Selecting a machine based on cable cross-section and load power
For quite some time now, modern homes have stopped using corks. They were replaced by more technological devices - automatic machines, also known as baggers, although some still call them traffic jams, but this is wrong, because the operating principle of a traffic jam and a machine is somewhat different. Since in this article we will consider the selection of a machine depending on the cable cross-section, there will be no talk about traffic jams.
So, the machine is a device that allows you to open the electrical circuit automatically in two cases:
- line current overload;
- occurrence of a short circuit (SC).
In the first case, overload occurs due to a malfunction of electrical appliances or their large number and power density. In the second case, due to a short circuit, electricity is consumed to heat the wires with the maximum possible current for this section. In addition to the above cases of circuit breakage, the machine provides the possibility of manual control. There is a switch on the body of the device that allows you to open the circuit.
The purpose of the circuit breaker is to protect the section of the electrical circuit for which it is installed, as well as timely opening of this section in the event of an overload or short circuit.
Nuances
In general, readers should not have any questions regarding the selection of packages according to the cable cross-section, but there are some subtleties that we did not mention above.
- A machine with which type of electromagnetic release to choose. In everyday life, machines of categories “B” and “C” are most often used. This is due to the fastest possible operation of package switches when the rated current is exceeded. This is extremely important when using appliances such as electric kettles, toasters and irons. Depending on the type of equipment used, you should choose a specific category; it is advisable to give preference to category “B” switches.
- A machine with a maximum switching capacity to choose. Depends on the location of the electricity input from the substation to the apartment, if in close proximity, then you should choose one with a switching capacity of 10,000 amperes, otherwise for city apartments there are enough devices for 5,000–6,000 amperes. You can play it safe and choose the option of 10,000 amperes; ultimately, this indicator only affects whether the machine will be operational after a short circuit.
- What type of wire to choose: aluminum or copper We strongly do not recommend purchasing aluminum conductors. Copper wiring is more durable and can handle higher currents.
How to calculate the power of a machine
In order to provide the most effective and accurate overload protection, the formula is used to calculate the machine’s power for a 220V network:
in which the rated current is expressed by I, the sum of the powers of all powered consumers including lighting devices is P, and the voltage of the electrical network is U. Thus, the value of the rated current will increase with an increase in the total power of consumers.
And for a 380V network, the power calculation of the machine is made according to the formula:
in which the cosφ value is added, meaning the power factor (the exact value can be found in Table 6.12 of the SP 31-110-2003 standard “Design and installation of electrical installations in residential and public buildings”). To simplify calculations in everyday conditions, cosine phi is taken equal to one. In general, this coefficient depends on the type of electrical receiver, for example:
- for lighting networks with fluorescent lamps, the power factor is 0.92;
- for lighting networks with incandescent lamps - one;
- for gas-light advertising installations - from 0.35 to 0.4;
- for computers without technological air conditioning - 0.65;
- for refrigerators and air conditioners with an electric motor up to 1 kW, cosφ is equal to 0.65, and with a motor of 1 - 4 kW, the power factor increases to 0.75.
Let's try to calculate the machine's power using an example. Let's say you are trying to protect a group of three kitchen outlets from short circuits. In one, a refrigerator with a power of 400 W is constantly turned on, in others, a microwave or kettle (1000 W) or a blender (300 W) is periodically connected. Let's calculate the total power if you want to simultaneously connect the most powerful devices: 400 + 1000 + 1000 = 2400 W. The current strength for a 220V network is as follows:
And we recommend choosing a machine based on power in favor of the closest 10A rating. A natural concern may arise: will it “knock out” when applying more voltage to such a nominal value? In fact, if you apply a load of 15 amps to a 10-amp protective device, the operation will occur in eight minutes, and if you apply 11 amps, then it will take as long as twenty minutes. During this time, the kettle will turn off and the load will again become acceptable - much earlier than the release switches on.
