OPERATING PRINCIPLE APPLICATION
A reed relay is a device used for switching electrical circuits.
Unlike electromechanical relays, in which switching occurs through mechanical action on contact groups, in reed relays the actuating element is one or more reed switches.
Depending on the purpose or class of the device, the contacts are closed or opened when the contact group is placed in a magnetic field.
This principle is widely used in various electronic sensors, for example, to monitor water levels.
The main difference between reed relays and electromechanical ones is their long service life, which is due to the absence of moving parts subject to wear and abrasion. Also, the low intensity of the control magnetic field and high speed make it possible to use this type of relay for switching control circuits of electronic units of highly sensitive devices.
Another advantage of reed relays over other relay switching devices is the protection of the contact group from moisture, dust and other adverse factors that can lead to premature wear and failure of the relay.
Reed switch operation
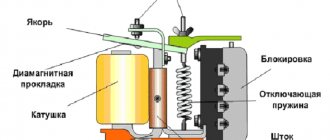
A simple relay with closure contacts consists of two cores with contacts having increased magnetic permeability. They are located in a sealed glass container with an inert gas or a mixture of gases. A pressure of 50 kPa is created in the cylinder. The inert environment prevents contacts from oxidizing. The reed switch cylinder is placed inside the control winding connected to direct current. When the power is turned on, a magnetic field is formed on the relay, passing through the contact cores, along the gap and closes through the control coil. Magnetic flux creates a traction force that connects the contacts to each other.
To keep the contact resistance to a minimum, the touching surfaces are coated with silver, radium, palladium, etc. When the power is turned off in the reed switch electromagnet coil, the force disappears and the springs open the contacts. In reed relays there are no friction surfaces of parts; the contacts have many functions, performing the work of a magnetic circuit, conductor and spring. To reduce the size of the magnet coil, the current density is increased. Use enamel wire to wind the coil. Reed switch parts are stamped, connections are made by soldering or welding. Reed switches use magnetic shields to reduce the activation zone.
Reed relay.
The springs in reed relays are installed without additional tension; they turn on immediately, without wasting time on starting. Instead of an electromagnet, permanent magnets can also be used. Such reed switches are called polarized. The pressing force of the contacts of a reed relay is determined by the magnetic force of the coil, in contrast to conventional electromagnetic relays, in which the force depends on springs. When opening, the reed switch works differently.
The system of relay magnets, under the action of electromagnetic force, magnetizes the cores of the same name, which repel each other and open the circuit. In a reed switch with switching, one of the 3 contacts is closed and made of non-magnetic metal. The remaining two contacts are made of ferromagnetic composition. Under the influence of a magnetic field, open contacts close, and closed non-magnetic contacts open. Although there is always a magnetic field, like the Earth’s field, such a field is not enough to trigger the reed switch, so it is neglected.
Main technical characteristics of reed switches
Due to the wide variety of designs of reed relays, with different functional purposes, there are characteristics that are relevant only for a specific type. Let's look at the main ones that are inherent in all types of reed relays:
- Vibration level - if the specified level is exceeded, the glass bulbs of the reed switches may crack, the contacts may close or open. This quantity is measured by the number of vibrations per second;
- The maximum voltage for contacts in a switched electrical network is measured in volts and kV, depends on the cross-section and material of the contacts, and is written as Umax;
- Allowable powerat which the contacts do not lose their ferromagnetic properties and ability to perform their functions. The power of the reed switch is determined by the material and cross-section of the contacts; the larger the cross-section, the greater the allowed electrical power of the network, designated in the technical documentation as Pmax measured in W; kW;
- The number of switching cycles is the number of openings and closings until the contacts wear out, at which point they can no longer fulfill their functional purpose. In some technical sources this is called the service life, denoted as N max, where N is the number of operations, usually estimated at 4-5 billion;
- Release time - the period of time from the moment the coil is de-energized until the contacts transition to their original state 0.2 - 1 μs;
- Reaction time – time from the moment current is supplied to the coil until the contacts close or open 0.5 - 2 μs;
- Contact capacitance - Sk, can only be in the open state of the contacts, depends on the gap between them and the geometric dimensions of the contact plates.
