Are organizations required to provide collective and personal protective equipment to workers?
In accordance with the provisions of Art. 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employers are required to equip hired employees with personal protective equipment free of charge if:
- employees perform labor functions in harmful or dangerous working conditions;
- employees work in special conditions, such as temperature or pollution.
Employers, both individual entrepreneurs and legal entities, are required to provide their employees with PPE (clause 2 of the appendix to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n, hereinafter referred to as the Appendix).
This order is not subject to revision and cancellation from 01/01/2021 within the framework of the regulatory guillotine, since it is included in the list of legal acts that are not subject to the provisions of Art. 15 Federal Law dated July 1, 2020 No. 247-FZ.
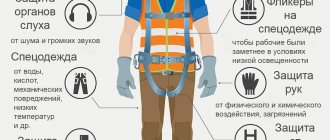
Personal protective equipment includes:
- workwear, shoes and other personal tools that can be used to protect an employee from exposure to harmful and dangerous factors, as well as from pollution (clause 3 of the Appendix);
- special substances related to flushing and neutralizing.
Note that, along with PPE, there are collective protective equipment used by groups of workers in certain conditions. The employing company is also obliged to equip its employees with them. In practice, the special substances mentioned above are often used as CSCs.
The employer is required to provide employees with both PPE and CPE.
In addition, purchase or rent PPE, ensure its storage, maintenance of functional condition and replacement at your own expense (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of the Appendix).
Procedure for storing protective equipment
Protective equipment must be stored and transported under conditions that ensure their serviceability and suitability for use; they must be protected from mechanical damage, contamination and moisture.
Protective equipment must be stored indoors.
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymer materials that are in use should be stored in cabinets, on racks, shelves, separately from tools and other protective equipment. They must be protected from acids, alkalis, oils, gasoline and other destructive substances, as well as from direct exposure to sunlight and heat radiation from heating devices (no closer than 1 m from them).
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials that are in use must not be stored in bulk in bags, boxes, etc.
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials that are in stock must be stored in a dry room at a temperature of (0-30) °C.
Insulating rods, clamps and voltage indicators above 1000 V should be stored in conditions that prevent them from bending or coming into contact with walls.
Respiratory protection equipment must be stored in dry rooms in special bags.
Protective equipment, insulating devices and devices for working under voltage should be kept in a dry, ventilated area.
Shielding protective equipment should be stored separately from electrical protective equipment.
Individual shielding kits are stored in special cabinets: workwear is on hangers, and safety shoes, head, face and hand protection are on shelves. During storage, they must be protected from moisture and aggressive environments.
Protective equipment used by field teams or for individual use by personnel must be stored in boxes, bags or cases separately from other tools.
Protective equipment is placed in specially equipped places, as a rule, at the entrance to the premises, as well as on control panels. Storage areas must have lists of protective equipment. Storage areas must be equipped with hooks or brackets for rods, insulating clamps, portable grounding, safety posters, as well as cabinets, racks, etc. for other means of protection.
Under what conditions are personal protective equipment issued to employees?
For employees who work in harmful or dangerous conditions, at special temperatures or in polluted conditions, PPE is issued by the employer free of charge (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of the Appendix).
PPE, as well as flushing and neutralizing substances, are provided to employees:
- in accordance with standard standards for issuing PPE and the corresponding type of substances;
- based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
The State Duma is considering draft law No. 1070354-7 “On introducing amendments to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in terms of improving mechanisms for preventing industrial injuries and occupational morbidity.”
According to this bill, standard norms and rules for providing workers with PPE will be established by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation.
The company, taking into account the position of the trade union, has the right to establish its own standards for the free provision of PPE, which presuppose a higher quality of equipment for workers with PPE than is provided for by standard standards. These internal corporate standards must be recorded in the company’s local legal acts (clause 6 of the Appendix).
The company, also taking into account the position of the trade union, can provide the issuance of personal protective equipment alternative to those provided for by the standard standards, provided that these personal protective equipment provide equivalent protection of workers from exposure to hazardous and harmful factors.
Bill No. 1070354-7 amends Art. 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding the development of standards for the free issuance of PPE based on the Model Standards, taking into account the results of an assessment of special working conditions and professional risks, the opinion of a trade union or other (if any) elected body authorized to represent the interests of workers.
The conditions provided for by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated 01.06.2009 No. 290n will now be enshrined in the Code.
Workers can only be issued PPE that has a certificate or declaration of conformity certifying that the PPE meets the safety criteria. If the protective equipment belongs to the dermatological category, then its use is possible only if there is a conclusion from the sanitary and epidemiological services or a certificate confirming the state registration of PPE of the appropriate type (clause 8 of the Appendix).
The employer does not have the right to purchase or rent PPE that does not have a valid certificate or declaration of conformity.
The protective equipment issued to the employee must be returned to the organization upon dismissal or transfer to another position in which the use of personal protective equipment is not necessary. In addition, if PPE expires, it must be returned to the employer for disposal.
What is the procedure for providing workers with personal protective equipment?
The first task that the employer solves when providing employees with personal protective equipment is informing employees about what protective equipment they are entitled to (clause 9 of the Appendix to Order No. 290n). In addition, the company must, during the introductory briefing on labor protection, familiarize the employee with the rules approved by Order No. 290n, as well as standard standards for the provision of PPE.
