Did you know that the first cars were electric and used lead-acid batteries? What we are accustomed to consider as the cars of the future - electric cars - appeared before the invention of the internal combustion engine (ICE). More than 100 years have passed since then, but the modern car battery has changed only qualitatively, remaining fundamentally the same as a century ago.
Today, a car battery is considered a consumable item that requires periodic replacement. Exactly how long the battery will last is a question of the quality of manufacture, operating mode, even the condition of the roads, but sooner or later it is replaced with a “fresh” one. What functions does it perform, what characteristics can it have, how to choose and how to extend the life of the battery - read in this article.
What is a battery (battery) and what is it for?
Modern cars are becoming more and more like complex electronic gadgets: smart controls, all kinds of “assistants”, automatic parking and even autopilot are only a small part of the digital “stuffing” that a car is rich in. And all this happiness constantly needs electricity, which must be constantly obtained from somewhere. It is the battery that acts as a storehouse of energy, from where it can be taken at any time. Yes, it performs its clear function: it accumulates a charge, then releases it and then accumulates it again. Great option!
The very concept of a battery is already so familiar to us that it is stupid to ask why it is needed. However, surprisingly few people can say exactly what a car battery does.
Its purpose can be described in three points.
- The battery provides the energy to start the engine at the start.
- The battery serves as a backup source of energy when it is needed beyond what the generator can provide (for example, when turning on the car's air conditioning).
- The battery powers electrical appliances when the engine is off and the generator is not running. For example, DVR, alarm, light, etc.
Purpose of the battery in a car
The battery is one of the key elements of a car. Working in conjunction with a generator in the vehicle's on-board network, it is a source of electric current. The main functions of the battery are as follows:
- Ensuring engine starting. The battery supplies power to the starter when starting;
- Providing power to consumers in the vehicle network when the engine is turned off;
- Provides power during travel if the generator is overloaded.
In addition, when working together with a generator, the battery smoothes out electrical current ripples in the on-board network.
The battery voltage for passenger cars is 12 volts. The capacity can range from 40 to 130 Ah. Starting current 300─1300 amperes. The values are valid for batteries in passenger cars and light commercial vehicles.
Batteries with a voltage of 24 volts can be installed on trucks and special equipment. Motorcycle vehicles use 6-volt models.
The following requirements are usually imposed on a car battery:
- small self-discharge;
- high starting current;
- compact dimensions;
- no or minimal maintenance.
Additionally, you can read the material about the types of batteries for cars.
Design and principle of operation of the battery
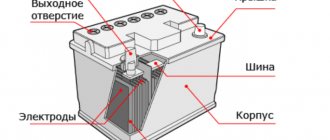
Anyone who has ever held a car battery in their hands knows how much this device weighs. The reason is that its body is densely filled with elements containing lead.
Battery device.
For passenger cars requiring 12-volt batteries, a standard layout is used.
- Six 2-volt elements (usually called banks) are combined into a common housing.
- Each of the elements consists of positive and negative electrodes: lead grids into which the active substance is “imprinted”. The electrodes are separated from each other by separators, so that they do not come into contact with each other.
- And all this is filled with electrolyte - a mixture of water and sulfuric acid.
The active substance on the grids differs in composition: lead dioxide is used for the anode (positive electrode), lead sponge is used for the cathode (negative electrode). In both cases, auxiliary substances (ligatures) are added to the lead components to improve battery performance.
Principle of operation.
The principle of operation of the battery
In the form described above, the battery is considered “charged”. When any device that requires energy is connected to the battery terminals, the lead components react with sulfur oxide and water. Sulfur and lead react and transform into lead sulfate and water. There is less acid in the electrolyte, more water, the density of the electrolyte decreases and after some time the sulfur concentration is not enough to react with the lead components. The battery is running low.
Main characteristics of the battery
Energy Conversion Ratio
The energy supplied to the battery when the battery is charging is greater than the energy it gives out during discharge. The excess of the “charge” energy to the “discharge” energy is based on the need to cover the costs of electrical and chemical processes.
To fully charge, you need 105–110% of the energy previously consumed. Thus, the conversion factor will be between 1.05 and 1.10.
Capacity
The capacity of the battery is proportional to the amount of electric current supplied to it. The unit of capacity is ampere hours (Ah).
Capacity indicators are affected by discharge current and temperature. It tends to decrease with increasing discharge current and decreasing temperature, in particular at values less than 0 degrees.
