The reasons why the automatic machine knocks out can be divided into three categories. The first reason is a defect in the machine itself, the second is something wrong with the load, and the third is problems in the controlled line. The solution to the problem of troubleshooting is to gradually localize sections of electrical wiring. The correct verification algorithm will significantly speed up and simplify the search.
Knocking out when putting electrical wiring into operation
In the case of new construction or major renovation of a home, new electrical wiring is laid and, accordingly, an electrical panel is installed with protection devices against leakage currents and short circuits.
After installing and turning on the machines, a malfunction appears. The difavtomat knocks out either immediately or after connecting the load.
In this case, a defect in the device itself is excluded, since it was checked upon purchase. The only thing you need to do is check the values of the breaking and rated current of the difavtomat.
They must correspond to the values previously calculated and indicated in the diagram. The second reason can be eliminated by replacing the load with a regular table lamp.
This is usually done on an already operating power supply system. When you turn on the electrical wiring for the first time, you need to start by checking the installation.
Checking the differential machine begins by turning on the device in test mode. If it works, it means it's working. The sequence of further actions is as follows:
- make sure the load is off;
- turn on the machine, if it is knocked out, it means that the conductors are connected incorrectly;
- make sure that the neutral wire is connected to the upper contacts marked N, and the phase wire is connected to contact L;
- check the lower contacts of the difavtomat for correct connection of the wires from the controlled line;
- try turning on the security device.
Pay attention to where the neutral wire comes from. It should go to the upper contact from the zero bus.
The neutral wire from the controlled line, coming from the distribution box, is connected to the bottom terminal. If it’s knocked out again, then you should check the connections in it itself.
How to connect a difavtomat
Let's start with installation methods and the order of connecting conductors. Everything is very simple, there are no special difficulties. In most cases, it is mounted on a dinrail. To do this, there are special protrusions that hold the device in place.
Dinrail mount
Electrical connection
The difavtomat is connected to the electrical network using insulated wires. The cross section is selected based on the nominal value. Usually the line (power supply) is connected to the upper sockets - they are signed with odd numbers, the load - to the lower ones - signed with even numbers. Since both phase and zero are connected to the differential machine, so as not to confuse it, the sockets for “zero” are labeled with the Latin letter N.
The connection diagram for the difavtomat is usually on the case
In some lines you can connect the line to both the upper and lower sockets. An example of such a device is in the photo above (left). In this case, numbering is written on the diagram through a fraction - 1/2 at the top and 2/1 at the bottom, 3/4 at the top and 4/3 at the bottom. This means that it does not matter whether the line is connected from above or below.
Connecting the difavtomat on the distribution panel
Before connecting the line, remove the insulation from the wires at a distance of approximately 8-10 mm from the edge. At the desired terminal, slightly loosen the fixing screw, insert the conductor, and tighten the screw with sufficient force. THEN the wire is pulled several times to make sure that the contact is normal.
Checking in the distribution panel
The most common installation errors occur in the distribution box; neutral conductors from different lines are connected or connections are changed. This is the sin of electricians who are accustomed to working only with circuit breakers. For them, it does not matter which line the neutral wire came from, since they control the current on the phase wire.
This is important for differential circuit breakers and RCDs, since they react to the difference in currents in the phase and neutral wires of the controlled line.
After making sure that the installation in the junction box is correct, try turning on the automatic switch.
If the device turns off again, then you need to check how the wires running from the junction box to the outlet are connected. Here, too, the neutral and ground wires are often confused. If everything is normal here, then the automatic machine will turn on and take control.
For particularly distrustful people who want to check the functionality of the automatic machine, you can do the following. Using an indicator screwdriver, you need to find the zero in the socket and connect it to ground.
Since no currents flow through the neutral and phase wires without load, the automatic circuit breaker will not react in any way. When you turn on a load, even a 100 W desk lamp, the device will immediately turn off.
Since the current in the neutral wire will be two times less than in the phase wire (due to its partial passage through the ground conductor), a current difference will arise. And it will trigger the electromagnetic release of the automatic device.
