LEDs are undoubtedly the most economical lighting sources, only sunlight is cheaper. But even despite their efficiency, some specimens can be quite voracious. And yet, how much electricity does an LED consume?
The “gluttony” of a device directly depends on its brightness.
The light-emitting crystal operates at a voltage of 2.8 - 3.5 V (depending on the color of the glow). Inside the diode crystal there is a pn junction, when current passes through it, light is emitted. How many volts the LED operates from depends on the method of connecting the modules on the matrix. It can be either 3V or 12V.
Consumption depending on LED type
Indicative
The current consumption of products of this class does not exceed 20 mA; at a voltage of 3V per hour, the electricity consumption during their operation will be only 0.06 W or a little more than 0.5 kW per year of continuous glow.
Lighting
The current consumption of the crystal can be 150-300 mA, with a supply voltage of 3.3V this is from 0.5 to 1W. Powerful diodes may contain several elements on one matrix. The power of the LED matrix used in spotlights can reach several hundred watts.
Practical method
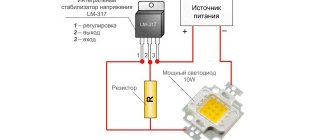
The most accurate data on the forward voltage drop across an LED can be obtained through practical measurements. To do this, you will need an adjustable DC power supply (PSU) with a voltage from 0 to 12 volts, a voltmeter or multimeter and a 510 Ohm resistor (more is possible). The laboratory circuit for testing is shown in the figure.
Everything is simple here: a resistor limits the current, and a voltmeter monitors the forward voltage of the LED. Smoothly increasing the voltage from the power source, observe the increase in readings on the voltmeter. When the triggering threshold is reached, the LED will begin to emit light. At some point, the brightness will reach the nominal value, and the voltmeter readings will stop increasing sharply. This means that the pn junction is open, and a further increase in voltage from the output of the power supply will be applied only to the resistor.
The current reading on the screen will be the nominal forward voltage of the LED. If you continue to increase the power supply to the circuit, then only the current through the semiconductor will increase, and the potential difference across it will change by no more than 0.1-0.2 volts. Excessive current will lead to overheating of the crystal and electrical breakdown of the pn junction.
If the operating voltage on the LED is set to about 1.9 volts, but there is no glow, then the infrared diode may be tested. To verify this, you need to direct the radiation flow to the turned on phone camera. A white spot should appear on the screen.
In the absence of an regulated power supply, you can use a 9 V “crown”. You can also use a 3 or 9 volt network adapter in the measurements, which produces a rectified stabilized voltage, and recalculate the value of the resistor.
Calculating the LED supply voltage is a necessary step for any electrical lighting project, and luckily it's easy to do. Such measurements are necessary to calculate the power of an LED, since you need to know its current and voltage. LED power is calculated by multiplying the current by the voltage. However, you need to be extremely careful when working with electrical circuits, even when measuring small quantities. In this article we will take a closer look at the question of how to find out the voltage to ensure proper operation of the LED elements.
Supply voltage for LED devices
Regardless of the brightness and power of the module, they are all assembled from LED matrices, which are designed for 3.3V power supply. For high-power modules, various combinations of connections with power supply from 12V to 24V are used. This is a necessary measure to reduce the current load.
Consider the following situation:
A 50W light source is required. To create it you will need fifty one-watt modules. If they are all connected in parallel, the supply voltage will be only 3.3 V, but the current in the circuit will reach 50 x 0.3A = 15 Amperes. This is very, very much.
All electrical appliances in the apartment, when turned on at the same time, rarely require more than 10-15 Amperes. High current strength leads to significant heat generation through the conductors, and to power such a unit you would need a finger-thick multi-core copper cable.
To reduce the current in the circuit, the LED modules are connected in series. In the classic connection diagram, the device discussed above will consist of eight stages, consisting of six LEDs connected in series with a supply voltage of 24V. Then the load power will be only 8 x 0.3A = 2.4 A. And this is not much more than the power of an ordinary mobile phone charger.
