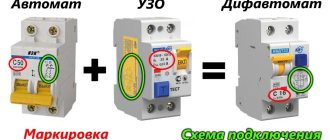
Purpose of devices
The main function assigned to circuit breakers is to protect the cable from short circuits and overload. In addition, the set of tasks for the device includes:
- transmission of rated load current during long-term use;
- stable maintenance of the network voltage potential with a guarantee of its insulation;
- the ability to manually control the state of the power contact;
- the ability to determine when an overload occurs and provide the necessary time for safe operation, after which power is removed from the connected consumers.
It is important to choose the right type of electrical circuit breaker, taking into account the technical characteristics of the network, since frequent power outages can have disastrous consequences for the connected devices.
To do this, it is worth understanding how a circuit breaker works. A device designed for high power is not always appropriate, since a dangerous situation in a domestic area may not be recognized. Current strength that goes beyond the permissible norm for the cable is often not detected by the circuit breaker as an emergency position. Then a short circuit can be caused by melting of the insulation, but by this time there is a risk of fire. A circuit breaker device with a lower power can often and regularly stop the supply of voltage to the consumer. As a result, the machine will stop functioning due to contact failure.
Electrical equipment care
Electrical equipment, like any other devices, needs care. Maintenance of circuit breakers is carried out according to a certain procedure with strict frequency. Users are often unaware of this need, but it exists. Electrical equipment is subject to wear and tear; oxidation of contacts, aging of insulation, wear of moving parts and other changes gradually occur. Therefore, the power calculation of a circuit breaker made 5 years ago may not correspond to the real state of affairs.
Probably, many of you have experienced situations when a flawlessly working network begins to act up. An obvious manifestation of this is when a circuit breaker frequently trips for no apparent reason. The reason may be in the device itself, but most often this happens due to problems with wiring and hidden defects in the electrical circuits of household appliances and equipment.
To identify and prevent such situations, there is loading of circuit breakers . It is carried out every three years using special equipment and is carried out to check whether the actual condition of the machine meets the requirements for the safe operation of electrical networks. The method for checking circuit breakers involves checking the insulation condition, the response time of overcurrent and heating protection, the condition of contacts and other parameters.
Regular maintenance ensures that problems are identified early, prevents more serious consequences, and ensures that networks remain safe for the foreseeable future. Detected malfunctions of circuit breakers are eliminated whenever possible, but most often in such cases a complete replacement of electrical devices is required, especially in the case of their small sizes.
Manufacturers of electrical products produce many spare parts for powerful industrial machines. For household or low-power equipment, only spare contact groups are usually produced. Therefore, replacing circuit breakers is a typical action when repairing electrical networks. Regular maintenance of electrical equipment is not a burdensome procedure at all, including in terms of money. Its main goal is prevention.
The technical characteristics of the machines also include the guaranteed number of on/off cycles. According to these indicators, circuit breakers have a service life measured in decades, provided that the devices are properly installed and maintained in a timely manner. They must fully comply with the network parameters. In addition, to extend their service life, you should not use faulty electrical appliances that cause frequent power outages.
Varieties by poles
Automatic machines can have from 1 to 4 poles, which is determined by the power of the connected electrical equipment and the number of network phases.
Classification according to the number of poles of circuit breakers:
- A single-pole circuit breaker is capable of protecting the network to which low-power devices are connected. Installation is carried out on the phase wire, the neutral wire is excluded.
- A two-pole device is relevant for a line to which fairly powerful household appliances are connected (washing machine, electric stove, boiler).
- Three-pole model. Intended for semi-industrial scale with connection of installations: pumps, devices for auto repair shops or construction work.
- The four-pole circuit breaker protects against short circuits and overloads of four-wire networks.
For a four-core cable, only three- and four-pole circuit breakers are installed.
Design and principle of operation of the machine
The following types of circuit breakers are produced:
- air circuit breakers;
- molded case circuit breakers;
- modular circuit breakers.