In Art. 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation amends the mandatory training for employees in the use (application) of personal protective equipment. Training will need to be carried out simultaneously with instructions on labor protection and first aid training provided for in Art. 214 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When issuing protective equipment to employees, the employer should pay special attention to:
- on the need to ensure compliance with PPE that is suitable for a specific employee in size and the nature of his work (clause 12 of the Appendix);
- the need to control and record the provision of personal protective equipment to workers in a unified accounting card, as well as when using software (clause 13 of the Appendix);
- the need to compare the specifics of issued PPE and standard standards defined for a specific type of activity of an employee, or those that are closest to his type of activity (clause 14 of the Appendix);
- there is no need to classify PPE depending on the position held by the employee - only the type of activity and profession matters (paragraphs 15, 16 of the Appendix);
- the need to provide additional personal protective equipment for employees performing a part-time job function - in accordance with the standards defined for this function (clause 17 of the Appendix);
- the need to temporarily provide PPE to employees transferred to another job, internship, practice, and other persons who operate on the territory of the employer company, but if these are employees of third-party organizations - for example, fulfilling their duties under an outstaffing agreement - then PPE should be provided to them their employers (clause 18 of the Appendix).
If the PPE is not provided to the employee in the required completeness, then the employing company should not allow him to work.
Having issued PPE to an employee, the employer is obliged to ensure that the person uses appropriate protective equipment (clause 26 of the Appendix).
If an employee refuses to use PPE or fails to comply with the rules of use, the employer will have the right to release such employee from work without pay.
The procedure for issuing and accounting for workwear is described in the typical “ConsultantPlus” situation. Sign up for a free trial access to K+ and follow the recommendations of experts.
The company must monitor the functionality and serviceability of personal protective equipment, conduct timely tests of protective equipment, and purchase the necessary technical means to solve these problems (clauses 29, 33 of the Appendix). If the protective equipment is being repaired or, for example, being washed, the employee must have a second, spare PPE at his disposal (clause 30 of the Appendix).
Calculation of primary fire extinguishing means
- Requirements of the Fire Regulations 2022
- Requirements of the Fire Regulations 2012
The procedure for determining the type and quantity of primary fire extinguishing means is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 16, 2020 N 1479 (as amended on December 31, 2020) “On approval of the Fire Regulations in the Russian Federation.”
Providing protection facilities with primary fire extinguishing means
When determining the types and quantities of primary fire extinguishing agents, the physical, chemical and fire hazardous properties of flammable substances, their interaction with fire extinguishing agents, as well as the area of premises, open areas and installations should be taken into account.
Equipment for technological equipment with fire extinguishers is carried out in accordance with the requirements of technical specifications (passports) for this equipment.
The choice of type and calculation of the required number of fire extinguishers at the protection facility (indoors) is carried out in accordance with the provisions of the Rules and Appendices No. 1 and 2 to the Rules, depending on the fire extinguishing ability of the fire extinguisher, the categories of premises for fire and explosion hazard, as well as the fire class. To extinguish fires of various classes, powder fire extinguishers must have appropriate charges: for class A fires - ABCE powder; for fires of classes B, C, E - BCE or ABCE powder; for class D fires - powder D. The choice of a fire extinguisher (mobile or portable) is determined by the size of possible fire sources. It is allowed to use fire extinguishers of a higher rank than those provided for in Appendices No. 1 and 2 to the Rules.
When choosing a fire extinguisher with the appropriate temperature limit for use, the climatic conditions of operation of buildings, structures, and premises are taken into account.
If combined fires are possible, then preference when choosing a fire extinguisher is given to one that is more universal in scope.
In public buildings and structures, at least 2 fire extinguishers are placed on each floor with a minimum extinguishing rating of a model fire in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to these Rules, and the distance to the fire extinguisher from a possible source of fire should not exceed the standards established by paragraph 406 of these Rules.
A room of category D for explosion and fire hazard is not equipped with fire extinguishers if the area of this room does not exceed 100 square meters. meters.
If there are several adjacent premises of the same functional purpose, the required number of fire extinguishers is determined based on the total area of these premises and taking into account the provisions of these Rules.
Each fire extinguisher sent from the protection facility for recharging is replaced with a charged fire extinguisher corresponding to the minimum extinguishing rank of the model fire of the fire extinguisher sent for recharging.
When protecting premises with fire extinguishers, one should take into account the specific interaction of fire extinguishing substances with protected equipment, products and materials.
Premises equipped with automatic fire extinguishing systems are provided with fire extinguishers for 50 percent of the estimated number of fire extinguishers, while the distance to the fire extinguisher from a possible source of fire should not exceed the standards established by paragraph 406 of these Rules.
(clause 406) The distance from a possible source of fire to the location of a portable fire extinguisher (taking into account partitions, doorways, possible obstructions, equipment) should not exceed 20 meters for administrative and public premises, 30 meters for premises of categories A, B and C1 - B4 for fire and explosion hazard, 40 meters - for premises of category G for fire and explosion hazard, 70 meters - for premises of category D for fire and explosion hazard.
