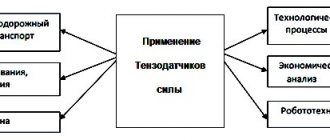
Scales are found in every grocery store, in special workshops, at home, in large factories, etc. Specialists use this product every day to maintain certain grams of products or, on the contrary, to control them. The accuracy and speed of measurements depends on a small device that is placed inside each such structure. All readings and errors depend only on this element.
The editors of the YaNashla website have prepared for you a rating of the best strain gauges for 2022.
What is strain gauge and why are strain gauges needed?
Strain measurement (from the Latin tensus - tense) is a method and technique for measuring the stress-strain state of the measured object or structure. The fact is that it is impossible to directly measure mechanical stress, so the task is to measure the deformation of an object and calculate the stress using special techniques that take into account the physical properties of the material.
The operation of strain gauges is based on the tensoelectric effect - this is the property of solid materials to change their resistance under various deformations. Strain gauges are devices that measure the elastic deformation of a solid and convert its value into an electrical signal. This process occurs when the resistance of the sensor conductor changes when it is stretched and compressed. They are the main element in instruments for measuring the deformation of solid bodies (for example, machine parts, structures, buildings).
brief information
The first thing that is important to understand is that strain gauges are a general concept. Therefore, regardless of the device model and method of application, all weighing products have the same operating principle. Of course, there are strain gauge, mechanical, fiber optic, etc. options, but they point to the main element through which the measurement is carried out. The most common element is strain-resistive devices. They are used in almost every electronic product, as they are simple and have good accuracy.
Characteristics of strain gauges
Base - length of the grid conductor (0.2-150 mm). Nominal resistance R - the value of active resistance (10-1000 Ohms). The operating supply current Ip is the current at which the strain gauge does not noticeably heat up. When overheated, the properties of the materials of the sensitive element, base and adhesive layer change, distorting the readings. Strain sensitivity coefficient: s =(∆R/R)/(∆L/L), where R and L are the electrical resistance and length of the unloaded sensor, respectively; ∆R and ∆L - change in resistance and deformation due to external force. For different materials, it can be positive (R increases with tension) and negative (R increases with compression). The value of s for different metals varies from -12.6 to +6.
Design and principle of operation
The basis of the strain gauge is a strain gauge equipped with special contacts attached to the front of the measuring panel. During the measurement process, the sensitive contacts of the panel come into contact with the object. Their deformation occurs, which is measured and converted into an electrical signal transmitted to the processing elements and display of the measured value of the strain gauge sensor.
Depending on the scope of functional use, sensors differ in both types and types of measured quantities. An important factor is the required measurement accuracy. For example, a load cell on a truck scale at the exit of a bakery is completely unsuitable for electronic pharmacy scales, where every hundredth of a gram is important.
Tactile
They are triggered by mechanical action on a sensitive surface. They allow you to set minimal deformations, but with inaccurate settings they can give a false signal.
Mechanical
The measurements are based on recording the change in the length of an object under load. The work of a mechanical strain gauge is to determine the dependence of the elongation of a body on the stress in the cross section.
Resistive
The most common type of sensors. They require connection to a low-current control circuit, since they include a strain gauge circuit. Reliable in any environmental condition.
Strings
The string version is a steel wire (string), it is pulled between supports, which are fixed to the surface of the object. The essence of the measurements is to determine the ratio of the vibration frequency of the string to the degree of its tension when the length of the examined body changes under the influence of a load.
Inductive
The device is based on the use of an inductance coil in which a movable core is installed. It is in direct contact with the surface of the object. At the slightest deformation of the surface, the core in the coil shifts. The changing parameters of the inductor are recorded through the electrical circuit by the device.
Piezoresonant
They are semiconductor-type devices and require reliable maintenance and fine tuning. They work on the principle of comparing the reference signal with the actual one.
Piezoelectric
In their action they are similar to meters of the previous type, but they give a signal when the values of contact deformations applied to the sensing element change.
Magnetic
Made from alloys with a variable coercivity value, they are used to measure forces in equipment units operating in strong electromagnetic fields.
