Circuit breakers are devices that are responsible for protecting an electrical circuit from damage caused by exposure to large currents. Too strong a flow of electrons can damage household appliances, as well as cause overheating of the cable, followed by melting and fire of the insulation. If you do not de-energize the line in time, this can lead to a fire. Therefore, in accordance with the requirements of the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules), operation of a network in which electrical circuit breakers are not installed is prohibited. AVs have several parameters, one of which is the time-current characteristic of the automatic protective switch. In this article we will tell you how circuit breakers of categories A, B, C, D differ and what networks they are used to protect.
Rated current of the machine
The time has come to figure out what the rated current of the machine actually means and what the protection operation current will be.
For those who understand the difference between effective and instantaneous values, I clarify that all parameters of machines associated with current or voltage are effective values, unless otherwise specified. According to GOST R 50345-2010 (clause 3.5.1), the rated current of a circuit breaker is the current value that determines the operating conditions for which it is designed and built. Brief and precise. A common mistake is that people often think that the rated current is the tripping current. In fact, a working circuit breaker will never trip at its rated current. Moreover, it will not work even at 10% overload. With a higher overload, the machine will turn off, but this does not mean that it will turn off quickly. A conventional modular circuit breaker has 2 releases: a slow thermal one and a fast-reacting electromagnetic one.
The thermal release basically contains a bimetallic plate, which is heated by the current passing through it. When heated, the plate bends and, at a certain position, acts on the latch and the switch turns off. The electromagnetic release is a coil with a retractable core, which, at high current, also acts on the latch that turns off the circuit breaker. If the purpose of a thermal release is to turn off the circuit breaker during overloads, then the task of an electromagnetic release is to quickly turn off during short circuits, when the current value is several times higher than the rated value.
Range of rated currents
I had to install circuit breakers with a rating of 0.2A.
But that's not all. In the same GOST R 50345-2010 there is chapter 5.3 entitled “Standard and preferred values”. According to it, the preferred values of the rated current of modular circuit breakers are: 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100, 125 A.
Selecting a machine according to cable cross-section
Let us consider the problem of choosing circuit breakers for home electrical wiring in more detail, taking into account fire safety requirements. The necessary requirements are set out in Chapter 3.1 “Protection of electrical networks up to 1 kV,” since the network voltage in private houses, apartments, and cottages is 220 or 380V.
Calculation of the cross-section of cable and wire cores
Voltage 220V.
– single-phase network is used mainly for sockets and lighting. 380V. - These are mainly distribution networks - power lines running along the streets, from which houses are connected by branches.
According to the requirements of the above chapter, internal networks of residential and public buildings must be protected from short-circuit currents and overloads. To fulfill these requirements, protection devices called circuit breakers were invented.
Automatic circuit breaker
This is a mechanical switching device capable of turning on, carrying currents in the normal state of the circuit, and also turning on, conducting for a specified time and automatically turning off currents in the specified abnormal state of the circuit, such as short circuit and overload currents.
Short circuit (SC)
an electrical connection of two points of an electrical circuit with different potential values, not provided for by the design of the device and disrupting its normal operation. A short circuit can occur as a result of a violation of the insulation of current-carrying elements or mechanical contact of non-insulated elements. Also, a short circuit is a condition when the load resistance is less than the internal resistance of the power source.
Overload current
– exceeding the rated value of the continuous permissible current and causing overheating of the conductor. Protection against short-circuit currents and overheating is necessary for fire safety, to prevent the fire of wires and cables, and as a result of a fire in the house.
Continuous permissible current of cable or wire
- the amount of current that constantly flows through the conductor and does not cause excessive heating.
VVGng cables with copper conductors
The value of continuous permissible current for conductors of different sections and materials is presented below. The table is a combined and simplified version applicable for household power supply networks, tables No. 1.3.6 and 1.3.7 PUE.
| Cross-section of current-carrying conductor, mm | Continuous permissible current, A, for wires and cables with copper conductors. | Continuous permissible current, A, for wires and cables with aluminum conductors. |
| 1,5 | 19 | — |
| 2,5 | 25 | 19 |
| 4 | 35 | 27 |
| 6 | 42 | 32 |
| 10 | 55 | 42 |
| 16 | 75 | 60 |
| 25 | 95 | 75 |
| 35 | 120 | 90 |
| 50 | 145 | 110 |
Types of protective devices
There are several types of AVs that are connected to the network in order to monitor the condition of the wiring and, if necessary, stop the current supply. They may be as follows:
- Mini models (small in size).
- Air (open type).
- Residual current devices (abbreviated name - RCD).
- Closed (device elements are housed in a molded housing).
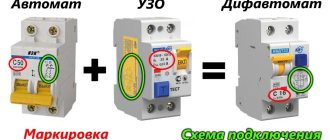
- Differential (circuit breakers combined with RCD).
Mini models
These devices are designed to operate in circuits where the load is low. They usually do not have additional adjustment functions. This series includes devices that can withstand a misfire current of 4.5 - 15A. They are not suitable for factory power, since the current strength in enterprises is much higher than their nominal value. Therefore, they are usually connected to household wiring.
The machines included in the product line of the French company Schneider Electric are very popular. The ratings of the AVs produced by this company can be 2 - 125A, so you can choose a package for home lines of various powers.
Air (open) devices
If the total power of the devices connected to the network is large, and the ratings of the machines mentioned above are insufficient, air protective devices should be chosen. The rated cut-off current of open-type bags is an order of magnitude higher than that of mini-models. Most often they are three-pole, but recently many companies have started producing four-pole machines.
Open type protective devices should be installed in distribution cabinets equipped with special DIN rails on the inside.
