Types of protection
There are several types of protection that should be considered when choosing the optimal system for a particular case.
When considering the question of why protection for electric motors is needed, it is worth taking into account situations that are different from standard ones and may pose a threat of harm not only to the equipment, but to specialists who may work nearby.
- Thus, to prevent the development and occurrence of an accident, various methods of protection are used.
- The best option, suitable in many cases, is a system for emergency shutdown of the engine from the power supply.
- Thanks to this, the system will simply de-energize the device, as a result of which it will turn off on its own.
In this way, it will be possible to prevent an emergency without damaging the equipment.
The system reacts to the temperature indicator, thus monitoring the normal operation of the engine. If the temperature in the block is exceeded and does not decrease, it cuts off the power supply to the entire engine.
Short circuit protection
In the event that an emergency mode appears in the main unit or in all engine control circuits, which reacts to short circuits, the engine is completely disconnected from the power supply.
The system itself reacts to an emergency situation and simply turns off the device to prevent its development.
- In fact, this is the entire protection of electric motors against short circuits.
- However, the protective system itself has several varieties, each of which is preferable in certain operating conditions of the equipment.
- The systems are a network of fuses, whose task is to trigger and shut down a certain unit in a timely manner.
- All of them are triggered virtually simultaneously, without any delay. This allows you to turn off the entire device at once.
The systems are represented by thermal relays for engine protection, automatic switches with an electromagnetic type tripping function. This is one of the most popular types of systems that are used at the moment.
What is a circuit breaker and how does it work?
An automatic current switch is an overcurrent protection device. It automatically opens and closes the circuit at a preset overcurrent value. If the current switch is used within the range of its operating parameters, opening and closing does not cause any damage to it.
Immediately after an overload occurs, you can easily resume operation of the circuit breaker - it is simply reset to its original position.
There are two types of circuit breakers: thermal and magnetic.
Thermal circuit breakers
Thermal circuit breakers are the most reliable and economical type of protective devices suitable for electric motors. They can withstand the large current amplitudes that occur during motor starting and protect the motor from faults such as locked rotor.
Magnetic circuit breakers
Magnetic circuit breakers are accurate, reliable and economical. The magnetic circuit breaker is resistant to temperature changes, i.e. Changes in ambient temperature do not affect its operating limit.
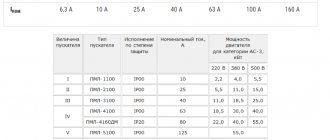
Compared to thermal circuit breakers, magnetic circuit breakers have a more precisely defined response time. The table shows the characteristics of two types of circuit breakers.
The circuit breaker is a protective device against overcurrent. It automatically opens and closes the circuit at a preset overcurrent value. The circuit is then automatically or manually closed
Operating range of circuit breaker
Automatic circuit breakers differ in the level of operating current. This means that you should always select a circuit breaker that can withstand the highest short circuit current that may occur in a given system.
The Importance of a Defense System
Thanks to electric motor protection devices, it was possible to significantly secure production workshops and factories. It is now possible to increase the operating time of devices, which has a positive effect on the productivity of the entire enterprise.
- A protective system against overheating allows you to protect equipment from the effects of elevated temperatures on components and systems
- s of the device.
- In this case, as a rule, overheating itself occurs as a result of a long but low load, at which little heating occurs.
- Thus, working in monotonous mode, the device gradually heats up above normal; for such cases, protection systems are needed.
It should be understood that protection against overheating is not needed in all components of the electric motor, but only in those where a voltage surge is possible in the event of a violation of the normal operating mode.
As a rule, they are installed on the engine head blocks, this allows them to influence the entire system through connecting nodes, thus simultaneously turning off the engine in the event of an emergency.
