Here we will talk about voltage stabilizers for apartments. If you live in a private house (in a cottage, in a country house), then you better read this article, since the electrical network in a countryside area still has its own specifics.
Before you start choosing a specific model, it would be nice to ask yourself the question: is a voltage stabilizer needed in the apartment? Maybe a surge protector or a voltage relay is enough?
Design and principle of operation of an electronic stabilizer
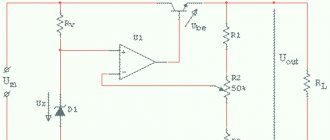
An electronic stabilizer usually consists of the following components:
- input and output voltage meters;
- a control chip that analyzes data from meters and, if necessary, turns on the voltage conversion process;
- transformer with the ability to switch windings to regulate voltage;
- a block of electronic keys (thyristors or triacs), which controls the switching of windings.
The operating principle of the electronic stabilizer can be described as follows:
When the voltage in the supply network changes, the difference between its actual and nominal value is recorded. The control microprocessor sends a signal to turn on a specific power switch that switches exactly that section of the transformer winding, the transformation ratio of which will provide the output voltage value closest to the nominal value.
The operating principle of electronic stabilizers is in many ways similar to the operation of relay-type devices. If in the latter the switching of the necessary windings of the autotransformer is carried out using electromechanical relays, then in electronic devices instead of them, power semiconductor switches - thyristors or triacs - are used, which are characterized by much higher speed.
Also, the design of the electronic stabilizer provides for operation in bypass mode - when the mains voltage is within normal limits, electricity is directed bypassing the transformer and directly supplied to the consumer.
Thus, electrical appliances are powered through an electronic voltage stabilizer as follows:
- If the parameters of the electric current correspond to the standard ones, it passes through the bypass without loading the main circuits of the stabilizer.
- If there is a drop or increase in voltage, the meter at the input of the stabilizer records this change.
- The stabilizer control chip issues the appropriate command and the electronic key unit is activated.
- The transformer windings are included in the circuit, which convert the voltages to the desired level.
High frequency transformer stabilizers
If these models are compared with the relay type, then the high-frequency voltage stabilizer has a more complex device and has more than two diodes. It has increased power.
The transformers in such a stabilizer are designed to withstand significant interference. As a result, such devices can protect various household devices in the house. The filter system is adjusted to different power surges and drops. Using voltage control, the current value can be changed. The value of the highest frequency in this case will increase at the input and decrease at the output. Changing the current in such a circuit is carried out in two stages.
- First of all, the transistor and output filter start working.
- Next, the diode bridge is connected to work.
- To complete the current changing process, the system needs an amplifier. It is most often mounted between resistors.
As a result, the temperature in the device is kept at the same level. The system additionally keeps track of the power source that affects the protective unit.
What is the difference between a triac and a thyristor stabilizer?
Electronic stabilizers can be built on the basis of thyristors or triacs.
| The principle of operation of a thyristor | The principle of operation of a triac |
| A thyristor is a semiconductor element that allows you to control the flow of current. It passes current in only one direction and has two states - “open” or “closed”. It can be controlled by applying a pulse to one of the inputs. In a stabilizer, a thyristor is used to connect the transformer winding. | A triac functions in a similar way to a thyristor. Its name is an abbreviation for the words “symmetrical thyristor”. The main difference from a thyristor is that a triac passes current in two directions. Therefore, in a triac stabilizer with the same parameters, you can use half as many electronic components. This makes it more compact and reliable. |
Clean entry
I wanted to get a clean input voltage as much as possible by clearing it of harmonics and eliminating all transients. The fact is that all stabilizers have some capacity between the input and output. Plus , interference can penetrate the output of the stabilizer through feedback circuits or a common wire. Therefore, at the input of the stabilizer we need to have the cleanest signal possible.
Sounds a little utopian? How to get a “clean” voltage at the stabilizer input? RC or LC filters can significantly reduce harmonics in the rectified voltage. What signal is considered clean enough?
Quite popular in tube amplifiers are rectifiers based on kenotrons , which, due to their design features, are asymmetrical, but nothing... these amplifiers sound!