Methodology for testing difavtomats
Each specific test method for protective disconnecting devices is developed taking into account the specific characteristics of the site in which they are operated.
In any case, it should be based on the algorithms discussed in the above standards. In the package of documents submitted for certification of the electrical measuring laboratory, it must be issued with a separate instruction.
It should be noted that tests of this type are carried out with the supply of powerful current pulses, which often leads to unscheduled operation of the RCD, therefore the practical technology for testing a difavtomat should include the assembly of special measuring circuits or switching separation of the machine and the RCD.
Considering the wide variety of hardware solutions for the differential module and, as a consequence, the unpredictability of their behavior, they most often resort to the second option, opening the circuits connecting the RCD and the AV.
Wires connecting the RCD and the machine
Measurement of time-current parameters is carried out using special equipment that allows monitoring the time parameters of powerful current pulses. Electrical laboratories providing this type of service usually use the UPTR device for these purposes.
UPTR device in operation
Tests and measurements are carried out using the diagram shown in the following figure:
UPTR circuit
The measurement results are recorded in a work log and, after mathematical processing, are drawn up in the form of a test report.
The electrical engineering laboratory "Mega.ru" accepts orders for testing all types of electrical installations, including residual current systems. You can clarify the details of cooperation and place an order for work by calling the numbers posted in the “Contacts” section.
Reasons for shutdown in a working electrical network
The reasons for knocking out automatic devices in a working network are the same as in newly introduced electrical wiring. When analyzing the situation, it is necessary to take into account the general condition of the electrical network:
- what wires were used;
- type of insulation;
- two-wire or three-wire wiring.
You need to find out if there is local grounding. On the latest models of automatic machines, an indication platform has appeared on the front panel. It helps to determine the reason for the triggering of the automatic device.
If, when knocking out the device, the pad did not go beyond the plane of the front panel, then this means leakage currents; if it did, then the operation of the device caused a short circuit or overload.
It may be the other way around, you need to look at the instructions for this device. This feature, of course, makes troubleshooting easier.
How to extend the life of a circuit breaker
Remember two tips:
- Do not overload the protected line with a current higher than the rated current.
- Do not turn off the machine under load.
If everything is clear with the first tip, then the second one is a little more complicated. When current flows through the contacts and you are about to separate them, an arc occurs. This happens due to the truth of the laws of commutation: “The current in the inductance cannot stop instantly.”
Even if the load is active, for example a heater, the cables have their own parasitic inductance. It is even more dangerous to open a circuit breaker if a load such as electric motors or lighting networks with a large number of chokes (DRL, DNAT, LL) is connected to it - the inductance is even greater, and so is the arc. Hence contact defects, their charring, accelerated wear and sticking.
We have become familiar with what defect is caused by what. Circuit breakers last quite a long time if they operate within rated conditions. Modern machines cannot be repaired, so we do not recommend disassembling them; it is better to replace them with a high-quality analogue, for example Moeller or ABB. For household appliances and active loads, use machines with the letter B; to connect a load with significant starting currents (motor), devices with the letter D are better suited, and the number after the letter indicates the amount of permissible current. Avoid connecting oxidized wires and always tighten terminals. By adhering to these tips, circuit breaker malfunctions will occur much less frequently, and you will not have to worry about the safety of the wiring in your apartment or house.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
You probably don't know:
- Socket malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
- How to find a short circuit in wiring
- Reasons for triggering the automatic device
- How to check the performance of an RCD
Published: 01/27/2018 Updated: 01/31/2018
Checking the circuit
If the differential circuit breaker trips due to a short circuit, this is the easiest to detect. A device connected to the line as a load usually does not work. It also has fuses that are probably blown, the body may be a little smoked or the wires may be a little melted.
If there are several devices in the line, then the faulty device is turned off and the automatic machine is turned on again. At the same time, he must take control. When you turn it off again, you need to see how quickly it happened.
If it's instantaneous, it means it's shorting somewhere else. Disconnect the load gradually. We removed one device, turned on the automatic machine, wait for a reaction.
