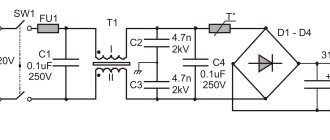
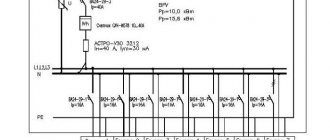
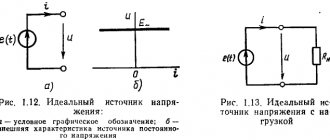
In accordance with the PUE (clause 1.2.18-20), with regard to ensuring the reliability of power supply, power receivers are divided into three categories.
Category 1 power receivers are those devices, the interruption of power supply to which can entail danger to human life, significant damage to the national economy, damage to expensive capital equipment, mass defects of products, disruption of a complex technological process, disruption of the functioning of particularly important elements of public utilities. The power supply for such electrical receivers must be provided from two independent sources; a break is allowed only for the period of automatic power restoration.
Third category of power supply reliability
This group included all other electrical receivers that did not fall into either the first or second categories. For household consumers, these are residential areas and houses. For industry - workshops where there is no serial production of products or auxiliary workshops. This group allows an interruption in power supply for the time necessary to repair (replace) electrical equipment, but should not exceed more than 1 day. When designing the power supply for these devices, it is necessary to take into account the methods of laying cables, redundancy of the transformer (when replacing the transformer), so that the repairs are completed within the time limits specified in the PUE.
It can be concluded that when designing a power supply system for both an industrial enterprise and household consumers, it is necessary to take into account the influence of various factors that will influence the reliability category. Also, analyze the responsibility and purpose of electrical receivers, their role in the technological (household) process, and the permissible power interruption time.
Electricity consumer groups by electricity consumption
The first and main group of electric motors are electric motors (electric machines).
Vasiliev Dmitry Petrovich
Professor of Electrical Engineering, St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University
Ask a Question
In installations that do not require speed control during operation, only AC electric drives are used (asynchronous motors with a power of up to 630 kW and synchronous motors with a power of up to 30 MW).
Unregulated AC electric motors are the main type of electrical receivers in industry, accounting for about 70% of the total power. In electrics, an electric motor is considered to be an electric motor with a power of 0.25 kW or higher. Lower power motors are considered as automation tools.
Various electrotechnological and electrothermal installations make up the second group of electric power plants, which accounts for about 20% of electricity consumption. These are indirect and direct resistance furnaces, arc and induction furnaces, dielectric heating installations, welding, electrolysis and galvanic (metal coating) and high-voltage electrostatic installations. The first and second groups of EP are combined under the general name “power load”.
The third mandatory group of electronic lighting is electric lighting, which can amount to tens of percent in terms of load. Electric lighting installations with incandescent, fluorescent, arc, mercury, sodium and xenon lamps are used in all enterprises for indoor and outdoor lighting.
The fourth group of electronic devices are information processing and control devices. The power consumption of this group is insignificant, but these devices have special requirements for the reliability of power supply and voltage quality.
Abrahamyan Evgeniy Pavlovich
Associate Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University
Ask a Question
It is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of “power receiver” and “consumer” (see Chapter 1). The consumer is always physically identified as an object (building, structure, territory) that has a specific production and economic name or territorial-administrative name (single - school, office, boarding house; series: house, block (village), microdistrict, city, district, region, country) .
The consumer can be one lamp at a checkpoint, a light bulb in a trade tent or on six hundred square meters, or an industrial giant - 100 thousand engines with a total installed capacity of 5 million kW. It should be borne in mind that the concept of “consumer” is used when planning, designing, and managing when considering the power supply of an object as a whole, and “power receiver” is used when solving narrow electrical problems.
The classification of power receivers by categories of power supply reliability is given in another article on our website.
Responsibility for energy quality
All obligations are assigned to the energy transmission organization. All interruptions in power supply, line repairs, shutdowns of main power lines.
Safety rules for operating electrical installations
The contract for the supply of electricity specifies all the details: category of power supply, quality, level of permissible losses, maximum line disconnection time, etc. If at least one of the points is not observed, the consumer has the right to demand compensation from the local energy transmission company for the inconvenience caused to him through the fault of the service provider. The amount of liability for inconvenience caused is determined by the scale of the consequences.
Only if there is information about the degree of liability in the contract, consumers have the right to demand compensation. Otherwise, achieving a positive result in court is extremely difficult.
