush currents in networks using three-phase circuit breakers that operate some time after the current exceeds the rated value. Thus, the motor shaft has time to spin up to the desired rotation speed, after which the force of the electron flow decreases. But the protective devices used in everyday life do not have precise settings. Therefore, the choice of a circuit breaker that allows you to protect an asynchronous motor from overloads and short-circuit overcurrents is more complicated.
Modern motor protection circuit breakers are often installed in a common housing with starters (the so-called motor starting switching devices). They are designed to perform the following tasks:
- Protecting the device from overcurrent occurring inside the motor or in the power supply circuit.
- Protection of the power unit from phase conductor breakage, as well as phase imbalance.
- Providing a time delay that is necessary so that the motor, which is forced to stop as a result of overheating, has time to cool down.
Control and protective automation for the engine on video:
- Shutting down the installation if the load is no longer supplied to the shaft.
- Protection of the power unit from long overloads.
- Protection of the electric motor from overheating (to perform this function, additional temperature sensors are mounted inside the unit or on its body).
- Indication of operating modes, as well as notification of emergency conditions.
It is also necessary to take into account that the circuit breaker for protecting the electric motor must be compatible with control and control mechanisms.
What types of circuit breakers are there?
To protect conductors of a single-phase 220 V network, there are single-pole and double-pole disconnecting devices. To single-pole wires, only one conductor is connected - phase, to double-pole wires, both phase and neutral. Single-pole circuit breakers are installed on 220 V indoor lighting circuits, on socket groups in rooms with normal operating conditions. They are also installed on some types of load in three-phase networks, connecting one of the phases.
For three-phase networks (380 V) there are three and four poles. These circuit breakers (the correct name is a circuit breaker) are installed on a three-phase load (ovens, hobs and other equipment that operate on a 380 V network).
In rooms with high humidity (bathroom, bathhouse, swimming pool, etc.) two-pole circuit breakers are installed. They are also recommended for installation on powerful appliances - washing machines, dishwashers, boilers, ovens, etc.
It’s just that in emergency situations - in the event of a short circuit or insulation breakdown - phase voltage can reach the neutral wire. If a single-pole device is installed on the power line, it will disconnect the phase wire, and the zero with dangerous voltage will remain connected. This means there is still a possibility of electric shock when touched. That is, the choice of machine is simple - single-pole switches are installed on some lines, and double-pole switches on others. The specific amount depends on the network condition.
Automatic machines for single-phase networks
For a three-phase network, there are three-pole circuit breakers. Such a machine is installed at the entrance and at consumers, to which all three phases are supplied - an electric stove, a three-phase hob, an oven, etc. The remaining consumers are equipped with two-pole circuit breakers. They must disconnect both phase and neutral.
Example of three-phase network wiring - types of circuit breakers
The choice of circuit breaker rating does not depend on the number of wires connected to it.
Calculation of an automatic machine for an electric motor
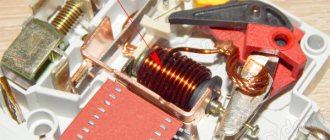
Until recently, the following scheme was used to protect electric motors: a thermal regulator was installed inside the starter, connected in series with the contactor. This mechanism worked like this. When a large current passed through the relay for a long time, the bimetallic plate installed in it was heated, which, bending, interrupted the contactor circuit. If the excess of the set load was short-term (as happens when starting the engine), the plate did not have time to heat up and trigger the machine.
Internal structure of the motor protection circuit breaker in the video:
The main disadvantage of this scheme was that it did not save the unit from voltage surges, as well as phase imbalance. Nowadays, the protection of electric power plants is provided by more accurate and modern devices, which we will talk about a little later. Now let’s move on to the question of how to calculate the machine that needs to be installed in the electric motor circuit.
To select a protective circuit breaker for an electrical installation, you need to know its time-current characteristics, as well as its category. The time-current characteristic does not depend on the rated current for which the AV is designed.
To prevent the circuit breaker from tripping every time the motor is started, the value of the starting current should not be greater than that which causes the device to immediately operate (cut-off). The ratio of the starting current and the nominal value is specified in the equipment passport, the maximum allowable is 7/1.
When calculating the machine practically, you should use the reliability coefficient, denoted by the symbol Kn. If the rated current of the device does not exceed 100A, then the value of Kn is 1.4; for larger values it is 1.25. Based on this, the value of the cut-off current is determined by the formula Iots ≥ Kn x Istart. We select the circuit breaker in accordance with the calculated parameters.
Another value that must be taken into account when selecting when the machine is mounted in an electrical panel or a special cabinet is the temperature coefficient (CT). This value is 0.85, and the rated current of the protective device should be multiplied by it when selecting (In/Kt).
Trip characteristics of protective circuit breakers
Class AB, determined by this parameter, is indicated by a Latin letter and is marked on the body of the machine before the number corresponding to the rated current.
In accordance with the classification established by the PUE, circuit breakers are divided into several categories.
MA type machines
A distinctive feature of such devices is the absence of a thermal release. Devices of this class are installed in circuits connecting electric motors and other powerful units.