If the protective device is monitored, then the disconnected device is also faulty; if not, then we turn off the next one until we are sure that all connected equipment is in working order.
If everything is normal with electrical appliances, then during an instantaneous shutdown there is a short circuit in the line. First of all, a short circuit can occur in sockets and junction boxes, at connection points. How to check the network in this case?
The malfunction can be determined visually by soot-black wires and melted insulation. If everything is fine there, I’ll check the entire line in sections from the automatic switch to the sockets for a short circuit.
You need to find the burnt wire and replace the entire section (part of the line from one junction of the conductors to another).
How does a differential machine work?
The difavtomat consists of working and protective parts. The first includes an automatic machine. It contains: a tripping system and a rack that resets the switch. Depending on the type of device, there are two-pole and four-pole RCDs. The tripping system has two releases:
The second part of the differential protection device includes a differential protection module. It is able to detect leaking current. In addition, this element converts current into mechanical action. At the same time, the reset rail turns off the switch.
The basis of the design of the difavtomat is a transformer that detects residual current.
Overload
Therefore, the shutdown occurs due to the operation of the thermal release. There are too many consumers on the line. This happens when several powerful devices are connected to one socket through a tee. It is necessary to remove part of the load, switch electrical equipment to other lines, if possible.
If the wiring cross-section allows, you can add the number of sockets and replace the difavtomat with a device with a higher rated current.
By the way, if the automatic device is triggered by a thermal release, it does not turn on immediately. It needs time for the bimetallic strip to cool. This is also a good sign for localizing and troubleshooting.
Purpose, technical characteristics and selection
The differential circuit breaker or differential circuit breaker combines the functions of a circuit breaker and an RCD. That is, this one device protects the wiring from overloads, short circuits and leakage current. Leakage current is formed when the insulation is faulty or when touching live elements, that is, it still protects a person from electric shock.
Difavtomats are installed in electrical distribution panels, most often on DIN rails. They are installed instead of the automatic + RCD combination, and physically take up a little less space. How specific depends on the manufacturer and type of execution. And this is their main advantage, which can be in demand when upgrading the network, when space in the panel is limited and it is necessary to connect a certain number of new lines.
Difavtomats are used to protect wiring from increased loads and people from electric shock.
The second positive point is cost savings. As a rule, a difavtomat costs less than a pair of automatic and RCD with similar characteristics. Another positive point is that you only need to decide on the rating of the circuit breaker, and the RCD is built in by default with the required characteristics.
There are also disadvantages: when one of the parts of the difavtomat is released and built, the entire device will have to be changed, and this is more expensive. Also, not all models are equipped with flags that can be used to determine why the device worked - due to overload or leakage current - which is fundamentally important when determining the reasons.
Characteristics and selection
Since the difavtomat combines two devices, it has the characteristics of both of them and everything must be taken into account when choosing. Let's figure out what these characteristics mean and how to choose a differential machine.
Designation of difavtomats on diagrams
Rated current
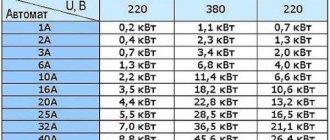
This is the maximum current that the machine can withstand for a long time without loss of performance. It is usually indicated on the front panel. Rated currents are standardized and can be 6 A, 10 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, 63 A.
Four-pole automatic circuit breaker for connection to a 380 V network
Small ratings - 10 A and 16 A - are placed on lighting lines, medium ratings - on powerful consumers and socket groups, and powerful ratings - 40 A and above - are mainly used as an introductory (general) circuit breaker. It is selected depending on the cable cross-section, in the same way as when choosing the rating of a circuit breaker.
Time-current characteristic or type of electromagnetic release
Displayed next to the rating, denoted by the Latin letters B, C, D. Indicates at what overload relative to the rating the machine is turned off (to ignore short-term starting currents).