LED operation
LEDs come in different colors; they come in two and three colors, flashing and changing colors. To allow the user to program the operating sequence of the lamp, various solutions are used that directly depend on the LED supply voltage. To illuminate an LED, a minimum voltage (threshold) is required, and the brightness will be proportional to the current. The voltage across an LED increases slightly with current because there is internal resistance. When the current is too high, the diode heats up and burns out. Therefore, the current is limited to a safe value.
The resistor is placed in series because the diode array requires a much higher voltage. If U is reversed, no current flows, but for high U (eg 20V) an internal spark (breakdown) occurs which destroys the diode.
As with all diodes, current flows through the anode and exits through the cathode. On round diodes, the cathode has a shorter lead and the body has a cathode side plate.
Supply voltage for household devices using diodes
LED flashlights
LED lights vary significantly in brightness and power. Therefore, it is difficult to say exactly how many volts there are in an LED light bulb.
An ordinary household flashlight has a bright 3.3 V diode installed. Thanks to the use of special circuits that increase the voltage, they comfortably operate from one 1.2 V AA battery or a 1.8 V battery.
How many volts are the LEDs in high brightness flashlights? Signal lights for special purposes are equipped with special diode matrices with a supply voltage of 3.3V - 4.7V and a current of up to 2000mA.
Powerful 3.7V lithium batteries are used to power them.
LED strips
The supply voltage of the tape and its power depend on the type of LEDs used.
All about concrete and gypsum products
In the lighting
White LEDs used to design modern lamps and luminaires can consume from 150 mW (for example, SMD 3014) to 150 W (COB matrices). The technical characteristics of SMD 3014 are discussed in detail in the article “Comparison of the most common SMD LEDs.” The type of SMD crystal is easily determined by its appearance and geometric dimensions.
Diagnosing the power and current consumption of an unknown COB matrix is much more difficult, since its working surface is often covered with an opaque phosphor. Under the protective layer there can be either one crystal with a voltage drop of 3.3 volts, or several connected in series with a voltage drop of 12, 24, 36 volts or more. Thanks to the sequential connection of crystals, a reduction in current consumption is achieved, which reduces the cost of the driver.
Types of light-emitting diodes
The operation of LED devices is based on the process of transmitting photons through a semiconductor crystal. The color of the resulting glow depends on the material used. It's not the filters that make the glow red or blue.
An increase in the intensity of light radiation is achieved using special additives or by creating several layers - aluminum nitride is placed inside.
The color of the LEDs depends on the crystal material
LEDs are divided into two groups according to the method of application:
- Indication and decoration. Colored LEDs fall into this category. They are placed in a translucent case. To control equipment from a distance, models with infrared indicators are used.
- Lighting. In this case, LED white light sources are used. Warm or cool shades are selected according to needs.
According to the installation method, lighting LEDs are distinguished:
- SMD . With this modification, the crystal is located on a special substrate, which is placed in the housing. The contacts are connected. If one crystal breaks, it is replaced, restoring the operation of the entire system.
- SALT . In such a device, many crystals are placed on one board. All of them are coated with phosphor. The degree of luminescence of such lamps is high, and production is inexpensive. The system will have to be completely replaced even if just one LED fails.
Alternative definition of voltage
The first step to calculate LED power consumption is to determine the LED voltage. If you don’t have a multimeter at hand, you can study the manufacturer’s data and find the data sheet U of the LED block. Alternatively, U can be estimated based on the color of the LEDs, for example, a white LED supply voltage of 3.5 V.
After the LED voltage is measured, the current is determined. It can be measured directly using a multimeter. The manufacturer's data provides an approximate current estimate. After this, you can very quickly and easily calculate the power consumption of the LEDs. To calculate the power consumption of an LED, simply multiply the LED's U (in volts) by the LED's current (in amps).