If the cabinet's protection class is IP55, then it can be placed outside the building. The body of this equipment is made of refractory metal and is reliably protected from moisture penetration, which ensures a high level of safety for the machines located inside it.
Airborne ABs have a great advantage over miniature ones. It lies in the ability to customize their nominal characteristics using special inserts that are placed on the active contact.
Enclosed circuit breakers
The body of these devices is cast from refractory metal, which ensures their perfect tightness and makes them suitable for use in harsh conditions. The maximum voltage that such machines can withstand is 750V, and the current is 200A. Closed AVs are classified according to the type of action into the following groups:
- Adjustable.
- Thermal.
- Electromagnetic.
The optimal type should be selected based on the tasks being solved.
The highest accuracy is achieved by electromagnetic closed circuit breakers, which determine with a minimum error the root mean square indicator of the active electric current and instantly de-energize the network in the event of a short circuit, avoiding serious consequences.
Electromagnetic machines are successfully used to control the functioning of motors in factory machines, as well as other powerful equipment, since they can withstand currents of up to 70 kA. The number indicating the current rating of the circuit breaker is printed on its body.
All types of enclosed switches can have two to four poles. Thanks to this, they can be used to protect electrical networks of any residential and non-residential buildings and structures.
Residual current devices
Residual current devices should not be used as independent protective devices, since their main task is to protect people from sudden electric shock. Therefore, it is recommended to install them together with the automatic circuit breaker, or to purchase a differential circuit breaker that already includes an RCD. In the first case, you need to take into account that the residual current device should be installed first, and then the circuit breakers.
If you change the installation order, a short circuit will lead to failure of the RCD as a result of too high a load.
Type of electromagnetic release
The machine is triggered after the current exceeds the permissible level. Networks often experience short-term overloads that occur when devices are turned on. Such devices include welding units, washing machines, and microwave ovens. In the event of short-term fluctuations, the protective switch does not operate because it has a short switch-off delay.
If a short circuit occurs, the contacts of the device may melt. To avoid this, the machine uses a built-in automatic device - a release. It provides protection for devices until cutoff currents appear, at which the line is cut off from the general network. The cut-off current value is indicated on the switch before the rating designation. Common types:
- B – exceeding the nominal value by 3-5 times;
- C – 5-10 times excess;
- D – 10-20 times.
In order to select a circuit breaker taking into account these data, you should use the rule:
- machines with the designation B should be chosen for houses in rural areas that receive electricity using overhead lines;
- C - a common option installed in new buildings and houses located near the substation;
- D – installed in enterprises with installed equipment with high starting current.
Protective devices marked B are difficult to find; it is better to choose products marked C.
TOP 5 machine gun models on the market this year
When choosing an AB, it is necessary to take into account the ratings of manufacturers of such devices.
The best machines (more precisely, their manufacturers) today:
- Schneider Electric. French company. The machines produced by it have long been tested in Russian conditions, serve for a long time and are reliable.
- General Electric. The disadvantage is the high price, but the reliability and workmanship are also excellent. The American manufacturer produces excellent AVs for three-phase networks.
- Siemens. Low price, but the quality is worse than the two leaders presented above. It's hard to find devices for sale. Initially, the brand was German, then it was acquired by Americans. AB's reliability and average cost make the company so popular.
- Contactor. The best Russian brand, but the prices are steep. It is better to purchase machines made in Europe, although Contactor is a good solution for lightly loaded networks.
Which manufacturers should you trust?
The choice of machine is made taking into account the manufacturer. Unknown manufacturers produce products that are rarely of high quality. Popular brands and companies include: ABB, Schneider Electric, Legrand and some others. Affordable products with budget prices are produced by EKF, IEK, TDM and others. In operation, many products behave almost identically, so you should not pay extra money for a brand with the same quality of products. Schneider Electric products are 3-5 times more expensive than IEK.
There are often counterfeits of expensive machines on the market. They can be easily distinguished by their weight, which is indicated in the accompanying documents. Light weight indicates the absence of any components in the product that ensure normal operation of the product. Let's look at some models from different manufacturers.
TDM - the product is manufactured in China in two series: VA 47-29 and VA 47-63. VA 47-29 has notches on the body for passive cooling. You can seal the device with special plugs, sold separately. VA 47-63 are produced without cooling notches. The price of all products is within 130 rubles.
The Chinese company Energia produces the same series as TDM, but with side recesses and a power indicator. Series 47-63 without indicator and recesses on the case.
IEK (China) products have gained great popularity among buyers, as have products from Decraft and EKF.
KEAZ is a plant in Kursk that produces products of the VM63 and VA 47-29 series. The switch set includes seals and a contact indication.
Hungarian GE products have significant weight and great popularity.
Moeller are manufactured in Serbia and Austria, they are analogues of Chinese circuit breakers, but are of higher quality.
Shneider Electric are painted green. Several series of products are produced. The cost is within 150-180 rubles. An alternative is the product of the Polish company Legrand TX.
Electricians in Russia love the products of ABB (Germany), which are distinguished by high quality, availability and reliability. Two series are produced: S-6000 and SH-4500 A. The products cost 250-300 rubles.
Briefly the principle of operation and purpose of circuit breakers
In the event of a short circuit, the circuit breaker is triggered almost instantly thanks to the electromagnetic splitter. At a certain excess of the rated current value, the heating bimetallic plate will turn off the voltage after some time, which can be found out from the current characteristic time graph.
