To eliminate the possibility of damage to electrical wiring and ensure its reliable protection from the negative effects of the environment when laid in the ground or walls of a building, you should be concerned about the presence of a special casing, which can act as HDPE pipe. You can learn about the features of the product, its varieties, selection criteria and installation options from this article.
HDPE pipe is used to protect the power cable in the ground.
Choosing a cable brand for laying in the ground
To organize the power supply of a building, street, landscape or decorative lighting, you will need special cable products, which are most often laid in the ground. This method is the most reliable and aesthetic. The underground cable is protected from adverse external influences such as wind, frost, and ultraviolet rays. The cable brand is selected based on the type of soil, its corrosiveness and further operating conditions.
For underground installation, only special types of cable can be used.
Both armored cables and products without special protective cover can be laid underground. In the first case, the wiring does not need additional protection. The cost of an armored cable for laying in the ground will be an order of magnitude higher than a product without a protective sheath. When laying unarmored cables, as well as crossing a power route with a road or railway or other communications, it is necessary to use special protective structures.
This can be brickwork or concrete slabs, with the help of which special channels are created.
Concrete, asbestos-cement, ceramic or steel pipes are often used. The easiest to install are protective cases made of HDPE or PVC pipes for cables. On a note! If the distance between the supporting objects is small, then open laying of the cable through the air is also allowed (in the country house, or in the local area).
Characteristics of armored cable for laying in the ground
An armored power cable for laying in the ground is represented by a product whose conductive cores are located inside a metal armored sheath. It provides them with reliable protection from mechanical damage. Armored cable is produced in several brands. Belonging to a certain group is indicated by a letter abbreviation that reflects the type of material of the current-carrying conductors (TC), armor, screens and outer shell.
The armored cable is protected by a metal sheath.
Using digital identifiers, you can determine the number of fuel fluids, their cross-section and voltage. Based on the material of the current-carrying conductor, copper and aluminum armored cables (A) are produced. A layer of insulation made of polyvinyl chloride (B), polyethylene (Pv) or in the form of a polymer composition (P) is applied over the core.
Based on the material and type of armor, the cable comes with wire (K) or tape (P) armor, lead (SB), or steel (B) protection. The tape casing gives the product additional mechanical strength and moisture resistance. The steel tape is applied in two layers, eliminating the formation of gaps, creating a continuous armor layer. The wire braiding gives the product high flexibility, which reduces the risk of cable breakage due to ground movement.
The protective hose can be made of polyethylene (Шп) or PVC (Шв). The wall thickness is in the range of 1.7-3.1 mm. Plastic hoses are sealed along their entire length. There are no dents or cracks in their structure. The polyethylene shell is more moisture resistant. The protective hose protects the armor protection of the product from mechanical loads, moisture, and chemicals contained in the soil. For example, VBBShv 5x10 is an armored cable for laying in the ground with PVC insulation, armor made of galvanized steel tapes without a cushion with a polyvinyl chloride sheath, has 5 copper cores with a cross-section of 10 mm².
The type of armored cable is selected based on operating conditions. When installing cable products in soils with a high content of aggressive chemicals, in areas exposed to electrocorrosion, preference should be given to products with aluminum protection or lead armor. In areas of soil subsidence or areas with strong mechanical impact, products with wire armor protection should be used. For standard operating conditions, an armored cable for laying in the ground 4x10 with an armor braid made of steel tapes will be sufficient.
There are many types of armored cables.
Using aluminum or copper armored cable
Aluminum or copper armored cable for laying in the ground is laid in a trench to a depth of no more than 70-80 cm. When installing several power lines, certain conditions must be observed. For cable products with a power of up to 10 kW, adjacent lines must be at a distance of more than 10 cm, and with a power of 20-35 kW - at least 25 cm.
Note! When installing an armored cable, it is grounded.
Laying the armored cable in the ground is carried out in the following sequence:
- preparing the trench according to the planned route plan;
- leveling and compacting the bottom of the trench, followed by pouring a layer of sand 10 cm high, which must be cleared of any large impurities that could cause damage to the integrity of the cable sheath;
- leveling the surface of the sand cushion;
- checking the cable for integrity;
- free laying of power threads on a sand cushion without tension, so as not to provoke the appearance of tensile forces during possible soil displacement;
- checking the cable line for the absence of short circuits, which is carried out between current-carrying conductors, TC and armor;
Aluminum or copper armored cable is laid to a depth of up to 80 cm.