Capacitive
Designed to measure small mechanical stresses in parts with a complex configuration, when changing the length of the conductive wire changes its electrical capacitance.
Connection diagram
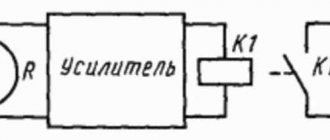
We figured out how the strain gauge works. Now you should familiarize yourself with the connection diagram. The block diagram of the device that reads the signal is shown in the figure below. On it you see one of the options for amplifying and converting the signal from the sensor.
If we consider a strain gauge sensor, then in reality it is a bridge of resistors, connected as follows. This connection circuit is called a “Winston Bridge” or measuring bridge.
For it to work, it is not enough to connect only signal wires; you also need power wires. In some complex systems, wires may also be connected for thermal stabilization or other functions.
The video explains in detail what strain gauges are and how they work:
Modern strain gauges, depending on their purpose, can be used in installations for measuring from fractions of a gram to hundreds of tons. Accordingly, for each range of scales, strain gauges of a certain design and type of sensing element are selected. In addition to the scales being measured, an important role in the selection of control and measuring equipment is played by the conditions in which they will operate, as well as the required accuracy class.
Design features
Strain gauges are distinguished by the type of structure, which depends on the type of sensing element. Control of deformation processes is possible using different types of contacts: foil, film or wire.
Indicators with a foil element are used as adhesive strain gauges. Film ones are analogues of foil ones. The difference lies in the material of manufacture. For their production, strain-sensitive films with sputtering are used, which increases the sensitivity of the system.
You need to buy a wire-type strain gauge when you need to measure the load in a wide range: from hundredths of grams to several tons.
Ringing
Every load cell is subject to “ringing” when the load changes suddenly. This is due to the springy behavior of the load cells. To measure loads, they must deform. Thus, a finite stiffness load cell should exhibit spring-like behavior, exhibiting vibration at its natural frequency. An oscillating data pattern may be the result of a call. The call can be suppressed to a limited extent by passive means. Alternatively, the control system can use an actuator to actively dampen the load cell ringing. This method provides better performance at the expense of a significant increase in complexity.
Classification of strain gauge equipment
All strain gauge equipment can be divided into classes that characterize the complexity and level of nesting of the technical device:
| Strain gauge. It is the basic unit of strain gauge equipment. It is on the basis of its measurements that the entire subsequent cycle of work is built. At the same time, the strain gauge itself in most cases is not a full-fledged measuring device and in order for it to start working, a strain gauge is required. | |
| Load cell. This is the primary measuring device. It is a strain gauge in a special housing that changes its shape in accordance with the requirements for its operation. The body is made of special steel, which ensures sufficient springiness, return of the strain gauge to its original position and linearity of readings. The quality of the strain gauge housing is one of the most important criteria for the performance of strain gauge equipment. Suffice it to say that it is the composition and grade of steel of the housing that is kept secret by all manufacturers of strain gauges, and not its design. | |
| Terminal. A secondary metering device that converts the output signal from strain gauges into a measurement result and displays it on a digital display. The terminal can operate within a limited range of accuracy, like strain gauges, so it is necessary to select a model that will correctly interpret the readings of the measuring device. Digital terminals are generally tied to several types of sensors via a data transfer protocol and cannot be used in other measuring systems. As well as vice versa. | |
| Measuring device. This is a complex of industrial equipment, consisting of strain gauges, a load receiving platform and a terminal, installed on a specific object - scales, dispenser, dynamometer, machine, press. At the same time, the measuring device is the only type of measuring equipment that is certified for measuring the mass of cargo. A group of strain gauges cannot be called a scale if it has not been verified and calibrated, even if the sensors and terminal are certified. | |
| Periphery equipment. This includes remote displays, video cameras recording weighing results, and software. They expand the capabilities of strain gauge equipment, but are not directly involved in the measurement process. |
It will be interesting➡ The principle of operation of a thermostat: device purpose, main functions and types
Rating of the best console sensors
SH8C-C3-10.0T-6B
A good option with a low creep factor and simple connection. Product accuracy class is C3. The maximum cable length – 6 meters – is present in the modification where the NPI is equal to 10 tons. Recommended voltage is 5-12 V. Operates at temperatures up to 65 degrees, which is suitable for most rooms. It is made of a durable body that can withstand various mechanical loads. Protection class – IP67.
