Wireless charging for mobile devices is a relatively new function of transmitting energy over a distance that can save the gadget owner from problems with tangled, torn or burnt wires. Every year the number of fans of contactless devices is constantly growing. Unfortunately, not all mobile devices can support contactless charging, but there is a proven way to work around this limitation.
Below we will examine in detail how wireless charging devices work, the design features of the devices, existing standards, methods of energy transfer, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the latest technology.
What is wireless charging
As the name suggests, wireless charging allows you to charge various devices without using wires.
This can be not only a phone, but also a camera, a tablet, a smart watch, headphones and other equipment. Naturally, for this to work, the device you're charging must support wireless charging. If there is no such support, then in some cases it can be implemented using a special case. This charging method saves a lot of time and eliminates the need for cables and connectors. The user just needs to place his phone on a special platform, and the battery will automatically begin to fill. And to interrupt the charging process, you just need to pick up the device, moving it 5-10 cm away from the energy source.
But it's not that simple
For wireless charging to work effectively, the charging coils and the phone coils need to be as close to each other as possible. Ideally, if their centers coincide, then the losses will be minimal. But we often see how phones are simply placed on any place on the site, and charging still proceeds as expected.
To make this possible, manufacturers make several coils on site. For example, you can place several coils next to each other, and put a few more on top in the gaps. Then the phone will almost always lie above one of the coils and will be charged.
In order for the charger to understand which coil needs to be used, it supplies current to each one in turn and thus determines which coil the phone is closest to.
Chargers also differ in power - for example, there are chargers for 5, 10 and 20 watts. In order for the charger to understand what power your phone is designed for and whether this charger was even suitable for the phone, it uses the same magnetic field to exchange data with the phone. If everything is in order, the charge goes on, if not, then everything turns off or charging proceeds at minimum power.
Qi wireless charging standard
Many people think that wireless charging has appeared quite recently, but this is a mistaken opinion. Back in 2008, Wireless Power Consortium introduced wireless charging technology using the WPC standard. This name is not fixed in people’s memory, so in various literature and descriptions you can most often find the designation Qi.
The WPC standard states that wireless charging works thanks to two coils interacting with each other. One of them is located in the platform, and the other is in the user’s phone. Therefore, it turns out that the magnetic field covers two coils, thereby charging the device’s battery.
Today, many airports and bus stations offer their visitors to charge their smartphone or tablet completely wirelessly. This is where the Qi standard is used. However, not every phone can be charged over the air, so if you want to purchase a similar technological platform, be sure to read the specifications of your device.
Wireless charging of smartphones. Answers to the most interesting questions
Reader rating for this article: 4.9
(141)
Talking about what wireless charging is is not the most original idea. If before 2022 many tech sites wrote about this, then after the release of the first Apple smartphones with wireless charging (iPhone 8 and iPhone X), such articles appeared literally everywhere.
That's why we have this dilemma. On the one hand, no one needs another reprint on the topic of wireless charging. But on the other hand, we didn’t write anything about it.
Well, they didn’t write and there’s no need to! — a person who has not read our article about how a smartphone battery works and how to charge it correctly would say. But if that article (on such a hackneyed topic) turned out to be interesting, maybe this one will turn out good too? Well, let's check it out!
First, we will talk about the general principle of how wireless charging works, and then we will move on to the most interesting and exciting issues.
How wireless charging works on smartphones
About the same as a regular charger that you use to charge your phone every day! Or did you think that inside that small box with a USB cable that needs to be plugged into a power outlet, the current only flows through the wires?
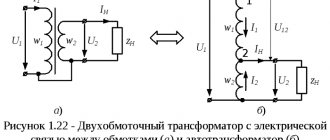
As we know, a smartphone needs 5 volts to charge, but the socket produces 220 volts. To prevent our device from burning out when connected to an outlet, it is necessary to lower the voltage. For this you need that same box called a power supply. Inside this block there is a transformer, the principle of which resembles the operation of wireless charging.
When you plug the power supply into a socket, the wire from it does not go straight into the smartphone, but is simply wound onto a coil and is not connected to anything else:
But how then does the current flow into the phone if the wire from the socket does not go anywhere? Wirelessly! And next to this coil there is another one, the wire of which is connected to the smartphone:
This clever trick allows us to lower or increase the voltage. And it works as follows.
When alternating current flows through a wire, an alternating magnetic field is created around it. The more current, the stronger this field. Why is this happening? Yes, this is just how our world works - a thrown stone falls down, and the movement of electrons in the wire is accompanied by the appearance of a magnetic field.