Rating of the automatic circuit breaker and its time-current characteristics
Category B - if the current is exceeded by 3-5 times, C - if the current is exceeded by 5-10 times, type D is turned off at loads that exceed the rating by 10-20 times. In apartments they usually install difavtomats of type C, in rural areas they can install B, in enterprises with powerful equipment and large starting currents - D.
Rated voltage and frequency
What networks is the device intended for - 220 V and 380 V, with a frequency of 50 Hz. There are no others in our distribution network, but still, it’s worth checking out.
Voltage and frequency for which the differential circuit breaker is designed
Differential machines can be double marked - 230/400 V. This means that this device can operate in both 220 V and 380 V networks. In three-phase networks, such devices are placed on socket groups or on individual consumers, where used just one of the phases.
As water automatic machines for three-phase networks, devices with four inputs are required, and they differ significantly in size. It is impossible to confuse them.
Rated residual current or leakage current (settings)
Displays the sensitivity of the device to the resulting leakage currents and shows under what conditions the protection will operate. In everyday life, only two ratings are used: 10 mA for installation on lines in which only one powerful device or consumer is installed, which combines two dangerous factors - electricity and water (instantaneous or storage electric water heater, hob, oven, dishwasher and etc.).
For lines with a group of sockets and outdoor lighting, difavtomats with a leakage current of 30 mA are installed; they are not usually installed on lighting lines inside the house - to save money.
Leakage current or settings on the differential machine
The device can simply have a value written in milliamps (as in the photo on the left) or a letter designation of the setting current can be applied (in the photo on the right), followed by numbers in amperes (at 10 mA it is 0.01 A, at 30 mA the number is 0 .03 A).
Differential protection class
Shows what type of leakage current this device protects against. There is a letter and graphic image. Usually they put an icon, but there can also be a letter (see the table).
| Letter designation | Graphic designation | Decoding | Application area |
| AC | Responses to alternating sinusoidal current | Placed on lines to which simple equipment without electronic control is connected | |
| A | Responses to sinusoidal alternating current and pulsating direct current | Used on lines that power electronically controlled equipment | |
| IN | Captures variable, impulse, constant and smoothed constant. | Mainly used in production with a large number of different equipment | |
| S | With a shutdown time delay of 200-300 ms | In complex circuits | |
| G | With shutdown time delay 60-80 ms | In complex circuits |
The choice of the differential protection class of the difavtomat is based on the type of load. If this is equipment with microprocessors, class A is required; for lighting or power supply lines of simple devices, class AC is suitable. Class B is rarely installed in private houses and apartments - there is no need to “catch” all types of leakage currents. Connecting class S and G circuit breakers makes sense in multi-level protection schemes. They are used as input if there are other differential shutdown devices further in the circuit. In this case, when one of the lower leakage currents is triggered, the input one will not turn off and the serviceable lines will be in operation.
Rated breaking capacity
Shows what current the automatic circuit breaker is able to turn off when a short circuit occurs and remain operational. There are several standard ratings: 3000 A, 4500 A, 6000 A, 10,000 A.
Breaking capacity of difavtomat
The choice of a difavtomat based on this parameter depends on the type of network and the range of the substation. In apartments and houses at a sufficient distance from the substation, difavtomats with a breaking capacity of 6,000 A are used; close to substations, they are installed at 10,000 A. In rural areas, when power is supplied by air and in networks that have not been modernized for a long time, 4,500 A is sufficient.
On the case this number is indicated in a square frame. The location of the inscription may vary depending on the manufacturer.
Current limiting class
For the short circuit current to reach its maximum value, some time must pass. The sooner power is removed from a damaged line, the less likely damage will occur. The current limiting class is displayed in numbers from 1 to 3. The third class - turns off the line the fastest. So choosing a difavtomat on this basis is simple - it is advisable to use devices of the third class, but they are expensive, but they remain operational longer. So, if you have the financial opportunity, install automatic machines of this class.
Current limitation of difavtomat
On the housing this characteristic is shown in a small square frame next to the rated breaking capacity. It can be on the right (for Legranda) or at the bottom (for most other manufacturers). If you did not find such a mark either on the case or in the passport, then this machine does not have a current limit.
