A power source is electrical equipment designed to produce, accumulate electrical energy or change its characteristics (defined according to GOST 30331.1-2013).
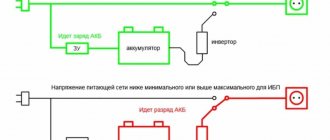
The power source in the electrical distribution network (see Figure 1 below) is a transformer installed at a step-down transformer substation. Power sources can also be: a local power plant, a separate low-power electric generator driven by an internal combustion engine, and even an isolation transformer, on the basis of which the IT system is implemented in the electrical installation part of the building.
Rice. 1. Power distribution system (TN-CS) (the picture shows the power supply)
Characteristics of available power supplies
When designing electrical installations in accordance with the IEC 60364 set of standards, it is necessary to know the characteristics of power supplies. In order to design a safe electrical installation that meets the requirements of the IEC 60364 set of standards, it is necessary to obtain relevant information from the electrical distribution network operator. Characteristics of power supplies must be included in the design and operational documentation of electrical installations. If the electrical network operator changes the characteristics of power supplies, this may affect the safety of the electrical installation.
Here are these characteristics (according to GOST 30331.1-2013):
- Type of electric current: alternating and (or) constant.
- Types of conductors used in electrical circuits of electrical installations:
— alternating current: phase (linear) conductor, neutral conductor, protective conductor;
— direct current: pole (linear) conductor, middle conductor, protective conductor.
Note - In one conductor, for example, in a PEN, PEM or PEL conductor, the functions performed by several conductors can be combined.
- Valid values:
— voltage and permissible voltage deviations;
— voltage losses, voltage fluctuations and voltage drops;
— frequency and permissible frequency deviations;
— maximum permissible current;
— total resistance of the ground fault loop before entry into the electrical installation;
— expected short circuit currents.
Standard values for voltage and frequency are given in IEC 60038.
Protective precautions inherent to the power supply include, for example, grounding the neutral in an AC electrical system or grounding the live mid-section in a DC electrical system.
However, following characteristics of any power source used and the normal range of these characteristics, if necessary, must be determined by calculation, measurement, collection of material or inspection :
- rated voltage(s);
- type of current and its frequency;
- expected short circuit current at the input of the electrical installation;
- the impedance of the ground fault loop of that part of the electrical system that is located outside the electrical installation;
- compliance with the requirements of the electrical installation, including ensuring maximum load;
- type and rated characteristics of the overcurrent protection device installed at the input of the electrical installation.
These characteristics should be evaluated for both external and internal power supplies. The requirements apply to main power supplies, safety system power supplies, and backup power supplies.
CONTENT
- 1 General classification 1.1 Functional
- 1.2 Packaging
- 1.3 Power conversion method
- 2.1 DC power supply 2.1.1 AC to DC power supply
- 2.2.1 AC adapter
- 5.1 Current limitation
- 6.1 Computers
Additional power supply types
In addition to the main power source, there will also be a backup electrical power supply and an electrical power supply for security systems. Let us give their definitions and examples.
A standby electrical power supply is an electrical power supply designed to maintain power to an electrical installation or parts thereof, or a part thereof, in the event of interruption of normal power supply, but for purposes other than safety.
An electrical security power supply is an electrical power source designed for use as part of a security electrical power system.
Where the presence of safety systems relevant to fire protection and other conditions for emergency evacuation of buildings is required, for example, by controls and/or if the provision of backup power is required by the administrative person establishing the technical requirements for the electrical installation, the characteristics of power supplies for safety systems and ( or) backup systems must be determined for each individually. Such power supplies must have adequate power, reliability, ratings, and switching times for the specified type of operation.
Note 1 - The need for installation of safety systems and their characteristics are usually regulated by the competent authorities, the requirements of which must be complied with.
Note 2 - Examples of safety systems are: fire detection, warning and fire evacuation control systems, emergency lighting on evacuation routes, emergency ventilation and smoke protection, internal fire water supply, installations for fire pumps, elevators for fire brigades, drainage equipment smoke and heat, critical medical equipment.
Power sources for security systems can be:
- rechargeable batteries;
- galvanic batteries;
- generator sets independent of the power supply used in normal mode;
- a separate transmission line of the electrical distribution network, virtually independent from the transmission line used in normal operation
The power source for the security system can be:
- non-automatic power source, which is started by the operator;
- automatic power source, which is started independently of the operator.
Depending on the switching time, automatic power supplies are classified as follows:
- No power interruption: The automatic power supply can provide continuous power under specified conditions during the transition period, such as voltage and frequency changes;
- with very short power interruption: automatic power supply can supply power within 0.15s;
- with short power interruption: automatic power supply can supply power within 0.5s;
- with medium power interruption: automatic power supply can supply power for 15s;
- with long power interruption: the automatic power supply can provide power for a period of time exceeding 15 s.
Links[edit]
- Quoted from U.S. Patent No. 4,937,722, High Efficiency Direct Coupled Switching Power Supply
:
The power supply may also include a breaker circuit that protects it from damage by clamping the output to ground if it exceeds a certain voltage.
"Archival copy". Archived from the original on 2013-04-21. Retrieved May 8, 2008.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Quote from US Patent No. 5402059: A problem may occur when the load at the switching power supply output is disconnected from the power supply.