The word variable only means that the current constantly changes its direction. That is, at first all the electrons move in one direction of the wire, and then in the opposite direction. In one second, the current in a socket changes its direction 50 times. This is what distinguishes alternating current from direct current, in which electrons always move in only one direction.
When the current changes direction, the direction of the magnetic field also changes (north and south). We can say that our conventional magnet (magnetic field) seems to turn over 50 times per second.
So, more than a century ago, people discovered that not only does current create a magnetic field around a wire, but the magnetic field itself generates electricity in another piece of wire if this wire is nearby.
And the coil is needed only to strengthen the magnetic field, because the magnetic fields of each turn of the wire overlap each other.
It turns out that when we plug in the power supply, current flows through the first coil and creates a magnetic field, which in turn causes electrons to move in the other coil, creating electricity there.
This is how easily current is transmitted “through the air” from one piece of wire to another!
If you're wondering how 220 volts turned into 5 volts, it's even simpler here. It turns out that the difference in voltage depends on the number of turns of the wire. If we wind the wire from a 220V socket, conditionally, into a coil of 220 turns, and we wind the second wire that will connect to the smartphone into a coil of 5 turns, then 220V on one side will turn into 5V on the other wire! That is why the picture shows a different number of turns:
If current can easily “flow” between two unconnected wires, there is nothing stopping us from splitting such a transformer in half by pulling out the second coil and placing it in a smartphone.
Now, in order to “send” energy through the air, you will simply need to place the smartphone on the charger so that their coils are in close proximity to each other (the blue arrows show the magnetic field):
That's the whole secret of wireless charging!
And if everything is clear with this, then we can move on to interesting questions.
— Why does everyone call these chargers wireless if they are connected to an outlet by wire!?
Exactly for the same reason why Wi-Fi is called wireless Internet, despite the fact that the router itself is connected to charging via a wire.
Of course, it would be much more convenient if charging worked similarly to a Wi-Fi router. That is, there would be a device in the house that simply “transmitted” energy into space. Need to charge your smartphone? Lower the shutter on your phone and turn on charging, like Bluetooth or NFC.
In principle, transmitting energy over long distances is a very real task and, perhaps, such technology will soon be available to smartphone users, but for now we must be content with electromagnetic induction.
— Why don’t all smartphones support wireless charging?
In order for a smartphone to be charged wirelessly, there must be a coil inside it, the wires of which are connected to the battery. If the manufacturer has not built in this coil, such a smartphone will not be able to charge wirelessly.
Here, for example, is what it looks like on the iPhone XR:
Credits: iFixit
In addition, if the smartphone has a metal back cover, there cannot be wireless charging there, since a current will appear in the cover under the influence of a magnetic field and it will begin to heat up greatly. This won't end well.
— Is it possible to buy any wireless charger for a smartphone or do you need a specific one?
Just a few years ago, there were several incompatible wireless charging standards on the market. The most popular of these was Qi (pronounced "Chi" or "Qi"), but there were others, such as PMA.
But since there was no fundamental difference between Qi and PMA, plus Apple chose Qi as the standard for the iPhone, PMA lost the battle. Today, almost all devices use the Qi standard, so if your smartphone is more or less modern, any charger of this standard will do.
— Do I need to turn off wireless charging from the outlet when it is not charging my smartphone?
There is no need for this. Wireless charging works in standby mode when there is no load. Naturally, practically no electricity is consumed and charging does not heat up.
Periodically, such a charger sends test pulses in anticipation of a response from the smartphone, and until it responds, the device will not turn on.
— Is it necessary to place a smartphone on charge in a strictly defined place with millimeter accuracy?
Millimeter precision is not required. But, nevertheless, the coils inside the smartphone and the charger must be located more or less accurately relative to each other.
If you buy the cheapest Chinese charger, most likely there will be only one coil inside it and you will have to watch every time where and how you put your smartphone so that the placement of the coils matches. Otherwise, the smartphone will either not charge at all, or the efficiency (efficiency) of charging will be extremely low and most of the energy will go to waste.
In ordinary (good) charges, several overlapping coils are placed at once:
When you put your smartphone on such a charger, it turns on exactly the coil that is closest to the phone's coil. So, when using a normal charger, you do not need to precisely position the smartphone. They just put the phone on charge and went about their business.
There are other interesting solutions. For example, when the coil inside a wireless charger can move - you put your smartphone, and it moves right under the phone’s coil.
— Does the case affect the operation of wireless charging?
