A magnetic starter is a low-voltage switching device designed to remotely turn off and turn on an electrical load in a network with a voltage of up to 1000 Volts. This device can be used both in industry and at home, so it is important to know about the nuances of choosing its characteristics. In this article we will tell you how to choose a magnetic starter based on power, current and other parameters.
Characteristics and types of starters by characteristics
Before choosing a contactor, you need to decide on the load, and make the choice based primarily on the load power. The parameters of contactors can be clarified on the manufacturers’ websites or from trading organizations, but here we will present and consider the most important ones. The main parameters (current, load power) are usually indicated on the starter housing.
Size (conditional dimensions) of the starter (contactor)
The most important parameter, the value characterizes the power and dimensions of the starter. There are the following starter sizes:
- zero value – for a maximum current of up to 6 A (through each working contact)
- the first - for a maximum current of up to 9 - 18 A (depending on the design of the contacts)
- starter 2 sizes – up to 25 – 32 A
- starter 3 sizes – up to 40 – 50 A
- starter 4 sizes – up to 65 – 95 A
- 5th size starter – up to 100 – 160 A
- sixth value – from 160 A and above
This means the current for application category AC-3 (for an inductive load), for category AC-1 (resistive or low-inductive load - for example, heating elements) the maximum current for the same starter will be one and a half to two times higher. The size of the starter determines how much power it can switch (three-phase circuit 380 V, inductive load).
- 1 – up to 2.2 – 7.5 kW
- 2 – up to 11 – 15 kW
- 3 – up to 18 – 22 kW
- 4 – up to 30 – 45 kW
It must be said right away that this power is really the maximum; you really need to look at the current value of a particular starter (usually the second and third digits in the name). The size of the starter is indicated in the name by the first digit. When the current is exceeded or the current is close to the maximum, the number of operations (reliability) decreases sharply, so the starter must be selected with a power reserve.
Number of contacts (poles)
Contactors are mainly produced with three working contacts (for switching) and one additional one. An additional, or latching, contact is needed for interlocking, or “self-powering,” to lock the contactor in the on state when using the standard switching circuit. Additional contacts can be normally open (most often used) or normally closed.
To increase the number of additional contacts, contact attachments are used, the use of which significantly expands the range of circuit solutions. In the USSR, such additional consoles were called PKI, now there are other models on sale, but the essence is the same.
Additional contact attachments PKI, etc.
The maximum current of additional contacts, as a rule, is equal (in starters of the first and second values) or less than the maximum current of the main contacts. There are also additional contacts (attachments) of the PVL time delay, in which the contacts are turned on or off after a delay time. Read more in the article about pneumatic time delay relays.
Contactor coil voltage
Electromagnetic coils of contactors are usually available in the following voltages: 24, 36, 110, 230, 380 Volts. Larger starters use higher power coils. The coils are also sold separately, and it can be easily replaced in the contactor if a different voltage value is needed.
Contactor coils
As a rule, in the presence of a neutral conductor, it is advisable to use contactor coils for a voltage of 220 V, and in its absence (purely three-phase consumers) - coils for 380 V.
How to replace the contactor coil?
Sometimes a contactor with a coil of the required voltage is not available, so you don’t have to buy the entire contactor you need. Many manufacturers sell coils for different voltages and contactor sizes.
In particular, this applies to IEK, KEAZ. Foreign manufacturers, as a rule, make contactors non-separable, and do not sell coils for them separately.
It is worth saying that contactor coils for the required voltages should be included in repair kits, since this can be considered a consumable item. The main malfunctions of coils are winding breakage and housing deformation.
To increase the service life of contactor coils or electromagnets that remain on for a long time, it is permissible to operate them at a voltage of 85-90% of the nominal voltage.
Criterias of choice
When choosing a starter, you should be guided by its basic technical characteristics, as well as some design features, which we will consider below.
Voltage (nominal) in the switched circuit
The vast majority of magnetic starting devices are used to start asynchronous electric motors that have a squirrel-cage rotor and are designed for an internal factory voltage of 220 V/380 V. If electric motors with a voltage of 380 V/660 V are used (which happens much less frequently), then a starter is also needed choose the voltage that matches them.
To control electric motors with the ability to reverse, you should purchase special reversible starting devices.
Rated current of main contacts
The ratio of the current values of the switching device and the current of the connected load is one of the most important parameters when choosing a starter. For PUs, the production of which is carried out in accordance with GOSTs, a conditional division into classes is used.
In order to select a device based on this parameter, you can use the following table:
Characteristics of PML
Wear resistance commutation
Its value is equal to the guaranteed number of operations declared by the manufacturer. All starting devices in this case are divided into 3 wear resistance classes: A, B, C. The first of them is the highest. It guarantees that the starter will withstand at least 1.5 million cycles. Class B corresponds to a value from 630,000 to 1.5 million cycles. Class B is the lowest. Devices classified under it can withstand from 100,000 to 500,000 operating cycles.
Mechanical wear resistance
This is an equally important characteristic, which shows the number of possible permissible switching on/off of the device without failure (in this case, all manipulations are performed without load, but purely mechanically). The value of this parameter, in contrast to operation under voltage, is much greater. Depending on the type of PU, it can range from 3 million cycles to 20 million cycles.
Number of poles
To power three-phase electric motors, in most cases three-pole magnetic starters are used. But sometimes situations arise (for example, when the source of the load is electric heating systems or lighting networks) when the best option would be to choose a multi-pole starter (among such foreign-made devices there are devices with eight or more poles).
Number of poles
Coil voltage (nominal)
Most of the starters used to control electrical equipment have coils installed in them, designed for the same voltage as the supply network. At the same time, sometimes there may be a need for a starter that has a coil with a voltage different from the mains voltage (for example, when installing automatic circuits). Currently produced PUs allow you to select a coil for any standard voltage (9, 12,24,36...380 volts, and some for a higher one).