The last two parameters in technical documentation can be formulated as the speed of closing and opening contacts in milliseconds, written as Tsp and Totp. These values indicate the speed of the reed switch; small-sized models have higher speed. The frequency of switching cycles can reach 1000 Hz.
- Breakdown voltage is the voltage value (tens of kV) at which an electric arc or spark breaks through between the ferrite contacts in the open state. This voltage characterizes the electrical strength of the reed switch, which largely depends on the materials from which the contacts are made, the coating and the gap between them;
- Field strength is the value at which contacts switch, sometimes this parameter is called magnetic force Vav - actuation. Triggering means the closure of contacts and Votp. Releases imply the opening of contacts.
- Resistance of the contact transition - has two values, measured in the closed state Rк (contact) in very small quantities. In the open state, Riz(insulation) is the insulation resistance within tens of MOhms.
Table: CHARACTERISTICS OF REED SWITCHES FOR CONTACT CLOSING
| Reed switch model | KEM-1 | KEM-6 | MK36701 | MKA-27101 |
| Type of reed switch modification | standard | standard | intermediate | intermediate |
| magnetic field strength, A | 54…110,1 | 37…50 | 51…80 | 31…60 |
| Response time interval, ms | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1,5 |
| Allowable switching power, W | 31 | 11 | 20 | 11 |
| Permissible switching voltage, V | 221 | 151 | 101 | 111 |
| Switching current value, A | 1,1 | 0,26 | 0,36 | 0,36 |
| Breakdown voltage, V | 501 | 501 | — | 501 |
| Contact resistance of a closed reed switch, Ohm | 0,09 | 0,11 | 0,071 | 0,121 |
| circuit frequency, Hz | 101 | 21 | 50 | 100 |
| Operating temperature, °C | -61…+123 | -61…+125 | -61…+100 | -61…+100 |
| Permissible vibration frequency range, Hz | 1…601 | 1…50 | 1…600 | 1…601 |
| Length and Ø of the cylinder, mm | 50/80 | 36/63,5 | 36/63,5 | 27/45,6 |
Parameters of switching and measuring reed switches
| Reed switch brands | MKS-27102 | KEM-3 | MKS-15101 | MKA-52181 | MKA-27801 |
| magnetic flux strength, A | 51…74 | 31…100 | 31…45 | 81 | 31…100 |
| Switching time interval, ms | 1,51 | 1,51 | 1,51 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Allowable switching power, W | 31 | 31 | 0,36.1 | 1,49 | 1 |
| Permissible switching voltage, V | 151 | 125 | 35 | 35 | 301 |
| Permissible switching current, A | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0,011 | 0,11 | 0,011 |
| Resistance of closed contacts, Ohm | 0,151 | 0,31 | 0,151 | 0,081 | 0,11 |
| frequency of closing and opening, Hz | 51 | 101 | 100,1 | 100,1 | 50.1 |
| Operating temperature intervals, °C | -61… + 125 | -61… + 125 | -61… + 125 | -61… + 85 | -61… + 85 |
| Vibration range, Hz | 1…2000.1 | 1…2000.1 | 1…2000,1 | 1…601 | 5…601 |
| Length and Ø of the cylinder, mm | 27/67 | 18/54 | 15/50 | 53/79,5 | 28/52,3 |
high power reed switches
| Reed switch brand | MKA-52141 | MKA-52142 | MKA-52202 |
| Reed switch modification | high voltage | high voltage | powerful |
| Switching magnetic flux strength, A | 100…200,1 | 300.1 | 180…300.1 |
| Switching time interval, ms | 3,1 | 3,1 | 8,1 |
| Allowable switching power, W | 51 | 51 | 251 |
| Permissible switching voltage, V | 5000.1 | 10000.1 | 380.1 |
| Permissible switching current, A | 3,1 | 3,1 | 4,1 |
| Breakdown voltage, V | 10000.1 | 15000.1 | 800.1 |
| Resistance between closed contacts, Ohm | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,3 |
| Operating temperature range, °C | -40…+85 | -60…+100 | -45…+60 |
| Permissible frequencies of vibration loads, Hz | 1…600 | 1…60 | 1…10 |
| Flask length and Ø mm | 53/5,4/80 | 52/5,5/90 | 52/7,0/0 |
Application of reed switches
Reed sensors and switches use:
- medical devices and communication devices;
- apparatus for submariners;
- synthesizers and keyboards;
- testing instruments, meters;
- automation and safety devices.
