Energy-saving lamps are devices with enormous luminous efficiency (the ratio between power consumption and luminous flux), which are now most used in everyday life, helping to save energy. Compared to incandescent light bulbs, energy-saving lamps can achieve energy savings and reduce cash costs by up to 85%.
Classification
Luminescent (gas discharge)
Often, the shape of this type of light source is a curved bulb, which allows it to be installed in smaller housings. These bulbs are equipped with a built-in choke.
Their most popular purpose is to install them instead of conventional incandescent light bulbs.
Most often you can find this type of light bulbs called “energy-saving”; this is not entirely correct, since there are many varieties of them.
Continuous action
This type of lamps improves color transmission much better and has lower light output. Their main advantage is the continuous spectrum radiation, which has a less detrimental effect on health.
Special colored
In addition to white light bulbs, there are the following varieties:
- with colored phosphor;
- with pink phosphor;
- with ultraviolet light;
LED
The main element of this type is the LED, which is used in all spheres of life. A distinctive feature is the use of safe components.
They have a unique housing designed for an LED source. A specially designed luminaire is much more reliable and energy efficient.
Table comparing power consumption of different types of lamps:
| Incandescent, W | Luminescent, W | LED, W | Light flux, Lm |
| 25 | 4 | 3 | 250 |
| 40 | 9 | 5 | 400 |
| 60 | 13 | 8 | 650 |
| 100 | 20 | 14 | 1300 |
| 150 | 30 | 22 | 2100 |
The simplest incandescent light bulbs have metal filaments; they glow when an electric current passes. Mostly thermal energy, not light.
Energy-saving lamps have a slightly different principle: they transmit about 25-30% of thermal energy, and the rest is light energy.
The power of energy-saving sources is in the order of 7 - 300W. The radiation power is much less than conventional incandescent devices, which have an approximate ratio of 1 – 5.
Comparison
Comparison table of energy-saving lamps and incandescent lamps
Designations:
- Radiation power is indicated in Watts (W/W). Depending on the power, the brightness of the light source depends, and accordingly, more electricity is consumed. Luminous flux, measured in lumens (Lm / Lm), characterizes the light power of the radiation flux.
- Luminous efficiency is a source indicator that shows the level of light produced by each watt of energy. This parameter is measured in Lm/W.
- Illumination - shows the degree of illumination of a particular room, measured in Lux (Lx). This characteristic shows the ratio of a unit of luminous flux to the illumination of a unit of area.
- Color rendering – this parameter indicates the degree of transmission of the color spectrum along with the natural one.
Rating of LED lamps for home
Among the TM LED sources, the following are popular:
- Maxus LED. This TM guarantees the durability of its product (up to 50 thousand hours), significant energy savings (90%), environmental friendliness (no harmful elements, radiation), safety (withstands voltage surges), reliability (minimal heating of the case).
- EUROLAMP – universal lamps for universal use. It is distinguished by exquisite forms and materials. The glass bulb distributes the light flux evenly and does not turn yellow during use. The compactness of the lamp allows it to be used in a wide range of activities.
- GLOBAL LED – simple, basic models. They are distinguished by a suitable price, high reliability, and durability. There is a uniform distribution of light without blinking or pulsation. Wide range of applications: home conditions, public lighting. Versatility thanks to the compact form of the product. This TM provides the market with economical, environmentally friendly products.
Marking
The domestic designation of energy-saving light bulbs contains a letter indicating the type:
- L – luminescent;
- B – white light;
- TB – white with a warm tint;
- D – daytime color;
- C – improved color rendering;
- E – improved environmental performance;
International designation is a digital designation, where the first digit shows the color rendering index, and the rest indicate the color temperature in hundreds of degrees Kelvin.
Table of characteristics of various types of light sources:
Based on the type of base, energy-saving sources are divided into:
- threaded;
- pin;
Plinth designation:
- 2D – curved configuration, in the shape of a square. The base has the shape of a rectangle 60 x 36 mm. Power – 16, 28, 36 W.
- G23 – has the shape of a tube folded in half. Power 5 – 14 W.