In the case, the smartphone will be located a little further from the coil, but if its thickness does not exceed 2-3 mm, this should not affect the received power. Therefore, there is no need to remove the case while charging. If it is too thick or the smartphone is located too far from the coil (say, further than 7 mm), charging is simply turned off.
The material of the case does not play any role, unless it is metal. If there are metal inserts on the case, you need to ensure that they do not overlap the coil. But even in this case, charging may not work. See the next answer for details.
— What happens if you put a metal object on the charger or there is something made of metal nearby?
Naturally, when a metal is exposed to an alternating magnetic field, electricity is induced inside and the metal object begins to heat up. This could result in the most unpleasant consequences, even a fire. But such a scenario is impossible even in theory.
The fact is that the Qi standard is not just a coil through which current flows and a magnetic field arises. In fact, wireless charging is a very smart device that will never turn on until it “agrees” with the smartphone.
In standby mode, wireless charging is unable to charge a smartphone or heat a metal object. It practically doesn't work. As soon as any metal object, including a smartphone coil, comes into the charging field, it begins to interrogate the device.
Having sent a request, the charger awaits a response. If the device confirms that it is fully compatible with the Qi standard, then the charger will check the device's position information. And if all these “metal object” checks pass successfully, only then will charging turn on.
Naturally, a simple piece of hardware “doesn’t have enough intelligence” to activate the charger.
But what happens if we place a smartphone on the charger, and there is a metal object (coin, ring, paper clip) or magnet nearby? After all, the smartphone will not tell the charger in any way, they say, there is something suspicious lying nearby and it is better to hold off on transferring energy for now.
That's right, he won't say! But this is not required. Charging does not stop communicating with the smartphone, which tells it a lot of information (received power, charge percentage, etc.). And if she notices that a certain amount of energy is bypassing the smartphone, charging immediately stops (or does not start at all). This technology is called Foreign Object Detection.
By the way, it is this “communication” between the charger and the phone that guarantees the timely shutdown of the charging process when the battery is fully charged.
— What happens if you put a phone that does not support this technology on a wireless charger?
Although this question may seem purely hypothetical, it actually has practical implications. The fact is that today car holders for smartphones with built-in wireless charging are very common. Therefore, some may be concerned about what will happen if an ordinary smartphone is placed in such a holder.
As you probably already guessed, nothing bad will happen, since the Qi standard necessarily requires agreement with the device before charging begins. What can you “talk” about with a smartphone that does not understand the “language” of wireless charging? Accordingly, charging simply will not work.
— Does wireless charging affect the operation of Bluetooth, Wi-Fi or NFC?
It would seem, what does Wi-Fi or Bluetooth have to do with it?
In fact, wireless charging operates at a specific frequency because the direction of the current changes thousands of times per second. When charging, electromagnetic waves are generated that can spread beyond the smartphone. But the operating frequency of Qi charging is from 100 to 300 kHz, while Wi-Fi and Bluetooth operate at 2.4 GHz, and NFC at 13.5 MHz.
Thus, wireless charging cannot in any way affect the operation of Bluetooth, Wi-Fi or NFC. However, it is quite capable of causing interference in the range of 100-300 kHz.
— Is wireless charging harmful to health?
If you put your hand on the wireless charger, nothing will happen, as it won't even turn on. When charging is working, its electromagnetic radiation is completely harmless to human health. As well as radiation from a smartphone or 5G towers.
— Does wireless charging kill your smartphone battery?
No stronger than wired charging. The battery is “killed” every day by the very process of charging and discharging, since after each such cycle the capacity is slightly reduced due to the chemical processes occurring inside the battery.
But what is truly harmful to the battery is very high temperatures. And here the situation is as follows. On the one hand, the wireless charging method is far from the most efficient. The charger consumes more energy than it delivers. And the smartphone receives less energy than the charging gives out. Some of this energy goes into heat.
By the way, in conventional charging, the coils do not just “dangle” in the air, but are wound on a special magnetic circuit in order to achieve the most efficient transmission of the magnetic field. There is no magnetic circuit here.
Often the heat generated is not enough to cause any harm to the battery. And fast wireless chargers are even equipped with a cooling system.
In addition, during the charging process, both devices do not stop exchanging information and if the temperature rises dangerously, the charger will begin to reduce power.
Overall, wireless charging is a completely natural method that is no more dangerous than wired charging.
PS
Don't forget to subscribe to our popular science website about mobile technologies in Telegram so you don't miss the most interesting things! If you liked this article, join us on Patreon for more fun!
How would you rate this article?
Click on the star to rate it
There are comments at the bottom of the page...