- backfilling the cable with a layer of sand 10 cm thick and then compacting it;
- backfilling the trench with soil to a height of 15-20 cm;
- laying warning polymer tape with the inscription “Caution cable”;
- final filling of the trench with soil with the formation of a small slide, which will eliminate the formation of failures in the process of soil subsidence;
- performing a control check for short circuit of current-carrying conductors to the ground.
HDPE pipe: what is it, abbreviation explanation
When laying an electrical cable without armor in the ground or wall of a building, it is necessary to ensure its integrity and protection from mechanical and chemical damage. For this purpose, it is placed in a special tube-shaped case. Previously, concrete or metal products were often used. They significantly complicated the process of installing power lines. This is primarily due to the significant weight of the products. The metal casing is prone to corrosion. When welding individual sections of the pipe, scale formed on the inner surface, which could damage the cable.
However, progress does not stand still. And today HDPE pipes are used for laying cables. What kind of pipe is this? Low-pressure polyethylene technical pipes are manufactured by extrusion at industrial enterprises, where the quality of the product is immediately controlled automatically, and then it undergoes additional control by specialists to identify possible defects.
Double-walled HDPE pipe for installation of electrical cables.
Two grades of polyethylene are used as raw materials: LDPE and MDPE. They contain a fire retardant, which makes the products resistant to fire. The structure of the material must be smooth, without cracks, swelling, sagging or other defects.
Some manufacturers produce electrical PE/HDPE pipes for cable laying from recycled materials, which reduces the cost of production. For their production, polyethylene crumbs are used, which is obtained after processing rubble waste, followed by crushing the resulting mass into a small fraction. This production feature does not affect the quality of technical pipes, but has a positive impact on environmental protection.
HDPE pipe: it is a protective case for the electrical cable
Technical HDPE pipes for cables are distinguished by strength, elasticity, frost resistance, resistance to chemical environments, the ability to bend without loss of performance, restore linear dimension, withstand significant mechanical and vibration loads, and temperature changes. The material is environmentally friendly and does not contain harmful impurities. The pipes are also light in weight and have a low price. Laying cables in the ground using a polyethylene sheath is quick and easy. A distinctive feature of the product is its black color. There are also gray options.
Note! The presence of white streaks on the pipe indicates a high content of high-density polyethylene in the composition of the material, which reduces the rigidity of the products. It is not recommended to use such pipes for laying communications.
The HDPE pipe acts as a protective casing for the cable.
The material is a dielectric, and therefore does not require grounding. The products have a smooth inner surface and uniform wall thickness, which facilitates easy and quick tightening of cable products inside the product. Individual sections are connected to each other by welding. The service life of such a casing is at least 50 years.
The operating temperature of the products ranges from -25 to 70°C. The density of polyethylene is 0.949-0.953 g/cm³. The working pressure of the material is determined by the type of pipe and is 0.25 MPa for light products, 0.4 MPa for medium-light, 0.6 MPa for medium and 1 MPa for heavy pipes. The coefficient of thermal expansion is 0.15-0.2 mm/mK. HDPE pipes belong to flammability classes B1 and B2.
Advantages and disadvantages
HDPE pipes for cable protection have the following advantages:
- Light weight compared to metal hoses.
- Good electrical insulating properties.
- Resistant to chemicals.
- High degree of wear resistance.
- Ability to withstand prolonged contact with an aggressive environment.
- Low thermal conductivity, due to which condensation does not form.
- Frost resistance. Pipes do not collapse when water freezes in them.
- Affordable price. For electrical work, pipes made from recycled materials are used, the cost of which is 30–50% lower than products made from primary polymer granules.
- Elasticity. It can be bent in difficult areas without using shaped parts.
- The smoothness of the inner walls makes it easy to pull the cable through.
- Sufficient rigidity.
- Bacteriological resistance.
- Resistance to mechanical damage and vibration loads.
- Low coefficient of linear expansion.
- Resistance to temperature changes.
Disadvantages include the ability of HDPE pipes to support and spread combustion. Therefore, they must be embedded inside fire-resistant materials, such as concrete screed, cement mortar, or laid in the ground.