How to choose a circuit breaker in the case of a three-phase input, which is relevant for private houses and some new buildings? You can either use the power factor formula or refer to the table.
General information about machines
Automatic switchboards
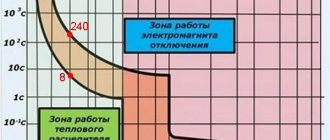
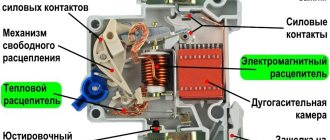
As a rule, automatic switches contain three types of electrical circuit releases: thermal, electromagnetic and mechanical. The first is designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent, the second - from short circuits in load circuits, the third - for operational switching of electrical circuits.
There are electrical circuit breakers that perform protective functions against overload and electric shock (ES). These are switches controlled by differential current with built-in protection against current overloads - difavtomats (DV).
Main technical characteristics of automatic circuit breakers (AB)
Ratings of machines for various electrical networks
Rated voltage is the value set by the manufacturer at which the AV’s performance is determined.
Rated current is the current established by the manufacturer that the AV is capable of conducting in continuous mode, in which the main contacts remain closed at the specified control ambient temperature (standard +30 °C).
The switch frequency is the industrial frequency for which the device is designed and to which the values of other characteristics correspond.
The rated maximum breaking capacity is the value of the ET, which can turn off the AV while maintaining its functionality.
The current limiting class is characterized by the shutdown time between the beginning of the circuit breaker opening and the end of the arc time. There are three classes of current limiting:
- the shutdown time of class 3 AB occurs within 2.5 – 6 ms;
- 2 classes – 6–10 ms;
- Class 1 – more than 10 ms.
There are several types of protective (time-current) characteristics of AV, the most popular are B, C and D
| Type of protective characteristic | Range of instantaneous tripping currents, reduced to the rated value of the current AB | Purpose |
| A | from 1.3In | To protect circuits in which temporary overcurrents cannot occur during normal operation. |
| IN | from 3In to 5In | To protect circuits in which minor temporary current overloads are allowed in normal operation. |
| WITH | from 5In to 10In | To protect circuits in which moderate temporary current overloads are allowed in normal operation. |
| D | from 10In to 20In | To protect circuits with significant temporary current overloads in normal operation. |
| K | from 12 I | For protecting industrial circuits using inductive loads. |
| Z | from 4 In | To protect industrial circuits using industrial electronic equipment as a load. |
Differential circuit breakers
Differential circuit breaker
Rated residual current IΔn – the value of the residual current specified by the manufacturer, at which the DV must operate under specified conditions.
Rated non-breaking residual current IΔn0 – the value of the non-breaking residual current specified by the manufacturer, at which the motor does not operate under specified conditions.
The rated differential maximum making and breaking capacity IΔm0 is the effective value of the alternating component of the expected differential current, which the DV can turn on, conduct and turn off.
There are three types of DV:
- S – with differential current response time delay.
- AC – operation is ensured with a sinusoidal alternating differential current, either applied abruptly or slowly growing.
- A – ensures operation with differential sinusoidal alternating current and differential pulsating direct current applied in an abrupt manner or slowly increasing.
Cables GOST 31996–2012
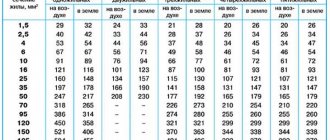
When choosing a machine, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the cables. The most important is the permissible current (Iperm). It shows at what maximum current the cable can operate throughout its entire service life. This table from the PUE contains information about permissible cable currents depending on the material and conditions of cable laying.