Write your opinion there for all readers to see!
If you only want to give a rating, please indicate what exactly is wrong?
How wireless phone charging works
The principle of operation of wireless charging is quite simple, of course, if you do not go into physical details. The user connects a special platform to a power source in advance, and then places the smartphone on it. It seems that everything is so simple, but in reality everything happens a little differently. An induction coil is built into the platform, which serves as a receiver and transmitter.
Exactly the same coil is located in the user’s phone. After connecting the platform to a current source, a magnetic field is formed around the coil. When you place the phone on the panel itself, interaction begins between the two coils. Electromagnetic waves are converted into electricity, which charges the phone's battery.
The process is shown more clearly in the image above. The yellow color shows magnetic waves that are converted into electricity.
Is Qi technology safe?
Some users mistakenly believe that Qi wireless charging may be harmful to health. The fact is that magnetic radiation is not ionizing. In terms of its effect on the body, it is similar to a mobile phone signal, a Wi-Fi signal, or a radio signal. At the same time, the mobile network signal that comes from the tower is stronger and continuous, while electromagnetic radiation disappears immediately after charging the smartphone battery.
The power of wireless chargers is 5 watts. It is not enough to have an effect on the human body. We can talk about a negative impact only if the power of such devices is 120 watts. But such models are not produced on an industrial scale. This explains the lack of wireless chargers for laptops. It is important to know that wireless battery charging technology has long been used in many models of electric shavers and electric toothbrushes, which once again proves its safety.
What is reverse wireless charging
Reverse wireless charging is an even more advanced version of this technology. It first appeared in 2018 on a number of Huawei and Samsung smartphones. Its essence boils down to the fact that with the help of one phone you can charge another, and completely wirelessly.
It is enough to lean the two devices against each other and activate the required function in the settings. This is very convenient as it eliminates the need for people to carry portable chargers with them.
Advantages and disadvantages of wireless charging
For the average user, the only and most important advantage of using a wireless phone charger is that there is no need to connect a special cable to the smartphone. Despite the fact that this type of charging a mobile device is called wireless, in any case you cannot get rid of the wire, since the charger itself is connected to an outlet.
As for the disadvantages, you need to remember that such chargers usually cost more than cable ones, and charging a smartphone with them takes about 2-3 times longer. However, as a new and interesting technology, as well as a solution in some unusual cases (for example, car wireless charging), this method of charging a smartphone can be a very interesting and practical solution.
Charging a smartphone using wireless charging takes about 2-3 times longer
How to use wireless charging
Using wireless charging is just as easy as using regular charging via a cable. However, for clarity, here are detailed instructions:
- Connect the wireless charger to a power source. This could be a computer USB port or a regular outlet. After performing this action, the device should give some kind of signal, most often light or sound.
- Place your phone on the wireless charging platform. Most often, there are no special requirements for this, but it is better to place the phone in the center of the block. If charging does not start, check whether this option is activated in the settings.
As you can see, the principle of operation is very simple, so any user can handle it.
Thus, wireless charging is a special platform on which the phone is placed to begin charging the battery. The principle of its operation comes down to the interaction of magnetic fields between two induction coils located in the phone and the device itself.
Which smartphones support wireless charging?
First of all, we want to note that not all gadgets today support the wireless charging function. Apple intentionally markets products that are not Qi compatible. In this case, we recommend purchasing a special case with a built-in induction coil.
Flagship devices generally always support Qi technology. These include such popular smartphone models as Samsung Galaxy S6, Sony Xperia Z4v, Samsung Galaxy S6 Active, Google Nexus 6, Motorola Droid Turbo, Nokia Lumia 930, Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge. Already, dozens of models from various manufacturers can be charged using a wireless accessory, which provides maximum ease of use for users.
What is the Qi standard? What other standards are there?
There are several competing wireless charging standards, designed primarily for phones.
Standards created:
- Qi
- P.M.A.
- A4WP
When buying a phone, you need to know which standard is supported in order to purchase a charger of the same standard. The standards are not compatible with each other.
The most common standard is Qi; it is implemented by many brands producing smartphones.
Qi standard
The standard was developed by the Wireless Power Consortium and is more widespread and implemented in devices by manufacturers of world brands:
- Samsung
- LG
- Motorola
- Huawei
- Sony
- Asus
and others.
On the official website you will find information about the standard and get acquainted with the list of devices using this standard. Many cafes, restaurants and other public places have Qi chargers that you can use for free to recharge your battery.
PMA standard
Similar to Qi, the standard applies the principle of electromagnetic induction. They are inferior in competition and have a smaller list of cooperating companies. The standard was developed by Powermat.
