For reliable operation of electrical devices and household appliances, high-quality supply voltage is required. Due to the dilapidation of electrical networks, excess of the seasonal and average daily load of subscriber power lines, the voltage in the network drops to an unacceptable level. This leads to unstable operation or complete failure of consumers' electrical receivers.
Network voltage deviation standards
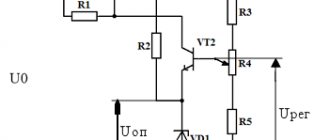
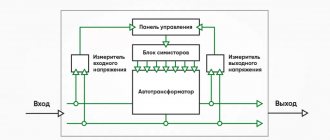
Relay voltage stabilizer device
The heart of any relay stabilizer is an ordinary autotransformer; we have already written about it in some detail; by clicking on the link you can find out what it is and how it works.
Now it’s worth saying that the autotransformer has several taps - taps from the winding, each of which forms a secondary winding, with a different transformation ratio of the incoming voltage. In this way, the voltage can increase or decrease, and we will look at how this works below.
In addition to the automatic transformer, another important part of any relay stabilizer is the control board. It contains a number of components and solutions, in particular a voltmeter that measures the incoming voltage and control circuits that are responsible for switching the stabilizer modes.
Power relays directly switch the corresponding taps of the secondary winding of the autotransformer with the output contacts of the stabilizer.
A relay is a kind of circuit breaker; based on a signal, it mechanically closes or opens an electrical circuit. Depending on the model of the device, the number of such relays - stabilization stages, as well as their type, may vary.
In addition to the above, any electronic relay stabilizer also has fuses, indicators and other components on board, but we will not describe them; their type and quantity can vary greatly depending on the model of a particular device.
Now, to better understand how it works, let's look at its diagram.
Description and structure of the inverter stabilizer
This advantage is achieved due to its specific structure, as well as a rather interesting operating principle. So, a classic invert stabilizer has:
- Several input filters.
- Voltage rectifier.
- Power corrector.
- Several capacitors.
- DC/DC converter.
- Microcontroller.
However, it is worth noting that voltage converters and rectifiers are inverters made on the basis of IGBT transistors. Thanks to them, high current values are converted to normal. At the same time, energy losses are very, very small.
Operating principle of a relay voltage stabilizer
First of all, the incoming voltage is measured in the stabilizer, then, depending on the results obtained, a signal is sent from the control board to open one or another relay, respectively, the electric current from one of the taps of the autotransformer, reduced or increased to the desired value, is supplied to the terminals of the stabilizer , to the consumer.
To fully understand the principle of operation of a relay stabilizer, you should definitely know about the operation of the autotransformer and its structure, if you have not yet read our article about it - now is the time to do so by following the link.
As an example of how a stabilizer works, let's assume that each tap of the autotransformer gives +/- 15 Volts of voltage change, it works as follows:
— If the voltage in the network is 220V , it is immediately transmitted to the consumer, the transformation ratio is 1. Accordingly, in the range from 205V to 235V (220V +/-15V), the voltage to the output of the stabilizer will be transmitted without changes.
— As soon as the incoming voltage drops to a value less than 205 Volts , the first secondary winding of the autotransformer is activated, with a transformation ratio of 1.075, thereby again producing 220 V (205 * 1.075) at the output. At this moment, the relay responsible for this tap of the autotransformer closes, releasing current to the output contacts of the stabilizer, and all others open.
Further, until the voltage drops another 15V i.e. up to 190V (205V-15V), this secondary winding will continue to operate with the same transformation ratio, thus, if the network voltage drops to 196V (switching limit to the next mode), the output is 211V (196 * 1.075).
— When the incoming voltage drops below 190V , the next relay is triggered, and the previous one opens, thereby turning on the next secondary winding of the automatic transformer, with a transformation ratio of 1.15 and the output voltage again becomes 220V (196 * 1.15) and so on, every 15V the winding switches to, say, 145V - after which the stabilizer goes into protection.
