Types of damage
Rice.
1. Damage to transformers Due to the fact that the transformer is put into operation together with other devices, any damage to the supply line, low-voltage circuits or inside the tank is equally dangerous.
Among the current types of accidents, the following should be noted:
- Short circuit between windings;
- Short circuit of the winding to the housing;
- Interphase faults in the line;
- Interturn short circuits;
- Damage to built-in equipment;
- Overheating of connection points and electrical contacts;
- Open circuit, violation of the integrity of connection points or windings;
- Failure to fasten the iron, loosening of the sheets when the yoke ties are loosened, followed by overlap or destruction of the turns.
Film protection of transformer oil
The most advanced is film protection of transformer oil. The expander is made detachable. It is filled with oil exactly to the connector and covered with an oil-resistant plastic film. The film is collected in folds. When the oil expands, the film is inflated with a bubble, but the oil does not come into contact with any gas, and its quality (degassing) is completely preserved (Fig. 5).
Fig.5. Film protection of transformer oil: Kr. Tr-ra - transformer cover; GR - gas relay; P - expander; M - oil; To the air; P - film separating oil and air
Fig.5. Thermosiphons for drying transformer oil: a - installation of a thermosiphon, b-d - designs of thermosiphons for 10 - 200 kg of silica gel adsorbent. I — transformer tank; 2 - expander; 3 - gas relay; 4 — thermosyphon filter; 5 - air dryer on. breathing tube
Oil protection from moisture is carried out using TSF thermosiphon filters (Fig. 5). TSF is a vessel filled with an adsorbent - usually silica gel or aluminum gel - a substance that absorbs moisture into its pores, but does not react with it chemically. When the silica gel is saturated with water, it is replaced with fresh one, and the wet one is dried at 400-500°C.
3% cobalt chloride is added to the adsorbent. His normal color is blue. When silica gel is saturated with moisture, the indicator turns pink. The color of the indicator can be observed through the TSF window. The amount of adsorbent is about 1% of the oil in the transformer. For powerful transformers - 0.75%.
The oil circulates through the TSF in a natural way: hot oil enters from the top of the TSF and, when cooled, falls down, giving moisture to the silica gel along the way.
Division of transformer protection into main and backup
Any type of damage in a transformer poses a potential danger to both the integrity of the equipment and the reliability of the entire power system. Therefore, it is extremely important to competently set up the operation of protections at power plants, traction and transformer substations, local transformer substations and transformer substations. For this purpose, transformer protection is conventionally divided into two categories - main and backup.
Basic protection is a type of automation that is aimed at analyzing the internal state of the transformer (windings, hardware, additional equipment). This type covers both the device itself and adjacent buses, wires, etc.
Backup protection covers those disturbances that occur outside the transformer but can directly affect its conductors and internal components. These are all kinds of overloads, short circuits and overvoltages in lines, on adjacent devices, etc.
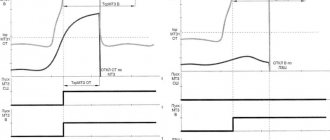
Rice. 2. Primary and backup protections
Nitrogen protection of transformer oil
The transformer is completely sealed. The air is replaced with dry nitrogen. When the oil expands, excess nitrogen is forced into an elastic container (Fig. 4).
The volume of the nitrogen expansion tank is selected based on
(m3),
where (t) is the mass of oil in the transformer.
Fig.4. Nitrogen protection of the transformer: A - nitrogen, 1 - transformer tank, 2 - gas relay, 3 - expander, 4 - thermosiphon dryer, 5 - shut-off valve, 6 - container for an elastic bag with nitrogen
Over time, the oil becomes saturated with nitrogen. This is not harmless to the transformer insulation: when heated, nitrogen bubbles are released, which can greatly deteriorate the dielectric strength of the insulation.
Types of protections and their essence
All protections for transformers must be fast enough to turn off the dangerous mode in time. Since when extremely large electrical quantities occur, it will easily lead to destruction of insulation, metal release, fires and other unpleasant consequences.
To prevent overloads, one or another type of protection is installed on the transformer. What kind of protection is used at step-down substations and in switchgear equipment is determined by local conditions and operating conditions.
Longitudinal differential protection
The scope of differential current protection covers both the power transformer itself and the connections surrounding it, right down to current load meters. The normal operating mode of each transformer is considered to be a uniform redistribution of the load between all three phases, when the electric current in each of them is approximately the same.
Longitudinal differential protection compares the current load in all phases. Since the current is approximately the same, their geometric sum should be equal to zero. As a result of the comparison, it turns out that the current component is absent or too small for the reaction. But, as soon as a short circuit occurs in one phase or between several at once, the currents in them will no longer compensate each other, and their sum will differ from zero, and a differential cutoff will work.
Rice. 3. Example of differential protection
Relay
To prevent damage to transformers, a fairly large number of relay protections are used. However, the oil level control relay deserves special attention. This type provides for monitoring the state of the insulating environment. Structurally, the relay is a float with contacts, which is held above the contacts of the actuation circuit.
If the emergency mode leads to an oil leak and a subsequent decrease below the norm, after which a breakdown may occur, a shutdown will occur. It can be located in the main tank or have backup relay protection in the expander, which will pre-signal the start of the process.
Thermal
The basis for thermal protection in transformers is a classic thermocouple. Its location is determined by the type of device, its power and dimensions, since overheating can lead to a violation of the insulating properties and lead to thermal expansion of the oil.
The most effective placements include:
- at the top of the tank;
- at high-voltage bushings;
- in the windings.
It has two stages - the first turns on backup fans or other cooling means. The second, if the first failed to reduce the overheating below the limit value, turns off the transformer.