Books on electric motors
• V.L. Likhachev. Asynchronous electric motors. 2002 / The book is a reference book that describes in detail the design, operating principle and characteristics of asynchronous electric motors. Reference data is provided for engines of previous years of production and modern ones. Electronic starting devices (inverters), electric drives are described., djvu, 3.73 MB, downloaded: 7198 times./
• Bespalov, Kotelenets - Electrical machines / Transformers and electrical machines used in modern technology are considered. Their decisive role in the generation, distribution, conversion and utilization of electrical energy is shown. The basic theory, characteristics, operating modes, examples of designs and applications of electrical generators, transformers and motors are given., pdf, 16.82 MB, downloaded: 2345 times./
• Electromash motor catalog / Asynchronous electric motors with squirrel-cage rotor - manufacturer’s catalog, pdf, 3.13 MB, downloaded: 1401 times./
• VEMZ engines catalog / Engine parameters and catalogue, pdf, 3.53 MB, downloaded: 1197 times./
• Dyakov V.I. Typical calculations for electrical equipment / Practical calculations for electrical equipment, theoretical information, calculation methods, examples and reference data., zip, 1.53 MB, downloaded: 2554 times./
• Karpov F.F. How to check the possibility of connecting several motors to the electrical network / The brochure shows the calculation of the electrical network for voltage fluctuations during the start-up and self-starting of asynchronous motors with squirrel-cage rotor and synchronous motors with asynchronous starting. The conditions under which starting and self-starting of engines are permissible are considered. The presentation of calculation methods is illustrated with numerical examples. The brochure is intended for qualified electricians as a guide when choosing the type of electric motors connected to a municipal or industrial power supply network., zip, 1.9 MB, downloaded: 1665 times./
• Operating manual for asynchronous motors / This manual contains the most important instructions for transportation, acceptance, storage, installation, commissioning, operation, maintenance, troubleshooting and troubleshooting for electric motors produced by Elektromashina. The operating manual is intended for three-phase asynchronous electric motors of low and high voltage series A, AIR, MTN, MTKN, 4MTM, 4MTKM, DA304, A4., pdf, 7.54 MB, downloaded: 2566 times./
• Thermal relay selection table. / Selecting a thermal relay., pdf, 34.01 kB, downloaded: 4145 times./
• Inozemtsev E.K. Repair of asynchronous electric motors / Inozemtsev E.K. Repair of asynchronous electric motors of power plants. The design and technical characteristics of asynchronous electric motors of the A and AO series are considered. A2, A02,4A, AI, 5A, 6A, A, KA, ADA, DAN, AN, AD, 2 AS VO, 4MTN, A2K, A2KP, DASK, VRA, AVR, AVRM, 2VRM, ZVRM, VRPV, AIUV, VRFV, AVT. The technology for repairing electric motors and their components, disassembly and assembly work is outlined. Devices for performing work are provided taking into account advanced repair methods and technologies. The issues of drying electric motors, as well as electrical testing and measuring windings are considered., djvu, 1.84 MB, downloaded: 735 times./
• Toroptsev N. D. Three-phase asynchronous motor in a single-phase circuit with a capacitor / Toroptsev N. D. Three-phase asynchronous motor in a single-phase circuit with a capacitor. 2000 - 72 s; ill. [Library of electrical engineering, supplement to the magazine "Energetik", Vol. 7(19)]. The features of using a three-phase asynchronous motor as a capacitor motor, as well as various switching schemes, are considered. Simple relationships are given to determine the working capacitance of the capacitor. The main technical data of three-phase asynchronous motors of the KA and 4A series (for agricultural purposes), as well as capacitors of various types are given., djvu, 1.84 MB, downloaded: 898 times./
• Starting and protection of AC motors / Starting and protection of AC motors. Starting and braking systems for AC motors. Protection devices and fault analysis of AC motors. Guide to selecting protection devices. Manual from Schneider Electric, pdf, 1.17 MB, downloaded: 2108 times./
Undervoltage protection
This system also protects the equipment from zero voltage, which can cause malfunctions. Security is ensured by several electromagnetic devices.
- Their task is to monitor the voltage, and when the value is unacceptably low, turn off the engine.
- In fact, the principle of operation is the same as that of the previous types of protection, but they help to avoid the occurrence of emergency situations of a completely different type.
- “Zero” protection also helps to protect motors from starting on their own after the mains voltage is restored.
- If there is no protection, then when the voltage drops, the motors stop working, and when the voltage in the network returns to normal, they turn on independently and continue to work.
- This can create very serious emergency situations, which is why it is necessary to install electromagnetic fuses-sensors.
It is noteworthy that you can independently configure these sensors, thus indicating the minimum voltage threshold, after which a planned shutdown of the engine should occur and prevent it from starting on its own.
Comprehensive protection
Universal motor protection units are comprehensive protection systems. Their task is to ensure complete safety during operation; they protect equipment from overheating, short circuits, voltage drops and self-starting.
Technically, they are much more complex than each individual type of protection separately. However, the level of security that can be achieved by installing them is higher, which is definitely an advantage.
The functioning of universal blocks is ensured by a given algorithm of actions, which reacts to certain changes in engine operation, taking the necessary measures to ensure safety.
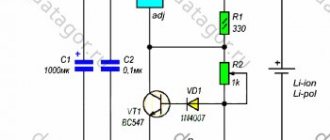
Operating principle of a thermistor
The critical values of the resistance/temperature relationship for motor protection sensors are defined in DIN 44081/DIN 44082.
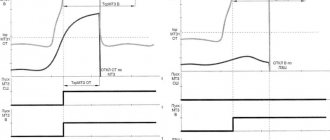
The DIN curve on the right shows the resistance in thermistor sensors as a function of temperature.
Compared to PTO, thermistors have the following advantages:
- Faster response due to lower volume and weight.
- Better contact with the motor winding.
- Sensors are installed on each phase.
- Provide protection when the rotor is blocked.