Reasons for the demand for HDPE pipes for laying cables in the ground
HDPE pipes are used as a protective casing for power supply, telephony, video surveillance, computer networks, control, fire and emergency alarm lines, which can be laid in an open, semi-hidden or hidden way. The case in the form of a HDPE pipe provides reliable protection of cable products from various mechanical and chemical influences. It also eliminates the possibility of electric shock in the event of damage to the network insulation and fire due to a short circuit. Thanks to the special design with a smooth inner surface, easy pulling of all types of cables into the pipe cavity is ensured.
HDPE pipes for cables in the ground are lightweight, which simplifies their transportation and installation. They are not susceptible to corrosion and the influence of other negative factors, so they do not need to create special conditions for storing products. Due to the elasticity of the material and bendability, PE technical pipes can be laid along any trajectory without the use of additional connecting elements, without losing the integrity of the structure.
HDPE pipes have numerous advantages of use.
Note! HDPE pipes should not be bent too much, as kinks may appear on the products, which will complicate further installation.
HDPE pipes do not conduct electric current, therefore they do not require grounding or cathodic protection devices. The products are able to withstand a wide range of temperatures without loss of technical and operational qualities. They do not accumulate condensation on the surface, due to low thermal conductivity, and do not emit harmful substances.
What types of products can be used to protect wires?
On the building materials market you can find all kinds of products that are suitable for laying utility lines in the ground. These can be not only HDPE collectors, but also PVC, asbestos or asbestos-cement, steel pipes. However, most often polyethylene materials are used to protect wires and power lines underground.
HDPE pipes (pipe for cable in the ground) come in several types:
- Corrugated light or heavy
- Hard with a smooth shell
- Double-layer (with 2 walls)
- Halogen-free.
The main types of pipes that can be used in the ground.
Collectors representing one type or another are designed for specific purposes. For example, products with double walls can be used for underground wiring, one of which is corrugated, and the second is a LDPE sheath. Corrugated pipe is not suitable for laying cables in the ground. Even though it is characterized by increased elasticity and strength.
If you need an HDPE pipe for underground cables, consider the purpose of its further use and technical characteristics. Thus, corrugated material is suitable for hidden electrical wires in rooms. Usually these are highways that are created during the arrangement of houses and run into the walls or ceiling. The most durable DSK corrugated collectors can even be used in the construction of a utility network in the floor (for pouring concrete or cement).
Depending on the number of cables in the intended network, the pipe may have different diameters. For example, if 2-3 wires with a cross-section of 95 mm² are laid, a product with an internal diameter of 63 mm can be used. They are sold in 15 m coils or in separate sections.
If it is necessary to lay a line of 2-5 cables with a cross-section of 25 mm² each, you can use collectors with an internal hole of 32, 40 or 50 mm, etc. Some manufacturers offer HDPE manifolds with large diameters ranging from 160 mm to 250 mm. Such materials are sold in 12 m lengths or 100 m (200 m) coils.
Types of HDPE pipes for laying cables in the ground
Manufacturers produce HDPE pipes in two variations: smooth and with a corrugated wall. They differ in individual technical characteristics and the possibility of installation under certain conditions.
Smooth technical HDPE pipes for cables have a rigid structure and high mechanical strength. They are black in color. Such pipes are produced in two variations: single-layer reinforced and two-layer unreinforced. The first option is used for laying cable products in concrete and brick structures, floor screeds. Double-layer reinforced pipes can be used in more difficult conditions.
Smooth pipe made of low pressure polyethylene.
Note! When making transitions and turns in cable ducts made of smooth HDPE pipes, special fittings should be used.
Corrugated HDPE pipes for cables can be used for both underground and above-ground installation of communications. They have two-layer walls, the inner layer of which is made of LDPE and has a smooth surface, and the outer layer is made of HDPE and has a corrugated structure. Such pipes have good flexibility, the ability to withstand significant loads, and the ability to lay them at different depths and curved sections.
Labeling of polyethylene products
Pipe marking is one of the methods for monitoring compliance of the quality of the product and its performance characteristics with the data given in the documentation. A quality mark must be applied to the polyethylene pipe. It shows that all standard requirements have been met. In addition, the trademark or full name of the manufacturer is indicated.
The pipe is marked with a code and number of the national or international standard according to which it is manufactured. The following is information about the material of the product. Marking of pipes made of PE 63; PE 80 and PE 100 are carried out as MRS 6.3; 8 and 10.
Note! Mandatory marking parameters are the minimum wall thickness and outer diameter size. The nominal pressure is also indicated on the pipe, which is expressed in bars. Nominal pressure is the medium pressure that can withstand the product at +20 °C for long-term operation.