In security systems, sensors on reed switches are used as relays. The security sensor includes a magnet and a reed switch. The simplest reed relay consists of a winding and a reed switch. Comparative characteristics of reed switches and other types of relays are presented in the table below.
Comparison of reed relays with other types according to their main characteristics.
Material on the topic: What is a condenser
The advantages of reed switch relays include:
- small dimensions, simple device;
- protection from moisture, burning of the contact group;
- no rubbing parts.
Reed relay device
Such reed switch sensors are widely used, but they also have disadvantages, such as susceptibility to mechanical damage. This is a big disadvantage for use in many systems. Reed switches are indispensable in alarm systems. Installing the sensor is not difficult. When the door is closed, the reed switch contact is closed. When the door is opened, the magnet attached to the jamb moves away from the reed switch, the magnetic force decreases, and the power circuit opens.
This serves as a signal to trigger the alarm circuit. The situation is similar with the use of reed switches in elevators. Reed switches are used to determine the location of the elevator car. Using magnets and a reed switch, it is easy to control lighting equipment. Electricity meters also have reed switches.
Types of models
High-quality reed relays are usually divided into several categories, which differ in the design of the contact group. Each variety has numerous positive characteristics that are highly valued by both specialists and home craftsmen. There are several types of reed switches on sale:
- With switching contact type.
- Traditional open-loop installations.
- Specific elements with closed contacts.
In addition to the main functional characteristics, experts also highlight technological parameters that divide sealed switching units into dry and mercury.
Tips for use
When using reed relays or sensors, you can give several tips that take into account the nuances of using such devices:
- When installing reed switches, avoid sources of ultrasound if possible; it can negatively affect the electrical parameters of the sensor and change them.
- A nearby magnetic field source can also change the characteristics and properties of the magnetic switch.
- Reed relays and sensors are resistant to shock and mechanical damage. Inert gas inside the sensor may escape upon impact due to a leak in the gas tank. This will disable the reed switch.
- When performing soldering, you must follow the instructions of the manufacturer of the reed switch sensor.
Soviet reed relays.
FAQ
- To dampen vibration, they install reed switches containing mercury, is this not dangerous to health?
The mercury is in a sealed glass flask and in a durable shell, so it is not dangerous. It is prohibited to disassemble; if it fails, it must be disposed of in accordance with the established procedure in specialized organizations.
- Ultrasounds can affect the performance of reed switches?
Yes, indeed, ultrasound can significantly change the characteristics of the reed switch; the structure of the magnetic field can change, as a result of which its strength will not be enough to switch contacts. Therefore, when choosing a reed switch location, the influence of ultrasound should be avoided.
Gersikons
Relays on reed switches have a wide variation in the return coefficient due to manufacturing technology errors. To increase the rated power and switching current, auxiliary contacts are built into reed relays to extinguish the arc. Such relays are called gersikons, or power sealed contacts. Industrial production produces hersicones for currents up to 180 amperes. Their switching frequency reaches up to 1200 switchings per hour. Gersikons are used to start asynchronous electric motors with a rated power of up to 3000 W.
It will be interesting➡ How is a photo relay used for street lighting?