Rated voltage
The standard voltage of each battery element corresponds to 2 V, and the voltage of the entire battery chain is equal to the number of galvanic cells. The machine's battery consists of 6 batteries, which corresponds to a nominal capacity of 12 V.
Cold crank current
This indicator characterizes the starting capabilities of the battery when operating in low temperature conditions. This parameter is measured at –18 °C. The voltage of a fully charged battery does not drop below the specified value for a certain amount of time. The current level affects the starting of the car engine, since the higher the current value in cold cranking, the easier the engine will be to start in the winter season.
Voltage
The voltage, the value of which is measured between the two pole terminals of the battery - the voltage at the terminals.
Gas release voltage is a parameter above which water is formed in the battery housing. This occurs when the voltage of the entire battery is exceeded, the maximum permissible value being 14.4 V.
The decomposition of water produces hydrogen and oxygen, which combine to form a gas. Warning - this is explosive!
Idle voltage or open circuit voltage is a state when there is no load at the battery outputs. Charge and discharge cycles change the open circuit voltage. When the amount of sulfuric acid between the galvanic cells is restored, the open circuit voltage comes to its final value - the resting voltage.
Types of batteries
In an attempt to improve the performance of car batteries, engineers have tried many methods. As a result, today we have different types of batteries, which differ in the chemical composition of the active components and design.
Classification according to the composition of the active substance
The first batteries used lead plates, but this design quickly ceased to suit engineers and consumers: it was heavy, ineffective, and short-lived.
- The first improvement was the addition of antimony to lead, which greatly extended the life of the battery.
- The next stage is to reduce the percentage of antimony to the optimal concentration. This approach made it possible to create low-maintenance batteries: they required topping up water much less often.
- Then metallic calcium began to be used to coat the plates - this is how calcium batteries (aka Ca-Ca) appeared. Calcium has seriously changed the operating parameters of batteries: in previous models, water loss due to electrolysis at 12 V required constant topping up, and calcium alloys made it possible to increase this threshold to 16 V. Thanks to this, it became possible to make maintenance-free batteries in a completely sealed, non-separable case.
But calcium batteries also have a huge disadvantage: sensitivity to full discharge. Calcium sulfate, which settles on the electrodes, does not completely decompose during charging, which means that one deep discharge of the battery can “kill” it.
The most modern solution is hybrid batteries (aka Ca+): calcium additives are only on the positive electrode (since this is where water decomposes during electrolysis), and the negative one is coated with low-antimony lead.
Classification by electrolyte type
Conventional liquid technology, in which a solution of acid and water was poured into the battery, caused many complaints. For example, sensitivity to tilt and vibration. The need to maintain the battery also did not add to the pleasure of using it. In general, this technology had room to grow.
AGM technology has replaced it. In an AGM battery, the electrolyte is “bound” by fibrous separator layers. Thus, the battery receives additional advantages: the separators compress the active layer and do not allow it to lag behind the plates, have greater conductivity than the liquid and contribute to the delivery of a more powerful current.
Battery types
All car batteries, as mentioned earlier, are identical in design and filled with electrolyte, only slightly differing from each other. Each modification is designed to achieve a specific goal to the detriment of other characteristics.
Battery with liquid electrolyte
They are open systems, i.e. gas released during charging may be released into the atmosphere. It has excellent performance characteristics, a long shelf life of up to 15 months, but there is no protection against electrolyte leakage.
Battery Economy
This type of battery is optimal in terms of cost and service life; it uses less lead. It has a reduced engine cold start power and a slightly reduced service life (4 years or 80,000 km). At the same time, a more favorable price, less weight and a low self-discharge current, which does not increase as the battery ages. Can be used in cars with a start-stop system.
Improved battery
They have the abbreviation EFB (Enhanced Flooded Battery) - an enhanced battery with liquid electrolyte. Structurally, they are distinguished by a thicker negative electrode grid, which provides high resistance to corrosion when loaded with high current, as well as the addition of carbon to the active mass of the negative electrode, which leads to improved charging ability.
It has protection against deep discharge and excellent performance characteristics, but there is no protection against electrolyte leakage.
Its design uses a passive mixing element; it reduces electrolyte stratification, i.e. the formation of layers with different concentrations of sulfuric acid, which is concentrated in the lower part of the galvanic cells, which leads to insufficient electrolyte density in the upper part. This occurs when charging and discharging processes are repeated frequently.