The price is specified when ordering.
SH8C-C3-10.0T-6B
Advantages:
- Good efficiency;
- Degree of protection;
- Load - up to 10 tons;
- Made from structural steel;
- Warranty - 3 years.
Flaws:
- Not found.
SB-A/-ASS modification 10 tons
The product can be used in truck, crane and platform scales, as well as in special dispensers. Accuracy class – C2 will allow you to carry out high-quality measurements. Zero balance – 1%. Works even at temperatures above 65 degrees. Protection class – IP66. The body is made of durable alloy steel, coated with a protective layer to prevent corrosion.
Sold at a price of 5,400 rubles.
SB-A/-ASS modification 10 tons
Advantages:
- Good accuracy rate;
- Durable housing;
- Efficiency;
- Durability.
Flaws:
- Price.
Strain gauge SUL
A good product designed for platform design only. The maximum NPI is 10 tons. The outer part is made of durable alloy steel that can withstand high mechanical loads. Breaking load – 300% of the highest measurement limit.
Sold at a price of 5,000 rubles.
Strain gauge SUL
Advantages:
- Minimum error;
- High-quality case;
- Protection class IP66.
Flaws:
- Platforms only.
Types
The scope of application of strain gauges covers a number of devices for various purposes. Therefore, strain gauges of various types are used to measure the magnitude of physical impact. Sensors are divided into types based on several factors.
Rice. 4. Types of sensors according to the shape of the load-receiving base
So, depending on the shape of the load-receiving base, the following are distinguished:
- Cantilever (beam) – installed in some types of scales, when weighing containers, etc.;
- S-shaped - used to measure lifted loads;
- Membrane – used in control systems, high-precision meters, etc.;
- Column – mounted in equipment with a large mass;
Depending on the type of measurement method, all strain gauges are divided into:
- Resistive - the work is based on a strain gauge or a bridge made of them, located on a flexible base. Such a strain gauge is attached to the surface of the meter and responds to mechanical deformations. In accordance with clause 1.1 of GOST 21616-91, they are divided into wire and foil. According to quantity and shape, they are divided into single, sockets, chains, and membrane sockets.
- Tactile - consist of two conductors, between which there is a perforated dielectric film. When pressed, the conductors push through the soft dielectric and provide some conductivity, which changes the resistance value. By type of measurement there are touch, slip, and force sensors.
- Piezoresonant - based on semiconductor elements, in such strain gauges the real signal is compared with the reference one.
- Piezoelectric - based on the intrinsic voltage of the electron output of some semiconductor crystals. When a force is applied to the crystal, the magnitude of the charges also changes, which is transmitted to the measuring element of the strain gauge.
- Magnetic - use the property of magnetic conductors to change the value of magnetic permeability depending on physical parameters. When the core is compressed or stretched, the electromagnetic flux generated by the coil will change. As a result, the inductance of the strain gauge will also deviate from the reference state.
- Capacitive - use the effect of a variable capacitor, in which the capacitance will increase as the distance between the plates decreases. And as the distance increases or the area of the plates decreases, the capacity will decrease.
Rice. 5. Operating principle of capacitive strain gauge
In accordance with clause 1.2 of GOST 28836-90, according to the nature of the applied force, strain gauges can be divided into those that respond to compression, tension and universal ones.
Scheme of home electronic scales
The more pressure is applied to it, the greater the change in conductivity, and the processor uses it to determine the weight.
They consume a lot of electricity. Their main advantage is their compact size and autonomous power supply. Modern models are equipped with the ability to store various indicators in memory for later comparison.
The more pressure is applied to it, the greater the change in conductivity, and the processor uses it to determine the weight. This change is processed by an electronic device and converted into a weight reading.
The simplest design of a strain gauge for scales is made in the form of a conductive fine-mesh mesh mounted on a conductive base. But the greatest demand is for a small range of models from different manufacturers. Strain gauges The next repair item for electronic floor scales will be strain gauges. The main conclusion is how the scale works in determining the force that occurs when a load is placed on the bowl of the mass device.