Permissible currents for cable depending on materials
| Open wiring | Cable cross-section, mm2 | Closed wiring | ||||||||||
| Copper | Aluminum | Copper | Aluminum | |||||||||
| Current A | Power, kWt | Current A | Power, kWt | Current A | Power, kWt | Current A | Power, kWt | |||||
| 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | |||||
| 11 | 2.4 | — | — | — | — | 0.5 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15 | 3.3 | — | — | — | — | 0.75 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 17 | 3.7 | 6.4 | — | — | — | 1 | 14 | 3 | 5.3 | — | — | — |
| 23 | 5 | 8.7 | — | — | — | 1.5 | 15 | 3.3 | 5.7 | — | — | — |
| 26 | 5.7 | 9.8 | 21 | 4.6 | 7.9 | 2 | 19 | 4.1 | 7.2 | 14 | 3 | 5.3 |
| 30 | 6.6 | 11 | 24 | 5.2 | 9.1 | 2.5 | 21 | 4.6 | 7.9 | 16 | 3.5 | 6 |
| 41 | 9 | 15 | 32 | 7 | 12 | 4 | 27 | 5.9 | 10 | 21 | 4.6 | 7.9 |
| 50 | 11 | 19 | 39 | 8.5 | 14 | 6 | 34 | 7.4 | 12 | 26 | 5.7 | 9.8 |
| 80 | 17 | 30 | 60 | 13 | 22 | 10 | 50 | 11 | 19 | 38 | 8.3 | 14 |
| 100 | 22 | 38 | 75 | 16 | 28 | 16 | 80 | 17 | 30 | 55 | 12 | 20 |
| 140 | 30 | 53 | 105 | 23 | 39 | 25 | 100 | 22 | 38 | 65 | 14 | 24 |
| 170 | 37 | 64 | 130 | 28 | 49 | 35 | 130 | 29 | 51 | 75 | 16 | 28 |
From this table you can find the required cable cross-section and permissible current depending on the wiring conditions, open or buried. For example, the power of all appliances in the apartment is 9 kW. For open single-phase copper wiring, the wire cross-section is 4 mm 2, current 41A, for closed - the nearest higher power value is 11 kW, cross-section 10 mm 2, current 50A. The nearest lower rating of the circuit breaker is 32A.
If there is doubt about the quality of the electrical wiring, then it is better to exercise caution and choose a machine with a rating lower than the value in the table.
The residential network has a branched structure: a current of different strength will flow in each branch, so the wires have different cross-sections. If you install one circuit breaker only at the entrance, it will not be able to protect individual sections of the wiring from overload. If the entire network is laid with a cable of the same cross-section, then this is an unjustified financial expense. The best solution would be to install the appropriate current on each section of the machine. The figure shows an approximate structure.
Installation of machines for the appropriate current
The figure clearly shows the load on each section and the cross-section of the wire. By installing appropriate circuit breakers, you can reliably protect the entire network from short circuits or overloads. In addition, at any time it is possible to select and disable one or another section, maintaining the functionality of the rest of the network.
When using powerful asynchronous motors in everyday life, especially 3-phase ones, for example, power tools, it is advisable to turn them on through a separate circuit breaker, since they have a large starting current, and when operating through a common circuit breaker, a power outage may occur even during normal operation of the equipment.
Video on the topic
This online calculator allows you to calculate and select a circuit breaker according to the cable cross-section to ensure reliable protection of the electrical network from overloads and short-circuit currents.
Why is it necessary to select a machine based on the cable cross-section?
One of the main characteristics of all electrical cables and wires is the long-term permissible current, the value of which depends on the cross-section of the cores; exceeding the long-term permissible network current leads to overheating of the cables, destruction of their insulation and, as a result, failure of the electrical wiring, therefore, in accordance with the PUE, electrical networks must be protected from overcurrents, i.e. overloads and short circuits, this protection is provided by automatic circuit breakers.
From the above it follows that for reliable protection of electrical wiring, the rated current of the circuit breaker protecting it must be selected in such a way that if the long-term permissible current of the electrical network is exceeded, the circuit breaker will switch it off, thereby preventing overheating of the cables.