Battery AGM
Absorbent Glass Mat is fiberglass with very high absorbency. They are also called recombination and are used on cars with a start-stop system and energy recovery function. In such batteries, the electrolyte is adsorbed by a fiberglass mat. They are a closed system, i.e. all galvanic elements are isolated from the atmosphere by valves.
It is protected against leakage, even if the battery case is damaged, the probability is insignificant and amounts to no more than a few milliliters. They have a long service life, excellent performance and high reliability. But, on the other hand, it has a high cost and higher sensitivity to elevated temperatures.
Gel batteries
There are also batteries with a gel-like electrolyte; it is formed by adding silicic acid to it. They are ordinary lead batteries. They have a very low probability of electrolyte loss, high cyclic resistance and reduced gas formation. Their mass distribution is limited by a number of serious disadvantages, such as: deteriorated starting properties at low temperatures, high cost, intolerance to elevated temperatures and the associated unsuitability for installation in the engine compartment.
Technical (operating) characteristics of car batteries
A car battery has quite a few operating parameters that are important when choosing a battery. If you make a mistake in even one of them, the battery will not be usable. Main characteristics.
- Capacity, Ah (ampere*hour).
- Starting current, A (ampere).
- Polarity.
- Execution of the case.
- Terminal type
- Mounting type.
Nominal battery capacity
Battery capacity is the amount of electricity that a battery can supply over a certain period of time. Measured in Ah (amps per hour). This is one of the main parameters not only of a car battery, but of any battery in general. The higher this indicator, the longer the battery can support the operation of the car’s electrical appliances while parked.
Battery parameters and characteristics
The parameters and characteristics of batteries are encrypted in their markings and now we will figure out what it means.
We will consider this issue using the example of the most common battery 6ST-55.
So, in the name of the battery, the number 6 means that the battery consists of 6 cans.
- ST – means that the battery is a starter one.
- 55 – indicates the battery capacity, which is 55 Amp*hour.
In order to understand what kind of battery you need, you need to know two parameters:
- Engine type;
- Engine size of your car;
Next, we will consider which engines and which batteries are suitable. This is the table for gasoline engines:
- Engines up to 1.6 liters. Batteries 6ST-45 are suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of 1.6 to 2.5 liters. 6ST-55 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of 2.5 to 3 liters. 6ST-60 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of 3 to 3.5 liters. 6ST-75 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of more than 3.5 liters. 6ST-90 is suitable for them.
For diesel power units, these parameters are slightly different:
- Engines up to 1.5 liters. 6ST-55 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of 1.5 to 2.0 liters. 6ST-60 is suitable for them;
- Engines with volume from 2 to 2.7 liters. 6ST-75 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of 2.7 to 3.5 liters. 6ST-90 is suitable for them;
- Engines with volume from 3.5 to 6.5 liters. 6ST-132 is suitable for them;
- Engines with a volume of more than 6.5 liters. 6ST-192 and more are suitable for them.
As you can see, due to the different operating principles of diesel and gasoline engines, batteries of different capacities are used for them.
For diesel powertrains, you will need larger batteries.
TOP battery rating
Many brands, many advice, difficult choices - these are the problems buyers face. We offer a small, our, subjective rating of battery brands.
- The first place in terms of quality and durability is rightfully occupied by OEM batteries. OEM is an analogue of a part that was installed from the factory. Of course, you will have to pay a lot more for a battery that proudly displays the Mercedes or Honda logo than for any other brand, but the result is worth it. The most popular battery brands on the market are Varta and Bosch. They have earned a reputation as reliable, trouble-free batteries that faithfully work out every penny invested.
- Among those who like to pay less and get more, the Topla brand is especially valued. This is, of course, not Bosch, but it may well please you with its long service life.
- And our hit parade is completed by budget brands Sada, Styer, Bi-Power and Ista. Although they are not expensive, they are quite capable of providing stable performance. You can remember them when you need a battery urgently, but you don’t have enough money.
Careful handling of batteries
If you remember that there is a battery under the hood and give it at least a minimum of attention, then it will last much longer than a battery that has been neglected. Ideally, you should read the battery operating rules, but these documents are very lengthy and few people are capable of this. You can mention the most important things to remember.
- Batteries do not like deep discharge, especially in the cold season. Charging conditions during short winter trips with a cold engine are critical, and a lot of energy is taken during starts. You need to monitor this and recharge the battery from an external source. Just keeping the engine idling won't do anything.
