general information
The white LEDs that are used today first appeared in 1996. However, only in 2005 they began to be used specifically as a lighting source. This type of light bulb is energy saving.
The luminous power of LED lamps is their main characteristic . It shows the energy efficiency of this type of lighting. The power of LED lamps is measured in watts. Manufacturers are gradually trying to increase the quality of the glow without changing their power. That is why the consumer receives a high-quality lighting source, but at the same time saves energy. For comparison, you can use an incandescent light bulb with a rating of 100 W. A LED with the same level of illumination will have only 12 W.
Main conclusions
When choosing LED light sources, you need to pay attention to such an important indicator as Lumen. This is an important unit of measurement that shows the amount of light emitted by a particular lighting element. It should be remembered that the illumination for incandescent lamps and LED devices is not equivalent. To determine a device with a suitable luminous flux, you need to carry out simple calculations taking into account the standard of illumination of a certain room, area, and ceiling height. Then you need to determine the number of light bulbs that will provide uniform illumination of the room. Diode devices are more suitable for this purpose as they last longer, are safe and are economical. In addition, it is possible to select the appropriate light temperature to make the atmosphere in the room comfortable.
Types of diode light bulbs
The first criterion for dividing is the material of the case:
- Glass (frosted or transparent);
- Aluminum;
- Plastic;
- Ceramics.
By type of base:
- Screw (letter designation – E);
- Pin (letter designation - G).
On the base, in addition to the letter indicating its type, numbers are indicated that indicate for the first type the diameter, measured in millimeters, and for the second type this is the length between the pins.
Thus, the following types of LEDs can be distinguished:
- E14 (bulbs with a smaller diameter base, suitable for some lamps);
- E27 (regular, which are suitable for installation, for example, in chandeliers, where the socket is designed for incandescent light bulbs);
- G4 (can be used, for example, to illuminate pictures).
- GU5.3, G9 (replacement for halogen bulbs);
- GU10 (used for built-in lamps that serve as lighting, as well as in hoods);
This list shows only the main types.
Base type
An important parameter that depends on the socket into which the lamp is to be inserted. Standard screw bases E27 (diameter 27 mm) and E14 (diameter 14 mm) are the most popular in everyday life. G4, GU5.3, GU10 – lighting elements with such sockets are designed to fully replace halogen lamps. GX53 are used for lighting fixtures built into furniture. G13 – rotating base, used in tubular lamps.
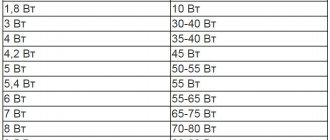
Power table for LED lamps
Depending on the type of paw on the base, the indicators may be as follows:
It is clear from the table that higher power LED bulbs produce greater luminous flux. Depending on the power of LED lamps, their purpose changes. An E27 or E14 light bulb with a power of 5 W will be sufficient for the home. But for a large workshop you will need a stronger light source.
At the beginning, the power of LED lamps for the home is indicated in the table. However, this is not the minimum value for this type of lighting. There are diode lamps with a rating of 2 W. And the maximum power of LED lamps can reach up to 180 W.
What is a lumen
When choosing light bulbs, power is not the main indicator, since it shows how much energy the device spends. For example, a 60W device is weaker than one rated at 100W. To find out the intensity of light, you need to define a unit of measurement such as Lm. Lumen is a more accurate indicator, since light bulbs with the same power, but different levels of efficiency (efficiency) and spectral composition, emit light of different intensities.
Lumens measure the amount of light that a lighting fixture emits in different directions. This physical quantity began to be used in the middle of the 20th century.
To determine the degree of illumination of a lamp, 2 important values are used - lumen and lux.
Important! Lumen is a value that represents the total luminous flux that a lighting element emits in different directions. Lux (Lx) demonstrates the amount of light that falls on 1 m² of surface. That is, the higher the Lm, the more illuminated the surface, and the greater the number of Lm, the brighter the lamp.
Thus, to evaluate the efficiency of a light source, you need to use the following formula: 1 Lx = 1 Lm/m². For example, if a lamp with a luminous flux of 100 Lumen illuminates 1 m², then the illumination will be equal to 100 Lux. If the same device is used on an area of 10 m², the degree of illumination will decrease. During calculations, it is necessary to take into account the luminous flux, which is directed in all directions.
LED bulbs emit directional light, unlike devices with incandescent filaments and fluorescent ones, which shine evenly in all directions. To ensure that the surface is equally illuminated, you need to purchase LEDs with lower brightness.
