General information about crane motors
Application area of crane motors
Crane (or, as they are also called, crane-metallurgical) electric motors are widely used in the construction, energy, mining and metallurgical industries. The main purpose of crane electric motors is to ensure reliable operation of the drive of cranes and other mechanisms operating in short-term and intermittent modes, as well as to drive mechanisms operating with frequent starts and electric braking (tower, portal, gantry, bridge cranes, elevators and various lifting mechanisms).
Design of crane electric motors
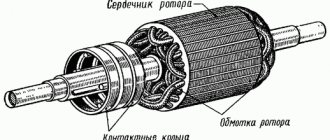
Crane electric motors of the MT series (MTF, MTH, MTI) are manufactured with a wound rotor, electric motors of the MTK series (MTKF, MTKH, MTKI) are manufactured with a squirrel-cage rotor. The range of crane electric motors (with squirrel cage and wound rotors) includes more than 80 standard sizes with rotation axis heights from 112 to 280 mm. All crane electric motors are manufactured as standard for temperate climates (climatic modification U1), and also, at the customer’s request, can be manufactured for operation in tropical climates (climatic modification T1) and for work in northern latitudes (version UHL). Due to their design features, all crane electric motors are capable of operating in “hot” shops of metallurgical plants. The crane motors are cooled using external airflow (IC 0141). The standard degree of protection of crane electric motors is IP44, the degree of protection of the terminal box and hatch of the slip rings of electric motors is IP 54.
Operating conditions for crane engines
The values of environmental climatic factors for normal operation of crane electric motors are regulated by GOST 15150 and GOST 15543.1 for various types of climatic modifications:
- the upper value of the operating temperature of the ambient air is not higher than 50°C, the lower value of the operating temperature: for U1 – not lower than 45°C; for UHL1 – not lower than 60°C; for T1 – not lower than 1°C.
- relative ambient humidity: for climatic versions U1, UHL1 - 80% at 15°C; for climatic versions T1, O1 - 80% at 27°C.
Crane electric motors are designed for operation in the following conditions:
- altitude above sea level – no higher than 1000 m.
- the environment is not explosive, does not contain live dust, aggressive gases and vapors in concentrations that destroy metals and insulation.
- dust content value - up to 100 mg/m3.
Features and purpose
Crane electric motors should be understood as electric drive units that move various mechanisms of crane installations. When considering lifting cranes as a component mechanism consisting of various components, the purpose of electric crane machines has several directions:
- Moving the crane installation itself along rails;
- Movement of crane installations in a vertical plane;
- Rotation of crane elements;
- Movement of lifting mechanisms to move the hook.
All manipulations with the load are carried out over a short-term period, therefore the operation of the crane electric motor must be carried out in intermittent modes, in which case the rotation speed range changes significantly. Because of this, they do not have to make long-term efforts, but the unit undergoes short-term loads and the effects of inrush currents. In addition to standard situations, the windings can be subject to overloads and overheating, therefore mechanism drives are manufactured with the following features:
- In most cases, these are closed-type electrical machines; the outer casing allows them to be protected from mechanical influences during operation. For metallurgical units, exceptions may be made, since the increased temperature makes it necessary to ventilate the windings.
- General industrial electric motors have improved insulation in terms of resistance to high temperatures, usually classes F and H. This allows the insulation resistance level to be maintained when it is heated.
- Relatively low shaft inertia, which reduces electrical energy losses during transient processes at operating frequencies.
- The magnetic system has good conductivity, which creates a powerful flow that can overcome serious load forces.
- A high level of overload relative to the rated operating currents is allowed. The coefficient can reach from 2 to 5, which is considered normal for a crane electric motor.
- Large spread of rotation speeds between minimum and maximum modes.
Some requirements for crane electric motors may be eliminated due to the peculiarities of operating modes and technical processes. And some types of specialization will be dictated by the type and design of the motor.
EXAMPLE OF DESIGNATION FOR CRANE ELECTRIC MOTOR TYPE 1:
- MT, AMT, DMT – series name
- K – rotor type, squirrel-cage rotor, absence of letter – wound rotor
- F - temperature index 155°C
Connection diagram for a wound rotor motor, time functions.
The connection diagram for a wound-rotor motor is shown in Figure 1. This circuit uses a time function control and a two-stage starting resistor. By turning on the QF circuit breaker, voltage is supplied to the control and power circuit. This leads to the activation of time relays KT1, KT2 which open their contacts. By pressing the SB1 “Start” button, the KM3 magnetic starter is connected, which: opens the contacts:
- KM3.3 - removes voltage from time relay KT1, which, after the end of the time delay, opens its contacts KT1.
closes contacts:
- KM3.1 in the stator circuit - the engine starts with two resistor stages connected to the rotor circuit, since the contactors KM1 and KM2 do not receive power. Before the time delay CT1 expires.
- KM3.2 - bypasses the “Start” button (allows you not to hold the SB1 button pressed)
- KM3.4 - in the circuit of coils of magnetic starters KM1 and KM2, but until the end of the time delay KT1, the starters KM1 and KM2 do not receive power.
Figure 1.1 GIF - animation of the operating diagram for starting an asynchronous motor with a wound rotor
For ease of viewing, all animation frames are posted at the end of the article.