This safety device protects the wiring from short circuits and overcurrents exceeding the calculated value for a given wire cross-section, which can heat the conductors to the melting point and cause the insulation to ignite. To prevent this from happening, you need not only to choose the right protective switch that matches the power of the connected devices, but also to check whether the existing network can withstand such loads.
Appearance of a three-pole circuit breaker
Wires must match the load
It often happens that in an old house a new electric meter, automatic machines, and RCDs are installed, but the wiring remains old. A lot of household appliances are bought, the power is summed up and an automatic machine is selected for it, which regularly holds the load of all switched on electrical appliances.
Everything seems to be correct, but suddenly the wire insulation begins to emit a characteristic odor and smoke, a flame appears, and the protection does not work. This can happen if the wiring parameters are not designed for such current.
Let's say the cross-section of the old cable core is 1.5mm², with a maximum permissible current limit of 19A. We assume that several electrical appliances were connected to it at the same time, making up a total load of 5 kW, which in current equivalent is approximately 22.7 A; it corresponds to a 25 A circuit breaker.
The wire will heat up, but this machine will remain on all the time until the insulation melts, which will lead to a short circuit, and the fire can already flare up in full swing.
NYM power cable
Protect the weakest link in the electrical wiring
Therefore, before choosing a machine according to the load being protected, you need to make sure that the wiring will withstand this load.
According to PUE 3.1.4, the machine must protect the weakest section of the electrical circuit from overloads, or be selected with a rated current corresponding to the currents of the connected electrical installations, which again implies their connection with conductors with the required cross-section.
If you ignore this rule, you should not blame an incorrectly designed machine and curse its manufacturer if a weak link in the electrical wiring causes a fire.
Melted wire insulation
Calculation of the machine's nominal value
We assume that the wiring is new, reliable, correctly calculated, and meets all requirements. In this case, the selection of a circuit breaker comes down to determining a suitable rating from a typical range of values, based on the calculated load current, which is calculated by the formula:
where P is the total power of electrical appliances.
This means active load (lighting, electric heating elements, household appliances). This calculation is completely suitable for a home electrical network in an apartment.
Let's say the power calculation is made: P = 7.2 kW. I=P/U=7200/220=32.72 A. Select a suitable 32A machine from a range of values: 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100.
This rating is slightly less than the calculated value, but it is practically impossible for all electrical appliances in the apartment to be turned on at the same time. It is also worth considering that in practice, the operation of the machine begins with a value 1.13 times greater than the nominal value, due to its time-current characteristics, that is, 32 * 1.13 = 36.16 A.
To simplify the selection of a circuit breaker, there is a table where the ratings of the circuit breakers correspond to the power of single-phase and three-phase loads:
Current circuit breaker selection table
The denomination found using the formula in the above example is closest in terms of power value, which is indicated in the red highlighted cell. Also, if you want to calculate the current for a three-phase network, when choosing a machine, read the article about calculating and choosing the wire cross-section
The selection of circuit breakers for electrical installations (electric motors, transformers) with reactive loads, as a rule, is not made based on power. The rating and type of current characteristics of the circuit breaker are selected according to the operating and starting current specified in the passport of this device.
Table for selecting wire cross-section by power
What wire cross-section is needed for 3 kW
Formula for finding current power
Smooth start of an asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor
New Year's greetings with humor
Rules for choosing denomination
The geometry of intra-apartment and house electrical networks is individual, so there are no standard solutions for installing switches of a certain rating. The general rules for calculating the permissible parameters of machines are quite complex and depend on many factors. It is necessary to take them all into account, otherwise an emergency situation may be created.
The principle of indoor wiring
Internal electrical networks have a branched structure in the form of a “tree” - a graph without cycles. Compliance with this principle of construction is called selectivity of machines, according to which all types of electrical circuits are equipped with protective devices.
This improves the stability of the system in the event of an emergency and simplifies the work to eliminate it. It is also much easier to distribute the load, connect energy-intensive devices and change the wiring configuration.
At the base of the graph there is an input machine, and immediately after the branching, group switches are placed for each individual electrical circuit. This is a standard scheme proven over the years
The functions of the input circuit breaker include monitoring the general overload - preventing the current from exceeding the permitted value for the object. If this happens, there is a risk of damage to the external wiring. In addition, it is likely that protective devices outside the apartment, which are already part of the common property or belong to the local power grid, will be triggered.
The functions of group machines include current control on individual lines. They protect the cable in a dedicated area and the group of electricity consumers connected to it from overload. If such a device does not operate during a short circuit, then it is insured by an input circuit breaker.
Even for apartments with a small number of electrical consumers, it is advisable to install a separate line for lighting. When you turn off the circuit breaker of another circuit, the light will not go out, which will allow you to eliminate the problem in more comfortable conditions. In almost every panel, the nominal value of the input machine is less than the amount on the group ones.
Total power of electrical appliances
The maximum load on the circuit occurs when all electrical appliances are turned on at the same time. Therefore, usually, the total power is calculated by simple addition. However, in some cases this figure will be less.
For some lines, the simultaneous operation of all electrical appliances connected to it is unlikely, and sometimes impossible. Homes sometimes specifically place restrictions on the operation of powerful devices. To do this, you need to remember not to turn them on at the same time or use a limited number of sockets.
The probability of simultaneous operation of all office equipment, lighting and auxiliary equipment (kettles, refrigerators, fans, heaters, etc.) is very low, therefore, when calculating the maximum power, a correction factor is used
When electrifying office buildings, the empirical simultaneity coefficient is often used for calculations, the value of which is taken in the range from 0.6 to 0.8. The maximum load is calculated by multiplying the sum of the powers of all electrical appliances by a factor.
