Home » Electrical installation » Electrician's tools » TML tip
The TML tip is a special device that allows you to create the best contact between the device wires and the network. The letter “T” in the marking indicates that the part is made of pipe. The letter “M” indicates that the product is made of copper, and the letter “L” means that the contact is tinned.
Copper tinned tip
In this article we tried to look at what tips exist and what they are intended for.
General information
Simply connecting a household appliance to the network is sometimes simply not enough. If there is poor contact, the wire will begin to experience various overloads when voltage is applied. Accordingly, this will lead to failure of the device or fire of the wiring.
Popular wire lugs
To avoid such unpleasant situations, you need to make sure that the connection is made securely. The TML tip can help cope with such problems. Manufacturers make this element from various materials, but copper is considered the highest quality.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main disadvantage of this type of connection is the lack of an insulating collar. This is not important during operation, but sometimes creates difficulties for servicing power lines. They also note that special dies are required for crimping. They are necessary due to increased requirements for contact reliability. For each cable section, they use their own version, designed for a specific core diameter.
Advantages:
- protection of the end from mechanical damage;
- resistance to high humidity;
- warning of increased heating;
- immunity to aggressive environments.
The contact is well maintained even with temporary (one-time) overloads or sudden temperature increases. The reliability of crimping depends on the choice of the bushing diameter, the use of a suitable matrix, and careful stripping of the insulation. It is better to do the latter only with a special tool so as not to damage the surface of the cores.
Termination and crimping
Tinned copper lugs TML are intended for terminating bare copper contacts. To install this device on the wire cores, crimping pliers are usually used. When making tips, manufacturers can use copper pipes with different diameters. During the manufacturing process, they are cut and then compressed on one side. Subsequently, a small hole is made, which is intended for the bolt.
Types of tips for crimping
Crimping of TML tips is carried out for the following purposes:
- to establish a connection between the electrical network and the required device;
- to establish contact within one device between several parts;
- for “splicing”, when there is a need to extend an existing wire by connecting another to it.
The main types of cable lugs for crimping according to the form of manufacture:
- ⚡
manufactured according to the manufacturer's specifications - ⚡
manufactured according to GOST - ⚡
manufactured according to German standards (DIN lugs)
What are the differences?
- ⚡
A significant difference between DIN lugs and others is the length of the shank into which the pressed wire is inserted; for DIN it is much longer. - ⚡
In addition, the blade width of the DIN lug is standardized and remains the same across different bolt holes. In other tips, the larger the bolt hole, the wider the blade. - ⚡
The thickness of the material of the DIN tips (the wall of the extruded sleeve) is higher than that of others - ⚡
DIN lugs are designed for wires of 2-3 flexibility classes. GOST and TU lugs are suitable for all flexibility classes. - ⚡
DIN lugs, due to their greater length, usually require three crimps with a press die. TU and GOST two are enough. - ⚡
Such tips must be crimped first near the contact blade, then following to the end of the pressed sleeve
Tip with viewing window
The TML(o) tip is one of the varieties of these elements. They are also made from copper. However, the main difference is that the design included a viewing window. This allows you to verify that the contact has been connected correctly. Most often, specialists use such varieties in industrial enterprises, so not everyone knows about the existence of this tip.
TML(o) is one of the types of tips
Kinds
There are two types of devices. The first type are cable lugs that do not have a coating, and the second are lugs that have a tinned coating.
Tinned TML tips are considered a better type than the uncoated ones. They are more practical to use, as they provide sufficient protection against corrosion, which, in turn, greatly increases the service life of the device. In addition, tinned contact is resistant to such types of acids as sulfuric, nitric and hydrochloric. Another advantage is that such TML tips are not afraid of exposure to moisture, air, as well as any other aggressive manifestations of the environment. It is worth saying that due to such a coating, the electrical conductivity of the device is still reduced, however, those indicators that are available are considered stable and acceptable for use.
Copper tips
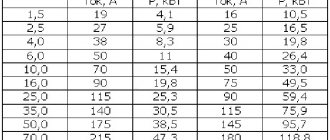
The most durable part is considered to be the one made of copper. A cheaper option is a brass ferrule. Many who have purchased these parts have probably encountered a large number of numbers on the packaging. Most often the numbers indicate:
- wire section;
- contact rod diameter;
- internal diameter of the shank.
There are several other types of tips, and to understand what they are, you need to understand the markings:
- The marking “TA” indicates that the part was manufactured from tubular aluminum.
- "SIP" indicates that the lug is an insulated self-supporting ring plate connector.
- The pin bushing element is designated as “NSHVI”.
- The most common marking is the designation “TML-10”. The number indicates the diameter of the wire, as well as the diameter of the contact rod.
Tip GOST 22002.1-82, 22002.2-82, 22002.3-82, 22002.4-82.
These standards regulate the production of stamped cable lugs with a closed shank, mounted on copper stranded conductors of wires and cables with a cross-sectional area from 0.35 to 16 mm². The tips are blind - 22002.1-82, GOST 22002.2-82, fork - GOST 22002.3-82 and hook-shaped - GOST 22002.4-82, which are manufactured in two versions: left and right.
The lugs are designed for connection to copper stranded wires and cables by soldering or crimping. Cable lugs intended for soldering connection can be manufactured without internal grooves.