Industrial electric generator ensures stable operation of production during power outages
It is customary to classify EP according to a number of indicators
- According to the type of current, all power receivers operating from the network are divided into three groups: alternating current of normal industrial frequency of 50 Hz (in some countries they use a frequency of 60 Hz), alternating current of high or low frequency, and direct current. Most electric power plants of industrial enterprises operate on three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
Vasiliev Dmitry Petrovich
Professor of Electrical Engineering, St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University
Ask a Question
High-frequency installations are used: for high-frequency power tools in assembly shops of the automotive industry and other continuous production processes, where the increased frequency (usually 175...200 Hz) allows making power tools lighter due to the use of high-speed motors; for electric drive of centrifuges in the artificial fiber industry - 100...200 Hz; for electric drives of woodworking machines, in which frequencies up to 400 Hz are used to obtain high wood cutting speeds (up to 20,000 rpm); in installations for induction through heating of metals for hot stamping and forging - from 500 to 10,000 Hz.
To obtain frequencies up to 10 kHz, predominantly thyristor converters are used; above 10 kHz, electronic generators are used.
Low frequency settings are used: 0.5... 1.5 Hz - for electromagnetic stirring of steel in electric furnaces; 2...5 Hz - for resistance electric welding by converting the frequency and number of phases in special welding machines, where the energy of a three-phase current with a frequency of 50 Hz is converted into the energy of a single-phase current with a frequency of 2...5 Hz; 10…40 Hz - for regulating the speed of electric drives of asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor, for example, to drive rollers of roller tables in rolling mills. Electrolysis shops, installations for the electrolytic production of metals, electroplating shops, some types of electric welding and electric motors are powered from a DC network.
- Based on the number of phases, one, two and three-phase electric generators are distinguished. All of them are connected to a three-phase network, taking into account the correspondence of the rated voltage to the phase and line voltage of the network. To turn on single-phase electric motors, a neutral (zero) wire is required.
- EDs are classified according to their rated voltage. General industrial EDs are manufactured for the following rated (linear) voltages: up to 1 kV - 36, 42, PO, 220, 380, 500, 660 V; over 1 kV - 3, 6, 10, 20 kV. According to the PUE, electrical installations that produce, convert, distribute and consume electricity are divided into electrical installations with voltages above 1 kV and electrical installations with voltages up to 1 kV (DC electrical installations - up to 1.5 kV). This allocation corresponds to significantly different design, operational and safety conditions.
For example, the most common solution up to 1 kV is to use a 380 V network voltage with a solidly grounded neutral. In this case, power EPs are connected to three phases, and lighting EPs are connected to a phase and a neutral wire for a phase voltage of 220 V without additional transformation.
- EDs are classified according to the method of specifying the rated power: for electric motors, the rated (active) powers are expressed in kilowatts (kW), and the mechanical power on the electric motor shaft (EM) is indicated in the passport data. In the electrical network, the ED consumes power.
Vasiliev Dmitry PetrovichProfessor of Electrical Engineering, St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University
Ask a Question
The concept of “connected power” is used only when considering a separate electric power supply; when we are talking about a group of electric power plants, the term “total rated power” or “installed power of the electric power group” is used. The nominal (installed) power of electric melting furnaces and welding installations is the (total) power of the transformers feeding them, expressed in kilovolt amperes (kVA).
The same applies to transformers, including transformers of converter and rectifier units. If these electric devices have low power and are connected to a network of up to 1 kV, then the power consumed from the network is also indicated; thus, for them the connected power coincides with the rated power.
- According to the operating mode, electric drives are manufactured for long-term, short-term and repeated short-term operation.
The term “sharply variable operating mode” of electric power supply is also known, which means the operating mode of powerful electrical receivers, accompanied by significant increases in load power, commensurate with the power of a short circuit and causing voltage fluctuations. Electrical receivers with sharply variable operating modes are motors of rolling mills, arc steel furnaces (AFFs), welding, etc. For unregulated drives, the most economical area of application of asynchronous and synchronous electric motors is determined by voltage. At voltages up to 1 kV and power up to 100 kW, it is more economical to use asynchronous motors; over 100 kW - synchronous motors (which is not always possible due to operating and starting conditions). Power up to 1,000 kW is the voltage range of 6 and 10 kV, determined by the possibility of manufacturing high-voltage asynchronous electric motors. Asynchronous motors with a wound rotor are used in powerful electric drives with a flywheel and with difficult starting conditions: in converter units, mine hoists.