After the dwell time has expired, KT1 is triggered and closes its contacts - current flows through the KM1 coil, the starter is triggered and bypasses the first stage of the starting resistor R. At the same time, KM1.1 de-energizes time relay KT2 with its normally closed contacts. Until the end of the time delay KT2, the engine accelerates only with the second stage of resistance. After the end of the holding time, the resistor is completely bypassed and the engine returns to its natural mechanical characteristic. The launch is over.
A crane electric motor is used to lift loads to different heights. Its peculiarity is that it is designed to operate in frequent starts. An ordinary engine, even a fairly powerful one, under such conditions overheats greatly and fails.
The crane's electric motor operates at 380 volts, although there are options for other power supply values. As a rule, these are three-phase asynchronous devices with a wound rotor, regulated using resistances. In some models of taps, instead of resistors, thyristor regulators with horizontal control of the opening angle are installed. Such schemes allow for a smooth start, which eliminates jerks and jolts, and also makes working with the crane more comfortable and safe. DC motors can be used for the same purposes.
EXAMPLE OF DESIGNATION FOR CRANE ELECTRIC MOTOR TYPE 2:
- MT, AMT, DMT, 4MTM – series name
- K – rotor type, squirrel-cage rotor, absence of letter – wound rotor
- F - temperature index 155°C
Designations of special versions of crane electric motors:
- F – presence of an independent ventilation system with a centrifugal fan
- 1F – presence of an independent ventilation system with an axial fan (self-ventilation is used by default)
- 2P – modification used for variable frequency drives
- B – presence of built-in temperature sensors type ST 14-2.
Explanation of the designations of a crane electric motor with an attached feedback sensor:
- G1 – with built-in pulse speed sensor model HOG 9
- G10 – with the possibility of installing a pulse speed sensor HOG 9 by the customer independently
- G2 – with built-in pulse speed sensor model HOG 10
- G20 – with the possibility of installing a pulse speed sensor HOG 10 by the customer independently
- G3 – with built-in pulse speed sensor model HOG 12
- G30 – with the possibility of installing a pulse speed sensor HOG 12 by the customer independently
- G4 – with built-in angular displacement transducer with sensor model LIR276A
- G40 – with the possibility of installing the LIR276A sensor by the customer
- G5 – with a built-in pulse speed sensor of a type individually agreed upon with the customer
- G50 – with the possibility of installing a pulse speed sensor of a type individually agreed with the customer
Overall and connecting dimensions of crane electric motors
| Type | d30 | l33 | h31 | b1 | b10 | b12 | d1 | d5 | d10 | l1 | l3 | l10 | l31 | h | h1 | h8 | b11 | l11 | h10 | Weight, kg | volume, m3 |
| 4MT 200LA6, 4MTM 200LA6 | 422 | 1053 | 500 | 16 | 318 | 80 | 65 | M42x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 133 | 200 | 10 | 33,9 | 400 | 350 | 24 | 270 | 0,22 |
| 4MT 200LB6, 4MTM 200LB6 | 422 | 1053 | 500 | 16 | 318 | 80 | 65 | M42x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 133 | 200 | 10 | 33,9 | 400 | 350 | 24 | 300 | 0,22 |
| 4MT 200LA8, 4MTM 200LA8 | 422 | 1053 | 500 | 16 | 318 | 80 | 65 | M42x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 133 | 200 | 10 | 33,9 | 400 | 350 | 24 | 275 | 0,22 |
| 4MT 200LB8, 4MTM 200LB8 | 422 | 1053 | 500 | 16 | 318 | 80 | 65 | M42x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 133 | 200 | 10 | 33,9 | 400 | 350 | 24 | 305 | 0,22 |
| MTF 411-6, MTH 411-6, 5MTF 411-6, 5MTH 411-6 | 422 | 1053 | 525 | 16 | 330 | 65 | M42x3 | 28 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 175 | 225 | 10 | 33,9 | 440 | 435 | 25 | 290 | 0,23 | |
| MTF 411-8, MTH 411-8, 5MTF 411-8, 5MTH 411-8 | 422 | 1053 | 525 | 16 | 330 | 65 | M42x3 | 28 | 140 | 105 | 335 | 175 | 225 | 10 | 33,9 | 440 | 435 | 25 | 296 | 0,23 | |
| MTF 412-6, MTH 412-6, 5MTF 412-6, 5MTH 412-6 | 422 | 1053 | 525 | 16 | 330 | 65 | M42x3 | 28 | 140 | 105 | 420 | 165 | 225 | 10 | 33,9 | 440 | 510 | 25 | 322 | 0,23 | |
| MTF 412-8, MTH 412-8, 5MTF 412-8, 5MTH 412-8 | 422 | 1053 | 525 | 16 | 330 | 65 | M42x3 | 28 | 140 | 105 | 420 | 165 | 225 | 10 | 33,9 | 440 | 510 | 25 | 328 | 0,23 | |
| 4MTM 225L6 | 465 | 1220 | 545 | 18 | 356 | 95 | 70 | M48x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 356 | 149 | 225 | 11 | 36,4 | 435 | 410 | 24 | 490 | 0,31 |