Correspondence of the power of LED lamps to other types of lighting
From the table we can conclude that diode lamps are less energy-consuming compared to others. With different powers, the luminous flux of LED lamps and the other two types remains the same.
Thus, the rated power of LED lamps that need to be installed in the house can be calculated based on the table above. Also on the packaging of some light bulbs there is information about equivalent indicators. For example, a 5 W LED light bulb corresponds to a 40 W incandescent light bulb. Moreover, in both cases they will have the same glow.
Electrical and light parameters
The parameters of incandescent lamps or the characteristics of incandescent lamps are usually divided into three groups - electrical, light and operational. Electrical parameters characterize the lamp as a consumer of electrical energy and determine the possibility of its connection to power sources (electrical network). Electrical parameters include the rated voltage and rated power of the lamp, the current is a derivative value and is determined by calculation.
Light parameters are more varied. The standardization of one or another determines the purpose of the lamp. For incandescent lamps intended for general lighting, the main technical characteristics are luminous flux and luminous efficiency. For signal lamps, an important parameter is brightness, for lamps - luminous intensity curves and the like.
Operational parameters determine the possibility and technical and economic feasibility of using lamps of this type in a particular lighting installation. In this sense, operational parameters should include both electrical and light parameters. Therefore, when talking about the operating parameters of lamps, they usually mean the service life of the lamps, the stability of the luminous flux, environmental parameters and a number of additional requirements.
The main electrical parameter of an incandescent lamp is the rated voltage of the lamp Ul.nom. For most incandescent lamps, this voltage corresponds to the voltage of the power source.
The bulk of incandescent lamps for general use are powered by electrical networks of power systems, which for lighting installations can be considered sources of unlimited power. Therefore, for a long time, for general purpose incandescent lamps, the supply voltage was also the rated voltage of incandescent lamps. All other electrical parameters of incandescent lamps were referred to this rated voltage. At the same time, the voltage in lighting networks often differs from the nominal voltage. Therefore, in order to improve the performance characteristics of lamps, according to GOST 2239-79, five supply voltage ranges have been introduced: 125 – 135, 215 – 225, 220 – 230, 230 – 240 and 235 – 245 V, and the rated voltage of lamps in accordance with the international classification is taken voltages 130, 220, 225, 235 and 240 V.
Limited power power sources (batteries, car generators, dry cells, etc.) are distinguished by the fact that the average values of their actual voltage do not correspond to the nominal voltage. Therefore, for incandescent lamps intended to operate from such power sources, in addition to the rated voltage, the so-called design voltage Ul.r is used, that is, the average voltage at which the incandescent lamp will operate. Accordingly, all its other parameters are related to the design voltage.
The second important electrical parameter of incandescent lamps is power. The rated power of an incandescent lamp of a given type, Pl.nom, is understood as the calculated electrical power that is released in an incandescent lamp of a given type when it is turned on at the rated (or rated) voltage. In practice, for a batch of lamps, this is the average power value for a fairly large group of lamps of this type. The possible spread in the power values of individual lamps is limited by the upper limit of permissible power for lamps of this type.
For certain types of lamps, in particular those intended to operate from chemical current sources, instead of the rated power, the rated current Il.nom is sometimes standardized, for which a limit on its upper value is established.
The main lighting characteristics of incandescent lamps are determined by the purpose of the lamp. For lighting lamps this is the luminous flux Fl. Almost the nominal luminous flux of a lamp is the average value of the luminous flux of a large batch of lamps of this type. In relation to each incandescent lamp, we can talk about the lower permissible limit of luminous flux. Limiting the upper limit does not make sense, since an increase in the luminous flux can be achieved by increasing the power of the lamp, the upper limit of which is limited, as well as by increasing the temperature of the filament, which will inevitably lead to a decrease in the service life of the lamp and rejection of the batch according to this parameter.
By changing the design and configuration of the filament body or using specially shaped bulbs, it is possible to obtain incandescent lamps with a given luminous intensity curve. For such lamps, in addition to normalizing the luminous flux, one or several values of luminous intensity Iv in given directions are normalized. The number of luminous intensity normalization points is determined by the ability to control the curve with a given accuracy.
Incandescent lamps have different luminosity L, which is associated with the variety of areas of their application. For example, spotlight lamps, lamps for signal devices, and film projection equipment have high brightness, the value of which is standardized in some cases. And, conversely, to illuminate residential premises, a reduced brightness is required, so such incandescent lamps are often produced in frosted bulbs.