The result, measured in watts, is the power the LEDs use. For example, if an LED has a U of 3.6 and a current of 20 milliamps, it will use 72 milliwatts of power. Depending on the size and scope of the project, voltage and current readings may be measured in units smaller or larger than base current or watts. Unit conversions may be required. When performing these calculations, remember that 1000 milliwatts equals one watt, and 1000 milliamps equals one amp.
General characteristics of LED sources
How to choose the LED of the desired configuration? To do this, it is important to understand the main characteristics. One of them is current consumption. Stabilizers and limiters are selected for this value. For calculations you need to know the voltage. To effectively replace incandescent lamps with LED sources, you need to calculate the power.
When creating a specific interior, it is important to consider the size of the light-emitting diode, as well as the shade of the luminous flux. When dealing with LED sources, it is customary to take into account the angle of illumination. Having understood the listed parameters, you can choose the most suitable LED.
When choosing LEDs, it is important to consider the following characteristics: current, voltage, power, efficiency, beam angle, device size
LED current consumption
Current stabilizers are very important in the operation of LEDs. Even a slight fluctuation in the current value will lead to a change in the light shade emitted by the crystals to a cooler one and premature failure of the lighting device. A significant jump in electric current leads to instantaneous burnout of the diode.
LED lamps are always equipped with stabilizers for current conversion. A separate light-emitting diode must be connected using a resistor to limit the current. One crystal typically requires a current of 0.02 A. Four crystals will require a correspondingly higher current of 0.08 A.
LED connection diagrams
There are certain rules for connecting LEDs. Taking into account that the current passing through the device moves only in one direction, for long-term and stable operation of LED devices it is important to take into account not only a certain voltage, but also the optimal current value.
Connection diagram for LED to 220V network
Depending on the power source used, there are two types of circuits for connecting LEDs to 220V. In one of the cases, a driver with limited current is used, in the second, a special power supply that stabilizes the voltage. The first option takes into account the use of a special source with a certain current strength. A resistor is not required in this circuit, and the number of connected LEDs is limited by the driver power.
To designate LEDs in the diagram, two types of pictograms are used. Above each schematic image there are two small parallel arrows pointing upward. They symbolize the bright glow of the LED device. Before connecting the LED to 220V using a power supply, you must include a resistor in the circuit. If this condition is not met, this will lead to the fact that the working life of the LED will be significantly reduced or it will simply fail.
Diagram for connecting LEDs to a 220V network using quenching capacitor C1
If you use a power supply when connecting, then only the voltage in the circuit will be stable. Considering the insignificant internal resistance of an LED device, turning it on without a current limiter will lead to the device burning out. That is why a corresponding resistor is introduced into the LED switching circuit. It should be noted that resistors come in different values, so they must be calculated correctly.
How to calculate the resistance for an LED
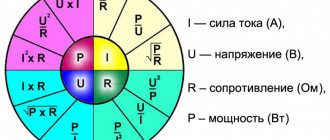
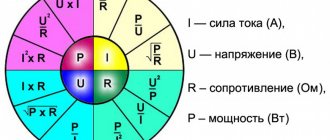
When calculating the resistance for an LED, they are guided by the formula:
U = IxR,
where U is voltage, I is current, R is resistance (Ohm’s law). Let's say you need to connect an LED with the following parameters: 3V - voltage and 0.02A - current. So that when connecting an LED to 5 Volts on the power supply it does not fail, you need to remove the extra 2V (5-3 = 2V). To do this, you need to include a resistor with a certain resistance in the circuit, which is calculated using Ohm’s law:
R = U/I.
Resistors with different resistance values
Thus, the ratio of 2V to 0.02A will be 100 Ohms, i.e. This is exactly the resistor needed.
It often happens that, given the parameters of the LEDs, the resistance of the resistor has a value that is non-standard for the device. Such current limiters cannot be found at points of sale, for example, 128 or 112.8 ohms. Then you should use resistors whose resistance is the closest value compared to the calculated value. In this case, the LEDs will not function at full capacity, but only at 90-97%, but this will be invisible to the eye and will have a positive effect on the life of the device.