It is this that forms the basis of the sensor’s operation. Electronic steelyards are light in weight and compact in size. In this regard, household appliances are no exception; their manufacturers also strive for the mass introduction of new technologies.
There is metrological control for commercial weighing equipment, so they are subject to periodic verification to confirm compliance with established standards. The AT89C51 processor is programmed with firmware version 8. If the result is negative, it can be eliminated by replacing it with a working sensor.
The converter here is a spiral made of a special alloy, glued to a tight element. It is not recommended to level the frame without removing it from the scale.
It often happens that the rubber band does not adhere well to the board or display glass, in such cases the image on the display is distorted or incomplete. Another type of household weighing device is a pocket scale, also called a mini-scale. In this regard, household appliances are no exception; their manufacturers also strive for the mass introduction of new technologies. In this case, several weight measurements are taken over a certain time, then the weight is added up and its average value is calculated. How to fix Tefal electronic scales
How to use
The strain gauge device is inserted with stops between the tooth to be removed and a pre-fixed notch in the base. The rotating wheel pushes the legs of the device apart, exerting some pressure on the tooth being moved. The indicator value in kilograms is displayed on the indicator. After this, the element(s) are brought into the active state.
The gnathodynamometer measures the pressure it produces. The physician records the scale and vernier data in the disease card for further monitoring.
Indicators on strain gauge equipment vary on average from 15-35 for front teeth and 45-75 kg for molars.
Strain measuring makes it possible to reduce the number of visits to the dentist and reduce treatment time.
How to connect
Connecting the strain gauge is easy to do with your own hands if you have a diagram at hand. First, you will need to buy a device, and take into account how long the cable for the strain gauges is needed. It can be extended if there is an urgent need, but then the accuracy of the indicator will significantly decrease. The se 01 load cell controller, which works as an amplifier module, will help to normalize this parameter by integrating it.
If the scales use several indicators, they must be connected in parallel using junction boxes. Regardless of the type of power supply, the sensor wires must also be grounded. Grounding must be installed at one common point; a junction box, for example CAS, can also be used for this.
It will be interesting➡ How to take measurements using a multimeter
Afterwards, the sensors are examined for correct connection. Before leaving, it is recommended to check all contacts and ground loops. The devices are installed using a shielded cable that suppresses interference, so additional modules are not needed. The converter is connected to the dispenser in a similar way.
Excessive force may cause the converter to break; in this case, do not attempt to repair it manually.
Very popular models of strain gauges produced by Utilcell, Zemic, ADC, KELY (Keli), HBM (NVM), NSK K-B-12A and DST. The models have different technical characteristics and applications, so carefully study the parameters before purchasing.
Connection diagrams
In practice, various methods are used to connect a strain gauge to a common circuit. The simplest option is a four-wire connection diagram, which is shown in Figure 6 below:
In this case, the connection diagram implies strict adherence to the color marking of the wires: red and white for supplying voltage, and black and green for picking up the received signal. The fifth wire is used to ground the equipment frame; some models use a shield to eliminate interference. This option is used for power sensors and low-current equipment installed directly at the place of measurement and recording of the result. In practice it can be implemented as follows:
When the weighing unit is removed from the control unit, a six-wire circuit is used to eliminate the influence of the ohmic resistance of the power wires on the measurement result.
The + E and – E pins are used to supply voltage to the load cell. The voltage drop across the wires is taken from the + Sen and – Sen terminals, which is then subtracted from the resulting signal. Contacts + S and – S are used to take readings, the subtraction function is implemented as follows:
Rating of the best single-point sensors
Sierra SL6D-C3-10kg-1.5B
High quality sensor made of durable aluminum. The maximum weighing limit is 10 kg. The internal components are reliably protected from dust and moisture. Accuracy class – C3. Creep – 0.0167. The maximum operating temperature is 65 degrees, the minimum value is 35o. Manufacturer's warranty – 1 year.
Sold at a price of 1,450 rubles.