| 4MTM 225M6 | 465 | 1110 | 545 | 18 | 356 | 95 | 70 | M48x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 311 | 149 | 225 | 11 | 36,4 | 435 | 370 | 24 | 390 | 0,28 |
| 4MTM 225L8 | 465 | 1220 | 545 | 18 | 356 | 95 | 70 | M48x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 356 | 149 | 225 | 11 | 36,4 | 435 | 410 | 24 | 470 | 0,31 |
| 4MTM 225M8 | 465 | 1110 | 545 | 18 | 356 | 95 | 70 | M48x3 | 19 | 140 | 105 | 311 | 149 | 225 | 11 | 36,4 | 435 | 370 | 24 | 390 | 0,28 |
| MTH 511-6 | 465 | 1110 | 570 | 18 | 380 | 70 | M48x3 | 35 | 140 | 105 | 310 | 251 | 250 | 11 | 36,4 | 500 | 480 | 25 | 415 | 0,29 | |
| MTH 511-8 | 465 | 1110 | 570 | 18 | 380 | 70 | M48x3 | 35 | 140 | 105 | 310 | 251 | 250 | 11 | 36,4 | 500 | 480 | 25 | 415 | 0,29 | |
| MTH 512-6 | 465 | 1220 | 570 | 18 | 380 | 70 | M48x3 | 35 | 140 | 105 | 390 | 271 | 250 | 11 | 36,4 | 500 | 600 | 25 | 520 | 0,32 | |
| MTH 512-8 | 465 | 1220 | 570 | 18 | 380 | 70 | M48x3 | 35 | 140 | 105 | 390 | 271 | 250 | 11 | 36,4 | 500 | 600 | 25 | 500 | 0,32 | |
| 4MTH 280S6, 4MTM 280S6 | 605 | 1265 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 368 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 430 | 40 | 740 | 0,57 |
| 4MTH 280L6, 4MTM 280L6 | 605 | 1439 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 457 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 520 | 40 | 970 | 0,64 |
| 4MTH 280S8, 4MTM 280S8 | 605 | 1265 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 368 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 430 | 40 | 740 | 0,57 |
| 4MTH 280M8, 4MTM 280M8 | 605 | 1345 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 419 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 480 | 40 | 820 | 0,6 |
| 4MTH 280S10, 4MTM 280S10, 5MTH 280S10 | 605 | 1265 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 368 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 430 | 40 | 715 | 0,57 |
| 4MTH 280M10, 4MTM 280M10, 5MTH 280M10 | 605 | 1345 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 419 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 480 | 40 | 825 | 0,6 |
| 4MTH 280L10, 4MTM 280L10, 5MTH 280L10 | 605 | 1439 | 740 | 22 | 457 | 125 | 90 | M64x4 | 24 | 170 | 130 | 457 | 190 | 280 | 14 | 46,8 | 540 | 520 | 40 | 975 | 0,64 |
| MTH 611-6 | 605 | 1335 | 775 | 22 | 520 | 90 | M64x4 | 42 | 170 | 130 | 345 | 256 | 315 | 14 | 46,8 | 650 | 575 | 35 | 805 | 0,63 | |
| MTH 611-10 | 605 | 1335 | 775 | 22 | 520 | 90 | M64x4 | 42 | 170 | 130 | 345 | 256 | 315 | 14 | 46,8 | 650 | 575 | 35 | 780 | 0,63 | |
| MTH 612-10 | 605 | 1435 | 775 | 22 | 520 | 90 | M64x4 | 42 | 170 | 130 | 445 | 256 | 315 | 14 | 46,8 | 650 | 645 | 35 | 890 | 0,67 | |
| MTH 613-6 | 605 | 1530 | 775 | 22 | 520 | 90 | M64x4 | 42 | 170 | 130 | 540 | 256 | 315 | 14 | 46,8 | 650 | 735 | 35 | 1045 | 0,72 | |
| MTH 613-10 | 605 | 1530 | 775 | 22 | 520 | 90 | M64x4 | 42 | 170 | 130 | 540 | 256 | 315 | 14 | 46,8 | 650 | 735 | 35 | 1050 | 0,72 | |
| MTH 711-10 | 790 | 1710 | 862 | 640 | 110 | 210 | 440 | 323 | 400 | 790 | 650 | ||||||||||
| MTH 712-10 | 790 | 1710 | 862 | 640 | 110 | 210 | 510 | 323 | 400 | 790 | 650 | ||||||||||
| MTH 713-10 | 790 | 1710 | 862 | 640 | 110 | 210 | 590 | 323 | 400 | 790 | 650 | ||||||||||
| 4MTH 400S8, 4MTNF 400S8 | 790 | 1735 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 560 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 710 | 1255 | 1,21 | |||||
| 4MTH 400M8, 4MTNF 400M8 | 790 | 1815 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 630 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 790 | 1405 | 1,26 | |||||
| 4MTH 400L8, 4MTNF 400L8 | 790 | 1885 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 710 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 860 | 1545 | 1,31 | |||||
| 4MTH 400S10, 4MTNF 400S10, 5MTH 400S10 | 790 | 1665 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 560 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 670 | 1280 | 1,16 | |||||
| 4MTH 400M10, 4MTNF 400M10, 5MTH 400M10 | 790 | 1736 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 560 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 710 | 1445 | 1,21 | |||||
| 4MTH 400L10, 4MTNF 400L10, 5MTH400L10 | 790 | 1816 | 880 | 25 | 686 | 110 | 35 | 210 | 165 | 630 | 280 | 400 | 790 | 790 | 1445 | 1,26 |
Crane electric motors, squirrel-cage and wound-rotor
View the price of crane electric motors
Crane electric motors of the MT series are designed to drive crane and other mechanisms operating in short-term and intermittent modes, including frequent starts and electrical braking. The engines can also be used for long-duty mechanisms.