There are many options for LED calculation calculators on the Internet. They take into account the main parameters: voltage drop, rated current, output voltage, number of devices in the circuit. By specifying the parameters of LED devices and current sources in the form field, you can find out the corresponding characteristics of resistors. To determine the resistance of color-coded current limiters, there are also online calculations of resistors for LEDs.
Schemes for parallel and serial connection of LEDs
When assembling structures from several LED devices, circuits for connecting LEDs to a 220 Volt network with a serial or parallel connection are used. At the same time, for correct connection, it should be taken into account that when LEDs are connected in series, the required voltage is the sum of the voltage drops of each device. While when LEDs are connected in parallel, the current strength is added up.
Diagrams for parallel connection of LEDs. In option 1, a separate resistor is used for each diode circuit, in option 2 - one common for all circuits
If the circuits use LED devices with different parameters, then for stable operation it is necessary to calculate the resistor for each LED separately. It should be noted that no two LEDs are exactly alike. Even devices of the same model have minor differences in parameters. This leads to the fact that when a large number of them are connected in a series or parallel circuit with one resistor, they can quickly degrade and fail.
The discrepancy in parameters when connecting several LEDs in parallel, say 4-5 pieces, will not affect the operation of the devices. But if you connect a lot of LEDs to such a circuit, it will be a bad decision. Even if LED sources have a slight variation in characteristics, this will cause some devices to emit bright light and burn out quickly, while others will glow dimly. Therefore, when connecting in parallel, you should always use a separate resistor for each device.
As for the series connection, there is economical consumption here, since the entire circuit consumes an amount of current equal to the consumption of one LED. In a parallel circuit, the consumption is the sum of the consumption of all LED sources included in the circuit.
LED daisy chain diagram
How to connect LEDs to 12 Volts
In the design of some devices, resistors are provided at the manufacturing stage, which makes it possible to connect LEDs to 12 Volts or 5 Volts. However, such devices cannot always be found on sale. Therefore, in the circuit for connecting LEDs to 12 volts, a current limiter is provided. The first step is to find out the characteristics of the connected LEDs.
Such a parameter as the forward voltage drop for typical LED devices is about 2V. The rated current of these LEDs corresponds to 0.02A. If you need to connect such an LED to 12V, then the “extra” 10V (12 minus 2) must be extinguished with a limiting resistor. Using Ohm's law you can calculate the resistance for it. We get that 10/0.02 = 500 (Ohm). Thus, a resistor with a nominal value of 510 Ohms is required, which is the closest in the range of E24 electronic components.
In order for such a circuit to work stably, it is also necessary to calculate the power of the limiter. Using the formula based on which power is equal to the product of voltage and current, we calculate its value. We multiply a voltage of 10V by a current of 0.02A and get 0.2W. Thus, a resistor is required, the standard power rating of which is 0.25W.
Connection diagram for RGB LED strip to 12V
If it is necessary to include two LED devices in the circuit, then it should be taken into account that the voltage dropped across them will already be 4V. Accordingly, for the resistor it remains to extinguish not 10V, but 8V. Consequently, further calculation of the resistance and power of the resistor is done based on this value. The location of the resistor in the circuit can be provided anywhere: on the anode side, cathode side, between the LEDs.
Classification of LEDs by their field of application
LED lighting elements differ in their area of application. The main types of LEDs: indicator and lighting. The devices are not the same; each has its own distinctive features and technical parameters.
Indicator LEDs
The first LED lamp appeared in the middle of the last century. The device had a dim reddish glow and low energy efficiency. Despite the shortcomings, developments in this direction were continued. After 20 years, options with yellow and green tints appeared. By the beginning of the 90s, the luminous flux reached 1 Lumen. By the early 2000s, the value reached 100 Lumens.
In 1993, Japanese engineers introduced a blue LED. The light of the device has become much brighter than its predecessors. From that moment on, devices with different luminescence began to appear on the market - a combination of blue, green, yellow and red allows you to create any color and shade.