Number of auxiliary contacts and their parameters
In addition to the main contacts, which serve to switch the main electrical circuits, most magnetic starters also have additional (auxiliary) ones, the operation of which occurs simultaneously with the operation of the main ones. Their main purpose is to connect signaling devices, blocking circuits, control circuits and others. All these additional contacts are divided into two types - normally closed and normally open. The former are closed when the main coil is turned off, and vice versa, and the latter are synchronous with it.
Possibility of reverse
To control reversible electric motors, you should choose reversible control units, inside of which there are two separate starters connected to each other.
Protection
In the basic version, magnetic starters, as a rule, do not have electrical equipment protection systems. If necessary, this block can be purchased additionally. In addition, as with all electrical equipment, when choosing a control unit, you should pay attention to the value of its climatic parameter (IP) - the worse the environmental conditions in which it will operate, the higher the value of this parameter should be.
Starter in housing
How does a circuit breaker work?
In the previous article we looked at the characteristics of circuit breakers, and now let's delve deeper. I…
Trigger parameters
For a variety of purposes, the following series of magnetic starters are produced: PA, PM, PMA, PME, PML. Based on the load parameters, the selection and use of these devices is carried out according to compliance.
PML series magnetic starter
1. The value of the electromagnetic starter is a conventional term that characterizes the permissible continuous currents of the contacts of the main power circuit. At the moment, there are the following numerical designations of quantities and the corresponding rated currents at a voltage of 380V in the AC-3 operating mode:
- “0” - 6.3 A;
- “1” – 10 A;
- “2” - 25 A;
- “3” - 40 A;
- “4” - 63 A;
- "5" - 100 A;
- “6” - 160 A;
- "7" - 250 A.
2. Operating mode of the starting device, which determines the nature of the switched load:
- AC-1, only active load, or low inductive load;
- AC-3, starting the electric motor and turning it off during rotation;
- AS-4, difficult starting of the engine, turning it off at low speeds and with a stationary rotor, countercurrent braking.
Magnetic starter sizes and categories of their application
3. Operating (switching) voltage of the relay coil, which can have the following values:
- Variable: 24; 36; 42; 110; 220; 380 V.
- Constant: 24V.
4.The number of additional contacts having this designation in Latin letters and Cyrillic letters:
- Normally open (NO), (NO);
- Normally closed (NC), (NC).
There are also special attachments that snap onto the starter housing, which additionally add several signal contacts.
PML series magnetic starter with snap-on attachment
5.Degree of protection of the device:
- IP00 - open, installed in heated rooms in closed electrical panels protected from foreign objects, water and dust;
- IP40 - manufactured in a housing, used inside unheated rooms where there is a small amount of dust in the air and water does not enter the device;
- IP54 - available in a housing, for indoor and outdoor use in places protected from precipitation and direct solar radiation.
6. The presence of a thermal relay that protects the connected circuits from prolonged overloads.
7. The presence of reverse, structurally implemented by combining in one housing two electromagnetic relays, each having three contact groups, with mechanical or electrical blocking of their simultaneous activation.
8. Wear resistance class, meaning the possible number of reliable switchings.
9.Additional controls.
Necessary parameter matching
Since the correct choice of an electromagnetic starter is the key to successful and uninterrupted operation of the connected electrical installations, it is necessary to comply with the above-described parameters of the characteristics of the switched circuit, control voltage, switching circuit, and type of environment. The most important rule is the requirement that the load current does not exceed the permissible contact current.
To connect an active load (without motors) of a certain power P, the strength of the flowing current I is determined from a simplified formula:
I=P/(√3*U) (A),
where U is the network voltage, 380 (V), .
According to the obtained value, select a starting device with a rated current not less than that calculated below in the table.
Magnetic starter selection table
Magnetic starter sizes
When the question arises about choosing a magnetic starter, then along with it arises such a problem as the required size of the starter.
In order to ensure decent operation of electrical appliances in those circuits that are switched by starters, it is required that the characteristics of the latter fully correspond to the operating conditions. There are seven parameters of this very value and each of them implies its own load current parameter. A slight discrepancy (upward) in the permissible current value is allowed.
The expression “magnitude” is a conditional term denoting how much current the selected magnetic starter can pass through the main operating contacts. When assigning a value, it is assumed that the starter operates at a voltage of 380 V, and its operating mode is AC-3.
Here is a list of differences between devices according to their values (currents depending on values):
- 0 – 6.3 A;
- 1 – 10 A;
- 2 – 25 A;
- 3 – 40 A;
- 4 – 63 A;
- 5 – 100 A;
- 6 – 160 A;
- 7 – 250 A.
The values of their permissible currents flowing through the contacts of the main circuit differ from those that I gave according to the following principles:
- category of use (it can be AC-1 -, AC3, AC-4 and 8 more categories);
- the first implies a purely resistive load (or with a small presence of inductance);
- the second is for controlling motors with slip rings;
- third – operation in the direct start mode of engines with a squirrel-cage rotor and connection thereof;
- the fourth is the start of motors with a squirrel-cage rotor, de-energizing engines that rotate slowly or are stationary, braking using the countercurrent method.
If you increase the number of the category of use, then the maximum contact current of the main circuit (if the switching wear resistance parameters are identical) will decrease.
The remaining eight categories are also distributed according to certain types of loads. However, in order for the overheating (thermal) protection to operate with the greatest efficiency, it is necessary to set the current setting value so that it is only slightly higher than the current consumption of the device switched by the starter. The most rational thing would be to have a small margin for adjusting the settings in both directions.
In addition to this value, starters have a number of other important indicators:
- category AC (I talked about it);
- voltage supplied to the control coil;
- presence of a thermal protection relay;
- number of additional contacts (to determine this parameter, it is necessary to take into account the control circuit);
- reversibility of the device (if it is necessary to control the engine with reverse, it makes sense to install a reversing starter);
- IP device security quality;
- class of the device in terms of resistance to wear (this parameter can be calculated by knowing indicators such as intensity of use and frequency of “on-off” cycles).