- 2G7 - similar to G23, this type works with ballasts. The base has 4 contacts.
- G24 – the shape is similar to G23, it has the shape of a quadruple folded tube. Output power 10 – 36 W.
- G53 – disc-shaped, 16-20 mm thick and 73 mm in diameter. The device has a curved shape. The power of this type is about 6 -11 W.
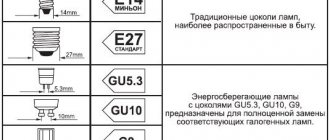
- E14, E27, E40 - have a screw-in Edison type base. The digital designation indicates the diameter of the base.
Characteristics of energy-saving light bulbs
We have become familiar with the types and main features of energy-saving light bulbs, now let’s look at the additional characteristics.
Colorful temperature
This parameter significantly affects a person’s well-being and mood, so when choosing a light bulb, consider its color temperature. Make your choice depending on the type of room where it will work.
Color temperature has nothing to do with the heating of the lighting fixture, although it is measured in Kelvin. In modern lamps it can vary in the range from 2500 to 6500 K.
Let's look at these values in more detail:
- 2500–2700 K is a warm yellow light. Great for creating a cozy and relaxing atmosphere (for example, in a small restaurant or as additional lighting in a bedroom or living room).
- 3000 K – the light still has a yellowish tint, but is closer to white. Good for reading area and library. With such lighting, the eyes do not become overstrained on the one hand, and do not lose concentration on the other. Also, such lighting is often used for halls and corridors.
- 3500 K is considered the color temperature of daylight. Makes the room visually larger - ideal for basic lighting in large rooms. Also used in schools, offices and galleries.
- 4100 K is a bright, cold light that hardly distorts the colors of objects. Helps to concentrate and invigorate, often used in hospitals and educational institutions.
- 6000 K – bright cold light with a blue tint. It conveys shades and texture well without distorting the color. Perfect for a workshop as auxiliary lighting or for visually highlighting an item (for example, in a display case). It is not recommended to turn it on for a long time, as the eyes get tired quickly and an irritable mood may arise.
As you can see, correctly selected color temperature of lighting is the key to health and comfort. It also affects human productivity. If in daylight it is conditionally 100%, then with a shift to more yellow light it decreases to 92–93%, and blue light reduces productivity to 78–80%.
Also, the choice of optimal color temperature may depend on the interior. For example, yellow walls will look bad with light bulbs above 5000 K, but for purple, cold lighting, on the contrary, is preferable to warm shades.
Dispersion angle, base and voltage
The scattering angle may vary for different types of lamps. A small angle (up to 60°) indicates a narrow beam of light, which is suitable for spot lighting of a separate area or illumination of paintings and small decorative elements. For closed lamps (for example, a table lamp), lamps with a scattering angle of 60–90° are suitable, and sometimes less than 60° (for illuminating objects on shelves, for example). Then the beam is more concentrated. If the lamp is open, this indicator should be at least 250°
There are several standards for the type of lamp base:
- E (Edison threaded base) is the most common type of base. The standard for domestic premises is E27, for sconces and floor lamps - E14, for large lighting fixtures - E40.
- G – lamps with a pin base.
- R – lamps with recessed contacts (powerful, used in stadiums, for example).
- B and S are used in stage and other equipment.
- P - in flashlights, projectors.
For household use, as a rule, some varieties E and G are chosen. A significant part of the lamps operate on mains voltage (220–240 V). But there are 9, 12 and 24 V options; they are usually used in built-in shelves, cabinets and other furniture where mains voltage can be life-threatening. Low-voltage lamps are connected to the network through power supplies that reduce the voltage.
Application area
Fluorescent lamps with different types of bases:
- Lamps with a 2D base are used for decoration, sometimes used for built-in lighting of modern shower stalls.
- Sockets of types G23, 2G7 are applicable in wall lamps with special holes.
- Base type G24 is intended for use in industrial and household luminaires.
- G53 sockets are produced in a sealed housing and are intended for wet rooms, for installing suspended and plasterboard ceilings.