- If, on the contrary, the voltage in the network increases above 235V , using the appropriate relay, the step-down secondary winding is activated, with a transformation ratio of 0.94, and again the voltage in the network is equalized to the required 220V (235 * 0.94).
I think that now the principle of operation of a relay stabilizer is clear to you, now let’s look at what strengths and weaknesses a stabilizer of this type has, and in what areas it is best used.
Which one is better to choose?
To decide which voltage stabilizer is better, relay or electromechanical, you should know exactly the network parameters. To do this, you can use a tester and take a series of measurements. If the voltage changes quickly and frequently within a certain time, and the load is of such a type that this can damage it, then it is better to choose a relay stabilizer. Moreover, it is inexpensive. If the changes are minor and the load requires high precision, then an electromechanical stabilizer will be the best choice.
It is somewhat more difficult to decide which voltage stabilizer is better - relay or electronic? Their operating principle is the same, only the electronic one is more expensive. Operating conditions and reliability may be important here. To work in cold conditions, you need to prefer an electronic stabilizer, and if the electronics of the equipment are sensitive to the voltage form, then it is better to give preference to inverter or relay stabilizers.
Advantages
Low cost
It is precisely because of their low price, relative to other types of stabilizers, that relay models are so popular. At the same time, in other respects, they completely cover the needs of the modern consumer in most cases.
Quite fast stabilization speed, on average 5-30 ms
Relay stabilizers react to changes in incoming voltage at high speed, and allow you to protect your electrical equipment even during sudden drops or surges
Simplicity and maintainability
Possessing a simple, understandable architecture, relay stabilizers do not have a mass of complex components that could fail. There are not many possible problems and all of them have been studied and described, are easily diagnosed and can be corrected at home, even if you have only superficial knowledge and skills in electrical repair.
Application area
Due to their good speed of processing voltage changes and low cost, relay stabilizers are widely used as industrial and home stabilizers.
They are successfully used for the following techniques:
- Household devices – TVs, refrigerators;
- Lighting;
- Air conditioning and ventilation systems;
- Laboratory instruments;
- Water supply and heating systems;
- Office equipment;
- Medical equipment.
A sufficiently high response speed ensures imperceptible switching when the network voltage changes. The exception is LED lamps. Since, unlike incandescent lamps, they do not have inertia and light up instantly, flickering will be noticeable during the switching process of the relay stabilizer. In the sound-reproducing equipment, clicks will be heard when the relay is switched.
There are certain limitations in the use of relay stabilizers for medical equipment. Equipment used to support human life is connected to electronic stabilizers that have backup batteries - uninterruptible power supplies.
When choosing a stabilizer for your home, the question may arise: which stabilizer is better - relay or electronic? A relay device is much cheaper, and if network surges occur rarely and by small amounts, and there are no capricious electronic equipment in the house, then a relay stabilizer has the advantage. In other cases, despite the price, you need to choose an electronic stabilization system.
Flaws
When switching frequently, power relays fail
One of the most significant disadvantages of relay stabilizers, in my opinion, is the possibility of failure of power relays if mode switching occurs quite often and intensively. Contacts oxidize over time or can burn at high currents, which greatly reduces the service life of the relay.
Clicking when switching relays
Another feature that can become a serious drawback if the relay stabilizer is installed somewhere near you is the sound of the relay switching, which clicks quite loudly.
Relatively high stabilization error, on average about 5-8%
Depending on the number of taps from the autotransformer - secondary windings and, accordingly, the number of relays in the circuit, the relay stabilizer has a degree of stabilization error, on average 5-8%, and this is quite a lot. As you can see from the calculations presented above, the stages at which stabilization occurs are within 15 Volts, which is equal to 6.8% of 220V; particularly sensitive electrical appliances can react to such indicators.
If you require normalization with greater accuracy, be sure to consider electromechanical voltage stabilizers.
Short-term interruption of current supply at the moment of relay switching
When switching a relay, during a change of modes, for a very short time, the current supply is interrupted when the contacts of one relay are already broken, and the second is just closing. In this case, a surge or voltage surge often occurs. This can have a negative effect on particularly sensitive electronic components and can also be reflected, for example, in a short-term change in the brightness of the lamps.