Buildings and structures for production and storage purposes with an area of more than 500 square meters. meters are additionally equipped with mobile fire extinguishers according to the standards provided for in Appendix No. 2 to the Rules.
Buildings and structures of category D for explosion and fire hazards are not required to be equipped with mobile fire extinguishers. Each fire extinguisher installed at a protection facility must have a serial number printed on the fire extinguisher body, the charging (recharging) date, and the trigger or locking device must be sealed.
In winter, water-based fire extinguishers must be stored in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Fire extinguishers placed in corridors and passages should not interfere with the safe evacuation of people. Fire extinguishers should be placed in visible places near exits from premises at a height of no more than 1.5 meters to the top of the fire extinguisher body or in special stands made of non-flammable materials to prevent falling or tipping over.
Industrial and (or) warehouse buildings of enterprises (organizations) not equipped with internal fire-fighting water supply or automatic fire extinguishing installations (with the exception of buildings that are not required to be equipped with fire extinguishing installations and internal fire-fighting water supply), premises and sites of enterprises (organizations) for the primary processing of agricultural crops , premises for various purposes in which hot work is carried out, as well as the territories of enterprises (organizations) that do not have sources of external fire-fighting water supply, or external technological installations of enterprises (organizations) located at a distance of more than 100 meters from sources of external fire-fighting water supply, must be equipped with fire protection shields. The required number of fire shields and their type are determined depending on the category of premises, buildings (structures) and external technological installations in terms of explosion and fire hazard. Standards for equipping buildings, structures, structures and territories with fire shields are given in accordance with Appendix No. 6. Fire shields are equipped with non-mechanized firefighting tools and equipment. Standards for equipping fire shields with non-mechanized tools and equipment are given in accordance with Appendix No. 7.
Water storage barrels installed next to the fire shield must have a volume of at least 0.2 cubic meters. meters and equipped with buckets. Sand boxes should have a volume of 0.5 cubic meters. meters and equipped with a shovel. The design of the box should make it easy to remove sand and prevent the ingress of precipitation. Sand boxes are usually installed with fire shields in areas where flammable or combustible liquids may be spilled. For premises of categories A, B, B1 - B4 and external technological installations of categories AN, BN and VN for explosion and fire hazard, a supply of sand of 0.5 cubic meters is provided. meters for every 500 sq. meters of protected area.
Blankets to isolate the source of fire must be capable of extinguishing fires of classes A, B, E and have a size of at least one meter wide and one meter long. In rooms where flammable and (or) combustible liquids are used and (or) stored, the dimensions of the canvas must be at least 2 x 1.5 meters. Blankets for isolating the source of fire are stored in waterproof, lockable cases (cases, packages), allowing these products to be quickly used in the event of a fire. The head of the organization ensures that the blanket for isolating the source of fire is checked once a year for the absence of mechanical damage and its integrity, with information entered into the log of the operation of fire protection systems.
The use of primary fire extinguishing means, non-mechanized firefighting tools and equipment for household and other needs not related to firefighting is prohibited.
Standards for the provision of portable fire extinguishers to objects of protection depending on their categories of fire and explosion hazard and fire class (with the exception of gas stations)
| Category of premises according to fire and explosion hazard | Class fire | Fire extinguishers with extinguishing grade model outbreak |
| A, B, B1 - B4 | A | 4A |
| B | 144B | |
| C | (4A, 144B, C) or (144B, C) | |
| D | D | |
| E | (55B,C,E) | |
| G, D | A | 2A |
| B | 55B | |
| C | (2A, 55B, C) or (55B, C) | |
| D | D | |
| E | (55B,C,E) | |
| Public buildings | A | 2A |
| B | 55B | |
| C | (2A, 55B, C) or (55B, C) | |
| E | (55B,C,E) |
Notes: 1. In rooms where there are different types of flammable material and different classes of fire may occur, fire extinguishers that are universal in scope are used. 2. It is allowed to use other primary fire extinguishing means that provide extinguishing of the corresponding class of fire and the extinguishing rank of a model fire, including portable fire extinguishing aerosol generators. 3. The choice of the type of fire extinguisher must be determined taking into account the safety of its use for people and property.
Standards for equipping premises with mobile fire extinguishers (with the exception of gas stations)
| Fire category of premises and explosion hazard | Limit protectable area (sq. meters) | Class fire | Number of fire extinguishers with extinguishing rank model hearth (at least pieces) |
| A, B, B1 - B4 | 500 | A | 2 - 6A or 1 - 10A |
| B | 2 - 144B or 1 - 233B | ||
| C | 2 - (6A, 144B, C) or 1 - (10A, 233B, C) | ||
| D | 1 - D | ||
| E | 2 - (6A, 144B, C, E) or 1 - (10A, 233B, C, E) | ||
| G, D | 800 | A | 2 - 6A or 1 - 10A |
| B | 2 - 144B or 1 - 233B | ||
| C | 2 - (6A, 144B, C) or 1 - (10A, 233B, C) or 2 - (144B, C) or 1 - (233B, C) | ||
| D | 1 - D | ||
| E | 2 - (6A, 144B, C, E) or 1 - (10A, 233B, C, E) or 2 - (144B, C, E) or 1 - (233B, C, E) |
Notes: 1. In rooms where there are different types of flammable material and different classes of fire may occur, fire extinguishers that are universal in scope are used. 2. It is allowed to use other primary fire extinguishing means that provide extinguishing of the corresponding class of fire and the extinguishing rank of the model fire. 3. The choice of the type of fire extinguisher must be determined taking into account the safety of its use for people and property.