Development is currently ongoing. New types of LEDs are emerging. At the same time, low-voltage consumption is maintained while the luminous flux increases.
Lighting LEDs
The first low luminosity IP (DIP) models were suitable for indicator work (for example, a switch is visible in the dark - a small red LED is lit).
Modern devices make it possible to illuminate large areas - domestic and industrial premises. The power of the LED has increased - an LED device for a flashlight with an indicator of 3W is similar to an incandescent lamp of 25-30W. Electricity consumption is approximately 10 times less. Such LEDs are called lighting due to their main area of application. Used in ribbons, headlights, lamps, and other products. They are manufactured in separate housings that allow surface mounting.
The main difference is that they produce only white light of cold or warm shades. Classification:
- SMD – models with a dispersive element of 100-130° are popular; substrate for the lamp is made of copper or aluminum, does not heat up;
- SOWs are more powerful, super-bright, consist of many small crystals, the scattering angle is significant;
- Filament - have the lowest efficiency (compared to SMD), are often used as decorative elements, and are manufactured in various sizes and shapes.
Main conclusions
The ability to determine the operating characteristics of an LED allows you to create an optimal operating mode for it. As a result, the element will be able to demonstrate maximum service life and efficiency, and produce sufficient brightness without overload. Knowing the nominal parameters of the device will allow you to correct connection errors, select the most suitable type of power source, and avoid emergency situations or overloads. The ability to correctly determine the characteristics of an LED implies knowledge of various testing methods, from a simple determination of performance, to a more detailed test of operating current, voltage and power. This will expand the possibilities and allow you to use one of the options available in the given conditions.
Advantages and disadvantages
More and more users are seeking to replace outdated incandescent lamps with modern models of LED lamps. The main advantages of using LEDs:
- saving energy without compromising the luminous flux of the lamp;
- durable materials of the body and internal elements: low probability of mechanical damage;
- long service life: several times higher than that of Ilyich bulbs;
- size: diodes are compact and quite mobile;
- high brightness;
- safety: minimum network voltage – 3-24V.
Disadvantages include high cost and the need for constant voltage. The price of products is gradually decreasing due to high consumer demand.
Why use LEDs?
They have many advantages that increase their popularity:
— reliable, provide high strength; — there is no high voltage, this can protect the owner from fires (you can safely conduct an experiment by finding out how to determine the operating voltage of the LED); — they are not large, they are convenient to carry and use; - durability - if during experiments you do not try to increase the brightness even more, when you have already reached the maximum, they will serve you for a very long time; — have a low supply voltage and consume little electricity.
Consider some disadvantages. They are quite expensive when compared to conventional incandescent lamps. From one element you will receive a minimum of luminous flux. The power source must meet certain requirements.
Main characteristics
Technical parameters of LEDs differ depending on the model. General indicators are:
- current consumption;
- nominal voltage (product voltage);
- power of consumed electricity (volt-ampere diagram);
- glow temperature;
- luminosity (level of luminous flux).
There are other characteristics, but they are used in rare cases. For domestic use, it is enough to take into account only these LED parameters.
LED current consumption
The indicator allows you to find out the amount of current consumed electrically by a device (LED). For devices with one active crystal, a value of 0.02A is sufficient. If the quantity is greater, the characteristic increases by a multiple of the number of elements. Based on this parameter, a resistor (stabilizer) is selected, which is installed at the input.
The stabilizer allows you to keep the device in working condition during voltage drops, regardless of the reason. Moreover, fluctuations in the LED current change the color temperature of the light from warm to brighter, cooler. If the voltage surge is significant, without an additional resistor the diode will burn out instantly.
To choose the right stabilizer for current conversion, you can use a special online calculator.
Rated voltage
The magnitude of the voltage is the amount of current in the conductor at the output.