Temperature of use
Most differential circuit breakers are designed for indoor operation. They can be operated at temperatures from -5°C to + 35°C. In this case, nothing is placed on the body.
Designation of increased frost resistance of the difavtomat
Sometimes shields are placed outdoors and ordinary protective devices will not work. For such cases, automatic machines are produced with a wider temperature range - from -25°C to +40°C. In this case, a special mark is placed on the body, which looks a little like an asterisk.
Presence of markers indicating the reason for the operation
Not all electricians like to install automatic circuit breakers, because they believe that the combination of protective circuit breaker + RCD is more reliable. The second reason is that if the device works, it is impossible to determine what caused it - an overload, and you just need to turn off some device, or a leakage current, and you need to look for where and what happened.
To solve at least the second problem, manufacturers began to make flags that show the reason for the operation of the automatic device. In some models, this is a small area, the position of which determines the reason for the shutdown.
A checkbox that shows the reason for the shutdown
If the shutdown was caused by an overload, the indicator remains flush with the body, as in the photo on the right. If the automatic circuit breaker operates in the presence of leakage current, the flag protrudes some distance from the body.
Type of design
There are two types of differential automatic machines: electromechanical or electronic. Electromechanical ones are more reliable, as they remain operational even if the power goes out. That is, if a phase fails, they can operate and also turn off the zero. Electronic ones require power to operate, which is taken from the phase wire and when a phase is lost, they lose their functionality.
Manufacturer and price
You shouldn’t skimp on electricity, especially on devices that protect wiring and life. Therefore, it is recommended to always buy components from well-known manufacturers. The leaders in the market are Legrand (Legrand) and Schneider (Schneider), Hager (Hager), but their products are expensive, and there are many fakes. The prices of IEK (IEK), ABB (ABB) are not so high, but there are also more problems with nm. In this case, it is better not to contact unknown manufacturers, as they are often simply ineffective.
The choice is actually not that small, even if you limit yourself to only these five companies. Each manufacturer has several lines that differ in price, and significantly. To understand the difference, you need to carefully look at the technical specifications. The price is affected by each and them, so carefully study all the data before purchasing.
Washing machine example
As an example, let’s look at cases where a washing machine turns off due to the operation of a automatic device. First of all, let's rule out a load fault.
To do this, instead of a machine, connect an iron or refrigerator to the same outlet. If the machine does not respond, then you should look for the cause of the malfunction in the washing machine.
Check whether the phase wire is shorted to the housing. It is possible that the brushes of the electric motor are worn out, and current flows through the graphite dust to the housing.
Measure the insulation resistance of the motor windings. If it drops below 7-10 kOhm, then the leakage currents are such that they can trigger the automatic circuit breaker. There is no need to go further than this, repairing a washing machine is not an easy task, it is better to call a specialist.
But the reason for the automatic switching off may not only be the load. If you put the washing machine back in place after repair, the situation may repeat itself again.
The fact is that the difavtomat, like the RCD, reacts to the total leakage current in the line: in the wires from the protection device to the load and in the machine itself. Therefore, the total leakage current with the control load and the washing machine may be such that in the first case the automatic machine will not work, and in the second it will turn off.
Therefore, in any case, measure the insulation resistance of the electrical wiring.
Briefly about circuit breakers
Automatic machines must be checked for functionality in order to avoid an emergency.
Circuit breakers or circuit breakers are electrical mechanisms whose main task, in the event of abnormal or emergency situations, is to de-energize the problem line or the entire room. It monitors the voltage in an electrical circuit in real time.
Automatic switches are widely used due to their reasonable price, reliability and ease of use, installation and maintenance. A large number of modifications allow the device to be installed in electrical installations of high and low power. Switches are also available with manual and remote control.
Other reasons
The reason for knocking out the automatic rifle can be anything. This includes increased humidity, which penetrates into the junctions of wires in sockets, junction boxes, and accidental damage to the insulation of wires hidden under the casing by screws or nails. There may be a manufacturing defect that does not appear until several years later.