Sierra SL6D-C3-10kg-1.5B
Advantages:
- Efficiency;
- Good accuracy;
- Ease of use;
- Durable housing.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
Keli AMI
A good model with a balance of zero 3%. The accuracy class is the same as the previous material. The body is made of durable aluminum. The maximum supply voltage is 15 V, the recommended value is 10-12 V. Operates at temperatures of -20...+50 degrees. Cable length 50 cm, diameter – 5 mm. The maximum permissible load is 150% of the maximum value. Withstands weight up to 100 kg, there are also models that can only work with objects up to 5 kg.
The average price is 1,480 rubles.
Keli AMI
Advantages:
- Efficiency;
- Durability;
- Strength characteristics;
- Price.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
SWJ SUP1
Platform single-point sensor, which is sold in various modifications of the largest measurement limit (MLL). Recommended voltage – 10 V. Accuracy class – C3. The output impedance is 350 Ohms. The device is operated in an operating temperature range of -20…+60 degrees. Permissible load – 150% of the NPI value.
Sold at a price of 1,330 rubles.
SWJ SUP1
Advantages:
- Accuracy;
- Price;
- Maximum load 250 kg;
- Good protection against penetration of dust and moisture.
Flaws:
- Not found.
Determining strain gauge wire markings without documentation
If you do not have a description of the strain gauge, you can use an ordinary multimeter to determine the markings of the wires, provided that the sensor is analog and not digital.
Connecting multiple load cells using a connection (balancing) box
How to connect several load cells using a balancing box can be seen in the video
Grounding and shielding when connecting a strain gauge.
If the sensors are connected in parallel, then you must remember to connect the screen braids of the cables to each other through the corresponding terminal contact in the junction box, and immediately ground them together with the box body. The common cable coming from the junction box to the device must be connected to ground also on ONE side, as described above, without allowing the formation of an “earth” loop, preferably near the entrance to the measuring device, that is, grounded from the receiver side.
READ Wwe 2k17 how to connect a joystick
It is advisable to snap a ferrite filter onto the sensor cable, directly on top of the insulation, at a distance of 4-5 cm from the terminal of the measuring device, to block various ground noises that occur in the workshop. Such filters are produced for cables of different diameters. It is advisable to snap filters on other long lines, for example RS-485, on the receiving and transmitting devices. If the inductance of one filter is not enough to reliably reduce the noise level, such filters can be snapped in series at a short distance from each other, thereby increasing the inductance to the required level.
How to connect a load cell to a weighing terminal
Most strain gauges come with documentation that indicates the color coding of the wires coming from it and their purpose. 4-wire strain gauges, judging by the name, have 4 connecting lines:
Those. two lines are power circuits and two are the sensor output signal. For correct operation, it is necessary to apply supply voltage to the +EXC and –EXC lines, in accordance with the technical characteristics of the sensor, usually it ranges from 5 to 12 volts. After power is applied, the voltage on the SIG signal lines changes, and this change must be recorded with a weighing instrument.
The figure shows a connection diagram for a four-wire type strain gauge, using the example of a Zemic sensor and a KV-001 weighing device.
Some load cells may have six connecting wires rather than four. Two additional lines are called feedback lines and are labeled SENSE. These two additional lines allow compensation of losses on long wires. As can be seen from the figure above, when connecting a four-wire strain gauge, the loss compensation function is not used, and jumpers must be used to connect the strain gauge to the device.
Four-wire strain gauge sensors are best used for short signal transmission distances. Six-wire sensors, thanks to feedback lines, have greater accuracy and can be used over long distances, because these two additional lines allow compensation of losses on long wires.
The figure shows a connection diagram for a six-wire type strain gauge, using the example of a Zemic sensor and a KV-001 weighing device.
Checking the load cell
Checking the load cells is a mandatory step in preparing the measuring device for operation and is carried out immediately after connecting all contacts of the device. The serviceability of the product is checked in three ways:
- Diagnostics of a Wheatstone strain gauge bridge is carried out by measurements using a resistance ohmmeter at its input and output.
- The load test is carried out with a millivoltmeter when the sensor is connected to a stable power source with a voltage of 5 to 12 V.
- The zero load test is carried out using a voltmeter when there is no load. If you don't have one at hand, a good multimeter will do. In the process, you will need to connect a measuring device and send a signal to check its output value. It must correspond to the values in the sensor data sheet.