Crane electric motors are designed for power supply from a 380 V, 50 Hz network with three output ends from the stator winding, and can also be manufactured for voltages of 220/380 and 380/660 V with six output ends for connecting the phases in a star or triangle. At the customer's request, crane electric motors are manufactured for other voltages and frequencies.
Crane electric motors MTF, MTH, MIT are manufactured with a wound rotor, MTKF, MTKH, MTKI motors are manufactured with a squirrel-cage rotor, one- and two-speed.
Crane electric motors MT(K)F are designed for moderate climates (version U1), motors MT(K)N are designed for work at elevated temperatures (version U1), for tropical climates (version T1) and for cold climates (version HL1).
Crane electric motors MT(K)I have a single climatic version 01 and, having certain heating reserves, allow operation in metallurgical production conditions
Cooling of electric motors - external airflow (IC 0141). The degree of protection of the motors is IP 44, the degree of protection of the terminal box and hatch of the motor slip rings is IP 54.
- Design according to installation method (1M):
- MT(K) 311, 312: IМ1001, IМ1002 - horizontal, with one and two cylindrical shaft ends;
- IM2001 - horizontal flanged with one cylindrical shaft end;
- IМ2011, IМ2012 - vertical flanged with one and two cylindrical shaft ends.
- IM1003, IM1004 - horizontal, with one or two conical shaft ends.
- IM2003 - horizontal flanged with feet, with one conical shaft end;
Crane electric motors MT(K)I 225 can be manufactured with cylindrical shaft ends in the design IM1001, IM1002, IM2001, IM2011, IM2012.
Crane electric motors MTF, MTKF, MTH, MTKH comply with GOST and the requirements of IEC regulatory documents. In terms of linking the power scale with the height of the rotation axis, MIT and MTKI engines comply with CENELEC and DIN standards.
Crane electric motors of the MT and MIT types have safety certificates of conformity with the Gosstandart of the Russian Federation and are produced under a license from the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
Technical characteristics of crane squirrel-cage electric motors:
| engine's type | Power at duty cycle 40%, kW | Rotational speed, rpm | Weight for IM1001,1003, kg | Stator current at U=380V, A | Rel. Max. moment. to nominal | Efficiency, % | Power factor | Height of rotation axis, mm | Heat resistance class |
| DMTKF 011-6 | 1,4 | 875 | 47 | 5,2 | 2,8 | 70,5 | 0,67 | 112 | F |
| MTKN 011-6 | 1,4 | 920 | 45,5 | 4,5 | 2,8 | 70,5 | 0,67 | 112 | N |
| DMTKF 012-6 | 2,2 | 880 | 54 | 7,2 | 2,8 | 73,5 | 0,70 | 112 | F |
| MTKN 012-6 | 2,2 | 915 | 49,5 | 6,5 | 2,8 | 73,5 | 0,70 | 112 | N |
| MTKN 111-6 | 3,5 | 865 | 77 | 8,9 | 2,75 | 74,5 | 0,8 | 132 | H |
| MTKN 112-6 | 5 | 890 | 85 | 12,8 | 3,35 | 76 | 0,78 | 132 | H |
| DMTKF 111-6 | 3,5 | 900 | 78 | 9,9 | 2,7 | 72,0 | 0,79 | 132 | F |
| DMTKN 111-6 | 3,0 | 910 | 78 | 9,5 | 2,7 | 68,0 | 0,70 | 132 | H |
| DMTKF 112-6 | 5,0 | 910 | 92 | 14 | 3,2 | 74,0 | 0,74 | 132 | F |
| DMTKN 112-6 | 4,5 | 900 | 92 | 12,7 | 4,1 | 71,5 | 0,75 | 132 | H |
| AMTKF 132 M6 | 5,0 | 905 | 103 | 12,6 | 2,1 | 87,0 | — | 132 | F |
| AMTKN 132 M6 | 4,5 | 905 | 103 | 11,7 | 2,3 | 87,0 | — | 132 | H |
| AMTKF 132 L6 | 7,5 | 905 | 120 | 18,5 | 1,4 | 87,0 | — | 132 | F |