Standards for the provision of fire extinguishers for railway rolling stock
| Name of the object of protection | Meter | Fire class | Number of fire extinguishers with extinguishing rank model hearth (at least pieces) |
| Electric locomotives | section | A, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Diesel locomotives | section | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Gas turbine locomotives | section | A, B, C, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) |
| Electric trains, diesel trains, diesel electric trains | |||
| 9 - 12-car | train | A, B, E | 6 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 6 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| 4 - 8-car | train | A, B, E | 4 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 4 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Rail buses, motor carriages | |||
| 1 - 2-car | train | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| 2 - 4-car | train | A, B, E | 4 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 4 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Refrigerated sections | section | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Cars intended for the carriage of passengers: | |||
| with water or combined heating | railway carriage | A, B, E | 1 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 2 - (34B, C, E) |
| with electric heating | railway carriage | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 2 - (34B, C, E) |
| Baggage, postal | railway carriage | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 1 - (34B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E), 1 - (34B, C, E) |
| Dining cars | railway carriage | A, B, E | 3 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 2 - (34B, C, E) |
| Double-decker carriages designed to carry passengers | railway carriage | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 3 - (34B, C, E) |
| Double-decker dining cars | railway carriage | A, B, E | 3 - (2A, 55B, C, E), 3 - (34B, C, E) |
| Service cars, service cars, testing and measuring laboratories | railway carriage | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
| Special railway rolling stock | railway carriage | A, B, E | 2 - (2A, 55B, C, E) or 2 - (2A, 55B, E) |
Notes: 1. In railway rolling stock, which contains different types of flammable material and different classes of fire may occur, fire extinguishers that are universal in scope are used. 2. It is allowed to use other primary fire extinguishing means that provide extinguishing of the corresponding class of fire and the extinguishing rank of the model fire. 3. The choice of the type of fire extinguisher must be determined taking into account the safety of its use for people and property.
If you have any difficulties in choosing fire extinguishers and their quantity for your facility, please contact us, we will advise you free of charge.
Determining the required quantity of primary fire extinguishing agents
1. When determining the types and quantities of primary fire extinguishing agents, the physical, chemical and fire hazardous properties of flammable substances, their relationship to fire extinguishing agents, as well as the area of production premises, open areas and installations should be taken into account.
2. Equipment for technological equipment with fire extinguishers is carried out in accordance with the requirements of technical specifications (passports) for this equipment or relevant fire safety rules.
3. The supply of imported equipment with fire extinguishers is carried out in accordance with the terms of the contract for its supply.
4. The choice of type and calculation of the required number of fire extinguishers in the protected room or facility should be made depending on their fire extinguishing ability, maximum area, as well as the fire class of flammable substances and materials:
class A - fires of solid substances, mainly of organic origin, the combustion of which is accompanied by smoldering (wood, textiles, paper);
class B - fires of flammable liquids or melting solids;
class C - gas fires;
class D - fires of metals and their alloys;
class (E) - fires associated with the burning of electrical installations.
The choice of fire extinguisher type (mobile or manual) is determined by the size of possible fires.
If they are large, it is necessary to use mobile fire extinguishers. 5. When choosing a fire extinguisher with the appropriate temperature limit for use, it is necessary to take into account the climatic conditions of operation of buildings and structures.
6. If combined fires are possible, then preference when choosing a fire extinguisher is given to one that is more universal in scope.
7. For the maximum area of premises of different categories (the maximum area protected by one or a group of fire extinguishers), it is necessary to provide the number of fire extinguishers of one of the types indicated in tables 1 and 2 before the “++” or “+” sign.
8. In public buildings and structures, at least two manual fire extinguishers must be located on each floor.
9. Category D premises may not be equipped with fire extinguishers if their area does not exceed 100 m2.
10. If there are several small premises of the same fire hazard category, the number of required fire extinguishers is determined in accordance with clause 14 and tables 1 and 2, taking into account the total area of these premises.
11. Fire extinguishers sent from the enterprise for recharging must be replaced with an appropriate number of charged fire extinguishers.
12. When protecting computer premises, telephone exchanges, museums, archives, etc. the specifics of the interaction of fire extinguishing agents with protected equipment, products, materials, etc. should be taken into account. These premises should be equipped with halon and carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, taking into account the maximum permissible concentration of the extinguishing agent.
13. Premises equipped with automatic stationary fire extinguishing installations are provided with 50% fire extinguishers, based on their estimated quantity.
