During a thunderstorm, many of us do not unplug household appliances and home electronics. Such negligence is usually very costly. Every year during the summer, information appears about damage caused by lightning.
Electronics and, above all, television and computer equipment are the most sensitive to lightning discharges. Its electronic components are usually configured to operate at low voltages of the order of a few volts, so the appearance of an overvoltage of even a hundred volts will completely destroy them.
Lightning protection for antenna
Antennas installed on our roofs are potential sources of danger to devices inside the building. A direct lightning strike into an antenna mast can result in complete destruction of electronic equipment, including fire of the entire installation. A lightning strike near an antenna does not cause such a sharp effect, but it may well damage parts and circuits inside electrical and TV equipment.
Lightning is an electrical discharge in the atmosphere with a current of 10,000 to 500,000 amperes and a voltage of ten million to a billion volts. A lightning discharge creates an electromagnetic pulse that can destroy electronic equipment within a radius of several kilometers from the point of impact.
However, there is a way to effectively protect all connected playback devices by connecting them to highly sensitive overvoltage protection devices. The methods you will learn about in this article, in particular lightning protection for antennas, will help protect your antenna installation and television equipment. Not only from direct lightning strikes, but also from currents induced in wires and from the introduction of high potentials.
Is grounding always necessary?
Many of us believe that a lightning rod installed on the roof can protect home appliances from lightning. Not everything is right here. A lightning rod really protects a building from a thunderstorm, since it receives and discharges the main lightning strike - its high-voltage discharge - into the ground. But while this happens, an electromagnetic field has time to be generated in the lightning rod, and stray currents are formed that can cause overvoltage in the electrical system of the house and in its power supply line.
Consequences of lightning and electromagnetic pulse
An antenna installed on a building that is not equipped with lightning protection means there is a very high probability of lightning hitting the antenna and the risk of electric shock.
What risks arise during a thunderstorm? For the antenna system and television receivers interacting with it, threats can spread in the following scenarios:
- interaction of the electromagnetic field of a lightning discharge with the loops of wires that exist in the building;
- If the antenna mast is not grounded, then with a direct hit on the antenna, lightning current can penetrate inside the building. Flowing through various types of conductive installations, damage the devices in them;
- a direct lightning strike to the power lines supplying the building;
- a discharge in the immediate vicinity of an object can pose a threat due to the partial influx of lightning electricity through conductors buried in the ground.
You may be interested in: Digital TV set-top box
The home television system is very vulnerable to power surges during a thunderstorm. Therefore, grounding the antenna is one of the important measures in the complex of its protection, but not the only one.
Regulatory Requirements
Electrical safety requirements that apply to television systems and cable networks can be found in the “Rules for Electrical Installations” (7th ed.), as well as in the instructions RD 34.21.122-87. The measures listed in these basic regulations concern the protection of antenna systems, including satellite ones, from atmospheric phenomena and lightning strikes.
Protection of antenna mast structures
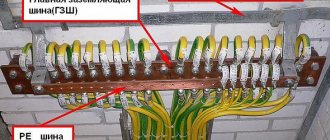
According to the requirements of the instructions for the design of lightning rods (VSN 1-93), lightning protection of antenna-mast structures from a direct discharge into them is realized by reliable grounding of the following components:
- supports supporting the antenna;
- the antenna structures themselves;
- feeder lines connecting them.
When organizing lightning protection, it is preferable to use so-called “natural” grounding elements (metal and reinforced concrete objects located in the ground, etc.) as grounding elements.
In a situation where access to natural grounding conductors is limited for some reason, specially equipped grounding systems should be used. When installing them, each branch of a separate lightning rod of lightning protection must be connected to a grounding device (GD) specially organized for it.
Types of lightning protection
Grounding an antenna, whether in the private sector or in a city high-rise, is a way to “bury” part of the energy in the nearest lawn in the event of a direct lightning strike. The method is natural, but not one hundred percent. There are additional precautions that are successfully used in television networks - the use of special lightning protection devices. See for yourself: a TV that is connected to the mains has an antenna connector. Thus, even an unplugged device can be damaged if a lightning strike hits the antenna. The antenna wire must pass through surge protection elements before being introduced into the building. Coaxial protection modules have been designed specifically for the purpose of lightning protection for coaxial cable.
For coaxial cable lightning protection to be effective, all cables in your home TV network must be protected.
Regulatory Requirements
When carrying out installation work, qualified specialists are guided by the requirements established by the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standards. The main document regarding antenna grounding is called EN 50083-1.