Naturally, the larger the “size” of the starter, the larger its size will be. For example, starters of the same brand of zero and third values differ in size by almost two times.
I hope that I have clearly explained to you the concept of starter size, what it depends on, as well as other important indicators of these devices.
Write comments, additions to the article, maybe I missed something. Take a look at the site map, I will be glad if you find anything else useful on my site. All the best.
Safety precautions
Electric current has neither color nor smell. It cannot be seen or heard, but its presence is felt by touch or with the help of special devices. Touching a person can have negative consequences, so it is necessary to observe safety precautions when servicing the starter.
- Non-conductive parts must be grounded.
- Do not work under voltage.
- Observe safety precautions when turning off the voltage.
- Hang prohibited posters and, if necessary, install fences.
- Use additional protective elements (insulating gloves, boots, scissors, mats, safety glasses).
- During installation and repair, you must use proper tools.
Installation of the device
It is best to install the device on a hard, rigidly fixed surface in a vertical position. Incorrect installation often leads to false switching on and off of the device. A flat mounting surface is not so susceptible to strong shocks, vibrations and shocks.
The end of one conductor is bent into a ring when connected to the contact terminal of the device. If two conductors with the same cross-section are attached, then the ends are attached in a straight line on both sides of the clamping screw.
If you connect a copper wire, then the ends need to be tinned. Before connecting aluminum wires, the ends must be cleaned with a file. No lubrication of the device is allowed.
Before work, check the serviceability of the moving elements of the device and the correct connection of the electrical circuit.
If a thermal relay is additionally installed, then the device should not be mounted near thermal objects, so as not to expose it to unwanted load.
Design and principle of operation of a magnetic starter
The basis is an electromagnetic system consisting of a coil, a stationary part of the core and a movable armature, which is attached to an insulating cross-arm with movable contacts. Wires from the electrical network are connected to the fixed contacts using bolted connections on one side, and to the load on the other.
To provide protection against erroneous switching on, contacts are installed on the sides or above the main block contacts, which, for example, in a reversible circuit with two starters, when one starter is turned on, block the second one from turning on. If two turn on at once, an interphase short circuit will occur, because changing the direction of rotation of an asynchronous motor is achieved by swapping 2 phases. That is, on the connection side of the electric motor, jumpers are made between the starters with alternating 2 phases on one of them. Also, one pair of contact blocks is required to keep the starter in the on state after releasing the “Start” button. We will look at the connection diagram in detail in the next article.
The principle of operation of the starter is quite simple. To turn it on, you need to apply operating voltage to the coil. When turned on, it consumes very little current through the control circuit; their power ranges from 10 to 80 watts, depending on the size.
When turned on, the coil magnetizes the core and the armature is drawn in, which at the same time closes the main and auxiliary contacts. The circuit closes and electric current begins to flow through the connected load.
To disconnect, it is necessary to de-energize the coil , and the return spring returns the armature to its place - the block and the main contacts open.
A thermal relay is installed between the starter and the 3-phase asynchronous motor, which protects it from overload currents in emergency situations.
Attention, the thermal relay does not protect against short circuits, so it is necessary to install the required size of circuit breaker in front of the starter.
The principle of operation of the thermal relay is simple - it is selected for a certain operating current of the engine, when its limit is exceeded, the bimetallic contacts heat up and open, which open the control circuit and turn off the starter. The connection diagram will be discussed in the next article.
Characteristics of circuit breakers using the example of TEXENERGO
A few years ago, I published articles on my blog on choosing circuit breakers and why…
Folk way of choosing
To connect asynchronous electric motors with a squirrel-cage rotor, there is also a “folk” formula, according to which the rated current In of the motor is taken equal to twice the power value in kilowatts, that is, if
P = 3.7 kW, then Inom = 3.7 * 2 = 7.4 A.
Based on this value, a magnetic starter contactor is selected so that its rated operating current is not less than this value. In such calculations it is assumed that contactors with a suitable rated load value are able to withstand the start of electric motors with a multiple excess of starting currents Ip over the operating rated In, therefore the calculation of starting currents is not performed. A starter with a rated current of 10 A is suitable for this connection.
Types of starters by purpose
Now I will give a couple of examples of starters - real circuits.
This starter circuit is assembled on three second-value contactors and is used to connect an electric motor according to a star-delta circuit. At the top left three phases are supplied, at the bottom three phases go to power the motor. Red wires – powering the contactor coils and checking operation. Protection (automatic motor) is not shown.
reversing starter with automatic motor
Here is a reversing starter, with two mutually interlocked contactors. Automatic engine protection motor - on the right.
Electromagnetic contactors (starters)
We need to bring some order to the terminology. Starters and contactors are often confused. To some they are the same thing, and some say that a contactor is just a big, powerful starter. But no one can really explain how powerful it is...
Previously, during the Soviet era, this was the case. Now starters that were produced or developed in those days are called starters (for example, PML, which is still produced in Ukraine), and new and foreign models are called contactors.
Electricians call the same devices starters, and sellers call them contactors. To be honest, I’m more used to talking about starters.
What is the difference between a contactor and a starter?
In fact, a contactor is a device consisting only of an electromagnetic coil and contacts. When voltage is applied to the coil, the contacts close (or open). The contactor does not contain devices for protection, fixation, switching, indication, etc. A starter is a device that contains a contactor as the main component element. In addition, the starter usually contains a thermal relay for protection against overcurrent, START and STOP buttons, an indication, can be enclosed in a housing, and have a circuit breaker for short-circuit protection. In other words, the starter is used to start (turn on) various electricity consumers.
Details on how a three-phase electric motor is connected to a starter and various circuits for connecting an electric motor are given in my article on connecting asynchronous motors. And another example of using starters is in the article about the hydraulic press circuit. Various circuits for switching on magnetic starters.
And if you are at all interested in what I write about, subscribe to receive new articles and join the group on VK!
The starter can contain two contactors. This happens in cases where reverse engine control is used, or during a soft start, when a powerful engine is turned on first in a star circuit and then in a delta circuit.