The work of our calculator is based on this principle, all you need to do is indicate the type of cable, copper or aluminum, the method of laying it, the cross-section of the cores and press the “CALCULATE” button, after which the calculator will independently determine the long-term permissible cable current in accordance with Chapter 1.3 PUE and will select the nearest standard value of the rated current of the machine.
Did you find this online calculator useful? Or maybe you still have questions ? Write to us in the comments!
Didn’t find an article on the website on a topic that interests you regarding electrical engineering? Write to us here. We will definitely answer you.
The purpose of a circuit breaker (hereinafter referred to as AB) is to protect electrical wiring and electrical equipment from short circuits (hereinafter referred to as short circuit) and overload. If you do not use such switches in the network, then over time an accident may occur, that is, a short circuit in electrical wiring, electrical appliances or power tools. If not a short circuit, then an overload in the operation of electrical equipment.
In the first and second cases, the wire or cable will heat up, which means the insulation will melt. The wires will short out, a short circuit will occur, which means fire, sparks and ultimately a fire.
To prevent this from happening, AVs are used as protection against possible unpleasant consequences.
How does AB protect electrical wiring and electrical appliances and tools? If, simply put, there is a special device inside this switch that provides instantaneous shutdown of the voltage supply if there is a short circuit or overload problem.
What determines the choice of cable cross-section?
The main task of preserving the original functionality of an electrical cable is to prevent it from overheating. This can be solved very simply if 1 mm2 is subjected to a load in the form of a long-term total current not exceeding 9 Amperes. When translating this indicator into a more familiar value for the average person - power, it turns out that a conventional cable with a cross-section of 1 mm2 can be used to power electrical appliances with a power consumption of up to 2 kW. If such numerical transformations cause difficulties, and a special online calculator
is not available at the right time, you just need to remember a few simple rules.
- Cable for lighting – core cross-section 1.5 mm2.
- Cable for all sockets, air conditioning, loggias - core cross-section 2.5 mm2.
- Cable for electric ovens – core cross-section 4 mm2.
- Cable for hobs and instantaneous electric water heaters – core cross-section 6 mm2.
Important! The cable supplying outlets and lighting systems may break, have branches and connections. And all others from the list presented above must be solid. This means that to organize power supply for, say, an oven, a special line of cable with a cross-section of 4 mm2 must be laid directly from the panel, and with the installation of a separate machine. This is a standard and there is no situation that would allow us to deviate from it and organize branches to power other power devices. Any joint on such a line is a minus to durability and reliability.
Main selection criteria
In order to choose the right introductory machine (VA), you need to know what characteristics you should pay attention to when purchasing
Rated current
This is the most important characteristic when choosing an input protective device. This property of the device indicates the maximum current, if exceeded, the power will be turned off within a certain time.
Regardless of whether the machine is introductory or provides protection for a specific line (wire), its calculation is made based on the maximum power of electricity consumers. The rating of the input device is selected by calculating the power (or current) of all consumers when simultaneously connected to the network, for greater safety, reducing the resulting number by 10-15%, rounding down to a lower value.
Number of poles
There are machines with different numbers of poles. Single-pole ones are used to protect individual lines. The functions of the input circuit breaker are usually performed by two, three or four-pole circuit breakers.
An important rule that will help you choose the number of poles is that for single-phase networks, two-pole circuit breakers are used, and for three-phase networks, three or four-port circuit breakers are used. Two-pole switches are made with a lever and a shutdown mechanism common to both poles. That is, in an emergency situation, two poles are disconnected at once (usually a phase is connected to one terminal, and zero to the second)
Such devices are often used in single-phase networks of residential premises of apartment buildings
That is, in an emergency, two poles are disconnected at once (usually a phase is connected to one terminal, and zero to the second). Such devices are often used in single-phase networks of residential premises of apartment buildings
Two-pole switches are made with a lever and a shutdown mechanism common to both poles. That is, in an emergency, two poles are disconnected at once (usually a phase is connected to one terminal, and zero to the second). Such devices are often used in single-phase networks of residential premises of apartment buildings.