| AMTKN 132 L6 | 7,0 | 900 | 120 | 18,5 | 2,3 | 87,0 | — | 132 | H |
| MTKI 160 M6 | 7,0 | 905 | 131 | — | 3,5 | 78,0 | 0,77 | 160 | H |
| MTKI 160 M8 | 5,0 | 675 | 131 | — | 3,0 | 77,0 | 0,68 | 160 | H |
| MTKI 160 L6 | 10,0 | 915 | 159 | — | 4,0 | 83,0 | 0,76 | 160 | H |
| MTKI 160 L8 | 7,0 | 680 | 159 | — | 2,8 | 80,0 | 0,69 | 160 | H |
| MTKF 311-6 | 11,0 | 910 | 155 | 28,5 | 2,9 | 77,5 | 0,76 | 180 | F |
| MTKN 311-6 | 11,0 | 915 | 185 | 26,7 | 2,9 | 81,0 | 0,77 | 180 | H |
| MTKF 311-8 | 7,5 | 690 | 155 | 21,8 | 2,7 | 73,5 | 0,71 | 180 | F |
| MTKN 311-8 | 7,5 | 695 | 185 | 21 | 2,7 | 78,5 | 0,69 | 180 | H |
| MTKF 312-6 | 15,0 | 930 | 195 | 36 | 3,2 | 81,0 | 0,78 | 180 | F |
| MTKN 312-6 | 15,0 | 925 | 205 | 35 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,78 | 180 | H |
| MTKF 312-8 | 11,0 | 700 | 195 | 29 | 2,9 | 78,0 | 0,74 | 180 | F |
| MTKN 312-8 | 11,0 | 700 | 205 | 29,2 | 2,9 | 81,5 | 0,70 | 180 | H |
| MTKF 411-6 | 22,0 | 935 | 255 | 51 | 3,3 | 82,5 | 0,79 | 225 | F |
| MTKN 411-6 | 22,0 | 935 | 255 | 51 | 3,3 | 82,5 | 0,79 | 225 | H |
| MTKF 411-8 | 15,0 | 695 | 255 | 40 | 3,2 | 80,0 | 0,71 | 225 | F |
| MTKN 411-8 | 15,0 | 695 | 255 | 40 | 3,2 | 80,0 | 0,71 | 225 | H |
| MTKF 412-6 | 30,0 | 935 | 315 | 70 | 3,3 | 83,5 | 0,78 | 225 | F |
| MTKN 412-6 | 30,0 | 935 | 315 | 70 | 3,3 | 83,5 | 0,78 | 225 | H |
| MTKF 412-8 | 22,0 | 700 | 315 | 60 | 3,2 | 80,5 | 0,69 | 225 | F |
| MTKN 412-8 | 22,0 | 700 | 315 | 60 | 3,2 | 80,5 | 0,69 | 225 | H |
| 4MTKM 200 LA6 | 22,0 | 935 | 253 | 48 | 3,3 | 87,0 | 0,80 | 200 | H |
| 4MTKM 200 LA8 | 15,0 | 705 | 260 | 40 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,70 | 200 | H |
| 4MTKM 200 LB6 | 30,0 | 945 | 279 | 61 | 3,3 | 87,5 | 0,85 | 200 | H |
| 4MTKM 200 LB8 | 22,0 | 700 | 290 | 54 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,75 | 200 | H |
| 4MTKM 225 M6 | 37,0 | 930 | 360 | 77 | 3,0 | 85,0 | 0,86 | 225 | H |
| 4MTKM 225 M8 | 30,0 | 700 | 360 | 72 | 2,8 | 84,0 | 0,75 | 225 | H |
| 4MTKM 225 L6 | 55,0 | 925 | 460 | 112 | 3,4 | 86,0 | 0,87 | 225 | H |
| 4MTKM 225 L8 | 37,0 | 700 | 450 | 85 | 2,8 | 85,0 | 0,78 | 225 | H |
| MTKN 511-6 | 37,0 | 930 | 360 | 77 | 3,0 | 85,0 | 0,86 | 250 | H |
| MTKN 511-8 | 30,0 | 700 | 360 | 72 | 2,8 | 84,0 | 0,75 | 250 | H |
| MTKN 512-6 | 55,0 | 925 | 460 | 112 | 3,4 | 86,0 | 0,87 | 250 | H |
| MTKN 512-8 | 37,0 | 700 | 450 | 85 | 2,8 | 85,0 | 0,78 | 250 | H |
Technical characteristics of crane motors with wound rotor:
| engine's type | Power at duty cycle 40%, kW | Rotational speed, rpm | Weight for IM1001,1003, kg | Stator current at U=380V, A | Rotor current, A | Rel. Max. moment. to nominal | Efficiency, % | Power factor | Height of rotation axis, mm | Heat resistance class |
| DMTF 011-6 | 1,4 | 880 | 56 | 5,2 | 9,0 | 2,5 | 89,0 | 0,66 | 112 | F |
| DMTF 012-6 | 2,2 | 895 | 63 | 7,5 | 11,5 | 2,3 | 87,0 | 0,68 | 112 | F |
| DMTF 111-6 | 3,5 | 900 | 92 | 18,7 | 15,0 | 2,2 | 86,0 | — | 132 | F |
| MTH 011-6 | 1,4 | 890 | 60 | 4,9 | 8,8 | 2,6 | 65 | 0,67 | 112 | H |
| MTH 012-6 | 2,2 | 895 | 68 | 6,9 | 11 | 2,7 | 70 | 0,69 | 112 | H |
| MTH 111-6 | 3,5 | 900 | 91 | 9,7 | 14,3 | 2,3 | 75 | 0,73 | 132 | H |
| MTH 112-6 | 5 | 930 | 101 | 13,7 | 15,7 | 2,7 | 79 | 0,7 | 132 | H |