When this happens, the power supply's output current decreases (or disappears if all loads are turned off). If the output current becomes small enough, the power supply output voltage may reach the peak secondary voltage of the power supply transformer. This is because when the output current is very low, there is not much voltage (if any) dropping across the inductor of the LC low pass filter. The capacitor in the LC low pass filter is charged to the peak voltage of the transformer secondary winding. This peak voltage is usually significantly higher than the average secondary voltage of the transformer. The higher the voltage on the capacitor, and therefore also on the output of the power supply, can damage the components in the power supply. Higher voltage may also damage any remaining electrical loads connected to the power supply. "Archival copy". Archived from the original on 2012-09-07. Retrieved May 8, 2008.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - “What is the difference between single-phase and three-phase AC power supplies?” . Aegis Power Systems
. Aegis Power Systems. Retrieved December 28, 2015. - "Bipolar power supplies operate over the entire voltage range". Electronic design
. 2012-10-19. Retrieved July 26, 2022. - "Overview of Cooling Methods for AC and DC Power Supplies". Aegis Power Systems
. Aegis Power Systems. - Malmstadt, Encke and Crouch, Electronics and Instrumentation for Scientists, The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc., 1981, ISBN 0-8053-6917-1, Chapter 3.
- "Power Converters for Electric Vehicles". Aegis Power Systems
. Aegis Power Systems.
Types of sources
There are several types of devices for generating current, each of which has its own main indicators, characteristics and features, listed in the following table:
| Source type | Current source characteristics |
| Mechanical | A special device (generator) ensures the transformation of mechanical energy into electrical energy. Currently, a large amount of current is produced using mechanical sources. |
| Thermal | The operation of the units is based on the principle of converting thermal energy into electrical energy. This transformation occurs due to the temperature difference between the semiconductors in contact with each other. Currently, current sources have been developed in which thermal energy is generated due to the decay of radioactive elements. |
| Chemical | Chemical options can be divided into 3 groups - galvanic, batteries and thermal. · A galvanic cell works through the interaction of 2 different metals placed in an electrolyte. · Batteries are devices that can be charged and discharged several times. There are several types of batteries with different types of cells included in their composition. · Chemical-thermal ones are used only for short-term work. They are mainly used in the field of rocketry. |
| Light | At the end of the 20th century, solar panels became quite popular, which “collect” light particles, which are subsequently converted into electrical energy. This occurs due to the output of voltage and due to the effect on light particles. |
You may be interested in this. Designation of various electrical equipment on diagrams.
Important! Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are determined by the principle of use, as well as the initial indicators of the generated energy.
Mechanical sources
Mechanical units are the simplest in terms of their use and arrangement. The characteristics of such generators are very easy to understand. Special devices generate energy, which is subsequently converted into electricity. Such devices are used in thermal power plants and hydroelectric power plants.
Mechanical
Heat sources
Thermal source options provide a unique operating principle. Energy is generated through the formation of a thermocouple, which... This means that a calculated temperature difference is provided at the ends of the conductors, the elements interact with each other, creating an electric field.
Thermal
Note ! Radioactive thermocouples are used in the space industry. The effectiveness of such use is possible due to the long service life and efficient power output.
As a result of this movement of charged particles from the hot part of the conductor to the cold part, an electric current arises. Moreover, the greater the temperature difference, the higher the effective energy indicator. In practice, thermocouples are often included in measuring instruments.
Light sources
Lighting devices for generating electricity are considered the most environmentally friendly, efficient and relatively cheap. A special panel of semiconductors absorbs light particles, which during such interaction produce a certain voltage.
Light
At the same time, light panels have a low efficiency rate of 15%. Panels of this type have found wide application - from household appliances to innovative developments in the space industry.
Important! Light sources began to be used instead of lithium batteries due to the high cost of the latter. Despite the fact that many industrial facilities require significant re-equipment to switch to light sources, the final savings occur already in the initial stages of operation.
Chemical sources
This group includes 3 main devices that differ in structure and operating principle:
- A voltaic cell is an option for generating electricity that can be used once. That is, after complete discharge, re-accumulation of charge on the internal substance is impossible. Such devices include salt, lithium or alkaline batteries.
- Batteries are divided into several types: lead-acid, lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium.
- Thermal elements - used in the space and innovation industries to produce short-term current with high performance. The practical application of the units is based on the need for backup power sources.
You may be interested in this Features of capacitors
Important! Chemical-thermal devices require initial heating to 500–600 °C to activate the solid electrolyte.
Chemical
Each industry uses its own version with specific parameters. In domestic conditions, batteries are mainly used; in production - batteries.
Operating principle
Each marking of current sources determines the principle of its operation. In a standard situation, energy is generated through the interaction of component parts, namely:
- Mechanical type. As a result of the interaction of mechanism parts, friction occurs. Due to this phenomenon, static electricity arises and is converted into current.
- Mechanical structures work by producing sequentially moving charged particles. The phenomenon occurs due to the interaction of a chemical element with an electrolyte. Charged particles leave the structure of the metal crystal lattice, becoming part of the conducting liquid.
- Solar batteries (light sources) work by knocking out charged particles from a dielectric (silicon) base under the influence of a light flux. This creates constant tension.
- Thermal. As a rule, these are 2 metal bases connected in series. One part heats up, while the other remains cooled. When the temperature regime changes, a temperature difference occurs, resulting in the movement of charged particles.
You might be interested in this: Connecting resistors
Important! Any change in the structure of a substance can lead to irreversible consequences that will manifest themselves during the operation of the device.