Sources equipped with E14, E27, E40 sockets are used in household sockets instead of incandescent lamps. This type of fluorescent light sources has large dimensions, therefore, replacement is not possible for all sizes of lamps.
Continuous spectrum sources produce light that has a beneficial effect on health. Unlike conventional linear spectrum light bulbs, they provide better color rendition.
Special colored sources are intended for general lighting, as well as:
- Having a colored phosphor - for lighting design (art lighting, city lights, inscriptions, signs).
- Possessing a pink phosphor , they are often used in the meat industry to give meat a marketable appearance.
- Ultraviolet light – suitable for lighting in darkened rooms, for disinfection (in medical institutions), and as decoration for entertainment venues.
LED light bulbs are used for household, industrial, and street lighting. LED sources have an emitter predominantly in one direction, allowing them to be used for directional and local lighting.
In addition to the above points, LED light bulbs are widely used for lighting museums and art galleries, since there is no ultraviolet component in the light spectrum.
The luminaires are used to control lighting in industrial and office premises, corridors, warehouses, public places, elevators, parking lots, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of luminescent sources include:
- High luminous efficiency , light flux is 5-7 times higher compared to incandescent lamps, allowing for energy savings of 80-85%.
- is illuminated .
- Possibility of manufacturing emitters with different properties: color temperature, various ultraviolet colors.
- Significantly less heating of the body and bulb compared to incandescent light bulbs.
- Longer service life , not requiring constant switching on/off of the light.
- No stroboscopic effect when lighting moving parts of equipment.
The disadvantages of fluorescent sources include:
- Relatively short service life when used in domestic use; sometimes this life can be compared with incandescent devices.
- Regular switching on/off is not recommended. This type of source is not used in New Year’s garlands, medical laboratories, or light alarms.
- When the room humidity is high, the capacitor drops out, which leads to an interruption in the electrical circuit. When used in conditions of high temperatures, the spectra of the bulbs become “reddened” and a large loss of light output occurs, and with a subsequent increase in temperature, complete failure occurs. This type is not suitable for rooms with high humidity and unheated conditions.
- Impossibility of use in emergency situations, or in the event of an emergency, since there is a minimum voltage that allows it to start.
- High temperatures inside the structure reduce the reliability of all its electronic elements.
- Flashing of switched off light bulbs due to electric current leakage in the circuit. Flashes and unpleasant sounds can be irritating and can also damage the light source.
- Mercury , which is also present in used devices, poses a danger if it is damaged.
The advantages of LED light bulbs include:
- Compared to conventional light bulbs , low power consumption allows for a service life of up to 20,000 - 60,000 hours.
- Easy to install.
- Low temperatures , high strength, and in most cases small sizes.
- Complete environmental safety , which helps preserve the environment.
- Does not contain mercury or other toxic and harmful substances.
The disadvantages of LED bulbs include:
- High cost , glow only in one direction.
- In inexpensive models, high-frequency flicker occurs.
- If it fails , the lamp must be replaced.
- Most models do not meet established standards.
- The harmfulness of the cold radiation of LEDs compared to other light-emitting elements.
- Reduced brightness due to LED burnout.
How to choose a lamp: answers to basic questions
How to choose a light bulb for your home is a question that concerns many inexperienced consumers. A number of conditions must be followed.
Where will the lamp be used?
For residential premises (bedrooms, children's rooms, living rooms), it is preferable to choose LED lamps. They give more natural light and do not flicker. An LED lamp is not suitable for wet rooms. When moisture condenses in a leaky lampshade, the LEDs quickly fail. Therefore, they are not recommended for use in baths, steam rooms, or outdoors without appropriate protection.
How often will the lamp turn on and off?
The predicted switching frequency allows you to determine which lamps are best to use for your home.
Energy-saving lamps are sensitive to switching frequency. This is especially harmful for gas-filled lamps. With a switching frequency of no more than 2,000 times over the entire service life, which ranges from 2,000 to 20,000 hours. On average - 5,000.
Fluorescent lamps cannot withstand frequent switching on/off. In addition, when turned on, a large amount of electricity is consumed, which minimizes the energy-saving effect.
For what purposes will the lamp be used?