Although such a scheme cannot be called “smooth”, there are special devices for smooth starting. Read my articles about the Soft Starter and about the Real Circuit for Switching on a Soft Starter.
Disassembled starter PML-1220 0*2B. The contactor and thermal relay are visible.
Contactors and magnetic starters
To bookmarks
Introduction
At the beginning of this article, I would like to immediately determine what the difference is between a contactor and a magnetic starter, since this question often baffles even the most experienced electrical specialists, while many believe that the difference between them lies in their design, overall dimensions or the value of the switched (rated) current, but this is not so. GOST 30011.4.1-96 will help us understand this issue, which provides the following definitions:
A contactor is a switching device with a single rest position, not manually operated, capable of switching on, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions, including during operating overloads.
A starter is a combination of all the switching devices needed to start and stop the motor, with overload protection.
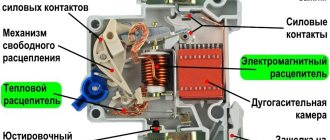
As follows from the definitions above, a contactor is a device designed to switch (turn on/off) any loads, i.e. any loads, while starters are a set of devices designed to control a specific electric motor, as well as providing its protection against overloads, while the contactors themselves are part of the starters:
As you can see in the picture above, the starter includes: a contactor - to turn the electric motor on and off, a thermal relay - to protect the electric motor from overloads, buttons - to control the contactor, all of the above devices are placed in a common housing.
Also, according to the same GOST 30011.4.1-96, starters come in the following types:
Direct-acting starter - A starter that supplies mains voltage to the motor terminals in a single step. Reversing starter - A starter designed to change the direction of rotation of a motor by switching its supply connections without necessarily stopping the motor. Bidirectional Starter - A starter designed to change the direction of rotation of a motor by switching its supply connections only when the motor is stopped.
Thus, a direct-acting starter is designed to start, stop and protect the electric motor, while a reversing starter, in addition to all of the above, allows you to change the direction of rotation of the motor.
As you can see in the picture above, the reversible magnetic starter includes two contactors; switching between them changes the phase sequence, which leads to a change in the direction of rotation of the electric motor. (For more information about changing the direction of rotation of the electric motor and the operating diagram of the reversing starter, see here.)
There are also so-called modular contactors - these are compact contactors designed for installation on a DIN rail, otherwise their design and operating principle are the same as those of conventional contactors.
Now, having understood the concepts of contactor and starter, let’s begin to study the principle of their operation.
Design and principle of operation of the contactor
As can be seen in the picture above, an electromagnetic contactor consists of the following main elements: a magnetic circuit consisting, in turn, of moving and stationary parts, an electric coil, power contacts designed to turn on and off the load, which include moving contacts that are attached to the moving parts of the magnetic circuit and fixed contacts that are attached to the upper part of the contactor body, block contacts intended for use in control circuits, as well as a spring that ensures that the power contacts are maintained in an open state.
The contactor is controlled by applying voltage to an electric coil; when an electric current passes through it, an electromagnetic field is created flowing through the magnetic circuit, while the stationary part of the magnetic circuit together with the electric coil work as an electromagnet which, as can be seen in Fig. 2 above, overcoming the resistance of the spring, attracts the upper moving part of the magnetic circuit with moving contacts attached to it, thus closing the power contacts; when the voltage is removed from the contactor coil, the electromagnetic field disappears, ceasing to attract the moving part of the magnetic circuit, which, under the influence of a spring, returns to its original position, opening the power contacts.
Most modern contactors include only one block contact, but some control circuits require more of them; in this case, an additional attachment with several block contacts is installed on the magnetic starter:
As you can see in the picture above, this attachment (contact block) is installed on the upper part of the contactor connecting to its movable power contacts.
Note: See here for control diagrams for contactors (magnetic starters).
Selection of contactors (magnetic starters) and their characteristics.
The selection of contactors and magnetic starters is carried out according to their following technical characteristics:
1) The required category of application is determined by the type of switched load
In accordance with GOST 12434-83 and GOST R 50030.4.1-2002, there are the following categories (areas) of application of contactors (starters):
2) By rated current
Rated current is one of the main characteristics that determines the maximum current that the contactor can withstand for a long time, as well as ensure its switching (on/off).
The rated current of a starter (contactor) for an electric motor can be calculated using our online calculator or using the method given below.
There are the following standard values of rated currents of contactors (starters), in Amperes:
6.3; 10; 16; 25; 40; 63; 80; 100; 125; 160; 250; 400; 500 Ampere
Note: Modular contactors are available for rated currents up to 100 Amps.
Often, contactors and magnetic starters, depending on their rated current, are conventionally divided into the following values (from zero to seventh value):
The rated current of the starter for controlling the electric motor can be selected based on its power according to the following table:
You can also calculate the starter current yourself using the following method:
The rated current of the starter must be greater than or equal to the rated current of the motor:
I no. MP ⩾ I nom. engine
The rated current of the motor can be found from its passport data, or calculated using the formula:
Inom=P/√3Ucosφη
Where:
- P - Rated power of the electric motor (taken from the motor’s passport data or determined by calculation);
- U - Rated voltage (voltage to which the electric motor is connected);
- cosφ - Power factor - the ratio of active power to total power (taken from 0.75 to 0.9 depending on the power of the electric motor);
- η - Efficiency factor - the ratio of the electrical power consumed by the electric motor from the network to the mechanical power on the motor shaft (taken from 0.7 to 0.85 depending on the power of the electric motor);
You can also calculate the motor current using our online calculator.
The rated current of a contactor used not to control an electric motor is determined based on the current of the electrical network it controls:
I no. contactor ⩾ I calculated networks
The estimated network current can be determined using our online calculator, or you can calculate it yourself using the formula:
I network =(P network *K p )/cosφ , Ampere
Where:
- Pnetworks—the total power of all electrical equipment connected to the contactor, in kilowatts;
- Kp - conversion factor (For a single-phase network 220V: Kp=4.55; For a three-phase network 380V: Kp=1.52);
- cosφ is the power factor, taken to be from 0.95 to 1 for household electrical networks and from 0.75 to 0.85 for industrial electrical networks.