Current cut-off
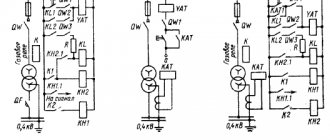
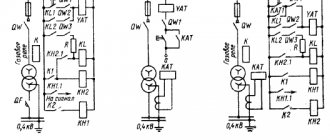
4. Example of current cut-off This type of protection is used to disconnect damage that could occur inside the transformer. It is located on the input side of the protected transformer, but the impact covers all windings from which voltage can be supplied. A special feature of its application is the power supply circuit that is used in the corresponding line.
So for three-phase circuits with an isolated neutral, the current cutoff should be installed in two phases. And when using circuits with a solidly grounded neutral, protection must be applied in each phase connection. When the transformer is turned off, there is no time delay at all.
The disadvantage of cutoff is that it only operates on high currents. Therefore, some phase-to-phase, turn-to-turn or ground faults in an isolated neutral circuit may go undetected. In practice, this is one of the simplest ways to turn off a transformer in emergency mode.
Gas protection
Gas relays, as a type of protection, have found wide application in oil-filled transformers, where transformer oil plays the role of a dielectric separating current-carrying elements and the grounded structure of the housing. During normal operation, step-down transformers do not affect the liquid dielectric, and the oil remains in a constant physical state.
But, in the event of interturn short circuits, contact of conductors with steel, or other situations inside the tank, arc burning or heating of the metal leads to local boiling of the oil. From this place the release of gases begins, which rise to the top point of the container.
Rice. 5. Example of gas protection
For the entire tank, the top point is the expansion tank, so a gas relay is installed in the connecting pipe between the expander and the transformer tank. Structurally, the gas protection is a float with two contacts. When immersed in oil, the float is in the open position. As soon as the released gases rise through the pipe, the float will fall and close the contacts, the oil transformer will turn off.
Jet protection
Used in transformers with primary and secondary windings at 110, 35, 10, 6, 3.3 kV, where it is possible to switch the voltage value under load. The on-load tap-changer is usually located in a separate tank inside the main tank, which isolates it from the high-voltage windings. Switching tap-changer positions under load can cause both normal switching phenomena and emergency ones. The latter lead to the release of oil from the tank to the conservator.
To react to such damage, jet protection is installed, since the flow of oil from the on-load tap-changer activates the measuring sensor. Next, the switch is turned off, which de-energizes the transformer windings.
Overcurrent protection
6. Example of overcurrent protection Overcurrent protection is used to operate in response to fault currents located in close proximity to the source. This includes damage both to the windings and to the nearest substation buses, to surrounding equipment, etc.
In practice, there are a large number of options for MTZ execution:
- From internal and external short circuits;
- MTZ with combined voltage starting;
- MTZ with voltage triggering and negative sequence voltage filter;
- Negative sequence combined with a device against three-phase short circuits;
In addition to emergency modes, an overload protection mode can be installed for MTZ. To do this, the operating current is set within certain limits. The setting is selected based on the maximum load value so that the circuit breaker does not trip during normal operation.
Zero sequence current protection
7. Example of zero-sequence current protection Designed to protect a transformer from a possible short circuit of either one or two phases to ground. These are situations when in a three-phase system the load symmetry is broken and relative to the zero point the sum of the currents will no longer be equal to zero.
The equilibrium of the system will be disrupted, which will provoke a power outage after a specified period of time. Often combined with automatic reclosure, then after a few seconds the circuit breaker is reclosed, in case the short circuit has cleared itself.
Special backup protection
Special backup protection is designed for autonomous backup of overcurrent protection along current circuits. Can be used on both the high and low side of the transformer. Their action is aimed at primary and secondary maximum currents that may arise in the immediate vicinity of the protected object. The operation of the SRZ, as a rule, has a time delay relative to the main overcurrent protection on the 110 - 220 kV side.
Current step protection
Like the previous option, it is a type of MTZ, which is arranged in the key of the operating sequence for different windings. Widely used in circuits where consumers are connected to a source with large inrush currents. However, the sensitivity of maximum protection is additionally tied to voltage, which ensures that automatic shutdown is blocked in the event of powering too powerful a load, since the voltage drop does not reach the set limit.
The stages are adjusted with such a time interval that the load switches are affected after the main current protection.
Undervoltage protection
In the event of a decrease in the supply voltage, two scenarios are possible - a remote short circuit, which is recognized by other protections as a large load or the connection of too large a total load. Both options have a detrimental effect on the operation of the transformer, therefore, both in emergency mode and in case of overload, a time delay is set, after which one of the following options occurs:
- shutdown of the emergency section;
- removal of non-priority consumers from work;
- automatic switching on of reserve.
More details about this type of protection in the article
Operating principle of gas protection
In typical power transformer protection you can find a gas relay. The relay consists of two compartments that perform various functions. The first chamber will serve to control the injection gas from the oil. It must be installed near the expansion tank. When the oil reaches a certain level, then the tank will begin to release it in certain quantities. In this situation, a special float will serve as a signaling device.
The indicator will not always show the oil level. Sometimes this device will monitor the passage of gases while diagnosing the operation of the transformer. A special worker can configure the correct operation of this relay. The second compartment of the device will be connected to the transformer circuit and will connect it, opening the path for the rising gas.
The membrane in the expansion tank will act as an indicator of pressure changes. If the pressure increases, then this process will compress the membrane and the diaphragm will begin to move. Movement can also occur as a result of changes in atmospheric pressure. As a result of this process, the transformer will stop working. The gas relay membrane is a delicate anti-corrosion part that may stop working correctly at the slightest damage.