Table 1
Standards for equipping premises with manual fire extinguishers
| Room category | Maximum protected area, m2 | Fire class | Foam and water fire extinguishers capacity | Powder fire extinguishers capacity, l / mass of fire extinguishing agent, kg | Freon fire extinguishers with a capacity of 2 (3) l | Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers capacity, l / mass of fire extinguishing agent, kg | |||
| 10 l | 2/2 | 5/4 | 10/9 | 2/2 | 5 (8)/3 (5) | ||||
| A, B, C (flammable gases and liquids) | 200 | A | 2 ++ | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | – | – | – |
| IN | 4 + | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | 4 + | – | – | ||
| WITH | – | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | 4 + | – | – | ||
| D | – | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | – | – | – | ||
| (E) | – | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | – | – | 2 ++ | ||
| IN | 400 | A | 2 ++ | 4 + | 2 ++ | 1 + | – | – | 2 + |
| D | – | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | – | – | – | ||
| (E) | – | – | 2 ++ | 1 + | 2 + | 4 + | 2 ++ | ||
| G | 800 | IN | 2 + | – | 2 ++ | 1 + | – | – | – |
| WITH | – | 4 + | 2 ++ | 1 + | – | – | – | ||
| G, D | 1800 | A | 2 ++ | 4 + | 2 ++ | 1 + | – | – | – |
| D | – | – | 2 + | 1 ++ | – | – | – | ||
| (E) | – | 2 + | 2 ++ | 1 + | 2 + | 4 + | 2 ++ | ||
| Public buildings | 800 | A | 4 ++ | 8 + | 4 ++ | 2 + | – | – | 4 + |
| (E) | – | – | 4 ++ | 2 + | 4 + | 4 + | 2 ++ | ||
Notes:
1. To extinguish fires of various classes, powder fire extinguishers must have appropriate charges: for class A - ABC(E) powder; for classes B, C and (E) – BC(E) or ABC(E) and class D – D.
2. For portable foam, water, powder and carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, double markings are given: old marking for body capacity, l / new marking for mass of fire extinguishing agent, kg. When equipping premises with portable fire extinguishers, it is allowed to use fire extinguishers with both old and new markings.
3. The “++” sign indicates fire extinguishers recommended for equipping the facilities, the “+” sign indicates fire extinguishers, the use of which is allowed in the absence of the recommended ones and with appropriate justification, the “–” sign indicates fire extinguishers that are not allowed for equipping these facilities.
4. In confined spaces with a volume of no more than 50 m3, self-acting powder fire extinguishers can be used to extinguish fires instead of portable fire extinguishers, or in addition to them.
table 2
Standards for equipping premises with mobile fire extinguishers
| Room category | Maximum protected area, m2 | Fire class | Foam fire extinguishers with a capacity of 100 l | Combined fire extinguishers with a capacity (foam, powder), 100 l | Powder fire extinguishers with a capacity of 100 l | Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, capacity, l | |
| 25 | 80 | ||||||
| A, B, C (flammable gases and liquids) | 500 | A | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | – | 3 + |
| IN | 2 + | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | – | 3 + | ||
| WITH | – | 1 + | 1 ++ | – | 3 + | ||
| D | – | – | 1 ++ | – | – | ||
| (E) | – | – | 1 + | 2 + | 1 ++ | ||
| V (except flammable gases and liquids), G | 800 | A | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | 4 + | 2 + |
| IN | 2+ | 1 ++ | 1 ++ | – | 3 + | ||
| WITH | – | 1 + | 1 ++ | – | 3 + | ||
| D | – | – | 1 ++ | – | – | ||
| (E) | – | – | 1 + | 1 ++ | 1 + | ||
Notes:
1. To extinguish fires of various classes, powder and combined fire extinguishers must have appropriate charges: for class A - ABC(E) powder; for class B, C and (E) - BC (E) or ABC (E) and class D - D.
2. The meanings of the signs “++”, “+” and “–” are given in Note 2 of Table 1.
14. The distance from a possible source of fire to the location of the fire extinguisher should not exceed 20 m for public buildings and structures; 30 m for premises of categories A, B and C; 40 m for premises of category G; 70 m for premises of category D.
15. At the facility, a person must be identified who is responsible for the acquisition, repair, safety and readiness for action of primary fire extinguishing equipment.
A record of checking the presence and condition of primary fire extinguishing equipment should be kept in a special free-form journal.
16. Each fire extinguisher installed at the facility must have a serial number painted on the body with white paint. A passport is issued for him in the prescribed form.
17. Fire extinguishers must always be kept in good condition, periodically inspected, tested and promptly recharged.
18. In winter (at temperatures below 1 °C), water-based fire extinguishers must be stored in heated rooms.
19. The placement of primary fire extinguishing equipment in corridors and passages should not interfere with the safe evacuation of people. They should be located in visible places near exits from premises at a height of no more than 1.5 m.
20. It is recommended to store asbestos fabric, felt (felt) in metal cases with lids, periodically (at least once every three months) dry and clean from dust.
What legal acts regulate the standards for issuing personal protective equipment to employees?
PPE, as well as special substances, are issued to employees in accordance with standard standards approved by the Government of the Russian Federation (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These standards are fixed in legal regulations, which can be divided into two main types:
- industry-wide;
- adapted to a specific sector of the economy.
The first type of legal acts include:
- Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 9, 2014 No. 997n;
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 1997 No. 70.
Order No. 997n sets out the standards for the free issuance of workwear, footwear and other PPE for all types of professions and positions characterized by employees performing their functions when exposed to harmful and dangerous factors, as well as at special temperatures and pollution.