Designation and marking
In normally closed notation, terminals in a circle are drawn intersecting. The designation of the three-contact device looks different. A circle is still drawn in the same way, but in it, on the one hand, two parallel segments are depicted, and on the other, a segment located in the center of the distance between them. The switching contact is also drawn on it.
According to Soviet standards, on diagrams and in literature, the reed switch is signed with the letter “K”, after which the serial number of the product on the diagram is placed. The foreign designation uses two Latin letters SF.
There is no standard for product labeling. Each manufacturer usually puts its own factory designation on the reed switch body: for example, KEM, TRA, ASMK, KA, KSK. Therefore, to find out what type a particular device is, you will need to look at the manufacturer’s datasheet.
Ferrite Reed Relays
This is a special class of reed relays with ferrite cores. They have a memory function. To make a switch in reed switches of this type, you need to apply a current pulse of reverse polarity in order to demagnetize the ferrite core. They are called memory hermetic contacts, or gelawns. Advantages of reed relays:
- The absolute tightness of the contacts makes it possible to use them in aggressive environments, under conditions of dust, humidity, etc.
- Small dimensions, light weight, simple design of the sensor.
- The increased operating speed makes it possible to use reed switches at high switching frequencies.
- Reliable operation in a wide temperature range (from -60 to +120 degrees).
- Wide range of applications combined with relay functionality.
- Availability of galvanic isolation of switching circuits and relay controllability on reed switches.
- Increased strength of electrical contacts.
- Long sensor life.
Disadvantages of reed switches:
- Low sensitivity of reed switch magnets.
- Excessive sensitivity of the sensor device to magnetic fields. This requires protective measures against magnetic forces.
- The reed switch cylinder is made of fragile material, sensitive to damage and shock.
- The switching power is small for both gersikons and reed switches.
- At high currents, the reed contacts open spontaneously.
- When operating on low-frequency voltage, the contacts open and close without control.
Reed relay in the diagram.
Reed switch is an ultra-precise, high-speed sealed switch controlled by a magnetic field. The number of its operations is up to five billion times. Based on it, magnetic field sensors and reed relays are produced for a wide variety of applications - from household appliances to aviation and astronautics. The article describes the features of choosing reed switches and provides a tabular overview of the wide range of these products produced by Littelfuse. The word "reed switch" is an abbreviation of the words "sealed contact". The first reed switch was developed in 1936 by the American company Bell Telephone Laboratories. Subsequently, they became widely used as sensors, and reed relays were created on their basis.
It will be interesting➡ Features of an electromagnetic relay
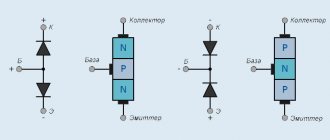
The reed switch consists of two ferromagnetic conductors having flat contacts, sealed in a glass capsule. Without an external magnetic field, the contacts are open and there is a small dielectric gap between them. In a magnetic field, the contacts close. The contact area of both plates has a sputtered or galvanized coating made of a metal that is very resistant to erosion (usually rhodium, iridium or ruthenium). The structure of contact coating layers is shown in Fig. 2a and 2b for rhodium and iridium, respectively.
Iridium, ruthenium and rhodium are very resistant to erosion platinum group metals. Thanks to the deposition of these metals, the number of contact activations reaches five billion times. Nitrogen is usually pumped into the capsule cavity. Some types of reed switches are evacuated to increase the maximum permissible switching voltage. The reed switch contacts in a magnetic field are magnetized, and a magnetomotive force equal to the magnetic field strength arises between them. If the magnetic field strength is high enough to overcome the elastic forces in the contacts that arise during their elastic deformation, then the contacts close. When the field weakens, the contacts open again.
Relay connection.