3) According to the rated voltage of the retractor coil
Coil voltage is a parameter characterizing the amount of voltage that must be applied to the terminals of the contactor coil for it to operate. Therefore, the nominal voltage of the coil also determines the voltage of the control circuit (voltage at the control buttons).
There are the following standard values for the rated voltage of contactor (starter) coils, Volts:
12, 24, 36, 48, 110, 127, 220, 380, 500, 660 Volts
The most commonly used are contactors with coils for 220 and 380 Volts, contactors with a coil for voltages of 48 Volts and below are usually used in rooms with increased danger (especially dangerous) in relation to electric shock to people, so that the voltage on the buttons of the control panels is safe .
4) According to rated insulation voltage
The rated insulation voltage of the contactor (starter) is the maximum network voltage for which the insulation of the contactor (starter) is designed; exceeding this value will lead to insulation breakdown and, as a consequence, failure of the contactor. Therefore, the rated voltage of the contactor must be greater than or equal to the mains voltage:
U nom. MP ⩾ U network
In networks with a voltage of 220/380 Volts, as a rule, contactors with a rated insulation voltage of 400 or 660 Volts are used.
Was this article useful to you? Or maybe you still have questions ? Write in the comments!
Didn’t find an article on the website on a topic that interests you regarding electrical engineering? Write to us here. We will definitely answer you.
↑ Up
5
https://elektroshkola.ru/kommutacionnye-apparaty/kontaktory-i-magnitnye-puskateli/
Functionality
Magnetic starters find very wide application in various branches of economic activity and industry.
The most common areas of their use are the following:
- turning on street lighting, in-plant and yard lighting of industrial enterprises;
- switching of electric thermal heating elements and devices (heating elements and infrared emitters) in electric heating systems;
- control of electric asynchronous motors;
- use as main starters for industrial automation networks.
The question of choosing a magnetic starter arises when developing a particular electrical circuit that requires its use, as well as when performing scheduled or emergency repairs, when an analogue should be selected instead of a failed element.
Types of magnetic starters
Rated current and supply voltage of the control coil
Rated current is the most significant parameter, selected according to the consumer’s power. The main question: how to count correctly? When starting, any electric motor briefly produces power, often 5-7 times the rated power. Nevertheless, such a load remains for a fraction of a second and does not affect the operation of the release.
Based on this, we take into account only the rated power
To determine the denomination, it is necessary to calculate In. The formula from the physics textbook will help us with this: In = P/(U √3xcosφ), where P is power (W), U is voltage (V), and cosφ is the power factor of the engine.
For clarity, let's consider a specific example: suppose that you have a three-phase machine with a capacity of 5.5 kW with cosφ = 0.8 (this value is written in the electrical equipment passport). When turned on, the network will flow:
5500W / (380Vx√3×30.8)= 10.6A.
You still need to add 30% of the reserve to the resulting value, as a result, the optimal value will be 13A.
For example, if In is equal to 11.8A, in no case should you take a 12A model, otherwise it will burn out when the power increases.
The power supply to the control coil is selected according to two criteria: the type of electric current (AC or DC) and voltage (from 12V to 440V - DC, from 12V to 660V - AC at a frequency of 50 Hz and from 24V to 660V - AC at 60 Hz). There are also universal models with a coil operating on both AC and DC current.
Magnetic starters PME and PAE
Magnetic starters of the PME and PAE series
| Starter type | Rated current, A at voltages 380/500 V | Overall dimensions, mm | Availability of thermal relay |
| PME-001 | 3/1,5 | 75x65x119 | No |
| PME-002 | 3/1,5 | 121x83x101 | Eat |
| PME-003 | 3/1,5 | 90x150x118 | No |
| PME-004 | 3/1,5 | 135x150x118 | Eat |
| PME-111 | 10/6 | 68x85x84 | No |
| PME-112 | 10/6 | 154x102x91 | Eat |
| PME-113 | 10/6 | 164x90x106 | No |
| PME-114 | 10/6 | 232x90x107 | Eat |
| PME-211 | 25/14 | 102x90x118 | No |
| PME-212 | 25/14 | 195x98x126 | Eat |
| PME-213 | 25/14 | 130x205x155 | No |
| PME-214 | 25/14 | 180x205x155 | Eat |
| PAE-311 | 40/21 | 214x114x144 | No |
| PAE-312 | 40/21 | 275x114x121 | Eat |
| PAE-313 | 40/21 | 214x239x114 | No |
| PAE-314 | 40/21 | 264x239x121 | Eat |
| PAE-411 | 63/35 | 290x183x135 | No |
| PAE-412 | 63/35 | 290x183x135 | Eat |
| PAE-413 | 63/35 | 275x343x135 | No |
| PAE-414 | 63/35 | 275x343x135 | Eat |
| PAE-511 | 110/61 | 335x200x156 | No |
| PAE-512 | 110/61 | 335x200x156 | Eat |
| PAE-513 | 110/61 | 320x338x170 | No |
| PAE-514 | 110/61 | 320x338x170 | Eat |
| PAE-611 | 146/80 | 380x230x190 | No |
| PAE-612 | 146/80 | 380x230x190 | Eat |
| PAE-613 | 146/80 | 385x435x190 | No |
| PAE-614 | 146/80 | 385x435x190 | Eat |
PMA series starters are designed to control asynchronous motors in the power range from 1.1 to 75 kW for a voltage of 380-660 V. PME series starters. PAEs have a switching capacity of up to 2,000,000 and a switching frequency of up to 1,200 per hour. The selection of contactors and starters is carried out according to the rated network voltage, the rated supply voltage of the contactor and starter coils, and the rated switching current of the electrical receiver.