There is one subtlety in the calculations - it is necessary to take into account the difference between the rated (total) power and consumed (active), which are related by the coefficient (cos (f)).
This means that for the device to operate, a power current equal to the consumed divided by this coefficient is required:
Ip = I/cos(f)
Where:
- Ip is the rated current used in load calculations;
- I is the current consumed by the device;
- cos(f) <= 1.
Usually the rated current is indicated immediately or through the indication of the cos (f) value in the technical data sheet of the electrical device.
For example, the coefficient value for fluorescent light sources is 0.9; for LED lamps – about 0.6; for ordinary incandescent lamps - 1. If the documentation is lost, but the power consumption of household devices is known, then for guarantee take cos (f) = 0.75.
The recommended power factor values shown in the table can be used when calculating electrical loads when rated current data is not available.
How to select a circuit breaker based on load power is described in the following article, the contents of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
Selection of core cross-section
Before laying a power cable from the distribution panel to a group of consumers, it is necessary to calculate the power of electrical appliances when they operate simultaneously. The cross-section of any branch is selected according to calculation tables depending on the type of wiring metal: copper or aluminum.
Wire manufacturers provide similar reference materials to their products. If they are missing, then they are guided by the data from the reference book “Rules for the Construction of Electrical Equipment” or calculate the cable cross-section.
However, consumers often play it safe and choose not the minimum acceptable cross-section, but one step larger. So, for example, when purchasing a copper cable for a 5 kW line, choose a core cross-section of 6 mm2, when according to the table a value of 4 mm2 is sufficient.
The reference table presented in the PUE allows you to select the required cross-section from the standard range for various operating conditions of the copper cable
This is justified for the following reasons:
- Longer service life of a thick cable, which is rarely subjected to the maximum permissible load for its cross-section. Re-wiring is not an easy and expensive job, especially if the room has been renovated.
- The bandwidth reserve allows you to seamlessly connect new electrical appliances to the network branch. So, you can add an additional freezer to the kitchen or move the washing machine there from the bathroom.
- The start of operation of devices containing electric motors produces strong starting currents. In this case, a voltage drop is observed, which is expressed not only in the blinking of the lighting lamps, but can also lead to breakdown of the electronic part of the computer, air conditioner or washing machine. The thicker the cable, the smaller the voltage surge will be.
Unfortunately, there are many cables on the market that are not made according to GOST, but according to the requirements of various specifications.
Often the cross-section of their cores does not meet the requirements or they are made of conductive material with greater resistance than required. Therefore, the actual maximum power at which permissible heating of the cable occurs is less than in the standard tables.
This photo shows the differences between cables made according to GOST (left) and according to TU (right). There is an obvious difference in the cross-section of the conductors and the tightness of the insulating material.
Calculation of the circuit breaker rating for cable protection
The machine installed in the panel must ensure that the line is disconnected when the current power goes beyond the range permitted for the electric cable. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the maximum permissible rating for the switch.
According to the PUE, the permissible long-term load of copper cables laid in boxes or in the air (for example, over a suspended ceiling) is taken from the table above. These values are intended for emergency situations when there is a power overload.
Some problems begin when relating the rated power of the switch to the long-term permissible current, if this is done in accordance with the current GOST R 50571.4.43-2012.
A fragment of clause 433.1 of GOST R 50571.4.43-2012 is given. There is an inaccuracy in formula “2”, and for a correct understanding of the definition of the variable In, you need to take into account Appendix “1”
Firstly, deciphering the variable In as rated power is misleading, if you do not pay attention to Appendix “1” to this paragraph of GOST. Secondly, there is a typo in formula “2”: the coefficient of 1.45 was added incorrectly, and this fact is stated by many experts.
According to clause 8.6.2.1. GOST R 50345-2010 for household switches rated up to 63 A, the conditional time is 1 hour. The set tripping current is equal to the nominal value multiplied by a factor of 1.45.
Thus, according to both the first and modified second formulas, the rated current of the circuit breaker must be calculated using the following formula:
In <= IZ / 1.45
Where:
- In – rated current of the machine;
- IZ – long-term permissible cable current.
Let's calculate the ratings of switches for standard cable sections for a single-phase connection with two copper conductors (220 V). To do this, we divide the long-term permissible current (when laying through the air) by a tripping coefficient of 1.45.
Let's choose a machine so that its face value is less than this value:
- Section 1.5 mm2: 19 / 1.45 = 13.1. Rating: 13 A;
- Section 2.5 mm2: 27 / 1.45 = 18.6. Rating: 16 A;
- Section 4.0 mm2: 38 / 1.45 = 26.2. Rating: 25 A;
- Section 6.0 mm2: 50 / 1.45 = 34.5. Rating: 32 A;
- Section 10.0 mm2: 70 / 1.45 = 48.3. Rating: 40 A;
- Section 16.0 mm2: 90 / 1.45 = 62.1. Rating: 50 A;
- Section 25.0 mm2: 115 / 1.45 = 79.3. Denomination: 63 A.
13A circuit breakers are rarely on sale, so devices with a rated power of 10A are often used instead.
Cables based on aluminum cores are now rarely used when installing internal wiring. There is also a table for them that allows you to select a section based on load
In a similar way, for aluminum cables we calculate the ratings of the machines:
- Section 2.5 mm2: 21 / 1.45 = 14.5. Rating: 10 or 13 A;
- Section 4.0 mm2: 29 / 1.45 = 20.0. Rating: 16 or 20 A;
- Section 6.0 mm2: 38 / 1.45 = 26.2. Rating: 25 A;
- Section 10.0 mm2: 55 / 1.45 = 37.9. Rating: 32 A;
- Section 16.0 mm2: 70 / 1.45 = 48.3. Rating: 40 A;
- Section 25.0 mm2: 90 / 1.45 = 62.1. Rating: 50 A.