To use the product, you need to know how the machine works. The circuit breaker consists of a housing made of dielectric material. The front panel of the device is used for marking. The back of the device has a DIN rail for mounting. Devices are attached to the DIN rail using a latch. This allows you to quickly mount and dismantle the device during installation work.
The device itself is a modular, non-dismountable design, without additional intervention - that is, it can be disassembled, but after first removing the four rivets that connect the two halves of the body. The circuit breaker consists of:
- lower and upper screw terminals;
- moving and fixed contact;
- electromagnetic release mechanism with coil and core;
- on/off handle;
- thermal release with a bimetallic plate, equipped with an adjusting screw;
- fastening latches.
The operating principle of the product is as follows. The device is turned on and off manually using the handle. The thermal release serves to protect against minor but long-term overloads; at large values, the bimetallic plate is heated, deformed, and then the circuit is turned off. This release has an adjustable shutdown.
The electromagnetic release switches off the network when a short circuit occurs in the electrical line. The electricity supply to consumers should be turned off.
Classification by time-current indicator
The number of false alarms of automatic circuit breakers under uneven load on the network is optimized due to different speeds of response to exceeding the rated current. The dependence of the network shutdown time on the strength of the flowing current determines the following types of circuit breakers:
- A. Available from European manufacturers. The most sensitive model. It responds instantly to deviations from the norm. Typically used to protect lines with connected high-precision equipment. (Current rating 2-3). Rarely installed.
- B. Designed for rooms equipped with old aluminum wiring. Suitable for long lines, lighting lines or circuits without possible sudden voltage changes. It turns off with a slight delay of 5-20 seconds at a current rating of 3-5.
- C. More often found in modern apartments to protect outlet lines into which a sufficient amount of electrical equipment is connected (washing machines, dishwashers, freezers, heaters, microwave ovens, LCD TVs). Shutdown occurs in 1-10 seconds at a current multiple of 5-10. This principle is needed to stabilize operation with a slight difference.
- D. Protection is optimal for lines with transformers or high inrush currents. Circuit breakers of this class cannot be connected to consumers oriented to work with protection classes C and B. At 10-20 rated current it turns off in 1-10 seconds. Lowest sensitivity to increased current. Sometimes it is customary to install it on the building itself in order to secure apartment automatic machines. If they suddenly do not work, the entire building will be disconnected from the network.
These are the most common types. The range of production models has been supplemented by three more groups: L, K and Z.
Marking and characteristics of circuit breakers.
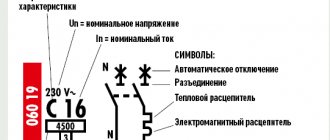
BA63 - type and series of circuit breaker
Rated current is the maximum current of the electrical network at which the circuit breaker is capable of operating for a long time without emergency shutdown of the circuit.
Standard values of rated currents of circuit breakers: 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 8; 10; 13; 16; 20; 25; 32; 35; 40; 50; 63; 80; 100; 125; 160; 250; 400; 630; 1000; 1600; 2500; 4000; 6300, Ampere.
Rated voltage - the maximum network voltage for which the circuit breaker is designed.
PKS is the maximum breaking capacity of the circuit breaker. This figure shows the maximum short circuit current that can turn off a given circuit breaker while maintaining its functionality.
In our case, the PKS is indicated at 4500 A (Ampere), this means that with a short circuit current (short circuit) less than or equal to 4500 A, the circuit breaker is able to open the electrical circuit and remain in good condition, if the short circuit current. exceeds this figure, there is a possibility of the movable contacts of the machine melting and welding them to each other.
Trip characteristic - defines the tripping range of the circuit breaker's electromagnetic release.
For example, in our case, a machine with characteristic “C” is presented; its operating range is from 5·In to 10·In inclusive. (Iн is the rated current of the machine), i.e. from 5*32=160A to 10*32+320, this means that our machine will provide instantaneous disconnection of the circuit already at currents of 160 - 320 A.