Finding such faults is quite a troublesome task and takes a lot of time, even in the case of open wiring. The easiest way is to find a break in the line and eliminate the fault by simply replacing the wire.
If necessary, replace the outlet with a waterproof one. Sometimes you come across low-quality wires with insulation that does not meet the declared characteristics. This also does not appear immediately. You'll have to change the wiring. If they laid it in corrugations, then you were lucky. You will do without dusty work.
Testing with a AA battery
A very simple method is to check the RCD using a AA battery. It allows you to check the functionality already during the purchase of the device.
To directly carry out testing, a piece of wire with a length of at least 10 centimeters is connected to any pole of the device. The second wire is connected at the bottom of the device during manufacture. After this, the AA battery is brought to both wires.
When the wires touch plus and minus, the RCD should trip. If this does not happen, you need to reverse the battery poles and repeat the test. If the device is working properly, the shutdown lever should be knocked out.
Connecting a zero with a zero bus after a difavtomat
In this case, 1 phase is removed from the RCD, and nothing is connected to the 0 terminal. This error is characterized by connecting zero to the 0 bus, and then to the load, bypassing the zero connector for connection. Result - the protection device is armed, the “Test” does not work, and when the load is further connected, the difavtomat will work and break the circuit.
Particular attention should be paid to appearance, i.e. make sure the body is intact. In some cases, the machine malfunctions precisely for this reason.
As practice shows, the installation of such protective devices should be entrusted to specialists with experience. This will allow you to get the desired result and not ask yourself the only question in the future - “Why does the automatic machine work?”
“Reverse” connection of the difavtomat
In this case, the connected phase (incoming) immediately goes to the input connector and goes to the load device, i.e. socket. This connection is correct, but with one exception - when connecting the poles, the terminals are swapped. This leads to the fact that 0 gets to the zero bus and then goes from it to the output connector instead of the input 0. As a result, the zero pole is connected back to the phase pole. The differential circuit breaker turns on, but “Test” does not function; when any load is connected, the differential circuit breaker is triggered.
How to check an RCD: 3 tips
An RCD device is needed in order to find out in time about a current leak, which can lead to dire consequences for human health. In order for the device to work properly, it is necessary to carry out performance tests from time to time.
It is important to note that it will not be possible to fully diagnose the device at home: this requires special tools
To be sure that the RCD is working correctly, it is necessary to check the device at least once every month. The residual current device must respond instantly, otherwise it does not perform its functions and can be considered inoperative. If you are not confident in the correctness of self-checking, it is better to seek help from a professional technician.
Test button:
- To conduct testing you do not need to be a qualified specialist. The test is carried out using a button located on the device body.
- The activation of the button when it is pressed simulates a current leak. The leakage current rating is set by the value of the test resistor, which has a built-in type.
- If the device was connected correctly, then after pressing the button, the RCD should immediately trip.
This test is more common than all others, since it does not require special skills to perform. It is reliable and safe. The standard functionality “let the device know” that a current leak has begun. At the same time, for the user this is just a check of the correct flow of current through the circuit.
Checking the RCD using a control lamp
Anyone who cares about their safety should carry out a control check of the correct operation of the RCD at least once every few months. You can check the operation of the RCD yourself using a practical and reliable method. The device works in such a way that when a current leak occurs, it is triggered.
To check the device in this way, you will need an electric wire, an electric incandescent lamp, a socket, resistances and special electrical tools. Before creating a leakage, it is necessary to calculate how much leakage current can be created. It depends on the current that flows through the electric lamp.
How to check the operation of an RCD using a lamp:
- Connect two resistors in parallel. For their power to be 10 W, the resistance must be 2.35 kOhm.
- Using wires, these connections are connected to an electric lamp.
- If there is a protective zero connection to the sockets in the room, then you can check the operation of the RCD using any socket.
- One wire must be connected to the phase, the other wire must touch the protective zero.
As soon as the action is completed, the device should work instantly. If there is no protective zero in the sockets, then checking each socket will not be possible. If this is the case, you can check whether the RCD is working through the electrical panel.