Current consumed by the coils of starters of the PME and PAE series in the attracted state of the armature
| Actuator | Rated current, A, at rated voltage, V | ||||
| Type | Magnitude | 127 | 220 | 380 | 500 |
| 0 | 0,1 | 0,5 | 0,04 | _ | |
| PME | I | 0,14 | — | — | — |
| II | 0,24 | 0,14 | 0,08 | 0,062 | |
| III | 0,255 | 0,13 | 0,087 | 0,0665 | |
| IV | 0,485 | 0,28 | 0,16 | 0,12 | |
| PAE | 0,16 | ||||
| V | 0,595 | 0,355 | 0,215 | ||
| VI | 0,895 | 0,515 | 0,29 | 0,22 | |
Note. The table shows the maximum values of steady-state currents: the starting current does not exceed the steady-state current by more than 6-8 times for PME and 10 times for PAE.
Winding data of PME-000 starter coils for a frequency of 50 Hz
| UH coils, V | 36 | 127 | 220 | 380 |
| Wire diameter, mm | 0,31 | 0,16 | 0,12 | 0,09 |
| Number of turns | 800 | 3000 | 5300 | 9000 |
Winding data of PME-100 starter coils for a frequency of 50 Hz
| UH coils, V | 36 | 127 | 220 | 380 | 500 |
| Wire diameter, mm | 0,38 | 0,2 | 0,15 | 0,11 | 0,1 |
| Number of turns | 660 | 2400 | 4150 | 7170 | 9430 |
Winding data of PME-200 starter coils for a frequency of 50 Hz
| Nominal coil voltage, V | Coil wire diameter, mm | Number of turns in the coil | ||
| Option | Option | |||
| first | second | first | second | |
| 36 | 0,57 | 0,67 | 442 | 426 |
| 110 | 0,33 | 0,38 | 1350 | 1300 |
| 127 | 0,31 | 0,35 | 1560 | 1500 |
| 220 | 0,23 | 0,27 | 2700 | 2600 |
| 380 | 0,18 | 0,20 | 4660 | 4500 |
| 500 | — | 0,18 | — | 5900 |
Note. The coils of the first option are wound with PETV wire, and the coils of the second option are wound with PEV-2 wire.
Winding data of PAE starter coils for a frequency of 50 Hz
| Coil voltage, V | 3rd starter value | 4th starter value | 5th starter value | 6th starter value | ||||
| wire diameter, mm | number of turns | wire diameter, mm | number of turns | wire diameter, mm | number of turns | wire diameter, mm | number of turns | |
| 36 | 0,62 | 350 | 0,90 | 260 | 1,20 | 198 | 1,56 | 147 |
| 110 | 0,38 | 1070 | 0,47 | 800 | 0,69 | 605 | 0,83 | 445 |
| 127 | 0,35 | 1230 | 0,47 | 920 | 0,64 | 700 | 0,83 | 516 |
| 220 | 0,27 | 2130 | 0,35 | 1600 | 0,49 | 1200 | 0,62 | 890 |
| 380 | 0,2 | 3680 | 0,27 | 2760 | 0,35 | 2070 | 0,47 | 1540 |
| 500 | 0,17 | 4850 | 0,23 | 3640 | 0,31 | 2730 | 0,41 | 2020 |
Mechanical and switching wear resistance
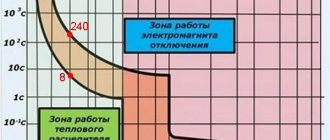
This characteristic shows the maximum number of on-off cycles - trips of the release. The more there are, the longer the service life will be.
This value is especially important for engines with frequent starts.
Mechanical wear resistance shows the number of on-off times in the absence of voltage. As a rule, the average mechanism can withstand about 10-20 million operations.
Electrical durability determines the permissible number of operation cycles and depends on the category of application. For example, if a contactor in AC-3 mode can withstand 1.7 million cycles, then in AC-4 it can withstand 200 thousand. As a rule, the manufacturer always indicates this characteristic in the technical data sheet.
Electrical wear resistance is divided into three classes:
- A - the highest, guarantees from 1.5 million to 4 million operations of the magnetic starter in operating mode;
- B - average, models of this class can withstand from 630 thousand to 1.5 million switchings;
- B - the lowest, the number of cycles from 100 thousand to 500 thousand.
What's new in the VK SamElectric.ru group?
Contactor coil voltage
Electromagnetic coils of contactors are usually available in the following voltages: 24, 36, 110, 230, 380 Volts. Larger starters use higher power coils. The coils are also sold separately, and it can be easily replaced in the contactor if a different voltage value is needed.
As a rule, in the presence of a neutral conductor, it is advisable to use contactor coils for a voltage of 220 V, and in its absence (purely three-phase consumers) - coils for 380 V.
How to replace the contactor coil?
Sometimes a contactor with a coil of the required voltage is not available, so you don’t have to buy the entire contactor you need. Many manufacturers sell coils for different voltages and contactor sizes.
In particular, this applies to IEK, KEAZ. Foreign manufacturers, as a rule, make contactors non-separable, and do not sell coils for them separately.
It is worth saying that contactor coils for the required voltages should be included in repair kits, since this can be considered a consumable item. The main malfunctions of coils are winding breakage and housing deformation.
To increase the service life of contactor coils or electromagnets that remain on for a long time, it is permissible to operate them at a voltage of 85-90% of the nominal voltage.
Characteristics of devices
Magnetic starters produced by manufacturers differ from each other in purpose, the absence or presence of control buttons, thermal relays, degree of protection and other characteristics.
The most popular are the following series of devices:
- PML. This abbreviation indicates that the device is intended for motors with shorted rotors and furnaces with weak inductive loads.
- PMA. This starter is designed for asynchronous three-phase AC motors.
- PME. Reversible connection of asynchronous three-phase electric motors with squirrel-cage motors is carried out using models of this series.
- KMI. It operates in the same modes as PML, and also directly starts asynchronous motors when power is connected.
Based on the load current of the main contacts, an electromagnetic starter can be:
- First magnitude. Load current 10 A and 16 A.