A three-pole (or four-pole) machine is used when introducing electrical cables into private houses with a three-phase network, as well as in industrial buildings and even in some apartments. A phase is connected to each terminal of the device (and zero if it is a four-terminal network). It, like a two-terminal switch, has one common lever for all poles and, in case of overload, turns off the power in all phases.
Time-current characteristic
It characterizes the instantaneous tripping current and is most often indicated on the device by the Latin letters B, C or D. The sensitivity of the protective device to inrush currents of electrical appliances and equipment depends on the time-current characteristics. For an input circuit breaker, this property is important, since it affects the operation of lower groups of circuit breakers.
The following types of machines are most often used based on their time-current characteristics:
- B – at a current value 3 - 5 times higher than the rated value, the electromagnetic switch of the device will operate and it will instantly turn off;
- C – the electromagnetic release will turn off the device when the current exceeds 5-10 times;
- D – will work when the current exceeds 10-20 times the rated current.
For the input circuit breaker in residential premises, devices with a time-current characteristic of type C are used, since most devices in the home do not have large starting currents and will not have a negative impact on the electrical network of the apartment or house.
The response characteristics of each device are indicated in the passport and instructions of the circuit breaker manufacturer.
Mounting method
All circuit breakers have a standard mounting and are placed on a DIN rail in the electrical panel. The same rule applies to introductory machines. The exception is special devices for industrial purposes, which can be mounted without a DIN rail on special fasteners.
Switch brand
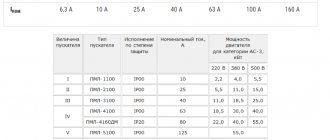
When choosing an input protective switch, as well as in the case of choosing any electrical devices, it is important to focus on a well-known manufacturer that has earned recognition. Such manufacturers provide a quality guarantee for their devices and produce reliable, durable and safe circuit breakers. The most popular machines today include machines from the following manufacturers:
The most popular machines today include machines from the following manufacturers:
Application of measuring instruments
To determine the diameter of the cores of wires and cables, various measuring instruments are widely used, showing the most accurate results. Basically, the use of micrometers and calipers is practiced for these purposes. Despite their high efficiency, a significant drawback of these devices is their high cost, which is of great importance if the tool is planned to be used only 1-2 times.
As a rule, professional electricians who are constantly engaged in electrical installation work use special devices. With the right approach, it becomes possible to measure the diameter of wire cores even on working lines. After obtaining the necessary data, all that remains is to use a special formula:
The result of the calculation will be the area of the circle, which is the cross-section of the wire or cable core.
Main selection criteria
In order to choose the right introductory machine (VA), you need to know what characteristics you should pay attention to when purchasing
Rated current
This is the most important characteristic when choosing an input protective device. This property of the device indicates the maximum current, if exceeded, the power will be turned off within a certain time.
Regardless of whether the machine is introductory or provides protection for a specific line (wire), its calculation is made based on the maximum power of electricity consumers. The rating of the input device is selected by calculating the power (or current) of all consumers when simultaneously connected to the network, for greater safety, reducing the resulting number by 10-15%, rounding down to a lower value.
Number of poles
There are machines with different numbers of poles. Single-pole ones are used to protect individual lines. The functions of the input circuit breaker are usually performed by two, three or four-pole circuit breakers.
An important rule that will help you choose the number of poles is that for single-phase networks, two-pole circuit breakers are used, and for three-phase networks, three or four-port circuit breakers are used. Two-pole switches are made with a lever and a shutdown mechanism common to both poles
That is, in an emergency, two poles are disconnected at once (usually a phase is connected to one terminal, and zero to the second). Such devices are often used in single-phase networks of residential premises of apartment buildings
Two-pole switches are made with a lever and a shutdown mechanism common to both poles. That is, in an emergency, two poles are disconnected at once (usually a phase is connected to one terminal, and zero to the second). Such devices are often used in single-phase networks of residential premises of apartment buildings.