There are two types of reed switches: SPST-NO (Single Pole, Single Throw Normally Open, that is, “one pole, one channel”) - a regular switch in which two contacts are normally open; SPDT-CO (Single Pole, Double Through Change Over, that is, “one pole, two channels - switching”) is a switch in which one contact is always normally closed and the second is normally open. The common plate is the only moving part of such a reed switch; in the absence of a magnetic field, it is closed with a normally closed relay contact. When a magnetic field of appropriate strength occurs, the common plate closes with a normally open contact. Both plates of the normally open and normally closed contacts are stationary.
The open contacts have a ferromagnetic coating, and the normally closed contact is made of non-magnetic material. When placed in a magnetic field, the moving contact and the normally open contact are magnetized in the same direction, and with sufficient magnetic field strength, the moving contact closes with the stationary ferromagnetic contact. When the external magnetic field disappears, the magnetization of the contacts weakens and they open. To ensure that the residual magnetization is minimal, high-temperature processing of the contacts is used in the manufacture of reed switches. A permanent magnet (Fig. 5) or a solenoid is most often used as a source of magnetic field for a reed switch.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each unit has both positive and negative characteristics. If the user knows all the strengths and weaknesses of the purchased product, he can choose the most suitable application for it. That is why before purchasing a reed relay you need to study its advantages:
- High degree of switching reliability. This parameter is almost twice as high as those typical for open contact groups. This effect is achieved due to the high resistance between the open contacts (can be in the tens of MΩ).
- Ease of use. This parameter is due to the fact that all contacts are isolated from the external environment, so the user does not need to worry about their cleanliness. In addition, there is no mechanical connection to a permanent magnet.
- Long service life. The number of relay operations is in the billions; no contact group can compare with this figure.
- Performance. For many models, the switching frequency is close to 1 kHz.
- You can control the equipment without the help of electricity.
- This type of switch is completely undemanding in terms of load selection.
When all the positive aspects have been studied, you can also become familiar with the disadvantages. If the master has the necessary experience, he will be able to eliminate minor defects. Among the main disadvantages of a reed switch, the following characteristics can be identified:
- Relatively small number of contacts.
- Large sizes that do not fit well with modern radio equipment.
- Quite low switching power.
- Vibration when triggered (this parameter does not apply to those models where mercury drops are filled into the capsule).
- Increased sensitivity to external magnetic fields.
- The glass bulb can be easily damaged if not handled properly.
Despite the significant predominance of positive characteristics, the reed relay is gradually being replaced by other semiconductor-type analogues (for example, a Hall sensor). The decisive role was played by the higher structural strength, the complete absence of rattling, as well as the small size.
Operating principle of a reed relay
The operation of a normally closed reed switch uses the principle of interaction of forces arising between magnetic bodies. In the electromagnetic field, impulses appear and are transmitted, electrons begin to move, causing movement and deformation of current-carrying contacts. Changing the position and state of the magnetic limit switch in a specific device or circuit leads to the opening of the contacts. Further changes in their position occur under the influence of other moving elements - buttons, end springs, disks, etc. Thus, the contacts are switched on and off alternately.
It will be interesting➡ A few facts about RKN (Voltage Control Relay)
This operating principle became the basis for the functioning of an intermediate reed relay that acts on a short circuit. Its design consists of two cores and a sealed durable glass cylinder filled with gas or a gas mixture. The cylinder itself is under constant action of electric current. The gases prevent the oxidation of the metal cores.
When a DC reed switch is connected to such a reed switch, a powerful magnetic field is formed around the cores. The presence of special gaps greatly facilitates the passage of this field between the parts of the relay. Next comes the emergence of an autonomous magnetic flux moving in a given direction. The joining of the cores is greatly accelerated by coating them with precious metals with lower resistance than conventional material. A constant magnetic flux is ensured by the design features of the reed relay.
The uniformity and integrity of parts is created through casting and stamping, and welding processes are used to connect them together. Therefore, the relay coil is magnetized to a minimum extent. A reed switch relay works according to this scheme, the principle of operation of which is quite simple. If the DC supply is interrupted, the contacts will open and the magnetic flux will disappear.