- Second magnitude. With a load current of 25 A.
- Third value - 40 A.
- Fourth magnitude - 63 A.
The voltage of the control circuits must correspond to the operating voltage of the coil. It can be 24V, 220V, 380V.
The number of contacts in the control circuit is commensurate with the number of additional contacts of the starter. Breaking and closing contacts are counted separately.
Based on the degree of protection, the device is:
- dust and waterproof design;
- secure execution;
- open execution.
The first ones are used for outdoor installation. The latter are installed in unheated rooms with a minimum amount of dust, with no prerequisites for moisture ingress. Still others are installed in closed cabinets.
A model with a thermal relay is installed when the electric motor may experience overload due to its modes.
A reversible electromagnetic starter is used to regulate a reversible electric motor. Such a device contains six power contacts, two electromagnetic coils, and a mechanical interlock.
In terms of wear resistance, devices are produced in 3 classes:
- Class, A - the highest commutation wear resistance;
- Class B - average commutation wear resistance;
- Class B - low switching wear resistance.
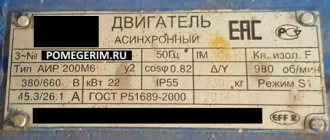
On the model body, the manufacturer must indicate: the size of the starter, switched currents, operating voltage, load power, compliance with GOST or TU.
ads
>
- industrial
- electrician
- useful
Electromagnetic starter series
The PML and PM12 series starters are currently most widely used. More expensive, but also higher quality starters of the PMU series and foreign companies, Legrand, ABB, Schneider Electric.
Magnetic starter size
When selecting a starter, the term “starter size” is widely used. This term is conditional and characterizes the permissible current of the contacts of the main circuit of the starter. This assumes that the main circuit voltage is 380V and the starter operates in AC-3 mode.
The maximum main circuit current is:
- “0” value - 6.3 A;
- “1” value - 10 A;
- “2” values - 25 A;
- “3” values - 40 A;
- “4” values - 63 A;
- “5” values – 100 A;
- “6” size – 160 A.
The permissible current of the main circuit contacts differs from those given above depending on:
- From application category - AC-1, AC-3 or AC-4:
- AC-1 - starter load is purely active or low inductive;
- AC-3 - direct start mode of a squirrel-cage motor, shutdown of rotating electric motors;
- AC-4 - starting an electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor, turning off stationary or slowly rotating electric motors, countercurrent braking.
With an increase in the application category number, the permissible current of the main circuit contacts, with equal parameters for switching wear resistance, decreases;
- From the voltage on the contacts of the main circuit. As the voltage increases, the permissible current of the contacts decreases.
- For some types of starters, the starter size is indicated at a main contact voltage other than 380V.
Coil operating voltage
Voltage range U of the control coil:
380 V,
- DC(constant U) 24 V
- normally open (NO), (NO)
- normally closed (NC), (NC)
- can be included in the starter or manufactured as a separate attachment.
Number of additional contacts
Differences between a relay and a contactor
Relays differ from contactors only in design and purpose, and the difference between them is sometimes barely distinguishable.
Usually,
- The relay does not have arc chutes.
- The relay is housed in a sealed housing.
- The relay is designed for low current and purely resistive loads.
- The relay has switching contacts, which means normally open and closed.
- The relay is not designed to connect a reactive three-phase load.
- A relay can have from 1 to 6 equivalent contacts, and a contactor must have 3 power and (as an option) 1-2 low-current contacts.
- The relay does not have additional functions or contacts, and the contactor can be supplemented with attachments for various installations and purposes.
- The relay is mounted on the panel and can be easily replaced using just your hands. In order to replace the contactor, you need to de-energize the equipment and use a screwdriver.
Starter Maintenance
Like any equipment, this electrical device periodically requires maintenance. The minimum maintenance program includes:
- Visual inspection. Damage and chips may occur due to prolonged use of the device. Therefore, it is necessary to check the appearance of the starter for damage and the presence of all parts and components. It is necessary to remove dirt from the body and from the surface of the core.
- Cleaning contacts. If there are traces of melting or carbon deposits on the contacts, then you need to clean them with a needle file.
- Mechanical check. The spring is inspected, it should be rigid, the coils should be at a distance from each other. The absence of jamming of the armature stroke is checked, and if it is detected, the rubbing parts are lubricated or ground.
- Checking the coil. If there are cracks on the body, melted insulation or carbon deposits on the contacts, the coil must be replaced. A hum during operation of the device indicates an interturn short circuit. Over time, the active resistance of the coil decreases. In all these cases, it is better to rewind or replace it.
- Monitoring the absence of a short circuit. If the device in the housing has metal parts, you need to make sure that there is no short circuit between them.
- Checking the thermal relay. If a thermal relay is installed on the 220 V magnetic starter, it is necessary to check the adjustment settings of this relay. It is problematic to do this at home; special test benches are needed for this.
How the PME-211 magnetic starter works
To turn on a single-phase load of low power, toggle switches, buttons, switches are used, the contact system of which is mechanically driven and designed for small currents. To start and stop a three-phase load, an electrical device is required that would simultaneously supply voltage to all poles of electrical receivers, quickly disconnect from the supply network, extinguish the electric arc at high phase currents, etc. One of such devices is a magnetic starter, which is most often used for controlling asynchronous motors, electric heating units (heaters, electric boilers) and various low-power transformers, lighting networks and other electrical equipment. Let's look at how the magnetic starter of the PME-211 series is designed, activated and connected to the network.
Magnetic starter device
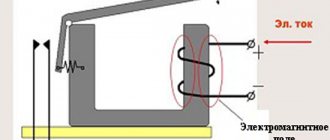
In addition to mechanical action, power contacts can be closed and opened using an electric drive. A fairly simple and common device is an electromagnet. Its most important ability is to attract metal objects when an electric current flows through its coil with a core, and to release it in the absence of current. Thus, an electromagnet has the ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. If you combine a coil with a core, a movable attracting part with a return spring and power contacts in one housing, you will get a ready-made switching device. All electromagnetic relays, contactors and starters operate on this principle. Although their operating principle is the same, they are structurally different.