For lamps used in optical devices, the efficiency of which is determined by the brightness of the filament, it is desirable to standardize the overall brightness of the filament. The difficulty of determining such brightness by measuring the luminous intensity and dividing the result by the area of projection of the filament body onto a plane perpendicular to the direction of the luminous intensity led to the fact that this standardization was abandoned, reducing the control of lamps to measuring the luminous intensity in given directions and the main geometric dimensions of the filament body .
Luminous efficiency η, which is an important light-technical characteristic of the quality of lamps and their main operational indicator, is currently excluded from the number of standardized values, since it is determined by calculation as the ratio of the luminous flux to the power of the lamp, measured at the rated voltage of the lamp. Luminous efficiency is at the same time the most important parameter of incandescent lamps, which determines the efficiency of generating luminous flux. The luminous efficiency of incandescent lamps increases with increasing their power; for lamps of the same power, it is greater for lamps designed for a lower rated voltage. For incandescent lamps of a given power and design, the luminous flux, which determines the luminous efficiency, depends on the temperature of the filament and its emissive properties. An obstacle to increasing the temperature of tungsten is an increase in the rate of its evaporation, which was largely overcome when using halogen cycles.
Colorful temperature
Possible indicators:
- From 2700 to 3000K;
- 4000K;
- 6500K.
This concept is also one of the characteristics of diode lamps. It is measured in Kelvin (K). The color of the glow depends on this indicator. For example, a color temperature value between 2700K and 3000K indicates that the light will be yellowish.
Lamps with a color temperature of 4000K have a white glow. This type of light is usually used in shopping centers. And if the indicator is 6500K, then the light will be cold white. Such lamps are used only in industrial premises.
For the home, lamps with a color temperature level of 2700K – 3000K are best suited.
Light flow
The parameter allows you to determine the amount of light energy produced by the LED. Measured in lumens (lm, lm). With its help, they can easily find an alternative to a traditional incandescent lamp, using the drawing discussed above. Knowing the luminous flux and power of the lighting device, the luminous efficiency value is determined - you need to divide the luminous flux by the power.
Life time
Despite the low power consumption of LED lamps, their service life is an important point. After all, if they break down quickly, then there is no point in purchasing them, since there will be no energy savings.
When purchasing diode light bulbs, the buyer is given a guarantee for the product. Typically the warranty period is from 3 to 5 years. This is already a good indicator. However, based on statistics, the service life is approximately 50 thousand hours, which corresponds to 6 years. However, many users note that the quality of the glow deteriorates over time.
Pros and cons of purchasing this type of light bulbs
Positive and negative aspects can be assessed using the following indicators:
- Price;
- Dimensions;
- Directional light;
- Ripple.
As for the first characteristic, we can say that the cost can be twice as much as for a regular light bulb. This is the main disadvantage of the product. However, it is worth considering that due to energy savings, the cost of the product will pay for itself.
When replacing a light bulb, you need to consider its size. LED dimensions may be larger compared to conventional ones. This may affect the appearance; the light bulb may stick out strongly from the lamp or may not fit there at all.
LED bulbs have a slightly different direction of light, which may be unusual at first. Their side lighting is poor.
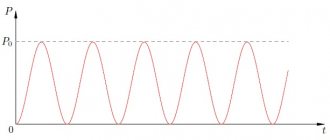
The positive thing is that there is no light pulsation. However, not all light bulbs have this phenomenon. You need to purchase a quality product to avoid pulsation that is unpleasant to the eye.
Some conclusions
An important characteristic of all types of light sources is power. The power of LED lamps is measured in watts (W). An important indicator is also the luminous flux. It directly depends on the power of the product. For home, 5-10 W is best. If you wish to replace, the equivalent power of LED lamps can be found in the table above.
Despite their considerable cost, light bulbs of this type will last a long time and save energy. Therefore, such an acquisition will soon pay for itself. When choosing, it is important to pay attention to the color temperature of the product. The color of the glow depends on this indicator.
How many lumens are in an incandescent lamp?
Even products with the same power may have different luminous flux, and this value may differ significantly. Below is a table that will allow you to convert watts to lumens and find out the approximate luminous efficiency of the product and the room illumination produced by LEDs and other sources.
Comparative characteristics of different types of light bulbs
| LED, W | Luminescent, W | Incandescent lamp, W | Luminous flux, Lm (approximately) |
| 2-3 | 5-7 | 20 | 250 |
| 4-5 | 10-13 | 40 | 400 |
| 8-10 | 15-16 | 60 | 700 |
| 10-12 | 18-20 | 75 | 900 |
| 12-15 | 25-30 | 100 | 1200 |
| 18-20 | 40-50 | 150 | 1800 |
| 25-30 | 60-80 | 200 | 2500 |