The marking may separately indicate the possibility of using gas pipes and pipes intended for carrying drinking water. The batch number and release date of the product are provided separately.
According to standards, a pipe can belong to one of six classes: heavy (T), medium-heavy (ST), medium-light (OS), medium (S), medium-light (SL), light (L).
Each pipe is marked with a marking that indicates the purpose of the product and its other important parameters.
Types of corrugated pipes for laying cables in the ground
Corrugated pipes, based on their ability to withstand external pressure, are divided into light, medium and heavy. The first option has high elasticity and the ability to bend without compromising the integrity of the product. Such pipes are used when laying electrical networks with a power not exceeding 1 kW. This could be television and telephone lines, household electrical equipment. Heavy corrugated pipes are additionally equipped with reinforcing mesh, due to which they are heavy and less flexible.
There are also halogen-free pipes that have increased fire protection. They do not emit hazardous compounds into the atmosphere even when exposed to open fire for a long time. Such products have the ability to self-extinguish. They are most often used for laying cables inside a building.
Corrugated pipes are divided into light, medium and heavy.
Based on the installation method, corrugated HDPE pipes can be with or without a cable pulling probe. The first option is more expensive. Such pipes make it easy and quick to pull the cable inside the product. Options without a probe provide more labor-intensive installation of cable products, which will require a special pulling mechanism.
HDPE pipes are painted in different colors depending on their purpose. Red products are used for high-voltage routes. Blue pipes are intended for laying telecommunications and communication lines, while black pipes are characterized by versatility.
HDPE pipe for cable: selection criteria
The main criterion when choosing HDPE pipes for cables is the throughput of the product. The value of the internal diameter of the pipe must correspond to the total cross-sectional area of the cable products that will be laid in its internal cavity. According to GOST, technical HDPE pipe is produced with a diameter of 16-225 mm with a wall thickness of 2-30 mm. Products with a cross section of up to 90 mm are produced in coils of 100 or 200 mm. Larger diameter pipes are manufactured in 12 m long sections.
On a note ! No more than 4 cables can be installed simultaneously in one HDPE pipe.
HDPE pipe with a probe for cable pulling.
The next important criterion is the strength of the product. Pipes with a small value are used for laying cables inside the building, and with a large value - underground. You can calculate the strength indicator yourself by determining the SDR parameter. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the ratio of the outer diameter to the pipe wall thickness. The lower this indicator, the higher the strength characteristics of the pipe.
Each factory product is marked with a marking that identifies the characteristics of the pipe, such as the name of the manufacturer, material of manufacture, SDR parameter, diameter, wall thickness, operating pressure, production standard, purpose and date of manufacture.
Cable corrugation, sizes, prices
Corrugated pipes for electrical networks are available in sizes from 16 mm to 65 mm. When choosing a size, you need to take into account that these products have two diameters - outer and inner. If you are going to lay several conductors - wires or cables - the diameter must be selected so that there is a clearance of at least half the radius. This requirement is based on the fact that when installed in groups (it is necessary, by the way, to take a special cable), it will heat up more and the presence of an air gap will contribute to better heat dissipation.
The price of corrugated electrical pipes depends on many factors
Size selection
The choice of corrugation diameter also depends on the area where it will be laid:
- for lighting fixtures - 16 mm;
- to sockets and switches - at least 20 mm;
- from the main distribution box to the next box, from the shield - at least 25 mm;
- the connection between two electrical panels is at least 32 mm, and it is better to have a spare second line;
- passage through the floors with rigid corrugation of at least 40 mm in diameter;
- laying low-current cables (telephone, internet, antenna, etc.) - from 25 mm.
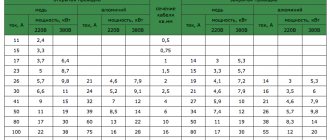
The diameter of the corrugation for laying the cable is selected depending on the number and cross-section of wires. Data for copper conductors are given in the table.
Table for choosing the diameter of the corrugation for cables and wires depending on the cross-section and number of wires
This information is for reference only, but you can use it as a guide. You can take a larger, but not smaller diameter.