- Section 35.0 mm2: 105 / 1.45 = 72.4. Denomination: 63 A.
If the power cable manufacturer declares a different dependence of the permissible power on the cross-sectional area, then it is necessary to recalculate the value for the switches.
The formulas for the dependence of current on power for single-phase and three-phase networks are different. Many people who have devices designed for 380 Volts make a mistake at this stage
How to determine the technical parameters of a circuit breaker by marking is described in detail here. We recommend that you read the educational material.
What is the rated current of the machine
Rated current is the maximum permissible value of electric current that the circuit breaker allows without disconnecting the network.
To understand and make a choice of a circuit breaker, you need to proceed from two factors:
- 1. Electrical cable cross-section - the cross-sectional area of an electrical wiring cable that is capable of withstanding a certain load power without heating.
- 2. Maximum load - the power of all electrical appliances connected to a given line at maximum operating mode.
When choosing a circuit breaker, you should not install a protective device with a current rating higher than the installed power cable can withstand. Such a machine will not protect the electrical wiring and the line overheating field will trigger.
In any case, the cross-section of the electrical cable, the rating of the machine and the load power are very closely related. The power cable can carry a current limited by its cross-section.
Therefore, the ideal option for installing an electrical network would be the following sequence: calculating the power of all consumers on the power line, calculating the cross-sectional area of the installed cable based on the maximum power of all devices, calculating the circuit breaker based on the selected cable.
Protecting the weakest link
The above example clearly shows the need to perform calculations of switch ratings, taking into account not only the total power of the connected devices, but also the throughput of the wiring from which the network is formed.
Often, especially in older buildings, electrical communications, even within the same apartment, may consist of conductors of different cross-sections. In this case, the thinnest wire is determined, and the calculation of the protective circuit is performed based on the minimum indicators.
The PUE clearly regulates this point, pointing out the need to protect the most vulnerable area in the network. The rating of the installed machine must be within the total power of the equipment connected to the network. Based on this, the wiring must withstand such a load. Otherwise, the protective switch is installed based on the minimum value of the cross-section of the conductors in the circuit.
If you ignore these requirements, then in the event of an accident, claims against manufacturers of household appliances will be unfounded. Due to the incorrect choice of the rating of the protective device, the danger of operating the network increases significantly.
Table for selecting a machine based on power Source www.stroimdom.com.ua
Current ratings of circuit breakers
The limit value of the nominal value is determined by the formula Ir ≤ Ipr/1.45, where Ipr is the permissible current in long-term mode for a certain wiring. If you plan to install a network, proceed as follows:
- clarify the consumer connection diagram;
- collect passport data of equipment, measure voltage;
- according to the presented diagram, they are calculated separately, the currents in individual circuits are summed up;
- for each group it is necessary to select a machine that will withstand the appropriate load;
- determine cable products with a suitable conductor cross-section.
Rules for choosing denomination
An example of choosing the machine's nominal value for each line
For correct conclusions, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the connected equipment. If the total current is calculated to be 19 amperes, users prefer to buy a 25A device. This solution assumes the possibility of applying additional loads without significant restrictions.
However, in some situations it is better to choose a 20A circuit breaker. This ensures a relatively shorter time for power outages when the current increases (temperature increases) with a bimetallic disconnector
This precaution will help maintain the integrity of the electric motor windings when the rotor rotation is blocked by a jammed drive.
Different response times are useful to ensure selective operation of protective equipment. Devices with lower latency are installed on the lines. In an emergency, only the damaged part is disconnected from electricity. The input machine will not have time to turn off. Power supply through other circuits is useful for maintaining lighting, alarms, and other engineering systems in working order.
Nuances when calculating
To simplify the calculation of power, it is customary to use not a percentage as a reserve, but multiplication by a coefficient. This additional number is generally considered to be 1.52.
In practice, it is rarely possible to load all three phases equally, therefore, when one of the lines consumes a lot of energy, the circuit breaker rating is calculated based on the power of this particular phase. In this case, the largest value of energy consumed is taken into account and multiplied by a factor of 4.55, and then it will be possible to do without using tables.
Thus, when calculating power, the parameters of the electrical wiring are first taken into account, and then the energy consumed by the protected circuit breaker of electrical equipment. Here we also take into account the correct remark from the electrical installation rules (PUE), indicating that the installed circuit breaker must provide protection for the weakest section of the circuit.
How does a circuit breaker work?
The main task of a circuit breaker (circuit breaker) is to capture excessive currents in the electrical network and instantly de-energize it
No matter what category the circuit breaker belongs to, it must be able to quickly de-energize the electrical network and thereby prevent damage to cables
Therefore, the main function of the circuit breaker is:
- Triggered in case of power overload. Everything here is quite simple, and if there is an excessively large load on the network, for example, due to a large number of connected electrical appliances in the house, the circuit breaker should trip and de-energize the home electrical network. If this does not happen, and the machine does not cope with its task, then the electrical wiring in the house may catch fire;
- React to overcurrent caused by a short circuit in the electrical wiring. Everything here is also clear. In the event of a short circuit, the electrical wiring is subjected to strong heating, and where it is thin, as is known, it breaks, therefore, if the machine does not work, the electrical wiring may be damaged and caught fire.
You should know that each circuit breaker is rated for a different amperage. The response time of the machine depends on the magnitude of the power supply overload. If this is a short circuit, then the circuit breaker will operate instantly, literally in a matter of seconds. If the overload is not too large, then the machine and electrical wiring can heat up for hours.