| DMTN 111-6 | 3,0 | 890 | 92 | 18,2 | 15,0 | 2,5 | 88,0 | — | 132 | H |
| DMTF 112-6 | 5,0 | 925 | 110 | 25,4 | 15,7 | 2,6 | 87,0 | — | 132 | F |
| DMTN 112-6 | 4,5 | 900 | 110 | 24,0 | 15,6 | 2,4 | 88,0 | — | 132 | H |
| AMTF 132 M6 | 5,0 | 905 | 120 | 11,0 | 15,2 | 2,2 | 87,0 | — | 132 | F |
| AMTN 132 M6 | 4,5 | 925 | 123 | 12,9 | 14,3 | 2,3 | 87,0 | — | 132 | H |
| AMTF 132 L6 | 7,5 | 900 | 140 | 16,0 | 18,8 | 2,2 | 87,0 | — | 132 | F |
| AMTN 132 L6 | 7,0 | 925 | 140 | 19,1 | 20,7 | 2,4 | 87,0 | — | 132 | H |
| MTI 160 M6 | 7,0 | 930 | 138 | — | 18,7 | 3,0 | 81,0 | 0,69 | 160 | H |
| MTI 160 M8 | 5,0 | 965 | 138 | — | 16,9 | 2,5 | 78,0 | 0,64 | 160 | H |
| MTI 160 L6 | 10,0 | 950 | 166 | — | 24,7 | 3,5 | 84,0 | 0,69 | 160 | H |
| MTI 160 L8 | 7,0 | 700 | 166 | — | 20,4 | 2,5 | 79,0 | 0,64 | 160 | H |
| MTN 211-6 | 7,0 | 945 | — | 16,0 | — | 2,7 | 87,0 | — | 160 | N |
| MTF 311-6 | 11 | 945 | 220 | 29,3 | 42 | 3,0 | 80,0 | 0,71 | 180 | F |
| MTN 311-6 | 11 | 940 | 220 | 29,3 | 41 | 3,0 | 80,0 | 0,71 | 180 | H |
| MTF 311-8 | 7,5 | 695 | 225 | 23,0 | 21 | 3,0 | 76,0 | 0,65 | 180 | F |
| MTN 311-8 | 7,5 | 700 | 225 | 23,0 | 21 | 3,0 | 76,0 | 0,65 | 180 | H |
| MTF 312-6 | 15 | 955 | 240 | 37,5 | 46 | 3,0 | 82,0 | 0,74 | 180 | F |
| MTN 312-6 | 15 | 950 | 240 | 37,5 | 46 | 3,0 | 82,0 | 0,74 | 180 | H |
| MTF 312-8 | 11 | 695 | 240 | 32,7 | 43 | 3,0 | 78,5 | 0,65 | 180 | F |
| MTN 312-8 | 11 | 705 | 240 | 32,7 | 43 | 3,0 | 78,5 | 0,65 | 180 | H |
| MTF 411-6 | 22 | 965 | 280 | 51 | 60 | 2,8 | 86,0 | 0,76 | 225 | F |
| MTN 411-6 | 22 | 965 | 280 | 51 | 59 | 2,8 | 86,0 | 0,76 | 225 | H |
| 4MTM 200 LA6 | 22 | 960 | 270 | 51 | 59 | 2,8 | 86,0 | 0,76 | 200 | N |
| MTF 411-8 | 15 | 710 | 280 | 44 | 48,8 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,62 | 225 | F |
| MTN 411-8 | 15 | 710 | 280 | 44 | 46 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,62 | 225 | H |
| 4MTM 200 LA8 | 15 | 720 | 275 | 44 | 46 | 3,2 | 83,0 | 0,62 | 200 | N |
| MTF 412-6 | 30 | 970 | 345 | 55 | 73 | 2,8 | 87,0 | 0,79 | 225 | F |
| MTN 412-6 | 30 | 970 | 345 | 55 | 72 | 2,8 | 87,0 | 0,79 | 225 | H |
| 4MTM 200 LB6 | 30 | 960 | 300 | 55 | 72 | 2,8 | 87,0 | 0,79 | 200 | N |
| MTF 412-8 | 22 | 720 | 315 | 58 | 57 | 3,0 | 83,0 | 0,70 | 225 | F |
| MTN 412-8 | 22 | 720 | 315 | 58 | 58 | 3,0 | 83,0 | 0,70 | 225 | H |
| 4MTM 200 LB8 | 22 | 715 | 305 | 58 | 58 | 3,0 | 83,0 | 0,70 | 200 | N |
| 4MTM 225 M6 | 37 | 955 | 390 | 80 | 80 | 3,0 | 87,0 | 0,81 | 225 | N |
| MTN 511-6 | 37 | 955 | 390 | 80 | 80 | 3,0 | 87,0 | 0,81 | 250 | N |
| 4MTM 225 L6 | 55 | 955 | 490 | 117 | 122 | 2,9 | 88,0 | 0,81 | 225 | N |
| MTN 512-6 | 55 | 955 | 490 | 117 | 122 | 2,9 | 88,0 | 0,81 | 250 | N |
| 4MTM 225 M8 | 30 | 715 | 390 | 74 | 70 | 2,9 | 85,0 | 0,72 | 225 | N |
| MTN 511-8 | 30 | 715 | 390 | 74 | 70 | 2,9 | 85,0 | 0,72 | 250 | N |
| 4MTM 225 L8 | 37 | 725 | 470 | 88 | 76 | 2,9 | 86,0 | 0,74 | 225 | N |
| MTN 512-8 | 37 | 725 | 470 | 88 | 76 | 2,9 | 86,0 | 0,74 | 250 | N |
| 4MTH 280 S6 | 75 | 955 | 740 | 149 | 180 | 3,2 | 89,0 | 0,86 | 280 | H |
| MTH 611-6 | 75 | 955 | 740 | 149 | 180 | 3,2 | 89,0 | 0,86 | 315 | H |
| 4MTH 280 L6 | 110 | 970 | 970 | 216 | 168 | 3,5 | 91,0 | 0,85 | 280 | H |
| MTH 612-6 | 110 | 970 | 970 | 216 | 168 | 3,5 | 91,0 | 0,85 | 315 | H |
