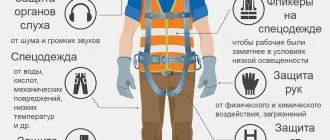
Means of protection against electric current, list, frequency of inspection, rules of application
Protective equipment against electric shock includes all devices, apparatus and instruments, the purpose of which is to prevent injury to people working with energized equipment.
Damage factors include not only electric shock, but also possible exposure to an electric arc or combustion products of electrical equipment. There are basic and additional means of protection. The first are those whose insulation provides complete protection from the operating voltage of electrical installations. They allow you to work and touch live elements that are energized. For equipment with voltages up to 1 kV, the main means of protection (hereinafter referred to as SZ) are considered to be dielectric gloves, special tools protected with insulated handles, electrical clamps, voltage indicators, insulating rods.
For electrical installations with voltages above 1 kV, the main
means of protection against electric current are the same as in installations up to 1 kV, plus devices that ensure safety during testing or measurements, as well as when carrying out repair work on electrical installations (cable puncture devices, cable damage marks, voltage indicators, insulating ladders , polymer insulators, etc.).
Additional protective equipment is also used (dielectric carpets, boots, galoshes, pads, caps, potential equalization rods, etc.), which are not able to guarantee safety, but reduce the risk of electric shock and the degree of its impact.
Depending on the impact, collective and individual means of protection are distinguished.
For electrical protection equipment, safety conditions must be observed: they must be stored dry and free of mechanical damage. Before use, a thorough inspection should be carried out, during which damaged specimens are rejected. Dielectric gloves, galoshes, carpets and boots should be no closer than half a meter from heating devices. In addition, they should not be exposed to direct sunlight or industrial liquids (oils, kerosene, gasoline, alkalis, acids, etc.).
The means of protection against electric current used must undergo regular testing, and the date of testing is marked on the product. SZ tests are carried out at the enterprise where they are used, or at nearby substations. Dielectric gloves should be checked every six months, insulated tools and voltage indicators should be checked once a year, and dielectric mats should be checked once every 2 years.
Basic and additional SZ in electrical installations
It should be noted that all electrically insulating means of human protection, to one degree or another, protect him from direct contact with conductive or grounded elements of electrical equipment or devices, including from electrically conductive surfaces.
Basic insulating agents
This category includes products whose material stably and reliably resists the operating voltage of electrical installations. Their use involves safe contact with live conductive elements without the risk of electrical injury or threat to life.
All main SZ, as mentioned above, differ in the type of application.
In electrical installations up to 1000 V:
- dielectric gloves
- insulating current clamp
- electrical installation tool kit with insulated handles
- current detectors
In electrical installations over 1000 V:
- insulating rods
- insulating clamps for measuring current strength
- voltage indicators
Additional insulating protective equipment
The division occurs by analogy with the main SZ.
In electrical installations up to 1000 V:
- dielectric galoshes
- dielectric mats and coverings
- insulating stands
In electrical installations over 1000 V:
- electrical installation tool set with insulated handles
- dielectric gloves
- bots
- dielectric mats and coverings
- insulating stands
Please note that while operating any electrical protective equipment or devices, it is strictly forbidden to touch their working surfaces, as well as the insulating material located behind the limit stop or ring! Also, in no case should you forget that using insulating rods, clamps or voltage indicators in electrical installations with voltages over 1000 V is only possible with dielectric gloves! In addition to the specified means and devices for protection in electrical installations, the following types of PPE are used:
- head protection helmets
- shields and goggles for eyes and face
- gas mask or respirators that protect the respiratory system from electric shock
- hand gloves
- belts and ropes that protect personnel from falling while working at height
Scale of injuries
There are the following scales of injury, which depend on factors:
The duration of a person's exposure to electric current. The higher the score, the greater the likelihood of injury and death.
The body's protective functions (along with body resistance) decrease with prolonged contact. It has been proven that with a lesion lasting 1-2 minutes, resistance can decrease by 25%. The negative impact on heart function increases. If an electric current passes through the main organ during a relaxed state, then its effect is most destructive. In such cases, fibrillation occurs.
Conditions of the body: physical fitness, resistance to stress, the presence of chronic diseases, the acute phase of the disease.
During an acute illness cycle or in the presence of chronic diseases, an individual is more vulnerable than a person who does not have serious health problems. Cardiovascular problems increase the likelihood of serious damage. The current flows along the path of least resistance, so those organs that do not work stably will be affected.
Dry skin has greater resistance than after moisturizing. Dissolved salts and acids reduce the resistance value by 1.5-2 times. Sweat and dirt increase the electrical conductivity of the skin. The effect of electric current in this case becomes more significant.
The specific resistance of the skin of the body has different meanings. The epidermis of the palms, face, groin areas, neck, where the thickness of its layer is minimal, has the smallest. Also, people with large builds have greater resistance. Areas of the body with a large number of sweat glands are considered vulnerable.