Resolution No. 70 sets the standards for the free issuance of warm workwear and footwear in relation to climate zones - also for all types of professions and positions. The jurisdiction of this legal act does not apply to a number of positions and specializations in special climatic regions.
The standards for issuing special substances to employees that fall into the category of flushing and neutralizing substances are established by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated December 17, 2010 No. 1122n.
It may be noted that those PPE that are used as signal clothing must be issued in accordance with the standards approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 20, 2006 No. 297.
In turn, the Russian Federation has also adopted legal regulations that establish standards for the issuance of personal protective equipment for certain sectors of the economy, such as:
- agriculture, forestry, fishing;
- extraction of minerals, as well as their processing;
- pulp and paper, woodworking industry, printing activities;
- chemical industry;
- metallurgy, mechanical engineering;
- electronics production;
- electricity, gas, water production;
- construction industry;
- transport, communications;
- the sphere of trade, investment, services;
- public administration;
- science, culture, healthcare, sports.
It is recommended to use industry standards first and turn to industry-wide standards only if the former do not contain standards that correspond to the types of work performed by the company's employees.
After the adoption of the draft Labor Code, the standard norms and orders of the Ministry of Labor will be revised taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations.
Supply of PPE to workers: employer’s responsibility and control over the fulfillment of its obligations
If the employer cannot provide the employee with the necessary PPE, then the employee has the right not to begin performing his work functions, while the company will be obliged to pay him a salary for downtime (clause 11 of the Appendix). Therefore, if an employer fails to comply with legal requirements to provide employees with personal protective equipment, he or she incurs direct economic losses.
The legislator makes corresponding amendments to the Labor Code. So, part 6 of Art. 216.1 of the draft Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the lawful refusal of an employee to perform work while maintaining wages. If employees are not provided with PPE, the employer faces a fine of at least 20 thousand rubles. up to 150 thousand rubles. in accordance with Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If the failure to issue protective equipment led to an incident at work, the employer may be held criminally liable in accordance with Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
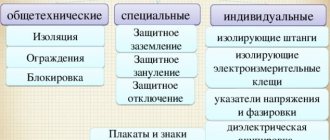
Control over the employer’s fulfillment of obligations to equip employees with PPE can be exercised by:
- labor inspectorate - in accordance with Art. 353 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- trade unions - in accordance with Art. 370 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
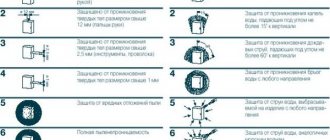
What applies to them
Primary fire extinguishing agents
According to Art. 43 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 123-FZ, primary fire extinguishing agents are intended for use by employees of organizations, personnel of fire departments and other persons for the purpose of fighting fires and are divided into the following types:
- portable and mobile fire extinguishers;
- fire hydrants and means of ensuring their use;
- fire equipment;
- blankets (fire-resistant fabric) to isolate the source of fire;
- portable generator aerosol fire extinguishers.
Primary fire extinguishing agents
Fire cloth
Fire blanket
On this topic ▼
Fireproof fabric or felt
Application and characteristics
Let's start with blankets to isolate the source of the fire. The presence of such blankets is required only for completing fire shields.
The method of using these primary fire extinguishing agents is simple, that is, we simply cover the flame, which disappears without access to the oxygen contained in the air.
It should be remembered that it will not be possible to extinguish a fire that is larger than the size of the bedspread.
Blankets are designed to isolate the combustion source from access to oxygen and are used only when the combustion source is small .
Fire equipment
Fire shield
The next type of primary fire extinguishing equipment is fire equipment. This includes special equipment, as well as equipment that can be used to extinguish a fire in the initial stage.
Basic fire equipment:
- crowbars (for opening doors, windows and other structures);
- fire hooks, hooks with a wooden handle (for dismantling and pulling away burning structures);
- kits for cutting electrical wires (scissors, dielectric boots and mats);
- pitchforks, shovels (bayonet and shovel);
- water containers and fire sand boxes (for storing extinguishing agents);
- buckets and hand pumps (for transporting water).
There is no specific list that would determine which equipment belongs to a firefighter and which does not. The specified equipment is also intended to be placed on fire panels. Sometimes you can see axes on fire shields, but now their presence is not required.
Fire equipment
On this topic ▼
Fire equipment and hand tools: types, standards, purpose
Types, norms, purpose
Fire shields must be placed in production and warehouse premises that are not equipped with internal fire-fighting water supply and automatic fire extinguishing installations, as well as on the territory of enterprises (organizations) that do not have external fire-fighting water supply, or when removing buildings (structures), external technological installations of these enterprises (organizations) ) at a distance of more than 100 meters from sources of external fire-fighting water supply.
Its main purpose is to ensure easy access for enterprise personnel to fire extinguishing means. To make it easy to determine the location, the shields are painted bright red (a contrasting color is allowed - white with a red border).
Fire shield
- ShchP-A – for extinguishing solid flammable materials (wood, textiles, etc.);
- ShchP-V – for extinguishing flammable liquids and plastics;
- ShchP-E – for extinguishing electrical installations;
- ShchP-SKh – for extinguishing at agricultural enterprises;
- ShchPP - for extinguishing in places where temporary hot work is performed (welding, surfacing, etc.).