- During long breaks in driving, it is better to recharge the battery, and store the car with the terminal removed. There are a lot of consumers in the electrical circuit of the car that do not turn off after removing the key.
- It is necessary to regularly monitor the voltage in the car network. With a partially faulty generator, it may be low or unstable, which will gradually drain the battery. And with low electrolyte density and severe frost, ice forms in the battery and it will no longer be possible to restore it.
- Overcharging is also harmful, although in a modern car this can only be done deliberately. Do not use chargers with an unknown operating principle. At a minimum, you should consult an auto electrician.
Video: Current sources. Battery
Tips for battery operation and maintenance
In order for the battery to last as long as possible, you need to pay very little attention to it. Here are some tips for operating a car battery.
- Deep discharge is the enemy of the battery. Every time the battery is discharged to zero, irreversible sulfation of the electrodes occurs, calcium batteries especially suffer from this. From time to time, it is advisable to fully charge the battery with a special charger and under no circumstances allow it to completely discharge.
- The second enemy is vibration. Due to strong shaking and regular impacts, the active layer falls off the plates. AGM batteries suffer less from this, liquid batteries suffer more.
- Battery terminals are prone to oxidation, which impairs contact. Periodically you need to pay attention to the condition of the terminals and, if necessary, clean them of oxides.
- Pay attention to the battery case. Dirt, oil, and moisture contribute to current leakage and self-discharge.
- Electrical problems can also damage the battery. Especially problems with the starter and generator - adjacent elements.
- A swollen case with traces of electrolyte indicates that it is time to buy a new battery. A damaged battery must not be used!
Electrode device
A lead-acid battery can be used as an example. Each cell of such a battery contains a pair of electrodes and separating plates, which are made of porous material that does not react chemically with acid. Such plates are designed to prevent short circuits of electrodes immersed in the electrolyte, and are called separators.
We recommend: Parallel battery connection diagram
The electrodes in such batteries are made in the form of flat lead grids. Powdered lead dioxide (in anode plates) and metal lead in powder form (in cathode plates) are pressed into the cells of such gratings. The use of powders is driven by the desire to increase the interface area at the electrolyte-electrode interface, which significantly increases the capacity of such a current source.
There are experimental samples of batteries in which lead grids are replaced with electrodes consisting of woven carbon fiber threads, which are coated with the finest lead coating. This technology allows you to use significantly less lead due to its distribution over a large area, which makes the battery not only smaller and lighter, but also increases its efficiency. The efficiency is higher than traditional ones, and the charging time is greatly reduced.
Links
- [protect.gost.ru/v.aspx?control=7&id=146532 GOST 15596-82] “Chemical current sources. Terms and definitions" [protect.gost.ru/document.aspx?control=7&id=146532 Chemical current sources. Terms and Definitions]
- GOST R 53165-2008 [protect.gost.ru/document.aspx?control=7&id=174450 Lead-acid starter batteries for automotive vehicles. General technical conditions.] Instead of GOST 959-2002 and GOST 29111-91
- [www.mami.ru/science/autotr2009/scientific/article/s01/s01_24.pdf On the contradictions in the theory of operation of a lead-acid battery Ph.D., prof. Kochurov A. A. Ryazan Military Automotive Institute]
- [youtube.com/watch?v=4IgHj2Uim_0 Video demonstrating how the battery works] on YouTube
- [atlib.ru/wiki/akb-avtomobilnyj-akkumulyator-4 Causes and signs of battery failure]
How to decipher the battery type by markings
The type of battery and its characteristics can be determined by its markings. There is a problem - different countries and regions have adopted different systems for designating battery parameters. Some of the characteristics can be printed in plain text, but in order to fully determine the type, sometimes you need to know the designation system applied to the battery nameplate.
Russia
Batteries from Russian manufacturers have a marking of 4 characters (groups of characters) 1234, where each character means:
- 1 – the number of cans by which the voltage can be determined on the basis that one can produces 2 volts;
- 2 – purpose of the battery (St – starter);
- 3 – capacity (A*h);
- 4 – execution.
Performance can be indicated:
- A – with a common cover;
- Z – maintenance-free;
- N – non-dry charged;
- P – envelope separator (EFB technology)
- another symbol.
For example, the 6St-55AP3 battery means a starter battery of 6 cells (12 volts) with a capacity of 55 Ah, maintenance-free with a common cover, manufactured using EFB technology. Obviously, such markings lack an important parameter - the highest current output. It is usually written in text.
An example of marking according to Russian standards.