As for the design of the circuit breaker and its operating principle, it is based on a bimetallic plate through which electric current passes. If it is too large, for which the machine is not designed, then the plate begins to heat up, which ultimately leads to the operation of the circuit breaker.
Circuit breakers “B” and “C” - what is the difference, categories of circuit breakers
Those people who are upgrading their home electrical network are often interested in the question of how exactly circuit breakers of categories “B” and “C” differ, because they are most often installed in household networks. The main difference between the machines “B” and “C” is the sensitivity of the electromagnetic release.
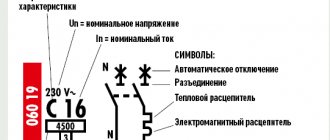
The letters A, B, C, D and K, Z indicate the characteristics of the release installed in the circuit breaker:
A - circuit breakers of this category have the highest sensitivity. If the rated current on the line where the category “A” circuit breaker will be installed exceeds 30%, the circuit breaker will turn off.
B - machines of this category are triggered when the rated current load is 3-5 times higher. Category “B” circuit breakers are designed for installation in electrical networks with no or minimal starting current (electric motors, etc.). In simple words, category “B” machines are more sensitive to passing current, and can work when starting powerful electric motors.
C - standard type automatic circuit breakers with an even greater overload capacity than class “B” circuit breakers. They are switched off if the rated current passing through the machine becomes 5-10 times higher. The response time of a category “C” machine is about 1.5 seconds. Such machines are designed to provide protection for general-purpose electrical networks.
Category D machines are rarely used in everyday life. Most often, these circuit breakers are used in electrical networks with large starting loads. Well, the last categories of machines are “K” and “Z”, they are used for special purposes, for example, to protect lines to which electronic devices are connected.
An example of how you can calculate the load in a kitchen
- electric kettle (1.5 kW),
- microwaves (1kW),
- refrigerator (500 Watt),
- hoods (100 watt).
The total power consumption will be 3.1 kW. To protect such a circuit, you can use a 16A circuit breaker with a rated power of 3.5 kW. Now let’s imagine that a coffee machine (1.5 kW) was installed in the kitchen and connected to the same electrical wiring. The total power removed from the wiring when connecting all of these electrical appliances in this case will be 4.6 kW, which is more than the power of a 16 Amp auto switch, which, when all devices are turned on, it will simply turn off due to excess power and leave all devices without power, including the refrigerator.
Circuit breaker power dissipation
Dissipation is the loss of electricity that is released into the environment in the form of heat. As an example, I will give the nameplate power dissipation values for VA 47-63 automatic machines (for new automatic machines at current values equal to the rated one):
| Rated current In, A | Power dissipation, W | |||
| 1-pole | 2-pole | 3-pole | 4-pole | |
| 1 | 1,2 | 2,4 | 3,6 | 4,8 |
| 2 | 1,3 | 2,6 | 3,9 | 5,2 |
| 3 | 1,3 | 2,6 | 3,9 | 5,2 |
| 4 | 1,4 | 2,8 | 4,2 | 5,6 |
| 5 | 1,6 | 3,2 | 4,8 | 6,4 |
| 6 | 1,8 | 3,6 | 5,5 | 7,2 |
| 8 | 1,8 | 3,6 | 5,5 | 7,33 |
| 10 | 1,9 | 3,9 | 5,9 | 7,9 |
| 13 | 2,5 | 5,3 | 7,8 | 10,3 |
| 16 | 2,7 | 5,6 | 8,1 | 11,4 |
| 20 | 3,0 | 6,4 | 9,4 | 13,6 |
| 25 | 3,2 | 6,6 | 9,8 | 13,4 |
| 32 | 3,4 | 7,5 | 11,2 | 13,8 |
| 35 | 3,8 | 7,6 | 11,4 | 15,3 |
| 40 | 3,7 | 8,1 | 12,1 | 15,5 |
| 50 | 4,5 | 9,9 | 14,9 | 20,5 |
| 63 | 5,2 | 11,5 | 17,2 | 21,4 |
As you can see, the circuit breaker also wants to eat. Therefore, you should not get carried away and stick machine guns wherever possible. Where do the losses occur? The main part falls on the thermal release. But there is no need to overdramatize the situation. These losses are proportional to the current flowing. Therefore, if, for example, the load is 2 times less than the rated load, then the losses will be correspondingly 4 times less, and in the absence of load there will be no losses. If they are presented as a percentage, then the values will be on the order of 0.05-0.5%, with the smallest percentage for the most powerful machines. In the contacts themselves, while the machine is new, losses are insignificant. But during operation, the contacts will burn out, the contact resistance will increase, and with it the losses will increase. Therefore, with an old machine, losses may be noticeably greater. How to measure losses -
Calculation of power consumption
In everyday life, you often have to deal with calculating power consumption, for example, to check the permissible load on the wiring before connecting a resource-intensive electrical consumer (air conditioner, boiler, electric stove, etc.).
Also, such a calculation is necessary when choosing circuit breakers for the distribution board through which the apartment is connected to the power supply.
In such cases, it is not necessary to calculate power by current and voltage; it is enough to sum up the energy consumption of all devices that can be turned on at the same time.
- Without getting involved in calculations, you can find out this value for each device in three ways:
- by referring to the technical documentation of the device;
- by looking at this value on the rear panel sticker;
- using the table showing the average power consumption for household appliances.
When making calculations, it should be taken into account that the starting power of some electrical appliances may differ significantly from the nominal one.
For household devices, this parameter is almost never indicated in the technical documentation, so you need to refer to the corresponding table, which contains the average values of the starting power parameters for various devices (it is advisable to choose the maximum value).