LED varieties of light bulbs can be used without restrictions in any room, with any lighting mode. They are suitable for all types of lighting fixtures. It is more profitable to use energy-saving lamps in those rooms where insufficient lighting is constantly experienced. They work well and stably without overheating for a long time.
Both types are sensitive to increased temperature. They are not recommended for use in tightly closed lampshades that do not have a forced cooling source or a massive aluminum radiator.
Limiting energy consumption in the home
Energy savings in the house become noticeable when all lamps in all lighting fixtures are completely replaced. Often 1-2 energy-saving light bulbs are screwed into a lamp or lampshade in inappropriate places: bathroom, toilet, closet. You should not expect a noticeable reduction in energy consumption from such a replacement.
It is much more effective to use an integrated approach:
- replacement of energy-intensive electrical appliances;
- complete replacement of light bulbs with LED lamps;
- installation of a modular “smart home” system that automatically regulates energy consumption.
Model overview
Energy-saving spiral lamp SVETOZAR
Price 155 rub.
Specifications:
- base – E14;
- power – 8 W;
- luminous flux – 380 lm;
- incandescent analogue power – 40 W;
- temperature – less than 3000 K;
- supply voltage – 220 V;
- hourly resource – 10,000 hours;
LED luminaire LED C37 E14 5W 4000K REV FROST
Price 200 rub.
Specifications:
- base – E14;
- power 5 W;
- incandescent analogue power – 40 W;
- supply voltage – 220–240 V;
- temperature 3300 – 5000 K.
- service life – 30000 hours;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XaDwd_kDHBI
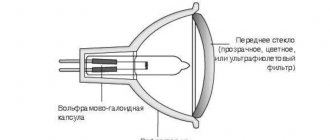
Types of devices
From the assortment presented by manufacturers, you can choose an energy-saving light bulb for your apartment in accordance with your personal needs and the characteristics of the room. Such lighting devices are a worthy alternative to Ilyich lamps. Three types of devices are used for household and office lighting
- luminescent;
- LED;
- halogen.
All of them have a high efficiency and at the same time minimize the load on the electrical network. This increases the level of safety when operating lighting devices and equipment available in the house. The latest LED ESLs are considered the most environmentally friendly, economical and safe for humans.
All products are manufactured with markings corresponding to the type of base. For lamps equipped with standard-sized sockets, E27 sockets are intended, for small-diameter sockets - E14 sockets. For floodlights, lamps marked E40 are used. The classification of energy-saving lamps by shape is represented by the following models:
- U-shaped;
- spiral;
- semi-spiral.
Spiral light bulbs are the most expensive, but not because they have better technical characteristics, but due to the complexity of the design. Quality depends directly on the manufacturing company. For example, Chinese analogues of expensive products are inexpensive, but they are unreliable in operation. Well-known companies provide a 3-year warranty, while cheap products will last no more than 1 year.
Tips for choosing
The following factors influence the choice of energy-saving light bulbs:
- The light output of LED sources is higher than that of fluorescent lamps.
- Environmental friendliness. The safest of all types of lamps are LED lamps, since fluorescent lamps contain mercury, which, if the body of the light source is damaged, can pose a threat to others.
- LED sources have no flickering , which contributes to more comfortable work. When emitting a light spectrum they have a light spectrum close to natural.
- As for color , LEDs have better color rendering.
To summarize, the biggest disadvantage of an LED source is its price. But for those who care about their health and the health of their loved ones, this type of light bulbs will pay off in full in the future.
Safety precautions when working with energy-saving fluorescent lamps
When screwing a light bulb into a socket, it should be held not by the tubes, but by the body. Manufacturers write about this on the packaging, but not everyone reads it. You can, of course, screw it in by the tubes, but very carefully and without applying much effort. If the light bulb does crack or break, collect all the fragments and ventilate the room well - the lamp contains toxic mercury vapor inside
. Although a fluorescent lamp emits several times less heat than a lamp, it contains electronic components inside that are afraid of overheating. Therefore, it is not recommended to use a fluorescent lamp in completely closed lampshades.
Druzhovka