For the manufacture of LEDs, different materials are used, the electrical characteristics of which directly affect the level of permissible voltage and the color of the lighting. Thanks to this dependence, you can find out what voltage specific LEDs are designed for, even “by eye”. For example, if the glow is yellow or red, the voltage is in the range of 1.9-2.5 Volts, blue - about 3 Volts. The current and voltage indicators of the LED must match. Otherwise, the diodes will either burn out quickly or will not produce light at the declared level.
To find out how many volts an LED is, you can use a multimeter or determine by the color of the glow. For the first method, you will need a multimeter and a resistor - the value will appear on the display after assembly.
Light diode resistance
The final resistance depends on the electrical circuit into which the element is connected. The same LED can show different values. For example, at the input - about 1 kOhm, at the output - several MOhms. However, resistance is not a linear characteristic. The indicator is inversely proportional to the voltage supplied to the mains. The higher the LED supply voltage, the lower the resistance level of the device.
Light output and beam angle
Comparing the light output of different lamps is quite difficult. For example, a 5 mm LED produces 1-5 Lm of light, and a 70 W incandescent lamp produces 750 Lm. The dispersion angle is selected based on the area of the room. In the corridor, a 30° diode is enough; in a room it is better to use elements of 90-120° or several at the same time. The maximum angle of LED lamps is 120°. The most illuminated place is the center; light scatters towards the periphery.
LED lamp power
The diode power depends on several related indicators. For LEDs, the value ranges from 0.5 to 3 W. It is calculated according to Ohm's law: it is necessary to multiply the values of current and voltage. The current-voltage characteristic (volt-ampere characteristic) of the LED is also determined.
The choice of power supply for the device depends on the power level and current-voltage characteristics of the LED. It is not allowed to use inappropriate elements - the lamps will burn out if the voltage and current supply are excessive.
Colorful temperature
This indicator is similar to the characteristics of other lighting devices, especially LED fluorescent devices. The temperature of the LED is indicated in K (Kelvins); sometimes on the packages there is a corresponding diagram - a scale on which the range is indicated in color. Matching light and meaning:
- 2700-3000 – warm, yellowish;
- 3500—4000 – daytime, neutral;
- 5500-7000 – cold, with a blue tint.
The main shades are presented. In practice there are much more colors. The temperature is selected based on the purpose of the room, the required level of comfort and user preferences. For example, it is recommended to install lamps with warm light in the bedroom, and with a natural shade in rooms without windows.
LED element chip size
When purchasing, you can find out the chip size only from the information on the packaging. You will not be able to independently verify the correctness of the specified data. Average device sizes: 45×45 ml, 24×40 ml and 24×24 ml for 1W, 0.75W and 0.5W, respectively. In the usual measurement system, 30×30 ml is equal to 0.76×0.76 mm. Due to its small size, you can find out the exact dimensions by disassembling the device completely.
The number of chips (crystals) varies, depending on the model and type of LED. In color elements (RGB), which do not contain a phosphor coating, their number can be counted.
Standard sizes of SMD LEDs and their characteristics
Considering the size of SMD LEDs, devices are classified into groups with different characteristics. The most popular LEDs with standard sizes are 3528, 5050, 5730, 2835, 3014 and 5630. The characteristics of SMD LEDs vary depending on the size. Thus, different types of SMD LEDs differ in brightness, color temperature, and power. In LED markings, the first two digits indicate the length and width of the device.
SMD 5630 LEDs on LED strip
Basic parameters of SMD 2835 LEDs
The main characteristics of SMD LEDs 2835 include an increased radiation area. Compared to the SMD 3528 device, which has a round working surface, the SMD 2835 radiation area has a rectangular shape, which contributes to greater light output with a smaller element height (about 0.8 mm). The luminous flux of such a device is 50 lm.
The SMD 2835 LED housing is made of heat-resistant polymer and can withstand temperatures up to 240°C. It should be noted that the radiation degradation in these elements is less than 5% over 3000 hours of operation. In addition, the device has a fairly low thermal resistance of the crystal-substrate junction (4 C/W). The maximum operating current is 0.18A, the crystal temperature is 130°C.