A three-pole (or four-pole) machine is used when introducing electrical cables into private houses with a three-phase network, as well as in industrial buildings and even in some apartments. A phase is connected to each terminal of the device (and zero if it is a four-terminal network). It, like a two-terminal switch, has one common lever for all poles and, in case of overload, turns off the power in all phases.
Time-current characteristic
It characterizes the instantaneous tripping current and is most often indicated on the device by the Latin letters B, C or D. The sensitivity of the protective device to inrush currents of electrical appliances and equipment depends on the time-current characteristics. For an input circuit breaker, this property is important, since it affects the operation of lower groups of circuit breakers.
The following types of machines are most often used based on their time-current characteristics:
- B – at a current value 3 - 5 times higher than the rated value, the electromagnetic switch of the device will operate and it will instantly turn off;
- C – the electromagnetic release will turn off the device when the current exceeds 5-10 times;
- D – will work when the current exceeds 10-20 times the rated current.
For the input circuit breaker in residential premises, devices with a time-current characteristic of type C are used, since most devices in the home do not have large starting currents and will not have a negative impact on the electrical network of the apartment or house.
The response characteristics of each device are indicated in the passport and instructions of the circuit breaker manufacturer.
Mounting method
All circuit breakers have a standard mounting and are placed on a DIN rail in the electrical panel. The same rule applies to introductory machines. The exception is special devices for industrial purposes, which can be mounted without a DIN rail on special fasteners.
Which machine to choose for 2.5 mm2 cable?
For consumers whose total power will not exceed 3.5 kW, we recommend using a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 sq. mm and protecting these lines with a 16A automatic.
For a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 sq. mm according to Table 1.3.6 of the PUE, the long-term permissible current is 27A. Based on this, you might think that a 25A machine will fit such a cable. But that's not true. By the way, for those who don’t know where to look, I publish this table:
According to the PUE, clause 1.3.10, a current value of 25A will heat up a 2.5 sq. mm cable to 65 degrees Celsius. This is a high enough temperature for constant operating modes.
It is also important to understand that not all manufacturers produce cables in accordance with GOST and its cross-section may be lower than declared. So the cross section could be 2.0 sq.mm instead of 2.5 sq.mm. The quality of copper also differs between factories and you cannot be guaranteed to accurately say what quality of cable you have.
Therefore, a reserve in cable protection is very important to avoid problems during the operation of electrical wiring. The choice of machine according to the cable cross-section is carried out as follows:
- I use a 1.5 sq. mm cable when installing alarms and lighting; it corresponds to a 10A machine;
- a 2.5 sq. mm cable is often used for individual sockets and socket groups, where the total power of consumers will not exceed 3.5 kW. It corresponds to the current ratings of 16A automatic machines;
- a 4 sq. mm cable is used in everyday life to connect ovens, washing machines and dishwashers, heaters and water heaters; they buy a 25A automatic machine for it;
- a 6 sq. mm cable is needed to connect serious powerful consumers: electric stoves, electric heating boilers. Machine rating 32A;
- a cable of 10 sq. mm is usually the maximum cross-section used in everyday life, intended for supplying power to apartments and private houses to electrical panels. Automatic 40A.
To calculate the electrical network at home, boldly and strictly follow the table and guide provided above. With the correct calculation of power lines and protective devices, everything will work for a long time and will not bring you any inconvenience or problems.
Selecting a circuit breaker by current
According to the rated current AB
The industry produces a wide variety of circuit breakers with rated current: 0.5A; 1A; 1.6A; 2A; 3.15A; 4A; 5A; 6A; 10A; 16A; 20A; 25A; 32A; 40A; 50A; 63A. In everyday life, it is mainly used from 6A to 40A.