Power drop at low voltage
Relay stabilizers produce the full power declared by the manufacturer only in a fairly narrow range of incoming voltages, often only up to 190 Volts, then the performance rapidly drops and at some point reaches only 40-50% of the nominal.
“Pure sine” and voltage holding accuracy
The classic relay stabilizer provides an accuracy of 5-7%,
Inverter – 1-2% and “pure sine”.
What to prefer in this or that case?
Let's try to figure it out with an example.
We know that currently gas boilers equipped with coolant circulation pumps are usually used for heating country houses. Circulation pumps were invented in 1929 and began to be widely used in domestic boilers in the 1950s. And all this time they worked perfectly with the “dirty sinus”, and a voltage retention accuracy of 5 - 7% was considered sufficient.
Relay stabilizers broadcast the network as it was 50 years ago, is and will be for at least the same number of years. And they provide 5-7 percent retention. That is, they provide the necessary and sufficient stabilization parameters.
As for inverter stabilizers, until 1933, when Kotelnikov’s theorem was proven, electronic inverters simply did not exist due to the lack of theoretical prerequisites, and then, until the advent of powerful and inexpensive field-effect transistors, they were very expensive.
Therefore, boiler manufacturers did not include network quality requirements in the operating regulations for their products (in all countries this is already stipulated by the standards for energy supply companies), stipulating only the operating and maximum voltages at which the boiler will operate for a long time.
The conclusion arises that to ensure reliable operation of a modern boiler, it is enough to have a classic relay stabilizer of appropriate power. And the presence of “pure sine” and an accuracy of 1 - 2% in inverter stabilizers does not add to the reliability of the equipment. These parameters of inverters in this case resemble an advertising ploy, as, for example, on the packaging of a detergent they write “20% - free.”
If it is necessary to protect precision measuring or medical equipment, these inverter parameters may be relevant.
Where are relay stabilizers used?
If we analyze all the pros and cons of a relay stabilizer, we can conclude that it can cope with most household tasks. Almost everywhere where precision stabilization is not required, but high speed is required, a relay stabilizer is simply irreplaceable.
In particular, relay stabilizers are actively purchased to equalize voltage in an apartment or country house, as well as in a garage. In addition, almost any household appliance that has a motor or heating element, for example, a refrigerator, washing machine, dishwasher, or power tool, works great with inexpensive and fast relay stabilizers.
When voltage drops or, conversely, power surges do not occur very often, but still happen during the day, for example, in a gardening community, where the voltage in the network often strongly depends on what your neighbors are doing at the moment, depending on this it can change rapidly, a relay stabilizer is the optimal solution.
If you have some kind of equipment that is sensitive to even the slightest voltage surges or electric current parameters, as well as to the accuracy of stabilization, for example, a high-quality audio amplifier, you should choose a different type of normalizer.
Rules for using the stabilizer
When you choose a relay type stabilizer, you must regularly maintain it, including annually thoroughly inspecting it inside the housing. When examining, you need to pay attention to:
- Reliability of fastening of conductor connections.
- The level of cooling and air circulation in the device body.
- Is there any damage?
- Accuracy of measurement indicators.
If weak connections or dust are detected, it is necessary to disconnect the stabilizer from the network and service it, cleaning it and tightening all contact fastenings. The room in which the voltage stabilizer is located must be ventilated and dry. The humidity in the room should not be more than 80%. When working in the stabilizer housing, the ventilation holes must have air access.
The best relay voltage stabilizers
Currently, there are quite a lot of players in the stabilizer market, large and small manufacturers, each with several lines of models, with different output power and functions, so it is not easy to name any specific successful products.
But of course, by studying the experience and reviews of our colleagues, suppliers and clients, we can identify several of the most optimal manufacturers in various categories of consumer properties, using the example of 5 kW - kVA models in particular:
ENTRY LEVEL
Of the most affordable, inexpensive , but at the same time quite high-quality relay voltage stabilizers, I advise you to take a closer look at the models of the following manufacturers: Resanta Quattro Elementi. These stabilizers are used especially successfully in the country house, garden plot or garage, as well as when powering household appliances or power tools.