Prices
Generally speaking, the cheapest is PVC cable corrugation, in the middle range - PP and HDPE, and the most expensive is metal corrugation. Moreover, the option with broaching is slightly more expensive than without it
When purchasing, you need to pay attention to the same wall thickness and color uniformity
Different materials, colors, wall thicknesses and different prices
Corrugated cables are sold in coils of 50 and 100 meters, less often you can find them in meters, but the price is then a little higher. In general, the price depends not only on the material, but also on the wall thickness. The cheapest is lightweight PVC corrugated cable, but sometimes it looks more like just a film. It’s hard to say what this can protect against. If you care about quality, it is better to purchase everything related to electrical equipment not in construction supermarkets like Leroy, etc. and in specialized ones. The quality there is usually better, and the prices, if higher, are reasonable. To give you an idea of the possible price range, we will summarize several types of corrugation with brief technical characteristics in the table.
| Name | Type | External diameter | Inner diameter | Broach | Price per meter | IP | Purpose |
| PVC corrugation | light | 16 mm | 11.4 mm | Yes | 2.4 RUR | ||
| Black corrugated HDPE pipe | DKS | 15.7 mm | 11.3 mm | Yes | from 7.5 rub/m | 55 | for hidden installation |
| Black corrugated HDPE pipe | DKS | 19.5 mm | 14.5 mm | Yes | from 8.9 rub/m | 55 | for hidden wiring |
| HDPE red double-wall pipe | tough | 50 mm | 41.5 mm | Yes | 78.5 rub/m | 44 | for hidden installation |
| HDPE pipe is heavy | heavy | 31 mm | 23.4 mm | Yes | from 9.7 rub/m | 55 | hidden gasket |
| PPL (polypropylene) corrugated pipe | light | 19.7 mm | 14.8 mm | Yes | from 28 rub/m | 55 | open, hidden gasket |
| Corrugated pipe polyamide | black | 21.2 mm | 16.8 mm | No | from 52 rub/m | 68 | open, hidden gasket, UV resistant |
| Corrugated pipe polyamide | gray | 21.2 mm | 16.8 mm | Yes | from 48 rub/m | 68 | open, hidden gasket |
Options for laying HDPE pipes for cable laying
Laying the cable underground in a HDPE pipe can be done above-ground or underground, or inside the building.
Regardless of the method of laying the protective casing, there are certain installation rules:
- The ambient temperature must not be lower than -30°C;
- if the cable depth is more than 2 m, a concrete channel with a wall thickness of 80-100 mm is provided;
- butt joints must be airtight; for this purpose, compression couplings, press fittings or butt welding are used;
- cables of different networks should not be located in the cavity of one channel;
Cables from different networks are placed in separate channels.
- It is prohibited to bend the pipe at an acute angle, this can lead to a break in the product;
- the length of the section between the boxes should not be more than 25 m;
- when laying cables in an open way outside the building, it is necessary to use black HDPE corrugation, which is resistant to ultraviolet radiation;
- To drain condensate, the pipe must be laid with an inclination towards the duct boxes, where moisture will collect.
Cable laying in HDPE pipe inside the building is carried out in the following sequence:
- marking the cable route;
- creating grooves in the enclosing elements of the room (if necessary);
- fastening the pipe to the building envelope. When laying along walls or along the ceiling, special holders with latches are used. Fastening to the ceiling is carried out using metal brackets;
- connecting pipeline sections;
- sealing holes. For wide and deep channels, cement mortar is used. To seal small holes, you can use plaster;
- pulling cable communications inside the channel, which must be in a free state without tension.
HDPE pipes for cable laying are placed in pre-dug trenches.
Laying pipes inside buildings
Usually, when installing hidden wiring, a smooth or corrugated pipe is used for the cable - this is not prohibited by technical standards or GOSTs.
For wall mounting, it is most convenient to use smooth pipes; for flooring, corrugated ones.
The principle and sequence of actions are given below.
- The required location is marked.
- Fixation is carried out, in the wall with clamps, in the floor with metal brackets.
- The wire is pulled using a special probe or a homemade broach.
- Next, the floor screed is poured or the groove in the wall is closed.
Important! When installing the wiring, tension on the cables is not allowed; you need to give a little slack to allow shrinkage.
It is also recommended to use corrugated HDPE pipes in segments with bends of more than 65⁰ - this will avoid refraction of the structure, and the cable will be in the pipe without additional load.
External cable laying in a pipe in the ground
Laying the cable in the ground in a corrugated cable is best done in a closed way with the construction of a trench in the ground. This option has more advantages compared to the installation of air routes. The cable in the ground will be reliably protected from precipitation, ultraviolet rays, temperature changes, wind loads and other adverse factors. In addition, it will be inaccessible to thieves of non-ferrous metals.