Depending on the purpose, fire shields are equipped according to a specific list:
Sandbox
- ShchP-A – air-foam fire extinguishers with a volume of 10 l, 2 pcs.; powder fire extinguishers with a powder mass of 9/10 kg, 1 pc. or with a weight of 4/5 kg, 2 pcs.; crowbar, 1 piece; gaff, 1 pc.; bucket, 2 pcs.; bayonet shovel, 1 pc.; shovel, 1 pc.; water container with a capacity of 200 liters or more;
- ShchP-V – air-foam fire extinguishers with a volume of 10 l, 2 pcs.; powder fire extinguishers with a powder mass of 9/10 kg, 1 pc. or with a weight of 4/5 kg, 2 pcs.; crowbar, 1 piece; bucket, 1 pc.; asbestos sheet or blanket, 1 pc.; bayonet shovel, 1 pc.; shovel, 1 pc.; sand box with a capacity of 0.5 m3 or more;
- ShchP-E – carbon dioxide fire extinguishers with a charge weight of 3/5 kg, 2 pcs.; powder fire extinguishers with a powder mass of 9/10 kg, 1 pc. or with a weight of 4/5 kg, 2 pcs.; hook with wooden handle, 1 pc.; set for cutting electrical wires, 1 pc.; asbestos sheet or blanket, 1 pc.; shovel, 1 pc.; sand box with a capacity of 0.5 m3 or more;
On this topic ▼
Fire shield
Equipment, requirements of norms and rules
- ShchP-SKh – air-foam fire extinguishers with a volume of 10 l, 2 pcs.; powder fire extinguishers with a powder mass of 9/10 kg, 1 pc. or with a weight of 4/5 kg, 2 pcs.; crowbar, 1 piece; gaff, 1 pc.; bucket, 2 pcs.; asbestos sheet or blanket, 1 pc.; bayonet shovel, 1 pc.; shovel, 1 pc.; forks, 1 pc.; water container with a capacity of 200 liters or more;
- ShchPP – air-foam fire extinguishers with a volume of 10 l, 2 pcs.; powder fire extinguishers with a powder mass of 9/10 kg, 1 pc. or with a weight of 4/5 kg, 2 pcs.; crowbar, 1 piece; bucket, 1 pc.; asbestos sheet or blanket, 1 pc.; bayonet shovel, 1 pc.; trolley for transporting equipment, 1 pc.; water container with a capacity of 20 liters or more; hand pump, 1 pc.; fire hose with a diameter of 18-20 mm and a length of 5 m, 1 pc.; protective screen 1.4x2 m, 6 pcs.; stands for hanging screens, 6 pcs.
Fire hydrant
Fire hydrant
Now let's move on to fire hydrants. It should be immediately noted that not all buildings require fire hydrants. The fire-prevention water supply system, on which fire hydrants are installed, is provided for during the design of the building.
On this topic ▼
Fire hydrant
Requirements, standards, maintenance and equipment
The fire hydrant includes a valve installed on the internal fire water supply, equipped with a fire connection head, as well as a fire hose with a manual fire nozzle. It should be noted that fire hydrants are located in fire cabinets, which may also contain fire extinguishers. The use of primary fire extinguishing means, such as fire hydrants, is also provided only at the initial stage of the fire.
In case of an already developed fire, only firefighters who have respiratory protection equipment can use fire hydrants.
Internal fire hydrants must be installed at such a distance that each point in the room can be irrigated by the calculated number of compact jets. The number of compact jets and recommended minimum water flow rates depending on the number of floors, volume of the building and its purpose.
Distance between two fire hydrants L
, m, is determined by the formula:
L=2R – (1.5÷2.0 m).
Fire hydrant operating radius
R.
Layout of fire hydrants
Action diagram
Fire hydrant operation diagram
1 – fire valve; 2 – half nut; 3 – sleeve; 4 – fire barrel with tip; 5 – compact part of the jet; 6 – fragmented part of the jet
Fire hydrants are installed at a height of 1.35 m above the floor of the room and are placed in cabinets labeled PC in heated rooms in easily accessible places (on landings, in lobbies, corridors, passages).
Method of use
- Open the fire cabinet.
- Roll out the fire hose.
- Open the faucet valve using the handwheel on the faucet valve.
- Apply water to the fire by pointing the fire nozzle.
Attention! Do not direct a stream of water at electrical wires, devices and installations that are live to avoid electric shock.
Purpose
Fire hydrant, PC
– a set consisting of a valve installed on the internal fire water supply and equipped with a fire connection head, as well as a fire hose with a manual fire nozzle.
The fire hydrant equipment includes:
- fire valve with a diameter of 50 or 65 mm, connected to a branch of the riser;
- pressure hose 10, 15, 20 m long with quick-locking half-nuts;
- fire nozzle with a tip (spray) with a diameter of 13, 16, 19 mm
Fire-technical equipment of fire hydrants
Fire hydrants are divided into:
- corner and straight fire hydrants;
- taps with internal and external threads.
Fire damper DU-65 angular
Fire damper straight KPK-65
On this topic ▼
Fire hydrant standards and installation rules at sites
Fire hydrants are selected depending on the type of fire-fighting equipment used. The scope of application of firefighting cranes is quite wide. They can be used in extinguishing fires of various substances and materials. Also popular are household taps designed to extinguish fires at an early stage in apartments or cottages from the drinking water supply.