Related material: How to connect a capacitor
The essence of the device
This state will last until the magnetic field is removed. As soon as the power lines stop influencing, the contacts will immediately open. For the next circuit, it is necessary to create a field around the device again. Thus, the reed switch is essentially a switch, the position of which depends on the strength of the magnetic flux affecting it.
According to the principle of operation, devices are classified into three types:
Depending on the normal position of the contacts, reed switches are used both to open the circuit and to close or connect lines. Therefore, they can successfully replace mechanical relays.
Device design
The term “reed switch” already contains the principle of its design. This word is formed from the three initial letters of each of two words - “tightness” and “contact”, which emphasizes both its functionality and purpose. After all, a working reed switch for opening or closing is, in fact, a connecting device, which is a contact pair or group placed in a sealed flask.
The contacts are placed inside the flask. The leads coming out of the device are soldered to them. The material used for the manufacture of contact groups is a ferromagnetic material, for example, steel, nickel coated with a resistant metal - rhodium or ruthenium.
Therefore, three parts of the structure can be distinguished:
In addition, the inside of the reed switch can be filled with mercury vapor. This type is called mercury. The contact surface is wetted with a drop of mercury, which reduces the electrical resistance of the contact pads, and therefore reduces chatter.
By studying the design of the reed switch, we can conclude that a critical indicator of the reliability of the device’s operation will be the quality of manufacture of the bulb, namely its tightness at the point of contact with the terminals.
Specifications
In addition to the reaction time, the device parameters determine the following characteristics:
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
Another important technical characteristic of a reed switch is its physical size. It depends on the dimensions of the cylinder, namely its length and diameter. As of 2022, the smallest reed switch in the world is considered to be a product manufactured in the USA by Hermetic Switch Inc, the length of its cylinder is 4.01 mm.
Reed switch: design, technical characteristics, operating principle and marking
Trimming leads with side cutters with one-sided sharpening is permissible (Figure 29), but it must be remembered that the flat side of the side cutter jaws should be on the side of the reed switch body. You should also pay attention to the quality of sharpening and the presence of play in the tool used.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
How it works. Reed switch Contacts are magnetic cores that are welded into the ends of the bulb, and their outer ends can be connected to an external electrical circuit. Ask, I'm in touch!
Purpose and scope
Reed sensors, despite being replaced by Hall sensors, still find application in many devices and systems:
- Keyboards for synthesizers and industrial equipment. The design of the sensors eliminates the possibility of sparks. Therefore, they are primarily used in explosive production areas where flammable vapors or dust are present.
- Household meters.
- Automatic security and position control systems.
- Equipment operating under water or in high humidity conditions.
- Telecommunication systems.
- Medical equipment.
Security systems use devices consisting of a reed switch and a magnet. They report the opening or closing of doors. Reed relays are also used, consisting of a contact sensor and a wire winding. This system has some advantages: simplicity, compactness, moisture resistance, absence of moving parts. Reed switches are also used in special areas - these are mechanisms for protecting against overloads and short circuits of high-voltage and radio electrical installations. These are also high-power radars, lasers, radio transmitters and other equipment operating under voltage up to 100 kV.
Various reed relays.
ORDER FORMULATION
In the order you must indicate: name and type of relay, rated supply voltage of the coil, type of delivery (for export), designation of technical conditions, quantity.
An example of recording the designation of a relay without a plug connector with six NO contacts with a 12 V coil when ordering it and in the documentation of another product:
- for domestic supplies to areas with temperate climates - “Relay RPG-9-05601U3, 12 V, TU 16-647.056-87, 1 pc.”;
- for export deliveries to areas with temperate climates - “Relay RPG-9-05601U3, 12V, export, TU 16-647.056-87, 1 pc.”;
- for export deliveries to areas with a tropical climate - “Relay RPG-9-05601O4, 12 V, export, TU 16-647.056-87, 1 pc.”