This regulatory act describes the necessary actions to prevent the destructive consequences of lightning striking an antenna. The requirements regulate work related to the protection of only permanent lightning protection systems or devices installed in campsites. They do not apply to amateur radio stations operating on the VSAT platform.
Regulatory acts also include several other documents, including:
- GOST P IEC 62305-2-2010.
- GOST R IEC 62305-1-2010.
- Order of Rosstandart number 795.
Lightning protection device
Lightning rod from direct lightning strike
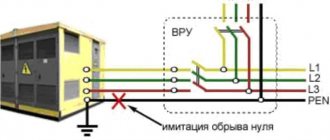
If your antenna rises alone above the roof and this is the highest point of your land, then you need to take a comprehensive approach to protecting your property and video equipment. First, you need to equip the roof of your house with a lightning rod and down conductor (ideally copper rod, 8 mm in diameter). To fix it on the roof, metal structures - holders - are mounted. The receiver is connected to the down conductor, and that to the grounding conductor. This may be a separate circuit, or there may be grounding switches located on your site if the wiring in the house was grounded.
Lightning protection for cable
The second stage of lightning protection is lightning protection for video circuits - a whole family of microdevices that operate on the principle of a fuse, which is installed in the form of a coaxial segment into a cable break. The purpose of any lightning protection is to neutralize the electromagnetic impact when lightning strikes an antenna installation. The design of lightning protection for television systems is such that when high voltage passes through it, its sensitive element - a fuse-link or a flask with gas - is destroyed, and the module leaves the telecommunication circuit, opening it. All cables require the correct selection of appropriate surge protection so as not to degrade the desired signal and, at the same time, provide effective protection.
Satellite antenna protection
The need to protect a satellite dish from a direct lightning strike is explained by the possible impact of strong electromagnetic fields on the receiving equipment, causing significant overvoltages.
In the absence of special lightning protection, a lightning strike can damage not only the circuits of the input and amplifier modules of satellite antennas, but also the power supply of the device.
As an extremely unpleasant consequence for the user of a severe thunderstorm, the possibility of damage to the receiver itself cannot be ruled out. All of the above is also true for satellite systems of the Tricolor type.
In order to protect the input circuits and the receiver itself from lightning strikes, a special fuse is inserted into the cable gap between the antenna and the receiver. When the safety element installed in the outlet from the plate is triggered, it is destroyed and is no longer used.
It is worth noting that a plate installed on the roof or wall of a house must also be reliably grounded, which provides additional lightning protection, protecting against lightning damage.
Source
How to ground a TV antenna in the country
Country houses and the antennas that summer residents install on them are very vulnerable targets in a thunderstorm: there is hardly a high enough “bait” for lightning nearby (tall old trees, mobile operator towers, etc.). Especially if the dacha farm is located on lands that are just being developed.
You may be interested in: Inventions of the TV
If in bad weather a direct electric discharge hits the antenna, then even a lightning rod installed nearby will not protect either the TV or the tuner in the house. The discharge will definitely reach the nearest outlets. And here we are talking about saving the house, not the equipment. A lightning rod is, of course, good, but it will not protect against induced impulses and statics. That is why the country antenna must be reliably grounded; it must have its own ground loop.
Pin grounding
How to do this? Nowadays the pin type of grounding is very popular. In the finished factory kit, most likely you will find this type of ground electrode. It comes with its own instructions so that you do not make mistakes during installation.
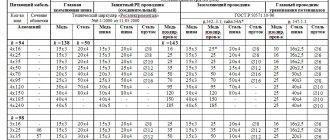
- For those who are used to doing everything themselves: prepare a grounding loop: metal fittings with a diameter of 20 mm (steel, stainless steel, copper are suitable). Cable wire (PV-16.0 sq. mm), as an antenna connector with a recessed circuit.
- Drive the ground electrode to a depth of two meters, leaving the end of the metal rod 20 cm above the soil. You must connect the wire to it using a clamp or welding. Connect the other end of the current collector to the antenna.
Selection of rods for modular pin grounding
Usually they come copper-plated with a standard length of 1.5 m. For basements with low ceilings, you can take a shorter one - 1.2 m.
The most common rod diameter is 14mm.
They say that the higher the contact patch with the ground, the better. This is certainly true. But don’t expect any super improved resistance characteristics when increasing the cross-section.
According to the formula for calculating grounding for a single vertical ground electrode, the diameter does not greatly affect the overall indicator.
Even if you increase it by 100%, the resistance will decrease by only 9%.