All tips are made from grade copper tape, from soft copper sheet grade and from brass semi-hard rolled grade L63 of increased (when stamped in the form of a chain) and normal accuracy. It is allowed to manufacture cable lugs from brass grades L68 and L70. For tips, coating is provided on the surface of the product. Coating options: Nickel, Tin, Nickel-Tin, Tin-Bismuth, Nickel-Tin-Bismuth. Each coating option has its own code, for example, “03” is Nickel. The coating code is indicated in the designation of the standard size of the tip, and the correspondence of the coating to this code can be seen in the table located in the standard or in the standard to which there is a link.
Tip GOST 22002.1-82.
According to the design of the clamping part, the tip has a blind shape with a straight closed shank.
Do not solder the joint of the shank of cable lugs intended for connection to wires by soldering. It is allowed not to solder the joint of the shank of lugs connected by crimping to wires with a cross-section of up to 4 mm2 with crimping form type I; in this case, the gap in the joint should be no more than 0.2 mm.
The nominal cross-sectional diameter of the cable lug is provided from 0.5 to 16 mm. The total length ranges from 15 to 47 mm.
An example of a tip symbol for convenient recording:
Where is a tip with a nominal cross-section of 2.5 mm2, intended for connection by crimping, under a contact rod with a diameter of 4 mm, made of brass, coated code 07:
Tip 2.5-4-LT-07 GOST 22002.1-82.
Tip GOST 22002.2-82.
According to the design of the clamping part, the tip has a blind shape with a bent closed shank.
The nominal cross-sectional diameter of the cable lug is provided from 0.5 to 16 mm. The total length ranges from 18 to 37 mm.
An example of a tip symbol for convenient recording:
Where, a tip with a nominal cross-section of 2.5 mm2, intended for connection by soldering, under a contact rod with a diameter of 4 mm, made of brass, coated code 07:
Tip P 2.5-4-LT-07 GOST 22002.2-82.
Tip GOST 22002.3-82.
The design of the tip is fork-shaped with a straight, closed shank.
The nominal cross-sectional diameter of the cable lug is provided from 0.5 to 10 mm. The overall length ranges from 14.6 to 37.8 mm.
An example of a tip symbol for convenient recording:
Where, a tip with a nominal cross-section of 2.5 mm2, intended for connection by soldering, under a contact rod with a diameter of 4 mm, made of brass, coated code 07:
Tip P 2.5-4-LT-07 GOST 22002.3-82.
Tip GOST 22002.4-82.
The design of the tip is hook-shaped with a straight, closed shank.
The nominal cross-sectional diameter of the cable lug is provided from 0.5 to 10 mm. The total length ranges from 15 to 39 mm.
An example of a tip symbol for convenient recording:
Where, a tip with a nominal cross-section of 2.5 mm2, intended for connection by soldering, under a contact rod with a diameter of 4 mm, version “P”, made of brass, coated code 07:
Tip P 2.5-4-P-LT-07 GOST 22002.4-82.
There are also analogues of these tips, manufactured according to industry standards:
| Standard | Analogue |
| GOST 22002.1-82 | OST4.775.005-81 |
| GOST 22002.2-76 | OST4.775.006-81 |
| GOST 22002.3-76 | OST4.775.007-81 |
| GOST 22002.4-76 | OST4.775.008-81 |
Pages with these products manufactured by our company: Tip GOST 22002.1-82. Tip GOST 22002.2-82. Tip GOST 22002.3-82. Tip GOST 22002.4-82.
For detailed information about the production of tips GOST 22002.1-82, 22002.2-82, 22002.3-82, 22002.4-82, please call;, or send requests electronically to [email protected]
Installing Items
At the moment there are 4 ways that allow you to install tips:
- Crimping.
- Screw.
- Welding.
- Soldering tips.
You can cope with the first installation option using 4 different tools. Each tool has its own qualities and properties that need to be studied before performing work. For example, to connect the power cable and the tip, you should use a more powerful tool.
How to crimp a wire
After selecting suitable tips and wires, you will need a special tool. Press pliers resemble pliers, at the end of which there is a special matrix into which lugs and an uninsulated section of the cable are installed.
This device allows you to ensure even pressure from the tip on all sides. Particular attention should be paid to the type of cable, which can be multi-core or with a monolithic core.
Single terminal crimp
To make a high-quality crimp, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations:
- To prevent the cores from falling out of the socket, the conductor should be fixed when placed in the tool matrix.
- The crimping is carried out using pliers until the snoring mechanism is activated, which allows you to block the tool from opening.
- if fixation is carried out manually, then control is carried out by pulling the hand. If the crimp is of high quality, the installation will be tight without movement.
- You can use a double-circuit crimping tool. Termination is performed by compressing the insulator and bushing in sockets with different diameters.
- Finally, you need to check the strength of the contact by slightly pulling the elements.
When performing crimping for the first time, it is worth practicing on an unnecessary piece of wire. It's better to ruin one tip than the whole wire.
Double terminal crimp
The connection of two phase conductors is carried out on one contact. When installing modular machines, they are connected using special jumpers. There are a pair of cables per contact.
In this case, it is recommended to use NShVI for two wires. Here are some installation features:
- two wires are installed inside the cuff at once;
- It is better to perform crimping using press pliers. When crimping a double tip, it is better to use a matrix with a cross section of 6 square meters. mm.
Crimping power cable lugs
To crimp the power cable, it is recommended to use a tinned copper termination, which is protected from oxidation. When cutting the cable, the edge may fluff up and become larger than the rest of the core. In this case, the edge can be removed using a sharpener. The cable should be unfolded so that the circle removes excess along the veins, but does not bend them.
You should not use the soldering method for crimping, since contacts made only with pure tin cannot be used on wires.
In order not to make a mistake with the size of the tip, when going to the store, it is better to take the cable with you and select a part of the required diameter on the spot.