Note:
- Standard response characteristics (provided for by GOST R 50345-2010) are characteristics “B”, “C” and “D”;
- The scope of application is indicated in the table according to established practice, but it may be different depending on the individual parameters of specific electrical networks.
Classification by design
There are three types of network protection circuit breakers:
- Modular device. Relevant for household networks with small currents flowing. Most often it has one or two poles.
- Cast. Used to work in industrial networks. The name was given due to the cast body.
- Air electric. Suitable for networks supporting high-power installations. Usually has three or four poles.
Table for selecting a circuit breaker based on cable cross-section
The choice of circuit breaker clearly depends on the cable cross-section. If the current of the machine is selected more than necessary, then the cable may overheat due to the flow of high current. If the machine is selected correctly, then if the current exceeds it will turn off and the cable will not be damaged.
Table for selecting a machine according to cable cross-section
Pay attention to the cable routing methods (installation type). Depending on where the cable is laid, the current of the selected circuit breaker may differ by 2 times!
According to the table, we have the initial cable cross-section, and select a circuit breaker for it. For us, as electricians, the first three columns of the table are most important.
Now - how to choose a circuit breaker if the power of the devices is known?
Separation according to rated breaking capacity
According to the criteria that determine the value of the short circuit current at which the circuit breaker will trip and subsequently cut off the voltage supplied to the consumer, three types are distinguished:
- 4.5 kA (4500 A). Most often used to protect power lines of private residential buildings with a resistance of 0.05 Ohm. Such models are practically not used; some countries have already banned their use.
- 6 kA (6000 A). Used to prevent short circuits in public places and residential areas where the resistance is approximately 0.04 ohms.
- 10 kA (10000 A). The machines are designed to protect electrical equipment for industrial use.
For domestic purposes, 6000 A is most often used.
Rated current calculation
The cross-section of the wiring is selected according to the rated current, which it can carry for a long time without heating up. It is determined according to technical documentation, otherwise additional calculations are made. These calculations will require the following input data:
- the first is the cross-sectional area of the wire;
- second, know the wire material;
- third is to decide on the installation method (external, hidden).
After determining the cross-section of the wire, using the reference table, determine the electrical characteristics of this electrical network.
Based on the calculated values, the operating characteristics and its nominal values are determined. These characteristics should not be greater than the calculated parameters.
Types of releases
The protection includes an electromagnetic and thermal release. The operation of each element is autonomous and does not depend on the state of each other.
The thermal release is a metal plate whose purpose is to respond to heat. To turn on the device, the plate must cool to the initial permissible temperature.
The operating principle of the circuit breaker depends on the specific situation.
Work mode
Electric machines are activated by raising the control lever. The charging and releasing mechanism switches to the active state. Switching of power contacts occurs: current flows between them (from stationary to moving). After this, the movement continues through the flexible connection to the coil of the electromagnetic release, and then through the flexible connection to the thermal release. The current enters the “supply” power line through the bottom terminal.
Mechanism of action during short circuit (SC)
Timely shutdown of the load supply is ensured by an electromagnetic release. The principle of operation of a circuit breaker during a short circuit boils down to the following scheme: a voltage exceeding the permissible norm, flowing through the electromagnetic coil of the release, forms a high-power magnetic field. As a result, the armature with the moving contact moves down, acting on the trigger lever, after which the load is turned off.
Thus, the immediately arising magnetic field provokes a reaction to de-energize the network before an emergency occurs.
During the occurrence of a discharge, combustion products are formed between the contacts, and the pressure inside the machine body also increases. It is necessary to eliminate side reactions, for which channels are provided in the machine box.
Overload
The network is protected thanks to a thermal release - a bimetallic plate. In this case, the current flowing through it may exceed the normal value, which leads to its overheating and subsequent bending. Reaching a certain bending angle, the plate acts on the trigger device, during which the machine turns off.