| 4MTH 280 M8 | 75 | 720 | 820 | 156 | 188 | 3,0 | 90,0 | 0,81 | 280 | H |
| 4MTH 280 L8 | 90 | 725 | 980 | 190 | 171 | 3,2 | 91,0 | 0,79 | 280 | H |
| 4MTH 280 M10 | 60 | 575 | 825 | 140 | 162 | 3,2 | 88,0 | 0,74 | 280 | H |
| MTH 612-10 | 60 | 575 | 825 | 140 | 162 | 3,2 | 88,0 | 0,74 | 315 | H |
| 4MTH 280 L10 | 75 | 575 | 975 | 175 | 150 | 3,0 | 89,0 | 0,73 | 280 | H |
| MTH 613-10 | 75 | 575 | 975 | 175 | 150 | 3,0 | 89,0 | 0,73 | 315 | H |
| 4MTN 400 L8 | 200 | 750 | 1480 | 407 | 271 | — | 93,5 | 0,80 | 400 | H |
| 4MTH 400 M8 | 160 | 750 | 1380 | 330 | 266 | — | 93,3 | 0,79 | 400 | H |
| 4MTH 400 S8 | 132 | 750 | 1230 | 272 | 271 | — | 92,3 | 0,80 | 400 | H |
| 4MTH 400 L10 | 160 | 600 | 1580 | 355 | 242 | 2,55 | 91,3 | 0,73 | 400 | H |
| 4MTH 400 M10 | 132 | 600 | 1420 | 285 | 249 | 2,1 | 91,3 | 0,73 | 400 | H |
| 4MTH 400 S10 | 110 | 600 | 1255 | 240 | 251 | 1,75 | 90,5 | 0,73 | 400 | H |
Dimensions of crane squirrel cage motors:
| engine's type | l1 | l10 | l21 | l31 | l33 | b10 | b11 | H | H31 | D20 | D22 | D24 | D25 | d | b | h |
| DMTKF 011-6 | 60 | 140 | 5 | 70 | 407 | 140 | 188 | 112 | 320 | 265 | 15 | 230 | 300 | 28 | 8 | 31 |
| DMTKF 012-6 | 60 | 159 | 5 | 70 | 442 | 159 | 210 | 112 | 320 | 265 | 15 | 230 | 300 | 28 | 8 | 31 |
| DMTKF(N) 111-6 | 80 | 190 | 5 | 140 | 713 | 220 | 290 | 132 | 342 | 300 | 18 | 330 | 250 | 35 | 10 | 38 |
| DMTKF(N) 112-6 | 80 | 235 | 5 | 135 | 574 | 220 | 290 | 132 | 342 | 300 | 18 | 330 | 250 | 35 | 10 | 38 |
| AMTKF(N) 132 M6 | 110 | 203 | 5 | 89 | 536 | 216 | 270 | 132 | 350 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| AMTKF(N) 132 L6 | 110 | 203 | 5 | 89 | 576 | 216 | 270 | 132 | 350 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| MTKI 160 M | 140 | 210 | 5 | 108 | 845 | 254 | 320 | 160 | 410 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 60 | 12 | 45 |
| MTKI 160 L | 140 | 254 | 5 | 108 | 910 | 254 | 320 | 160 | 410 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 60 | 12 | 45 |
| MTKF(N) 311 | 110 | 260 | 5 | 155 | 637 | 280 | 350 | 180 | 444 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 50 | 14 | 53,5 |
| MTKF(N) 312 | 110 | 320 | 5 | 170 | 712 | 280 | 350 | 180 | 444 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 50 | 14 | 53,5 |
| MTKF(N) 411 | 140 | 335 | 5 | 175 | 749 | 330 | 440 | 225 | 527 | 350 | 19 | 300 | 400 | 65 | 16 | 66,4 |
| MTKF(N) 412 | 140 | 420 | 5 | 165 | 824 | 330 | 440 | 225 | 527 | 350 | 19 | 300 | 400 | 65 | 16 | 66,4 |
| 4MTKM 200 L | 140 | 305 | — | 133 | 910 | 318 | 400 | 200 | 500 | — | — | — | — | 65 | 16 | 66,4 |
| 4MTKM 225 M | 140 | 311 | — | 149 | 945 | 356 | 435 | 225 | 545 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| 4MTKM 225 L | 140 | 356 | — | 149 | 1054 | 356 | 435 | 225 | 545 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| MTKN 511 | 140 | 310 | — | 251 | 945 | 380 | 500 | 250 | 570 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| MTKN 512 | 140 | 390 | — | 271 | 1054 | 380 | 500 | 250 | 570 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
Dimensions of crane motors with wound rotor:
| engine's type | L1 | L10 | L21 | L31 | L33 | B10 | B11 | H | H31 | D20 | D22 | D24 | D25 | d | b | h |
| DMTF 011-6 | 60 | 140 | 5 | 70 | 513 | 190 | 240 | 112 | 290 | 265 | 15 | 230 | 300 | 28 | 8 | 31 |