Not what you expected, right? Therefore, there is no particular point in overpaying and buying the thickest possible pins.
Take the minimum allowable according to the standards.
In addition to copper-plated ones, there is another type of threaded rods - couplingless galvanized ones. In them, the rod is simply screwed into one another. On the edge of one pin there is an external thread, on the other - an internal one.
It is impossible to say for sure which is better, copper or zinc. Every manufacturer always praises their products.
However, keep in mind that copper plating, although resistant to corrosion, is only as long as it is not damaged.
And it can be scratched very easily. For example, when using gas wrenches, tightening couplings.
Or when entering rocky soil, knocking off the top layer with the sharp edges of pebbles.
In this case, the copper protective coating is destroyed and the scratch site begins to actively oxidize. Next, there is a gradual but inexorable destruction of the steel core, as a result of which the overall resistance of the entire circuit sharply deteriorates.
That is why the copper coating should be as thick as possible. The recommended value is at least 0.25mm (including thread!).
With zinc the opposite is true. Such pins are not particularly afraid of external damage. In them, zinc is a reducing agent relative to the steel core.
Therefore, here zinc will corrode first, and only then steel. And as long as the entire zinc layer does not deteriorate, the steel core will feel good.
Nevertheless, the warranty periods indicated by manufacturers are approximately as follows:
copper-plated rods – 30 years
galvanized – from 20 to 30 years
There are also stainless steel sets.
These are intended for those who do not save at all on electrical costs and want to make a circuit that is called “for centuries.”
What not to do when grounding
As you know, the Russian people are cunning when it comes to invention. Often this trick turns against the owners themselves. The common myth that organizing residential grounding using jumpers in an outlet is a good example of this. Due to technical ignorance, and more often arrogance, residents resort to various tricks that have nothing to do with electrical safety. Regarding grounding your home TV network in case of a thunderstorm, know that no qualified electrician will advise you to do the following:
- attach the television antenna stand to the house ventilation duct or to the chimney;
- fix antenna cables near electrical cables or water pipes;
- use house engineering systems as grounding. Imagine what can happen when a powerful electric spark hits a gas pipeline!
Many have seen in films what happens when a hair dryer falls into a full bathtub. The same effect can be expected if lightning strikes a water supply or sewer network.
Antenna Installation Recommendations
The choice of location for fixing the television antenna and its orientation in space depends on many factors, including:
- type of antenna;
- location of the plot of land;
- the nature of the terrain;
- intensity of external interference;
- interference caused by power supply indicators, type of AFU.
When installing a TV antenna on the roof, the base is most often a mast. A steel pipe with a diameter of approximately 35-40 mm is suitable.
An alternative to a metal product can be a wooden one - made of timber (50 by 50 mm). Such a mast is fixed on rafter beams. The receiving device must rise above the roof by at least 2 m. If a wooden beam is chosen, a thick copper wire or bus is laid over it. The second end of the circuit is connected to a grounding device, which is either a busbar or ground electrodes buried in the ground.
What not to do:
- Attach the antenna mast to ventilation ducts or chimneys, to electrical infrastructure objects, racks with communication wires, and dormer windows.
- Fix the guy wires of the receiving device so that they are located near vibrators, electrical wiring, water pipes or window sills.
Why do you need to ground the antenna?
Outdoor antennas pick up the signal better than indoor ones. The latter work well only in places where there is a sufficient signal level. Therefore, many owners of country houses and country houses prefer to install these types of antennas. But it takes a lot of skill to first install the TV antenna and then ground it.
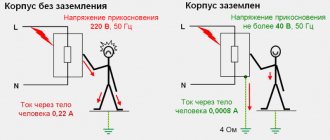
The debate about whether it is necessary to do grounding at the dacha is quite relevant. Most experts say that grounding is necessary to reduce electrical voltage to a level that is safe for humans.
In grounding, down conductors are connected to a grounding device (it consists of a grounding conductor and a grounding conductor) to redirect the lightning discharge to the ground. Thus, the likelihood of fire from an electrical discharge is significantly reduced.
Grounding is necessary in order to protect the antenna and equipment from atmospheric discharges. This is necessary so that during a thunderstorm lightning does not strike the antenna, damage the TV, and also does not pose a danger to the residents of the house. In addition, with a grounded TV antenna, image quality improves and there is less interference.
Types of receiving antennas
A set of channels is provided to users through broadcasting on specific frequency bands. There is analogue television and digital. Each broadcast occurs on different bands, the antenna must be appropriate.