When purchasing an AV, you need to choose a rating so that it operates until the moment when the current does not exceed the capabilities of the wiring.
Therefore, you need to know what cross-section you need to lay the wire (cable) to the consumer or group of consumers and their power. The nominal value of AB will depend on this.
| Rated current of the circuit breaker, A | Electrical circuit load, 220 V |
| 10 | Lighting, alarm |
| 16 | General purpose sockets |
| 25 | Air conditioners, water heaters |
| 32 | Electric stoves, ovens |
| 40; 50 | General input |
Calculation of consumer power
Each electrical network in an apartment or house can be divided into sections (rooms). Depending on what devices are planned to be used in a particular area, electrical wiring calculations are made. Typically, the electrical wiring zones for each machine are divided among themselves into each room of the apartment or house. One section of wiring for one room, the second for another, and the third for the kitchen and bathroom. In this situation, such powerful consumers as electric stoves, ovens, water heaters, and heating boilers stand apart. This technique requires a dedicated power line, so in modern homes designed for use with electric stoves, a separate circuit breaker is installed to provide power to the device.
Calculating the required current for a particular section of wiring is quite simple. To do this, use the formula I=P/U, according to which I is the current strength, P is the power (in watts) of all operating electrical appliances on this line, U is the network voltage (the standard is 220 volts). To calculate, you need to add up the power of those electrical appliances that you plan to use on the line, and then divide the resulting sum by 220. From here we get the current strength, according to which you will need to select a cable of a certain cross-section.
As an example, let’s take an area (room) and calculate for it a machine and a cable of the required cross-section. The following will work simultaneously in the room:
- vacuum cleaner (1300 W);
- electric iron (1000 W);
- air conditioning (1300 W);
- computer (300 W).
Let's add these indicators (1300+1000+1300+300 = 3900 W) and divide them by 220 (3900/220 = 17.72). It turns out that the current strength is 17.72, we select the optimal cable cross-section for this based on the table, take a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm or 4 mm square (be sure to take it with a reserve) and a circuit breaker with a rated protection current of 20 amperes.
It is worth mentioning that you should not choose a circuit breaker with an overestimated rated current, since if the electrical network is overloaded (exceeding the continuous-permissible current for a particular wire), the wiring will start to catch fire. The rating of the machine must correspond to the value of the continuous-permissible current of the conductor or be less.
Experienced electricians repeatedly say that you should not install cables with a small cross-section because they are cheap; you should choose a cable with a reserve to avoid overloading the electrical section and causing a fire in the wiring. But choosing a powerful machine gun is contraindicated!
The wiring is installed once, it is difficult to replace it, but replacing the switch in the event of a significantly increased load is much easier.
At the moment, more and more powerful electrical appliances are appearing, so it’s worth taking care in advance in case you decide to use a more powerful vacuum cleaner or add some additional device to the room.
Installation and installation of automatic machines in apartment panels
Electrician services for installation and selection of automatic machines (circuit breakers)
Installation and replacement of circuit breakers (circuit breakers) is the primary task of an electrician when repairing and replacing electrical wiring. During any repair or reconstruction of construction projects, be it a small apartment, a residential building, or a shopping and entertainment complex, electricians occupy one of the first lines. Old protection systems are morally and physically outdated. A large amount of technological equipment in production, ventilation and air conditioning systems. Washing machines, dishwashers, ovens, and hydromassage baths in apartments required additional safety measures. The installation of automatic circuit breakers along with differential circuit breakers and RCDs (residual current devices) ensures correct operation of electrics and protection of group lines from short circuits and overloads. At SK Elit-Service LLC you can order the services of an electrician for the installation of a switchboard and a protection and automation system. The company's electricians carry out any orders for the replacement and installation of automatic circuit breakers (circuit breakers) for individuals and organizations with consistent quality, compliance with SNiPs (building codes and regulations) and PUE (rules for electrical installations).