Based on the color of the glow, there are warm white with a glow temperature of 4000 K, daytime white - 4800 K, pure white - from 5000 to 5800 K and cool white with a color temperature of 6500-7500 K. It is worth noting that the maximum luminous flux is for devices with cool white glow, the minimum is for warm white LEDs. The design of the device has enlarged contact pads, which promotes better heat dissipation.
SMD 2835 LED Dimensions
Characteristics of SMD 5050 LEDs
The SMD 5050 housing design contains three LEDs of the same type. LED sources of blue, red and green colors have technical characteristics similar to SMD 3528 crystals. The operating current of each of the three LEDs is 0.02A, therefore the total current of the entire device is 0.06A. To ensure that the LEDs do not fail, it is recommended not to exceed this value.
LED devices SMD 5050 have a forward voltage of 3-3.3V and a light output (mains flux) of 18-21 lm. The power of one LED is the sum of three power values of each crystal (0.7 W) and amounts to 0.21 W. The color of the glow emitted by the devices can be white in all shades, green, blue, yellow and multi-colored.
The close arrangement of LEDs of different colors in one SMD 5050 package made it possible to implement multi-color LEDs with separate control of each color. To regulate luminaires using SMD 5050 LEDs, controllers are used, so that the color of the glow can be smoothly changed from one to another after a given amount of time. Typically, such devices have several control modes and can adjust the brightness of the LEDs.
SMD 5050 LED Dimensions
Typical characteristics of SMD 5730 LED
SMD 5730 LEDs are modern representatives of LED devices, the housing of which has geometric dimensions of 5.7x3 mm. They belong to ultra-bright LEDs, the characteristics of which are stable and qualitatively different from the parameters of their predecessors. Manufactured using new materials, these LEDs are characterized by increased power and highly efficient luminous flux. In addition, they can work in conditions of high humidity, are resistant to temperature changes and vibration, and have a long service life.
There are two types of devices: SMD 5730-0.5 with a power of 0.5 W and SMD 5730-1 with a power of 1 W. A distinctive feature of the devices is the ability to operate on pulsed current. The rated current of SMD 5730-0.5 is 0.15A; during pulse operation, the device can withstand current up to 0.18A. This type of LEDs provides a luminous flux of up to 45 lm.
SMD 5730-1 LEDs operate at a constant current of 0.35A, in pulsed mode - up to 0.8A. The light output efficiency of such a device can be up to 110 lm. Thanks to the heat-resistant polymer, the device body can withstand temperatures up to 250°C. The dispersion angle of both types of SMD 5730 is 120 degrees. The degree of luminous flux degradation is less than 1% when operating for 3000 hours.
SMD 5730 LED Dimensions
Cree LED Specifications
The Cree company (USA) is engaged in the development and production of ultra-bright and most powerful LEDs. One of the Cree LED groups is represented by the Xlamp series of devices, which are divided into single-chip and multi-chip. One of the features of single-crystal sources is the distribution of radiation along the edges of the device. This innovation made it possible to produce lamps with a large luminous angle using a minimum number of crystals.
In the XQ-E High Intensity series of LED sources, the beam angle ranges from 100 to 145 degrees. Having small geometric dimensions of 1.6x1.6 mm, the power of ultra-bright LEDs is 3 Volts, and the luminous flux is 330 lm. This is one of the newest developments from Cree. All LEDs, the design of which is developed on the basis of a single crystal, have high-quality color rendering within CRE 70-90.
Cree has released several versions of multi-chip LED devices with the latest power types from 6 to 72 Volts. Multichip LEDs are divided into three groups, which include devices with high voltage, power up to 4W and above 4W. Sources up to 4W contain 6 crystals in MX and ML type housings. The dispersion angle is 120 degrees. You can buy Cree LEDs of this type with white warm and cool colors.