Table of power/current consumption of household electrical appliances
| electrical appliance | Power consumption, W | Current strength, A |
| Washing machine | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Jacuzzi | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Electric floor heating | 800 – 1400 | 3,6 – 6,4 |
| Stationary electric stove | 4500 – 8500 | 20,5 – 38,6 |
| microwave | 900 – 1300 | 4,1 – 5,9 |
| Dishwasher | 2000 – 2500 | 9,0 – 11,4 |
| Freezers, refrigerators | 140 – 300 | 0,6 – 1,4 |
| Electric meat grinder | 1100 – 1200 | 5,0 – 5,5 |
| Electric kettle | 1850 – 2000 | 8,4 – 9,0 |
| Electric coffee maker | 630 – 1200 | 3,0 – 5,5 |
| Juicer | 240 – 360 | 1,1 – 1,6 |
| Toaster | 640 – 1100 | 2,9 – 5,0 |
| Mixer | 250 – 400 | 1,1 – 1,8 |
| Hairdryer | 400 – 1600 | 1,8 – 7,3 |
| Iron | 900 –1700 | 4,1 – 7,7 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 680 – 1400 | 3,1 – 6,4 |
| Fan | 250 – 400 | 1,0 – 1,8 |
| TV | 125 – 180 | 0,6 – 0,8 |
| Radio equipment | 70 – 100 | 0,3 – 0,5 |
| Lighting devices | 20 – 100 | 0,1 – 0,4 |
Current limiting class
Let's move on. An electromagnetic release, although called instantaneous, also has a certain response time, which reflects such a parameter as the limitation class. It is indicated by one number and for many models this number can be found on the device body. Basically, machines with current limiting class 3 are now produced - this means that from the time the current reaches the trigger value until the circuit is completely broken, no more than 1/3 of the half-cycle will pass. With our standard frequency of 50 Hertz, this turns out to be about 3.3 milliseconds. Class 2 corresponds to a value of 1/2 (about 5 ms). According to some sources, the absence of marking of this parameter is equivalent to class 1. The highest class that I came across is 4th for OptiDin machines manufactured by KEAZ.
What is it needed for
The machine is considered a device whose main task is to ensure safe use of the electrical network. He also deals with protecting equipment from overcurrent, which is considered an overload short circuit. Such equipment is turned on and off from an electrical circuit. It is equipped with either an electromagnetic release or a combined type. Thanks to this, the circuit can be protected. Its main advantage is the fact that it allows you to protect an electrical installation or transformer substation from short circuits, network overloads and breakdowns as a result of frequent network outages.
Network protection as the main task of a circuit breaker
It has on its body markings of the rated current, switching capacity, current limiting class, rated breaking capacity and time-current response characteristics of the release system. It can be single-pole, two-pole, three-pole and four-pole and is suitable for the network phases corresponding to the name.
Important! Most often it is used to protect an electric stove or other kitchen heating appliances. It is also used to protect the lighting system with motor and transformer systems.
Unacceptable mistakes when purchasing
There are several mistakes that novice electricians can make when choosing a circuit breaker based on current strength and load. If you choose an automatic protective device incorrectly, even slightly missing the rating, this can lead to many unfavorable consequences: the circuit breaker will trip when the electrical appliance is turned on, the electrical wiring will not withstand current loads, the service life of the circuit breaker will be quickly reduced, etc.
The first and most important thing you should know is that when concluding a contract, new subscribers order the energy capacity of their connection. From this, the technical department makes calculations and selects where the connection will take place and whether the equipment, lines, TP can withstand the load
Also, based on the declared power, the cable cross-section and the rating of the circuit breaker are calculated. For residential subscribers, an unauthorized increase in the input load without upgrading it is unacceptable, since the power has already been declared according to the project and the supply cable has already been laid. In general, the nominal value of the introductory machine is chosen not by you, but by the technical department. If you end up choosing a larger circuit breaker, everything must line up. Always focus not on the power of household appliances, but on the electrical wiring. You should not select a machine only based on the characteristics of electrical appliances if the wiring is old. The danger is that if, for example, to protect an electric stove you choose a 32A model, and the cross-section of the old aluminum cable can only withstand a current of 10A, then your wiring will not withstand it and will quickly melt, which will cause a short circuit in the network. If you need to choose a powerful switching device for protection, first of all replace the electrical wiring in the apartment with a new, more powerful one. If, for example, when calculating the appropriate rating of the machine for the operating current, you came up with an average value between two characteristics - 13.9A (not 10 or 16A), give preference to the larger value only if you know that the wiring will withstand the current load 16A. For a dacha and a garage, it is better to choose a more powerful circuit breaker, because a welding machine, a powerful submersible pump, an asynchronous motor, etc. can be used here. It is better to provide for the connection of powerful consumers in advance, so as not to overpay later on the purchase of a switching device of a higher rating. As a rule, 40A is quite enough to protect the line in domestic use. It is advisable to select all automation from one, high-quality manufacturer. In this case, the likelihood of any discrepancy is minimized. Buy products only in specialized stores, or even better, from an official distributor. In this case, you are unlikely to choose a fake and, moreover, the cost of products from a direct supplier is, as a rule, slightly lower than from intermediaries.
That’s the whole method for choosing the right machine for your own home, apartment or cottage! We hope that now you know how to choose a circuit breaker based on current, load and other equally important characteristics, as well as what mistakes should not be made when purchasing!