Note! Before starting work, you should inspect the cable for the integrity of its sheath.
The process of laying cables in a trench is carried out in the following sequence:
- marking for the future trench;
- excavation of soil to the required depth;
- compacting the bottom of the trench with the arrangement of a sand cushion 10-15 cm thick;
- laying HDPE pipes;
- joining sections using resistance welding. The use of fittings is not allowed, since the integrity of the route may be compromised;
- pulling cable products inside the pipe without tension using metal wire or a special nylon broach;
- filling the case with a layer of sand 10-20 cm thick;
- backfilling the trench with soil.
On a note! To make it easier to find an already laid route in the future, it is recommended to install signal posts above it.
Only intact pipes are suitable for use, without any damage or kinks.
Nuances and features
Laying cables in the ground is a labor-intensive process. It takes a lot to dig a trench, and then carrying the cable is also not easy. Burying is a little easier, but also not the most pleasant experience. If after a couple of years the insulation becomes leaky, you will have to repeat everything again, which will not make anyone happy. It’s clear that it’s better to do everything once and more reliably. The fact is that you can lay the cable in a trench without a protective sheath. This will not contradict the norm. And if you install a high-quality armored cable, it will last a long time.
For greater reliability, it is advisable to lay the cable in double-walled special corrugation or asbestos-cement pipes
But if you are laying a regular VVG or NYM, for greater reliability, it is better to lay it in a double-walled corrugated hose DKS along its entire length. In the right places, you additionally put on cases made of stiffer pipes or the same booster tube but of a larger diameter. Asbestos-cement or plastic thick-walled pipes are also often used. When laying the cable in this way in the ground, the risk of its premature failure is much lower - most of the loads fall on the pipes, and not on the protective sheath and conductors.
Laying the cable in the ground in plastic or asbestos-cement pipes or corrugated hoses has one more advantage: there is a high probability that, if necessary, it can be replaced by simply tightening it in place of the old one. The new one is tied to the old one, the old one is pulled out, and the new one “crawls” in its place. But this is not always possible: over time, both the pipe and the corrugated hose can collapse - the effects of ice and soil loads contribute to the destruction of the protective shells.
This is what a cable not intended for laying in the ground may look like after a few years.
From all this it follows that although laying cables in paper insulation does not contradict the standards, it is better to use plastic insulation - PVC or cross-linked polyethylene. Paper, even with special impregnations, deteriorates much faster than polymers, which brings the replacement period closer. Laying cables in the ground still requires significant effort and labor, so it is better to lay more durable materials.
How to join two pieces
It is more reliable to lay the cable in the ground in whole pieces - without connections. If one piece of the required length cannot be found, to connect, bring both parts to the surface, place a sealed mounting box and connect the conductors in it. It’s not worth making couplings without experience and special equipment, or burying them underground - they will quickly fail and will have to be dug up and remade. And a serviceable connection is always convenient - you can reconnect the contacts if you need to.
This is what a normally made coupling looks like
How to enter the house
When entering a house, bathhouse, outbuilding, passing the cable under the foundation is unacceptable. Even if it is a shallow strip foundation. In general, when pouring the tape to enter the cable into the house, mortgages are embedded in it. This is a piece of pipe that protrudes a few centimeters beyond the foundation. The cable is inserted into it.
The cross-section of this embed should be 4 times larger than the cable cross-section. And to prevent living creatures from getting into the remaining gap, after laying the mortgage is sealed. To seal, you can use the old-fashioned method - a rag soaked in cement milk, or fill everything with polyurethane foam.
Entry of underground power cable through the foundation
If a mortgage was not made during construction, you will have to drill a hole in the foundation, insert and seal a pipe. Further, all the technology is the same.
Another option: raise the cable in a metal pipe to a certain height along the wall of the house. They usually raise it to the level where the introductory cabinet hangs. At this height, install a mortgage in the wall (the same metal pipe with the same parameters and rules) and lead the cable into the house through it. This method is suitable if your foundation is a monolithic slab or you simply don’t want to disturb the solidity of the tape.