The magnitude of the current by gender and age. Women and children will suffer more than men under the same incident conditions.
What does an electrical burn look like on a child?
During stress, the body's protective functions also decrease, therefore, people who are stress-resistant are less vulnerable.
An area with a lower relative atmospheric pressure is a more dangerous area. Rarefaction (low oxygen content in the air) increases the negative impact of a physical quantity.
Network characteristics: voltage class, type and current, network frequency, etc.
The voltage class is of secondary importance compared to the concept of current during an incident. At the same voltage, the current strength can differ thousands of times.
The perceptible current is up to 1.5 mA. Causes discomfort when passing through the skin. In most cases it is harmless.
Not releasing current. (3-5 mA). Causes contraction of muscle tissue. When the parameter increases to 15mA, the victim begins to experience significant pain. It becomes impossible to free yourself.
Fibrillation current 100mA..5A. There are disturbances in the functioning of all body systems.
When the 5A threshold is exceeded, an electric shock occurs instantly as a result of cardiac and respiratory arrest. Prolonged exposure leads to death.
It has been proven that the influence of alternating current in networks up to 0.4 kV is much more dangerous than direct current. Further, the danger of the latter becomes greater (at a frequency of 50 Hz). When the operating frequency increases to 10 kHz, the body is exposed to thermal effects (electrical burns).
The circumstances of the incident - location, speed of provision of first aid.
Humidity in the room, actions during the passage of charges through the body, quality of care, etc. have a major impact on the outcome of the case.
Pathways for electric current to travel through the body. If the charges pass without affecting internal organs, then the chances of survival are high.
The most dangerous chains are hand-arm and hand-leg chains, i.e. those in which vital organs suffer. Touching reflexogenic areas is also dangerous (chest, neck, temples).
Electrical injury to a person
There are a number of cases when contact with electricity does not pose a danger to the body:
- Contact in dry rooms with 20 V networks. A person will not receive electrical injury when touching dangerous objects. With this effect, no convulsions occur, and the victim can free himself.
- 12 V is considered safe in damp rooms.
Lighting in children's rooms is used at 12 V. This measure is used to reduce the risk of injury to the child.
Classification of electrical injuries
Electrical injuries are classified according to the following criteria:
- At the location of the electric shock injury;
In general, three types of traumatic injuries by currents of different origins are defined:
- Industrial electrical injuries - if a person was injured at work while working with equipment powered by electricity;
- Domestic injuries from electricity received in domestic conditions. Mostly, housewives and small children are susceptible to household electrical injuries. The main reasons are ignoring safety requirements when handling household appliances (washing machines, electric microwaves, irons);
- Natural electrical injuries – as a result of exposure to natural electricity. A classic example is a lightning strike, which is a discharge of atmospheric electricity.
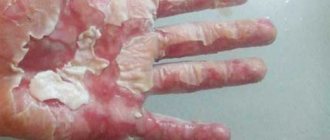
In Fig. Below is a typical household electrical injury - a burn to the hand after an electric shock from a faulty electrical appliance.
Household electrical injury
- By the nature of the current (duration of exposure);
The temporary nature of the effect of current leads to two types of electrical injuries:
- Instant electrical injuries resulting from the action of an electric discharge for a short period of time (so-called electric shock). They have life-threatening injuries that require urgent medical attention;
- The chronic course of electrical injuries associated with the long-term and imperceptible influence of electric fields on a person. For example, personnel working near powerful high-voltage generators are susceptible to chronic electrical injuries. Symptoms of chronic damage are manifested in increased fatigue, tremors, high blood pressure, sleep disturbances, and memory impairment.
- Based on the nature of the lesion, the following were determined:
- Local electrical injuries, characterized by local (local) damage to a specific part of the body;
- General electrical injuries, which are extensive damage to the body as a result of electric current flowing through it. With general electrical injuries, cardiac and respiratory arrest may occur, leading to the clinical death of the injured person.
According to statistics, damage from electric shocks is distributed as follows:
- 20% of all cases are local electrical injuries;
- 25% – general injuries;
- 55% are mixed, in which local and general lesions of the body simultaneously appear.
First aid for electric shock
In case of any type of electric shock to the body, it is necessary to provide emergency assistance to the victim, otherwise the health condition may deteriorate significantly and lead to death. The first step is to shut off the power supply using a switch, unscrew the plugs, or, as a last resort, interrupt the current-carrying wiring. If the current flow cannot be stopped, you need to quickly invent isolation for yourself and the victim, then drag them to a safe distance and call for medical help. Before the arrival of honey. workers, if necessary, provide emergency assistance to the victim in the form of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Tags: machine, ampere, beat, sconce, view, generator, house, , grounding, replacement, sign, insulation, how, design, , installation, voltage, lighting, potential, rule, touch, wire, start, , work, repair, switch, row, light, lamp, network, connection, connection wire, resistance, means, ten, type, current, installation, shield, electricity, effect