Europe
In Europe, two standards are used:
- DIN - 5 digital characters;
- ETN – 9 digits.
The DIN standard indicates the battery capacity with the first three digits - 500 must be subtracted from the indicated digit. The remaining two characters indicate the battery type.
The ETN standard is simpler, more visual, and more informative:
- the first character means the range of battery capacity (for a 12 volt battery, the number 5 means the highest value of 99 A*h, 6 - 100..199 A*h, 7 - up to 299 A*h);
- second and third positions – capacity;
- symbols at positions 4,5,6 – battery version;
- the remaining numbers (7,8,9) are the highest current output.
Thus, the marking 555065042 means a 12-volt battery with a capacity of up to 99 A*h (the following numbers clarify - 55 A*h), with a cranking current of 420 amperes (042).
European marking according to the ETN standard.
Asia
In Asia, the 6-character ABCDEF marking is adopted, where:
- AB – capacity (in unknown units);
- C – battery form factor;
- DE – length or other body size in cm;
- F – R or L – battery polarity.
To determine parameters by marking, you need to have correction tables. Thus, the number 55 in positions AB means a capacity of 44 Ah.
Examples of Asian markings.
North America
There are several marking systems here. The most common is the five-character one:
- the first digit indicates the purpose of the battery (A – car);
- second, third – form factor;
- the remaining positions are current output in amperes.
The remaining parameters are printed on the body in text.
North American designation for battery.
From the video you will learn how to find out the production date of EDCON, VARTA, BOSCH, EXIDE, BAREN, FIAMM batteries.
Battery self-discharge
When the battery is idle, its capacity gradually decreases; this process is called self-discharge. In stores, fully charged batteries are stored for no more than a year. The capacity spontaneously discharges due to electrochemical processes occurring at the electrodes. The main component of the lead alloy from which the negative electrodes are created interacts quite actively with sulfuric acid. Hydrogen is released, and the amount of lead in the alloy gradually decreases.
In a working battery, a conductive film is formed on the surface from a mixture of dust, water and the released electrolyte. This creates the most favorable conditions for self-discharge, so it is recommended to keep the battery clean.
The drop in capacity has a number of features, knowledge of which will allow you to reduce the rate and magnitude of self-discharge:
- the purer the sulfuric acid and distilled water used in preparing the electrolyte, the lower the self-discharge, for this reason it is not recommended to use contaminated sulfuric acid used in industry;
- the rate of self-discharge decreases with decreasing temperature; at subzero temperatures, the capacity practically does not drop, so it is recommended to store the battery in appropriate conditions;
- increases the rate of self-discharge; deep discharge of the battery;
- The longer the battery life, the more intense the self-discharge becomes and attention to battery maintenance is required.
Self-discharge is a natural phenomenon, but its rates vary. The optimal value is a 1% drop in capacity during the day.
What differences might there be in the design?
Before purchasing a battery, you need to clearly understand which battery is needed for a particular car. In addition to production technology and basic electrical parameters, batteries have differences in design. If you make a mistake in this regard, installing the battery under the hood will be problematic, if not impossible. Problems may also arise during operation.
Dimensions
Battery sizes vary even within the same technology. It is difficult to fool physics, and, for example, increasing the battery capacity will always cause an increase in size. You also need to understand that a 24-volt battery will always be larger in size than a 12-volt battery. Each manufacturer has a range of battery sizes. Therefore, before purchasing, it would be right for the car owner to measure the dimensions of the installation space for the battery, as well as determine the maximum possible height. The measured data can be recorded somewhere; it will be useful in the future (although batteries are usually not purchased every year). This will eliminate doubts and requests from the seller to allow you to try on the battery at the installation site - he has the right to refuse.
Literature
- Kashtanov V.P., Titov V.V., Uskov A.F. et al.
Lead-acid starter batteries. Guide.. - M.: Military Publishing House, 1983. - P. 21-23, 176. - 148 p.
| : Incorrect or missing image | To improve this article it is desirable:
|
| Electric batteries | Lead Acid | Silver-zinc | Nickel-cadmium | Nickel-salt | Nickel metal hydride | Nickel-zinc battery | Lithium-ion | Lithium polymer | Lithium Iron Sulfide | Lithium Iron Phosphate | Lithium titanate | Vanadium | Iron-nickel |
| Fuel cells | Direct methanol | Solid oxide | Alkaline |
| Models | Battery | Electric battery | Fuel cell |
| Device | Anode | Cathode | Electrolyte |