Stabilizers from these manufacturers are often installed in apartments and cottages, boiler rooms and other places where reliability is important, both in stabilizing and protecting electrical appliances from the negative effects of poor-quality electrical current parameters.
Inexpensive and high-quality relay stabilizer RESANTA ACH-5000/1-C (~ 5400 rubles)
Quattro elementi stabilia 5000 - Another affordable relay stabilizer with good reviews (~6000 rubles)
MORE..
PRICE QUALITY
In terms of price/quality ratio , with an emphasis on reliability, quality and functions, such as a wider range of stabilization, additional protection and filters, the most interesting manufacturers of relay stabilizers, according to a large number of consumers, are: Energy and Rucelf of the following models:
One of the most successful models of relay stabilizers, combines affordable cost and high reliability RUCELF StAR-5000 (6500 rubles)
Energy ACH 5000 is a Russian-made relay stabilizer, in a compact, portable design, 7 stages of stabilization. (~7000 rubles)
ADVANCED MODELS
The most expensive and advanced relay stabilizers, with the maximum number of options, a high degree of stabilization and other high-level characteristics, which are designed for installation in more critical places that are demanding in terms of quality, reliability and accuracy of voltage parameters, for example, in production, in cafes, shops and etc. produced by manufacturers: Lider, Energy, Uniel
Energy Voltron 5000 is a professional high-quality relay voltage stabilizer, with very good characteristics and additional functions. (~9000 rubles)
Uniel-rs-1-5000ls - relay stabilizer with the widest stabilization range, high response speed, its characteristics are compared with ... (~ 12,000 rubles)
If you know other worthy manufacturers or successful models of relay stabilizers, be sure to write in the comments to the article. In addition, ask questions, and if you have comments or criticism, express them.
If you think that a relay device is not what you are looking for, be sure to study the features of stabilizers of other types and read reviews of models for different typical cases, all this and much more awaits you in upcoming articles, follow the release of new materials, subscribe to our VKontakte group.
What are the disadvantages of double conversion stabilizers?
Most often, one single drawback is indicated for these devices - the cost, which is indeed slightly higher than that of other types of stabilizers of similar power. However, you should understand that when buying a high-quality inverter stabilizer, you are paying for best-in-class technical characteristics. Undoubtedly, you can find a device cheaper, but it is unlikely to provide protection of a similar level, and, as you know, they do not skimp on security. In addition, repairing broken household appliances can be much more expensive than a one-time purchase of an inverter stabilizer, the service life of which is at least 10 years (for Shtil models).
Sometimes, when talking about the disadvantages of inverter stabilizers, they mention the noise that accompanies the operation of their forced cooling system. The rotation of the fans is indeed not silent, but their volume does not exceed the volume of sound emanating, for example, from a personal computer. In this situation, much depends on individual perception - if such a noise level causes discomfort, then a fan-cooled stabilizer should not be placed in the living room. Moreover, there are inverter stabilizers with natural (fanless) cooling - their power is quite enough to power electrical appliances used in such premises.
Note! Some manufacturers are just mastering the production of models of this type and produce rather “crude” products that have more disadvantages than indicated in this section!
Comparison of the main characteristics of different types of stabilizers
A comparison of the main technical characteristics of relay, electronic and inverter stabilizers is given in the table:
| Stabilizer type | Type of regulation | Reaction time, ms | Input voltage range, V | Output voltage stabilization accuracy, % | Network distortion correction | Input power factor correction | Autonomous load power supply, ms |
| Inverter | continuous | 0 | 90-310 | 2 | There is | There is | 200 |
| Relay | discrete | up to 20 | 160-260 | from 5 to 10 | No | No | — |
| Electronic | discrete | 5-20 | 130-270 | from 5 to 10 | No | No | — |
Note!
The technical characteristics of some voltage stabilizer models may differ from the values given in the above table.