Requirements
- The design of fire hydrants must allow one person to open the shut-off device and supply water at an intensity sufficient to extinguish the fire.
- The design of the connecting heads of fire hydrants must allow the connection of fire hoses used in fire departments.
Fire cabinet
Fire cabinets have holes for ventilation, are manufactured in accordance with NPB 151-96 “Fire cabinet” and are painted white or red.
Fire cabinet
Fire cabinets provide the possibility of placing one or two manual fire extinguishers.
Requirements for fire cabinets
- Fire cabinets and multifunctional integrated fire cabinets must provide placement and storage of primary fire extinguishing equipment. The completeness of multifunctional integrated fire cabinets is accepted in accordance with Table 26 of the appendix to this Federal Law.
- The design of fire cabinets and multifunctional integrated fire cabinets must allow the equipment contained in them to be used quickly and safely.
- On this topic ▼
Fire cabinets
Requirements, types, classification, standards
Dimensions and installation of fire cabinets and multifunctional integrated fire cabinets should not lead to obstruction of escape routes. - Fire cabinets and multifunctional integrated fire cabinets must be made of non-combustible materials.
- The external design and information about the contents of fire cabinets and multifunctional integrated fire cabinets are determined by fire safety regulations adopted in accordance with Art. 4 of this Federal Law of the Russian Federation.
Fire extinguishers
Fire extinguishers
Fire extinguishers are one of the most common types of primary fire extinguishing agents. First of all, because they are required almost everywhere: in road, water and air transport, in buildings and in individual premises and even in territories. Today, a large number of different fire extinguishers are produced for all occasions. Fire extinguishers may differ in the following ways:
- by type of fire extinguishing agent used;
- according to its intended purpose, depending on the type of charged fire extinguishing agent;
- by size of mass and method of delivery to the fire site;
- based on the principle of displacement of the fire extinguishing agent;
- by operating pressure value;
- if possible and the method of restoring the technical resource.
Based on the type of fire extinguishing agent used, fire extinguishers are divided into:
On this topic ▼
Fire extinguishers
Types, classification, scope and classes of fires
- aquatic (AW);
- foam: air foam (AFP) and chemical foam (OCF);
- powder (OP);
- gas: carbon dioxide (CO); freon (CH);
- combined.
According to their intended purpose, depending on the type of charged extinguishing agent , fire extinguishers are divided into:
- for extinguishing fires of solid flammable substances (fire class A);
- for extinguishing fires of liquid flammable substances (fire class B);
- for extinguishing fires of gaseous flammable substances (fire class C);
- for extinguishing fires of metals and metal-containing substances (fire class D);
- for extinguishing fires of electrical installations under voltage (fire class E).
Most often, fire extinguishers are designed to extinguish several classes of fire.
Based on their weight and method of delivery to the fire site, fire extinguishers are divided into:
- portable (weighing up to 20 kg);
- mobile (weighing at least 20, but not more than 400 kg).
Based on the principle of displacement of the fire extinguishing agent, fire extinguishers are divided into:
- downloads;
- with a cylinder of compressed or liquefied gas;
- with a gas-generating element;
- with thermal element;
- with ejector.
According to the operating pressure, fire extinguishers are divided into fire extinguishers:
- low pressure (working pressure less than or equal to 2.5 MPa at ambient temperature (20 ± 2) ° C)
- high pressure (working pressure above 2.5 MPa at ambient temperature (20 ± 2) ° C).
According to the possibility and method of restoring the technical resource, fire extinguishers are divided into:
- rechargeable and repairable;
- not rechargeable.
Diagram of a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher | Diagram of a powder fire extinguisher | Diagram of an air-foam fire extinguisher |
Requirements for fire extinguishers
On this topic ▼
Fire extinguishers
Location rules, requirements for premises
- Portable and mobile fire extinguishers must ensure fire extinguishing by one person in the area specified in the technical documentation of the manufacturer.
- The technical characteristics of portable and mobile fire extinguishers must ensure human safety when extinguishing a fire.
- The strength characteristics of the structural elements of portable and mobile fire extinguishers must ensure the safety of their use when extinguishing a fire.
Results
Russian employers whose production infrastructure is characterized by harmful and dangerous working conditions are required to equip their employees with personal protective equipment free of charge. The main legal regulations, the provisions of which the employer must follow when providing PPE to employees, are the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n.
You can get acquainted with other aspects of ensuring labor safety at an enterprise in the articles:
- “Dangerous and harmful production factors (list).”
- “What are the responsibilities of a labor protection employee (list)?”
- “What are the responsibilities of an employer in the field of labor protection?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What other responsibilities does an employer have?
Providing protective clothing and other equipment to protect the health of workers is not the only task of the employer in this area. In addition, he must:
- control expiration and use dates;
- keep records of equipment;
- check the availability of a certificate for a particular product;
- carry out audits of existing PPE.
From time to time, the enterprise may conduct a special security assessment. It is carried out by a certification organization. Its purpose is to verify the compliance of the accounting data on the availability and quality of special equipment with the actual data. The assessment of the provision of workers with personal protective equipment is documented in the appropriate protocol. The form of this document is provided below.