How to introduce an underground cable into a house through a wall
When using an armored cable, the armor must be grounded. To do this, a wire in a sheath is welded/soldered to the armor, it is in the shield. If this is not done, when the phase breaks through, it will most likely end up on the armor. If someone touches the armor, at best they will receive an electrical injury, at worst they may die. If the protective metal shell is grounded (or rather, zeroed), the breakdown will trigger the machine, which will turn off the power until the causes are identified and eliminated.
If there are several cables
If several cables are laid underground at the same time, the distance between them should be at least 10 cm. If you decide to lay them in pipes or corrugated hoses, a separate one for each.
If there are several cables, they are placed each in its own sheath or simply placed in parallel at a distance of 10-15 cm from one another
How to tighten into a corrugation or pipe
There are two types of corrugations for underground cable laying - with and without a probe. It's easier to take with a probe. This is a thin wire to which the wiring is tied to tighten it inside. The wire is pulled out and the cable is tightened in its place. It's simple.
Cable laying in the ground: corrugated HDPE pipe with a probe for easier pulling
Read also: Voltmeter measuring mechanism system
If the pipe or corrugation does not have a probe, problems may arise. If the cable is stiff enough, you can simply tuck it inside. This is usually not difficult, but can take quite a lot of time.
This trick will not work with a soft conductor - it will twist and cling to the walls. But in this case, too, there is a way out. First, string or thin rope is threaded into the pipe. A cable is tied to it and pulled inside.
How to thread the twine? Using a vacuum cleaner. Fix one edge of the twine well, and lay the rest in an unfolded form, but without lumps or loops, in the pipe. On the other side, connect the vacuum cleaner, close the second inlet. By creating a rarefied atmosphere, the string flies out from the other side.
Trenchless cable laying in the ground in a HDPE pipe
In cramped areas where it is not possible to dig a trench, a trenchless method of laying power cables in the ground is used. For this, special equipment is used to drill the soil in a horizontal direction. The cost of laying a cable in the ground per linear meter will be 1.5-2 times higher than the cost of trench laying communications, and starts from 350 rubles.
Work begins with drilling a so-called “pilot” well using a special tip. It is mounted on a flexible rod, which allows it to overcome natural obstacles in the ground. To control the trajectory of movement and correct its direction, the tip has a navigation device and cooling holes. Simultaneously with drilling, a concrete solution is supplied, which cools the tool, strengthens the walls of the channel, protecting it from collapse, and reduces the friction force that occurs when pulling through the line of communications.
Next, the well is expanded using a trimmer, which is installed in place of the drill head. Then the pipe is pulled into which the cable products are first inserted. The structure is attached to a special rod of the HDD installation, with the help of which it is pulled through the well.
The use of HDPE pipes for cable products is a reliable, convenient and cheap option for laying power communications. With the right choice of products and compliance with all installation rules, you will be able to obtain a safe and durable wiring that will not be influenced by many external factors.
Areas of application
The use of HDPE pipes in the agricultural industry and when drilling wells has its own characteristics, so you should not stop your attention on this. It is much more important to understand how polyethylene pipes can be used in private houses and apartments. The use of polyethylene pipes is largely due to a number of positive qualities inherent in them, including:
The use of polyethylene pipes is largely due to a number of positive qualities inherent in them, including:
- High mechanical strength, due to which the reliability of the design is achieved;
- Elasticity, which also has a positive effect on the reliability and durability of pipes;
- Excellent resistance to most aggressive chemicals;
- Complete resistance to electricity.
Installation of HDPE pipelines is carried out in different ways, depending on what kind of system needs to be created.
Electrical lines
When installing electrical networks, you can use both smooth and corrugated pipes - the effectiveness of wire protection does not depend on this. In any case, HDPE pipes are excellent for laying cables due to their excellent flexibility and zero conductivity of electricity.
The possibilities for using pipes for electrical installation are quite extensive: if necessary, installation can be carried out in open space, inside walls or underground (read: “Types of HDPE pipes for cables in the ground - which ones are best to use and how to install them”). In the latter case, high-quality and tight pipe connections come to the fore.
To achieve reliable joining of HDPE pipes, you can use two methods:
- Welding individual parts of the pipe directly or using couplings;
- Hot pipe casing (the pipe is heated and forcefully inserted into the socket, resulting in a tight connection).
Water pipes
You can lay water pipes from HDPE pipes with your own hands using various devices and methods:
- Compression fittings;
- Fittings for diffuse welding;
- Butt welding;
- Electrofusion connection.
The choice of a suitable method depends on the requirements for the future system and the available equipment.