The collapsible body consists of three parts. The upper part of the cover closes the power contacts and extinguishes the electric arc during switching. Made from press material containing asbestos. In addition, the technical characteristics of the starter are indicated on the cover, such as series, rated voltage of the retractor coil, designation of power contact terminals, etc.
Fixed power and blocking contacts are fixed on the middle part, as well as movable ones on the traverse with an anchor.
And the third, the base, in which the retractor coil with the core is located. The collapsible body is cast from carbolite - phenol-formaldehyde resin with various mineral and organic fillers. This type of dielectric has high heat resistance and is difficult to ignite.
Let's take a closer look at all the elements of the PME-211 magnetic starter.
Magnetic core. The core and armature are made in the form of an W-shaped disconnected magnetic circuit. Like any other magnetic system for alternating current, it consists of sheets of electrical steel, insulated from each other to reduce eddy currents. To avoid shocks when turned on and strong vibrations during operation of the PME-211 magnetic starter, the contact points between the armature and the core are polished and smooth, and short-circuited turns made of non-magnetic material are additionally installed on the outer rods.
Power and blocking contacts are made in the form of rectangular plates of various shapes and thicknesses made of brass with soldering made of technical silver. The use of alloys with this precious metal is due to their resistance to electric arcs and mechanical shocks when turning the magnetic starter on and off. The content of technical silver in PME-211 is 10-11 grams.
on the retractor coils , and on magnetic starters of various brands the brand, wire diameter and number of turns are also written. The higher the voltage the coil is designed for, the higher the number of turns and the active resistance of its wire. If a voltage is applied to the coil above or below its rated value (380 V instead of 220 V and vice versa), this will lead to abnormal operation of the magnetic starter (loud crackling noise when the armature and core interact, failure of the magnetic starter to operate, etc.) and the coil will exit building.
In no case should the rated voltage be applied to the pull-in coil separately from the magnetic circuit, since in this case the magnetic flux will be closed on the turns of the coil, which will increase the current flowing through it and the coil will “burn out”.
A magnetic starter works on the following principle . When an alternating voltage is applied to the coil, an alternating electric current begins to flow in it, which, in turn, creates a magnetic flux in the core and armature, overcoming the resistance of the air gap. As a result, the magnetized armature is attracted to the core, closing the power and blocking contacts of the starter!
Technical characteristics of the magnetic starter PME-211-UHL4V
The main technical characteristics of the starter are given on the starter plate or on the top cover.
- alternating voltage of magnetic starter coil: 220 V, 380 V;
- rated voltage and current of the power circuit: at 380 V - 25 A, at 660 V - 14 A;
- rated power of the connected electric motor: no more than 11 kW;
- climatic modification UHL4 and wear resistance category B;
- fastening the case with screws;
- 2 normally open and 2 normally closed blocking contacts are installed.
Together with magnetic starters, thermal relays of the PTT brand of the appropriate size can be used to protect power equipment from prolonged overloads and from phase failure!
To change the rotation of the electric motor rotor, reversible magnetic starters are used, which are two starters of the same series, mounted on the same base, electrically connected, having electrical and mechanical interlocks that prevent the simultaneous activation of both starters.
On electrical circuit diagrams, magnetic starters are designated as follows:
Decoding magnetic starters
All used magnetic starters differ from each other in rated current, in the presence or absence of thermal relays (overload protection), in climatic design, overall dimensions and other parameters.
PME- X1 X2 X3 X4 X5, where
PME - magnetic starter series
X1 - rated current: 1 - 10A, 2 - 25A.
X2- version according to the degree of protection:
X3 – design of starters according to purpose and the presence of a thermal relay:
1-irreversible starter without thermal relay;
2-irreversible with thermal relay;
3-reversible without thermal relay;
4-reversible with thermal relay;
X4 – climatic version: U3, UHL4.
4 comments to the post “How the PME-211 magnetic starter works”
Interesting article about magnetic starters. Write an article on how to maintain magnetic starters!
The magnetic starter consists of two parts: the starter
and
contact block
.
Although the contact block
and is not the main part of a magnetic starter and is not always used, but if the starter operates in a circuit where additional contacts of this starter must be used, for example, reversing an electric motor, signaling the operation of the starter or turning on additional equipment by the starter, then for multiplication of contacts, just and serves as a contact block or, as it is also called,
a contact attachment
.
Switching principle
The closure of the contacts of the power circuit is carried out by a contactor - a device in which a group of contact plates coupled to the armature of an electromagnetic relay is closed to fixed contacts connected to the input and output terminals for connecting the supply voltage of the network and load lines.
Thus, with the help of low currents in the electromagnetic relay coil and low-current control signals, it is possible to switch high-current circuits of large loads. The small current and low voltage of the signal circuit makes the operator’s work much safer, and for automatic monitoring and control systems it gives a wide scope for their use, thanks to the introduction of computerized algorithms into the process.
This is interesting: At whose expense will electricity meters be replaced in 2022: let’s look into it thoroughly
Connection diagram for 220 V
Any electrical connection diagram contains 2 circuits, including for a single-phase network. The first is the power one, through which power is supplied. The second is a signal one. With its help, the operation of the device is monitored.
The connected contactor, thermal relay and control buttons form a single device, which is marked as a magnetic starter in the diagram. It ensures the proper functioning and safety of electric motors under various operating conditions.
Contacts for connecting the device's power are located in the upper part of the case. They are designated A1 and A2. So, for a 220 V coil, 220 V voltage is supplied. The order in which “zero” and “phase” are connected does not matter.
On the bottom of the case there are several contacts marked L1, L2, L3. The power supply for the load is connected to them. Whether it is constant or variable is not important, the main thing is the limitation of 220 V. The voltage is removed from contacts T1, T2, T3.