- For terrestrial analogue TV, a meter antenna (MF) is required. The signal is transmitted and received in the range of 1-300 MHz.
- Digital broadcasting is performed on shorter waves, which correspond to the range of 0.3-3 GHz. A decimeter antenna (UHF) is required, which will pick up shorter waves than when transmitting an analog signal.
- If you need to receive meter and decimeter waves at once, then you need broadband devices. The design contains vibrators of different sizes to operate at different frequencies.
Depending on the location, there are external and internal. The first ones are installed outdoors, on the roofs of houses and other places. They can be used in an apartment building for all residents at once or for one in the case of an individual connection. Internal ones are installed at home. They may not even have a cable, but are attached directly to the TV.
There are also:
What are you connecting the antenna to? To digital set-top box 53.55%
To TV 46.45%
Voted: 394
Lightning protection as a means of protecting equipment from power surges.
I'm not scaring you, but about 40,000 thunderstorms occur on planet Earth every day. That is why protecting equipment from thunderstorms and static electricity is not an unnecessary attribute, but a vital necessity.
Regardless of how you look at it, it’s spring outside! And after spring comes summer with its thunderstorms and frightening lightning.
It is no secret that the open position of the antenna makes it the most likely target of lightning strikes, so special protective measures are required.
The question arises... what happens if lightning hits a satellite dish?
My answer is... a direct hit is a complete fuck-up. And don’t believe the “smart specialists” who, for good money, assure you that they will provide and install protection against a direct lightning strike on a satellite dish, head, etc.
In reality, there is protection from overvoltage!
They occur on a satellite dish because an electromagnetic field collects there, which causes a voltage surge.
Without protection, the most common breakdown is damaged circuits of the input signal and power supply, and even the circuits of the receiver itself.
It will be possible to effectively protect all connected playback devices only if highly sensitive surge protection devices are first connected to them.
There are many ways to protect satellite receivers.
The lightning protection device is connected to the gap in the antenna cable, between the satellite dish and the receiver itself.
More specifically, if your antenna has one converter, then directly to the converter, and then to the protection device we connect the antenna reduction cable.
It is not possible to talk about 100 percent reliability of lightning protection devices in a direct lightning strike, but they will provide protection from power surges during lightning discharges.
During a thunderstorm, even when the discharge does not hit your satellite dish specifically, but very close by, an electromagnetic field collects on the satellite dish, which causes a voltage surge on the satellite dish and the antenna cable.
This leads to short-term voltage surges of tens of thousands of volts.
To ensure safe use of your receiver, it is enough to install lightning protection.
They are designed to protect the input stages of receivers from induced electromagnetic pulses (static electricity), which can arise in the wire path as a result of the action of electromagnetic fields during a thunderstorm.
The Dr.HD Surge Protector device is designed to protect the input tuner of a satellite receiver, terrestrial and cable devices from a short-term lightning discharge that can occur in the vicinity of an installed antenna or coaxial cable.
Dr.HD Surge Protector is mounted into the cable break near the satellite receiver or screwed directly onto the LNB IN input of the receiver and allows you to protect the tuner from electromagnetic pulses (overvoltages) induced on the converter or coaxial cable during a thunderstorm.
When triggered, the lightning protection device Dr.HD Surge Protector or TS 2006 RTM burns out and cannot be used again.
And remember, the miser pays twice, because... equipment that fails as a result of a lightning discharge is not subject to warranty repair, only as a beer stand.
FM antenna design for receiver
Such antennas are designed to convert radio waves in the FM range into electrical signals perceived by the receiver. The simplest designs are a vibrator, half the size of a wave. Such antennas do not have directional properties and perceive too much interference radiation from the surrounding space. If the FM receiver is mobile, you can, by making some movements, find the best direction of the signal. For stationary receiving radio devices, a wave channel tuned to the broadcast receiving beam is more suitable, while the best sound quality will be on a couple of channels (mostly radio stations of this type broadcast in a range of about 10 megahertz).
Read also: Fuel consumption standards 2018
Additional Information. If it is necessary to expand the radio broadcast beam, you can connect 2-3 half-wave vibrators in parallel in a vertical position and solder them onto round cylinders.
The required 50 ohm resistance is not always achieved; such an FM antenna must be amplified with devices for matching. Thus, vibrators can be mounted on cone-shaped guides, representing a fan, “opened” from the center to the borders.
When using steel and sheet metal in construction, it is possible to obtain even 300 ohms. Thus, it turns out to receive a fairly large number of FM channels. To further expand reception in this range, it is sometimes necessary to assemble and connect an antenna array.