| DMTF 012-6 | 60 | 159 | 5 | 70 | 548 | 190 | 240 | 112 | 290 | 265 | 15 | 230 | 300 | 28 | 8 | 31 |
| DMTF(N) 111-6 | 80 | 190 | 5 | 140 | 673 | 220 | 290 | 132 | 342 | 300 | 15 | 330 | 250 | 35 | 10 | 38 |
| DMTF(N) 112-6 | 80 | 235 | 5 | 135 | 713 | 220 | 290 | 132 | 342 | 300 | 15 | 330 | 250 | 35 | 10 | 38 |
| AMTF(N) 132M6 | 110 | 203 | 5 | 89 | 660 | 216 | 270 | 132 | 350 | 300 | 19 | 350 | 250 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| AMTF(N) 132L6 | 110 | 203 | 5 | 89 | 700 | 216 | 270 | 132 | 350 | 300 | 19 | 350 | 250 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| MTI 160M | 110 | 210 | 5 | 108 | 845 | 254 | 320 | 160 | 410 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| MTI 160L | 110 | 254 | 5 | 108 | 910 | 254 | 320 | 160 | 410 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 42 | 12 | 45 |
| MTN 211 | 110 | 243 | 5 | 150 | 731,5 | 245 | — | 160 | — | 300 | — | 250 | — | 40 | — | — |
| MTF(N) 311 | 110 | 260 | 5 | 155 | 859,5 | 280 | 350 | 180 | 444 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 50 | 14 | 53,5 |
| MTF(N) 312 | 110 | 320 | 5 | 170 | 834,5 | 280 | 350 | 180 | 444 | 300 | 19 | 250 | 350 | 50 | 14 | 53,5 |
| MTF(N) 411 | 140 | 335 | 5 | 175 | 1027 | 330 | 420 | 225 | 525 | 350 | 19 | 300 | 400 | 65 | 18 | 66,4 |
| MTF(N) 412 | 140 | 420 | 5 | 165 | 1102 | 330 | 420 | 225 | 525 | 350 | 19 | 300 | 400 | 65 | 18 | 66,4 |
| 4MTM 200L | 140 | 305 | — | 133 | 907 | 318 | 400 | 200 | 500 | — | — | — | — | 65 | 16 | 66,4 |
| 4MTM 225M | 140 | 311 | — | 149 | 960 | 356 | 435 | 225 | 545 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| 4MTM 225L | 140 | 356 | — | 149 | 1070 | 356 | 435 | 225 | 545 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| 4MTH 280S | 170 | 368 | — | 190 | 1090 | 457 | 540 | 280 | 740 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
| 4MTH 280M | 170 | 419 | — | 190 | 1170 | 457 | 540 | 280 | 740 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
| 4MTH 280L | 170 | 457 | — | 190 | 1260 | 457 | 540 | 280 | 740 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
| 4MTH 400S8 | 210 | 560 | — | 280 | 1472 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| 4MTH 400M8 | 210 | 630 | — | 280 | 1552 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| 4MTH 400L8 | 210 | 710 | — | 280 | 1622 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| 4MTH 400S10 | 210 | 560 | — | 280 | 1402 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| 4MTH 400M10 | 210 | 560 | — | 280 | 1473 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| 4MTH 400L10 | 210 | 630 | — | 280 | 1553 | 686 | 790 | 400 | 880 | — | — | — | — | 110 | 25 | (106,8) |
| MTN 511 | 140 | 310 | — | 251 | 1110 | 380 | 500 | 250 | 570 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| MTN 512 | 140 | 390 | — | 271 | 1220 | 380 | 500 | 250 | 570 | — | — | — | — | 70 | 18 | 71,4 |
| MTN 611 | 170 | 345 | — | 256 | 1265 | 520 | 650 | 315 | 775 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
| MTN 612 | 170 | 445 | — | 256 | 1345 | 520 | 650 | 315 | 775 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
| MTN 613 | 170 | 540 | — | 256 | 1439 | 520 | 650 | 315 | 775 | — | — | — | — | 90 | 22 | 91,8 |
Drawings of crane squirrel-cage electric motors:
Drawings of crane electric motors with a wound rotor: