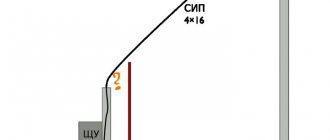
When installing an electrical input into a house, each of us thinks about how it is better to do it - overhead or underground?
Installation of air SIP is always much faster and several times cheaper.
However, situations arise when it is more advisable to run the power cable into the house underground.
Firstly, it is more reliable. And secondly, it does not spoil the facade of the building or the appearance of the surrounding area.
Often these two methods are combined. Initially, an input is made to a special pipe stand from a support.
And from this distribution cabinet the cable is laid in the ground and brought into the house. When the support is located not far from the building, some SIP wires are mounted directly on the facade.
But we will turn specifically to the underground input. Let's look at what difficulties you will encounter when laying cables in the ground and place special emphasis on common mistakes when performing this work, which ultimately, sooner or later, lead to failure of the cable line.
Which cable to lay
Cable installation in the ground can be done in two ways:
- without any protection (using armored KL grades)
- in pipes or special corrugation
Let's look at the first method first. Here, as a rule, a cable with tape armor is used - VBBbShv or AVBbShv.
It is not at all necessary to use armor of the type AABL, AAShV, where there is a one-piece cast protective shell made of aluminum. It could just be ribbons overlapping each other.
In this case, armor protects not so much from external influences (someone started digging where they shouldn’t), but from deformation and traction forces during soil heaving.
Mistake #1
Never bury ordinary grades of home wiring cable in the ground without protection.
The same applies to the SIP wire. It cannot be laid in the ground, even in pipes.
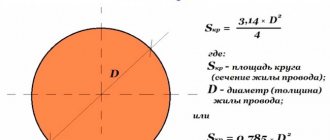
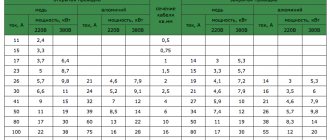
Select the cable cross-section according to the connected load, but not less than 10mm2 for copper or 16mm2 for aluminum.
You can often find videos on YouTube where copper CLs with 6mm2 conductors or 10mm2 aluminum are used. This is explained by the supposedly small number of electrical appliances in the house or country house.
In terms of load, this may be enough for you, but in terms of compliance with the requirements for the minimum cross-section of the PEN conductor, you will have a violation. For single-phase power supply, the cable must be three-wire, for three-phase power supply, it must be five-wire.
Types of cable for a 15 kW network
You need to know which cable to use to enter a private house: 3-phase or single-phase. Connecting using the first option implies reducing the load on the network and the rating of the input machine. The disadvantage is that the size of the distribution panel will be larger than with a single-phase connection, since the power switches will occupy 3-4 modules.
Also, three-phase residual current devices are larger in size. But this type of input cable makes it possible to connect asynchronous electrical devices, boilers, electric stoves or heating systems to the house.
Since the voltage in a three-phase network is 380 V, for protection you will need a three-way circuit breaker before entering the network into the house. It will help avoid the risk of fire and electric shock, and also provide protection against short circuits in the electrical network. Wires differ in the material from which the core is made. Copper cables have lower resistance than aluminum cables, but are more expensive.
Sectional view of 15 kW wire Source elektrik-a.su
Cables for power supply differ in the type of input:
- Airy . For this purpose, the AVK, SIP or AVVG (VVG) models are used. They have the ability to transmit current up to 1 kV and withstand temperatures from -50 to +48 ° C. The disadvantage of the air input is the use of jumpers necessary for the normal connection of the cable to the shield. The rules for wiring the electrical network indicate that such jumpers are unacceptable, but if this point is agreed upon by the supplier company, then when the connection is installed, a seal will be placed on it.
- Underground . For this type of connection, AVBbShV (aluminum) or VBBShV (copper) wire with an armored coating, galvanized tape and a protective hose is used. This is necessary to protect the cable from ground fault or mechanical damage.
For each type of connection there are certain connection and installation standards. If the cable is not installed correctly, all electrical devices may be subject to a short circuit or breakage from voltage surges, since improper power distribution leads to inefficient use of the network.
3 phases and zero Source isu.org.ua
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the installation of electrical networks
Digging a trench for cables - distances and dimensions
The selected cable should be carefully laid in the trench. What size should it be, what distances should be maintained when excavating it?
Mistake #2
Firstly, this trench cannot be dug close to the foundation of the house.
It is necessary to maintain a certain distance of 60cm.
After laying in the ground, the cable should not fall on the line of action of the foundation force, directed at 45 degrees from the base.
Standardized clearances from plants and trees on your site are also required. Here are the minimum dimensions for underground cable laying from nearby utilities, structures and obstacles.
What dimensions should this trench have? Here you can focus on the standard project A5-92 “Laying cables with voltage up to 35 kV in trenches” -.
The cable depth is 0.7 m. Please note that this is the distance from the surface to the top of the cable itself.
Mistake #3
Taking into account the fact that there will be a sand cushion of 10-15 cm underneath, the total depth of the trench should be at least 900 mm.