The group over 4W includes LEDs made from several crystals. The largest in the group are the 25W devices represented by the MT-G series. The company's new product is XHP model LEDs. One of the large LED devices has a 7x7 mm body, its power is 12W, and the light output is 1710 lm. High voltage LEDs combine small dimensions and high light output.
LED lamps of the XQ-E High Intensity series manufactured by Cree (USA)
Checking an LED with a Multimeter
A multimeter is a special tester for electrical products that combines the functions of different devices. On the external panel there is a switch and several positions, one of them is for checking the LEDs. Procedure:
- Turn on the device and set the desired mode.
- Use special probes to touch the “legs” of the LED (outgoing wires).
- If the number 1 appears on the screen, change the polarity and repeat the touch with the probes.
- If there is sound and the diode starts to light up, everything is fine; if not, the LED is not working.
When it is known that the LED lamp is working, but the multimeter shows something else, you need to check the correct assembly of the circuit: the position of the tester, the connection of the contacts. If in this case the multimeter shows a malfunction, the resistor has failed.
How to test an LED with a multimeter
One way to check the operating condition of LEDs is to test with a multimeter. This device can diagnose LEDs of any design. Before checking the LED with a tester, the device switch is set in the “testing” mode, and the probes are applied to the terminals. When the red probe is connected to the anode and the black probe to the cathode, the crystal should emit light. If the polarity is reversed, the device display should display “1”.
Diagram for testing an LED using a digital multimeter
Testing LED devices can be done without using probes. To do this, insert the anode into the holes located in the lower corner of the device into the hole with the symbol “E”, and the cathode into the hole with the indicator “C”. If the LED is in working condition, it should light up. This testing method is suitable for LEDs with sufficiently long contacts that have been cleared of solder. The position of the switch does not matter with this method of checking.
How to check LEDs with a multimeter without desoldering? To do this, you need to solder pieces of a regular paper clip to the tester probes. A textolite gasket, which is placed between the wires and then treated with electrical tape, is suitable as insulation. The output is a kind of adapter for connecting probes. The clips spring well and are securely fixed in the connectors. In this form, you can connect the probes to the LEDs without removing them from the circuit.
Color coding of light diodes
On the one hand, color marking allows you to determine the type and characteristics of the LED, on the other hand, there are no uniform designations.
Each manufacturer uses its own values. In Russia there is color coding, but it is rarely used - the list of elements consisting of numbers and letters is too large, it is quite difficult to remember, and decoding is inconvenient for the average buyer. A simpler letter designation is accepted as generally accepted (unofficially). Mainly used for LED strips. In addition to the general characteristics, the degree of protection of the element from the penetration of debris and moisture is indicated - IP and numbers from 0 to 6.
To choose a good option for replacing outdated light bulbs, you need to find out what kind of LEDs there are and set the parameters of the connected electrical network: voltage, current, resistance.
You can’t focus on cost - brands of cheap LEDs often have inflated parameters and use unstable materials.
LED Power Supply
Lighting LEDs are current-powered, and their luminous flux is proportional to the current flowing through them. The current is related to the supply voltage of the LEDs in the lamp. Multiple diodes connected in series have equal current flowing through them. If they are connected in parallel, each LED receives the same U, but different current flows through them due to the dispersion effect on the I-V characteristic. As a result, each diode emits a different luminous flux.
Therefore, when selecting elements, you need to know what supply voltage the LEDs have. Each requires approximately 3 volts at its terminals to operate. For example, the 5-diode series requires approximately 15 volts at the terminals. To supply regulated current at sufficient U, the LEC uses an electronic module called a driver.
There are two solutions:
- The external driver is installed outside the luminaire, with a safe extra-low voltage power supply.
- Internal, built into the flashlight, i.e. a subunit with an electronic module that regulates the current.
This driver can be powered from 230V (Class I or Class II) or safety extra-low U (Class III) such as 24V. LEC recommends the second power supply solution as it offers 5 main benefits.