Class A devices
Type A machines, as was said, have the highest sensitivity. The thermal release in devices with time-current characteristic A most often trips when the current exceeds the nominal value AB by 30%.
The electromagnetic trip coil de-energizes the network for approximately 0.05 seconds if the electric current in the circuit exceeds the rated current by 100%. If for any reason, after doubling the electron flow, the electromagnetic solenoid does not work, the bimetallic release turns off the power within 20 - 30 seconds.
Automatic machines with time-current characteristic A are connected to lines during operation of which even short-term overloads are unacceptable. These include circuits with semiconductor elements included in them.
Class B protective devices
Devices of category B are less sensitive than those of type A. The electromagnetic release in them is triggered when the rated current is exceeded by 200%, and the response time is 0.015 seconds. Triggering of a bimetallic plate in a breaker with characteristic B at a similar excess of the AB rating takes 4-5 seconds.
Equipment of this type is intended for installation in lines that include sockets, lighting devices and other circuits where there is no starting increase in electric current or is of minimal value.
Category C machines
Type C devices are the most common in household networks. Their overload capacity is even higher than those previously described. In order for the electromagnetic release solenoid installed in such a device to operate, it is necessary that the flow of electrons passing through it exceeds the nominal value by 5 times. When the thermal release is exceeded five times the nominal value of the protection device, the thermal release is triggered within 1.5 seconds.
Installation of circuit breakers with time-current characteristic C, as we said, is usually carried out in household networks. They do an excellent job as input devices to protect the general network, while category B devices are well suited for individual branches to which groups of sockets and lighting fixtures are connected.
Circuit breakers category D
These devices have the highest overload capacity. To trigger the electromagnetic coil installed in a device of this type, it is necessary that the electric current rating of the circuit breaker be exceeded by at least 10 times.
In this case, the thermal release is activated after 0.4 seconds.
Devices with characteristic D are most often used in general networks of buildings and structures, where they play a backup role. They are triggered if there is no timely power outage by circuit breakers in individual rooms. They are also installed in circuits with large starting currents, to which, for example, electric motors are connected.
Protective devices categories K and Z
These types of machines are much less common than those described above. Type K devices have a large variation in the current required for electromagnetic tripping. So, for an alternating current circuit this indicator should exceed the nominal value by 12 times, and for a direct current circuit - by 18. The electromagnetic solenoid operates in no more than 0.02 seconds. Triggering of the thermal release in such equipment can occur when the rated current is exceeded by only 5%.
These features determine the use of type K devices in circuits with exclusively inductive loads.
Devices of type Z also have different actuation currents of the electromagnetic tripping solenoid, but the spread is not as great as in AB category K. In AC circuits, to turn them off, the current rating must be exceeded three times, and in DC networks, the value of the electric current must be in 4.5 times more than nominal.
Devices with Z characteristic are used only in lines to which electronic devices are connected.
Visually about the categories of machines in the video:
Modern electrical protection devices for power units
Modular automatic motors, which are universal devices that successfully cope with all the functions described above, are very popular.
In addition, they can be used to adjust shutdown parameters with high accuracy.
Modern automatic motors come in many varieties, differing from each other in appearance, characteristics and control method. As when selecting a conventional device, you need to know the value of the starting current, as well as the rated current. In addition, it is necessary to decide what functions the protective device should perform. Having made the necessary calculations, you can buy an automatic motor. The price of these devices directly depends on their capabilities and the power of the electric motor.
Selecting a circuit breaker based on short-circuit current
The selection of a circuit breaker for protection against short circuit (short circuit) is carried out based on the calculated value of the short circuit current at the end of the line. The calculation is relatively complicated, the value depends on the power of the transformer substation, the cross-section of the conductor and the length of the conductor, etc.
From the experience of carrying out calculations and designing electrical networks, the most influential parameter is the length of the line, in our case the length of the cable from the panel to the outlet or chandelier.
Because in apartments and private houses this length is minimal, then such calculations are usually neglected and circuit breakers with characteristic “C” are selected; you can, of course, use “B”, but only for lighting inside an apartment or house, because such low-power lamps do not cause a high inrush current, and already in the network for kitchen appliances with electric motors, the use of machines with characteristic B is not recommended, because the machine may be triggered when the refrigerator or blender is turned on due to a jump in the starting current.
Features of protection of electric motors in industrial conditions
Often, when turning on devices whose power exceeds 100 kW, the voltage in the general network drops below the minimum. In this case, the working power units are not switched off, but their speed is reduced. When the voltage is restored to normal levels, the motor begins to gain speed again. In this case, its operation occurs in overload mode. This is called self-starting.
Self-starting sometimes causes false alarms. This can happen when, before the temporary voltage drop, the installation had been operating in normal mode for a long time, and the bimetallic plate had time to warm up. In this case, the thermal release sometimes trips before the voltage returns to normal. An example of a voltage drop in a car's electrical network in the following video:
To prevent the shutdown of powerful factory electric motors during self-starting, relay protection is used, in which current transformers are connected to the general network. Protective relays are connected to their secondary windings. These systems are selected using complex calculations. We will not present them here, since in production this task is performed by full-time power engineers.