We recommend reading:
{SOURCE}
What is important to know when connecting electrical appliances
So, having calculated the approximate rating of the required machine, you need to give an explanation regarding the power. Many people wonder whether it is possible to plug in very powerful electrical appliances into a regular outlet, such as an electric boiler, for example.
According to the rules of the PUE, connecting an electric boiler with a power of more than 3 kW to a regular outlet is unacceptable. And each outlet has its own specific characteristics. Most often, home sockets are rated at 16 amperes, and, therefore, electrical appliances with a power of no more than 3.5 kW can be connected to them.
Therefore, any more or less powerful electrical appliance must be connected only through a separate circuit breaker. Moreover, it is the phase wire that is supplied to the circuit breaker, and not the working zero. Thus, knowing the approximate power of the equipment, you can easily calculate the rating of the circuit breaker.
Types of slot machines
Classification of circuit breakers occurs according to the following parameters:
- number of poles;
- rated and limit currents;
- the type of electromagnetic release used;
- maximum power switching capacity.
Let's look at it in order.
Number of poles
The number of poles is the number of phases that the machine is capable of protecting. Depending on the number of poles, machines can be:
- Single pole. Protection is provided for one output wire, one phase.
- Bipolar. As a rule, these are two combined single-pole circuit breakers with one common control knob. In a situation where the current of one of the machines exceeds the permitted load, both devices are switched off. Two-pole circuit breakers are used to completely disconnect the load (one phase), turning off the working phase and the working zero.
- Three-pole. They are used with three-phase circuits; if the load is exceeded, three phases are switched off simultaneously. Such machines also have one common circuit breaker.
- Four-pole. Similar to two-pole, but designed to work with three-phase circuits. When the load is exceeded, three phases and the working zero are opened simultaneously.
Rated and limiting currents
Everything is simple here - such a current strength at which the machine will open the circuit. At the rated current and even a little more than stated, work will be carried out, but only when the limit current is exceeded by 10–15% will a shutdown occur. This is due to the fact that quite often the starting currents exceed the maximum possible currents for a short period of time, so the machine has a certain reserve of time, after which the circuit will open.
Type of electromagnetic release
This is a part of the machine that allows you to open the circuit in the event of a short circuit, as well as in the event of an increase in current (overload) by a certain number of times. Releases are divided into several categories, let's look at the most popular:
- B - opening when the rated current is exceeded by 3–5 times;
- C - when exceeded by 5–10 times;
- D - when exceeded by 10–20 times.
Maximum power switching capacity. This is the value of the short circuit current (determined in thousands of amperes) at which the machine will remain operational after the circuit opens due to a short circuit.
Selecting the breaking capacity
The selection of a packager based on the maximum permissible load current is described above. But the network circuit breaker must also turn off when a short circuit (short circuit) occurs in the network. This characteristic is called breaking capacity. It is displayed in thousands of amperes - this is the order currents can reach during a short circuit. Selecting a machine based on its breaking capacity is not very difficult.
This characteristic shows at what maximum value of the short-circuit current the circuit breaker remains operational, that is, it will not only be able to turn off, but will also work after being turned on again. This characteristic depends on many factors and for accurate selection it is necessary to determine the short-circuit currents. But for wiring in a house or apartment, such calculations are done very rarely, and are based on the distance from the transformer substation.
Breaking capacity of automatic protective switches
If the substation is located close to the entrance to your house/apartment, take a circuit breaker with a breaking capacity of 10,000 A; for all other city apartments, 6,000 A is enough. If the house is located in a rural area or you are choosing a circuit breaker for a summer residence, it may well be enough and a breaking capacity of 4,500 A. The networks here are usually old and short-circuit currents are not large. And since the price increases significantly with increasing breaking capacity, the principle of reasonable savings can be applied.
Is it possible to install bags with a lower breaking capacity in city apartments? In principle, it is possible, but no one guarantees that after the first short circuit you will not have to change it. He may have time to turn off the network, but will be inoperative. In the worst case scenario, the contacts will melt and the machine will not have time to turn off. Then the wiring will melt and a fire may occur.
Principle of operation
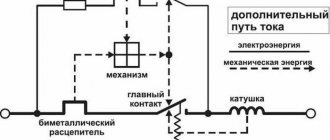
The main element of the device is an electromagnetic one with a thermal release. The first guarantees protection against short circuits, the second - against overvoltage. An electromagnetic device is a coil with a core, which is placed on a special spring and, under normal conditions, creates an electromagnetic field that attracts the coil core. At the moment of a short circuit, the electric current increases and exceeds that nominally stated according to the technical characteristics. This current flows through the release coil and increases the field. As a result, the circuit is de-energized.
The heating unit comes into operation when an overload occurs. This is a bimetallic strip with metal A and B.
Important! At the moment of overvoltage, current flows to the plate, it heats up and, due to the property of B to expand, the surface bends and the movable type of contact opens.
You might be interested in PML magnetic starter
The principle of operation of any circuit breaker
General characteristics
An automatic electrical switch is a switching device that passes through its structure a current of rated strength. When necessary, it turns off the circuit, for example, during a short circuit or when power consumption increases. Currently, there is a single-phase, two-phase and three-phase device, answering the question of what types of electrical machines there are. They differ from each other in the number of elements that disconnect the current.
What does it look like
The device is designed to protect the electrical circuit so that overloads and short-circuit currents do not occur. It can be reused many times. It always works reliably.
Note! The main parameter of an electric machine is the number of rated current transmissions, the current energy that is needed for household electrical appliances to work normally. In a private house and city apartment, a 6-63 ampere machine is installed. Experts recommend dividing the electrical network at home into a pair of circuits and installing each circuit on its own switch.
Protection of electrical equipment from overcurrent as the main purpose