A4WP standard
Unlike the previous two standards, this one uses Rezence technology with a significant number of advantages:
- charges through obstacles (stack of papers, notepad, etc.),
- one platform can charge several gadgets,
- metal objects located nearby do not interfere with the operation of the device.
Having such advantages, it still remains unpopular.
How to use Qi charging
The phone models listed on the official website are equipped with a built-in knowledge base of the Qi standard. They are compatible with chargers with the “Qi” icon. To recharge the battery, the phone must be placed on a special platform, charging begins automatically.
Does the phone get hot?
The back of the device and the wireless charger become slightly warm, similar to when using a cable. Heating occurs at the point where energy is transferred. Therefore this should not be a cause for concern. You need to periodically check whether the device itself is heating up, which may indicate problems with the battery.
How to tell if your phone supports Qi wireless charging
You can find out on the official website of the developer. Find the Products tab, which contains a complete list of models that support this standard.
Are there any alternatives to wireless charging?
A few years ago, information flashed here and there about a new development capable of wirelessly charging not only a smartphone, but also other devices. At the same time, she had to do this at the same time. The idea was to install a pillar in the center of the room that could create a large field. Objects located in this field could work without wires.
There was also this: CES 2022: Wireless charging of almost any device
Considering that such a “breakthrough” invention never went into production, it’s worth thinking about why this happened. Most likely, the reasons included radiation hazardous to human health, significantly stronger than from the charging station, and high energy consumption.
On the second point, we can add that due to losses during the transfer of energy from the charger coil to the coil in the smartphone, electricity costs will increase. Considering small consumption, the difference will be several rubles per month. In larger installations, energy consumption will be significantly higher. Accordingly, losses at such distances will make you think about the feasibility of this idea.
Alternative to wireless charging - another wireless charging
There is no full-fledged alternative to wireless charging, but there are, so to speak, sub-alternatives. I'm talking about those cases when wireless charging is built into PowerBank, table lamps, cabinets and other furniture that can be bought even at IKEA. Only the price of such devices is often steep.
How powerful are wireless chargers?
Currently, the most common input and output power ratings are in the range of 5 to 20 watts. As a rule, developers do not hide the level of capabilities of their devices, openly talking about it at presentations or indicating data on the packaging of smartphones/tablets/headphones.
Sometimes voltage is indicated in volts and current in amperes. There is a simple and understandable formula for calculating the key indicator for us: power in watts is voltage in volts multiplied by current in amperes.
In this matter, you should know that with a sufficient level of input power, the device will be able to produce maximum output power. For example, the Belkin Boost Up Special Edition charger has a power of 7.5 Watts, and the Smaung EP-P5200 docking station has a power of 10 Watts. It is also important to take into account the factor that is supported by your mobile device (for the Galaxy S10 it is 10 W, for the iPhone X it is 7.5 W).
Qualitative characteristics of the device
If you have studied the question of how to use wireless charging for your phone, it doesn’t hurt to become familiar with its advantages and disadvantages, and its impact on human health. Armed with this knowledge, making the final decision will be much easier.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage is that you no longer have to connect wires to the smartphone itself, which often get lost, twisted, fall into the paws of pets, and are therefore seriously damaged.
Unfortunately, it’s still not possible to completely forget about wires. Wires are excluded only in relation to the smartphone, but the charger itself is still connected to the outlet using wires and an electrical plug.
Another drawback that can cause disappointment to the purchaser is the sufficient charging time of the mobile device.
If you decide to purchase such an innovative device, you will also have to be prepared for the fact that the cost of wireless charging is several times higher than its wired counterpart.
Health effects
Every working mechanism emits electromagnetic waves. A modern person who cares about his health is concerned with the question of how harmful such radiation is, and whether the risk of pathological changes in the body is eliminated when being in close proximity to a working wireless charger.
The alarm is quite understandable, since articles appear in the media from time to time in which they draw the reader’s attention to the dangers that modern technical means provoke. However, experts assure that these are nothing more than myths, since the danger to human health is completely excluded.
IMPORTANT. The electromagnetic waves involved in the wireless charging process are accompanied by a low frequency, so any negative impact on humans is excluded.
The same waves pass through a person every day, but technical progress has nothing to do with this. The sun emits exactly the same waves in strength and frequency.
In addition, it is important to understand that it is unlikely that anyone will constantly stand near the charger throughout its entire operating cycle. For this reason, engineers, doctors and other specialists confidently refute the myth regarding the harm of chargers to human health.