Heating up the bimetal takes time. The duration depends on the degree of excess of the applied current and can be several seconds or last up to an hour. This property allows you not to turn off the power in the event of short-term or accidental excess current in the network. The lower limit of the permissible value at which the thermal release is triggered is set by the manufacturer. The correct operation of the thermal element can be influenced by the ambient air temperature. The technical parameters indicated in the marking are relevant for temperatures up to 30 degrees. In a cool room, the current can reach a value higher than the permissible value; in a hot room, it can trigger at a lower value.
The thermal release is slower than the magnetic release, but has the advantage of being more accurate and easier to set up.
Calculation of the rated power of the machine
The rated power of the machine is the operating power that the switch allows without shutting down. The calculation is carried out using a simple formula:
P = U*I*cos(f), (1)
where P is the power in W, is the voltage of the electrical network in V, I is the current in A passing through the protection device, cos(f) is the cosine (f), which determines the ratio of the active load to the total load. Using formula (1), the current strength in normal operating mode is determined. This formula is applicable for a single-phase network. It is also applicable for a three-phase network, but it is necessary to take into account phase shifts. The values of these quantities are usually given on the equipment.
Marking
All circuit breakers, regardless of the manufacturer and their type, are marked according to a single scheme, including the main parameters:
- manufacturer's name or logo;
- type indication, according to the manufacturer's series number and catalogue;
- operating voltage value: designation of alternating current is a wavy line, direct current is a straight line, combined is two lines at once;
- the value of the operating current (indicated without the measurement value in amperes), the type of time-current characteristic is indicated before the current value;
- operating frequency (in the case when only the set frequency is used);
- short circuit switching capacity (in Amperes);
- the degree of protection is indicated in the form of IP;
- The current limit class is indicated in a rectangle (value from 1 to 3);
- designation of the terminals: for connection to the neutral conductor - N, for connecting the protective line - grounding symbol.
The lever itself contains a status designation: “off”, “on” or “1”, “0”. While turning off occurs automatically, turning on can only be done manually.
A circuit breaker reduces the risks caused by short circuits or sudden blackouts to a minimum.
Operating principle
Externally, the device has a heat-resistant plastic case with a handle responsible for starting and ending work. It has a latch at the back and screw terminals at the bottom.
The main thing in the circuit breaker is the structural unit, namely the main contact system, arc extinguishing system, drive with release and auxiliary contact. The contact system can be one-, two- or three-stage. The arc extinguishing system includes chambers with arc extinguishing grilles or narrow slots.
Regardless of the design, there is a maximum operating current that does not break the machine, since due to excess voltage the contacts burn or weld.
You might be interested in this: Electrical diagram of the apartment
A circuit breaker is made with the addition of a manual or motor drive. It can be stationary or mobile. The drive is needed to switch the system on and off automatically. The system also contains a direct-acting relay. This is an electronic trip unit that includes levers, latches, rockers and trip springs.
Design
The device works very simply. The mains voltage goes to the top terminal, which is connected to a fixed contact. Energy flows from it to the moving contact. He already transfers it to the copper conductor and the thermal release. Finally, current is supplied to the bottom terminal. In the event of an accident, for example, an overload or a short circuit, the protected electrical circuit is switched off due to the fact that the electromagnetic release begins to operate.
Note! It is important to note that an electromagnetic release is an element with a solenoid that has a movable steel core that is held in place by a spring. When the current voltage exceeds, an electric field appears in the coil. The core gets inside the coil and overcomes the spring resistance. As a result, the release is triggered. Without an accident, the electric field strength is not enough to cause decoupling.
Operating principle
Classification of electrical machines
There are several typical circuit breaker shutdown characteristics: A, B, C, D, E, K, L, Z
- A
– for breaking long-distance circuits and protecting electronic devices. - B
- for lighting networks. - C
- for lighting networks and electrical installations with moderate currents (current overload capacity is twice that of B). - D
– for circuits with inductive loads and electric motors. - K
– for inductive loads. - Z
– for electronic devices.