Functions of three-phase machines
Before choosing an automatic switch, you should understand its functionality. Users are often mistaken into thinking that the device protects household appliances. The machine does not respond to its electrical indicators, only triggering in the event of a short circuit or overload. The three-phase functions include:
- simultaneous maintenance of several single-phase circuit zones;
- preventing the formation of overcurrents on the line;
- joint work with AC rectifiers;
- protection of high-power equipment;
- increased power due to the installation of a special converter;
- fast response in short circuit mode on a line with a large number of consumers;
- the ability to turn off manually using a switch or switch;
- Compatible with optional safety terminals.
What are circuit breakers for and how do they work?
Modern AVs have two degrees of protection: thermal and electromagnetic. This allows you to protect the line from damage as a result of prolonged excess of the flowing current of the rated value, as well as a short circuit.
The main element of the thermal release is a plate made of two metals, which is called bimetallic. If it is exposed to a current of increased power for a sufficiently long time, it becomes flexible and, acting on the disconnecting element, causes the circuit breaker to operate.
The presence of an electromagnetic release determines the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker when the circuit is exposed to short-circuit overcurrents, which it cannot withstand.
This makes it possible to protect the wire and devices from an electron flow, the value of which is much higher than that calculated for a cable of a particular cross-section.
Device characteristics
The correct selection of a 3-phase machine consists not only of determining its operating conditions, but also the power and type of load that will be connected to it. Incorrectly selected module power leads to deterioration of the protection of the electrical wire , and such a device itself can become a source of an emergency.
But still, no matter how important it is to choose the right power, automatic devices are also characterized by other technical parameters that affect their operation. The main ones include:
- operating voltage - determines the value at which the circuit breaker operates without deteriorating its parameters (usually a difference in the range of 15% is allowed);
- rated current - a parameter directly related to power, indicating the limit value of the current at which the protective module is triggered;
- power consumption - automatic devices are low-power devices;
- wear resistance - indicates the number of guaranteed cycles of turning the machine on and off;
- minimum and maximum operating temperature - the range in which the technical parameters of the protective module do not change;
- rated breaking capacity - the highest load value at which the switch can break the line while maintaining its functionality;
- response time - determines the interval during which the load is disconnected from the power line;
- time-current characteristic - divided into classes, each of which corresponds to the instantaneous tripping current (for example, type C is used for a current exceeding the rated value 5-10 times).
In addition to technical parameters, automatic devices are also characterized by quality indicators. The most common ones include the type of drive, the method of connecting external conductors, the design of the cut-off, and others.
Calculation of consumer power
Each electrical network in an apartment or house can be divided into sections (rooms). Depending on what devices are planned to be used in a particular area, electrical wiring calculations are made. Typically, the electrical wiring zones for each machine are divided among themselves into each room of the apartment or house. One section of wiring for one room, the second for another, and the third for the kitchen and bathroom. In this situation, such powerful consumers as electric stoves, ovens, water heaters, and heating boilers stand apart. This technique requires a dedicated power line, so in modern homes designed for use with electric stoves, a separate circuit breaker is installed to provide power to the device.
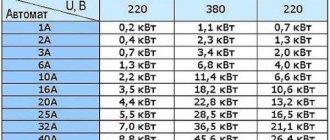
Calculating the required current for a particular section of wiring is quite simple. To do this, use the formula I=P/U, according to which I is the current strength, P is the power (in watts) of all operating electrical appliances on this line, U is the network voltage (the standard is 220 volts). To calculate, you need to add up the power of those electrical appliances that you plan to use on the line, and then divide the resulting sum by 220. From here we get the current strength, according to which you will need to select a cable of a certain cross-section.
As an example, let’s take an area (room) and calculate for it a machine and a cable of the required cross-section. The following will work simultaneously in the room:
- vacuum cleaner (1300 W);
- electric iron (1000 W);
- air conditioning (1300 W);
- computer (300 W).
Let's add these indicators (1300+1000+1300+300 = 3900 W) and divide them by 220 (3900/220 = 17.72). It turns out that the current strength is 17.72, we select the optimal cable cross-section for this based on the table, take a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm or 4 mm square (be sure to take it with a reserve) and a circuit breaker with a rated protection current of 20 amperes.
It is worth mentioning that you should not choose a circuit breaker with an overestimated rated current, since if the electrical network is overloaded (exceeding the continuous-permissible current for a particular wire), the wiring will start to catch fire. The rating of the machine must correspond to the value of the continuous-permissible current of the conductor or be less.
Experienced electricians repeatedly say that you should not install cables with a small cross-section because they are cheap; you should choose a cable with a reserve to avoid overloading the electrical section and causing a fire in the wiring. But choosing a powerful machine gun is contraindicated!
The wiring is installed once, it is difficult to replace it, but replacing the switch in the event of a significantly increased load is much easier.
At the moment, more and more powerful electrical appliances are appearing, so it’s worth taking care in advance in case you decide to use a more powerful vacuum cleaner or add some additional device to the room.