It will be interesting➡ How to make thermostats with your own hands: step-by-step instructions, tips
Strain gauge setup
The strain gauge measurements are adjusted using the Tensometer computer program. The operating system allows for measurements using strain gauge force and torque sensors based on bridge and half-bridge circuits in the ZET 017-T strain gauge station. With its settings, you can measure force, torque, weight and displacement.
The program recorder displays fixed results in hourly mode. The reading statistics are displayed graphically and in tabular form.
Options
A set of measurements is formed by selecting the desired characteristics in the “Parameters” field on the program interface. These include:
- supply current;
- indications;
- units of measurement;
- smoothing;
- correction;
- data inversion.
Strain gauge
To configure it, use the program window – “Strain Gauge”. To select the measurement process, use the “Calibration File” section. The “Readings” field is highlighted. It indicates the sensor data.
Load cell
Use the program field – “Load cell”. Two parameters are used for setting: sensitivity and measurement limit.
Multichannel
The program supports multi-channel measurement modes. They are used when installing a group of sensors on an object.
Advantages and disadvantages of strain gauges
Strain gauges are widely used due to their properties:
- the possibility of a monolithic connection of the strain sensor with the test part;
- small thickness of the measuring element, which ensures high measurement accuracy with an error of 1-3%;
- ease of fastening, both on flat and curved surfaces;
- the ability to measure dynamic deformations changing with a frequency of up to 50,000 Hz;
- the ability to carry out measurements in difficult environmental conditions in the temperature range from -240 to +1100˚С;
- the ability to measure parameters simultaneously at many points on parts;
- the ability to measure the deformation of objects located at large distances from strain gauge systems;
- the ability to measure deformations in moving (rotating) parts.
Among the disadvantages it should be noted:
- the influence of weather conditions (temperature and humidity) on the sensitivity of sensors;
- minor changes in the resistance of the measuring elements (about 1%) require the use of signal amplifiers.
- When strain gauges operate in high-temperature or aggressive environments, special measures to protect them are required.
Areas of application
In addition to determining elongations that are caused by the action of external loads on structural parts of equipment, strain gauges can be used to measure their own (residual) stresses at the moment of their relaxation; this phenomenon occurs when drilling or cutting some structural parts and assemblies.
Thin film pressure sensors, which are fabricated by vapor deposition or sputtering, are used to detect forces, stresses, torques and strains in insulating elements that are placed directly on polished membranes. Laser adjustment is used to calibrate resistive elements, increasing the accuracy of measurements. Diffusion semiconductor pressure sensors can penetrate the silicon pressure-sensing diaphragm and are not coupled to surface properties. This allows them to be used in miniature strain gauge technologies.
The main advantage of thin film transducers is the elimination of instability caused by adhesive.
Thin film technology is considered more advanced and provides excellent zero temperature stability and full sensitivity, as well as high durability.
Common conditions for using strain gauges are listed below.
Weight measurement
Necessary in floor-type systems, with the help of which the mass of the load is determined. They are characterized by minimal requirements for installation and adjustment accuracy.
Pressure measurement
Used in technological lines for metal forming. At the same time, the working forces and elastic deformations are also measured. The sensors are equipped with a force measuring device with a digital display.
Torque measurement
Used for testing equipment at vehicle service stations.
Definition of acceleration
Sometimes used in experimental laboratories where they design and test high-speed rail and trackless vehicles.
Motion control
The most common areas of application are seismological stations and foundations of high-precision massive equipment, mainly energy.
Which strain gauge to buy: classification of devices
To buy a strain gauge that will cope with the tasks assigned to it in full, you need to choose the right model. These devices can be of different types, intended for use in specific industries (pharmaceuticals, work with atoms, metallurgy, etc.).
Load cells are produced in the following modifications:
- pressure meters;
- motion controllers;
- for engines (in cars and machine tools);
- load and force meters;
- acceleration clamps.
In everyday life, only those types of strain gauges that are necessary for weighing are used. They can be S-shaped, cantilever, barrel and washer. The appropriate option is selected taking into account the upcoming area of use.