Not 0.8m, as many recommend, but 90cm, and certainly not 0.7m.
Where did all these numbers even come from? Why can’t you just bury the cable in your yard to the depth of a spade bayonet? Why such torment?
You are not doing the installation in a public place on a city street or at a construction site where heavy vehicles will drive.
The most important reason for such a depth is to ensure optimal temperature conditions for the cable.
By laying it as close to the surface of the earth as possible, you will lose the main advantage of underground installation - the lack of influence of ambient temperature and weather conditions.
The upper layers of the soil warm up much more, and moisture after good rains simply will not reach the cable sheath if it lies at 70 cm. The same cannot be said about 30-40cm.
The second aspect of such a depth of laying is pressure. The deeper the cable lies, the more evenly the pressure from above is distributed on it.
Especially under external influences - a car driving along the KL highway, something heavy was placed on top, etc.
Mistake #4
If your entrance to the house runs from a support across the road, then here you need to bury the cable to an even greater depth - 1000 mm.
The minimum trench width is calculated by the formula = cable diameter + 100mm on each side for a sand bed.
By the way, so that such labor-intensive work on digging a trench does not go to waste, some additionally lay a grounding loop in it. Just don’t forget about the minimum margins of 300-350mm.
Well, in the case of protecting the cable with a pipe, the circuit is not a hindrance at all. After all, it is not necessary that it be in the shape of a triangle or square.
And if the geometry of the site and the location of the input allow, the same trench is adapted for simultaneous installation:
- input cable
- cable to video intercom
- street lighting
- power supply for sliding gate automation
Subscriber branch cable cross-section
The regulated procedure for laying conductors through the air is specified in the rules for electrical installations. The requirements of the rules are established for power lines with voltages up to 1000 V.
Calculations of the cable cross-section should be based on the operating mode: normal, emergency or installation. Since the branch is standard, you should select the normal (nominal) mode. The PUE provides for the minimum permissible wire cross-section:
- It is allowed to use a wire made of a standard aluminum alloy (not heat-treated) with a cross-section of at least 25 mm².
- When using a conductor made from a combination of steel and aluminum (heat-treated), its cross-section should also be 25 mm².
- If a copper wire is laid, its cross-section can be 16 mm².
The above indicators are suitable for standard ice wall thicknesses of no more than 10 mm. If the thickness reaches 15 mm and above, then the cross-section of the aluminum and steel-aluminum cable remains unchanged, and the copper conductor must be increased to 25 mm².
Information is presented in Chapter 2.4 of the PUE.
Backfilling the trench with sand
Mistake #5
The bottom layer of the trench must be filled with sand; do not skip this step.
Otherwise, sharp pebbles and other foreign elements in the ground will damage the insulation after some time.
Mistake #6
The sand must be compacted. Do not lay the cable on a loose base.
What to do if you don’t have sand in stock and don’t want to order it? In this case, sift the excavated soil.
The fraction of individual elements after sifting should be no more than 5 mm.
Is it possible to do without this sand pillow or its equivalent? Why is it even needed? No you can not.
In addition to protecting the insulation from sharp objects, it plays another important role. The layer of sand under and above the cable is practically not subject to heaving.
It can be easily compacted, as a result of which there is no subsidence of the soil in the trench. No drawdown - no voids.
Namely, they lead to local overheating of the cable. The result is a situation where, in the place where a shallow hole is formed, the cable heats up significantly more than in the same area, but a couple of meters away.
Due to the temperature difference, the cable begins to “pull”. Under significant loads, the PVC insulation bursts and subsequently begins to actively suck moisture through these microcracks.
Well, don’t forget about the drainage properties of sand. Even if water reaches a depth of 0.7 m, it will pass through the sand without stopping near the cable line itself.
Some examples of input cable protection
The best protection for the input cable is its insulation and the method of laying it in a place where no one can reach it. This can be a method of laying underground or by air. To prevent the harmful effects of natural conditions, the conductor can be laid in a special PVC pipe, but few do this, due to the significant increase in the cost of the structure.
To protect the wire in the wall, it is best to use a metal pipe. A replacement for metal can be PVC, which has a more affordable price.
Correct cable routing
The cable itself is laid in a “snake” trench.
SNiP 3.05.06-85 stipulates that cables in trenches should be laid with a margin of 1-2%. This reserve is precisely provided by the snake.
Just don't go overboard with the bends.
Mistake #7
But making a reserve in the form of rings is not allowed.
Why are these extra bends needed at all? As it turns out, not for emergency repairs at all. If the CL is laid in a perfectly flat straight line, then the temperature deformations that accompany the operation of the CL will sooner or later damage the input.
Mistake #8
Before and after installation, do not forget to test the insulation of the cable cores with a megometer.
Read how to do this correctly in a separate article.
A small layer of sand is again poured on top of the laid cable.
How cable tension is done
After fixing the conductor on special rollers, begin to tension it. This requires the following tool:
- hand winch;
- stretching device;
- dynamometer.
The hand winch is attached to the nearest support using anchor bolts, and the cable is pulled along it using a tensioning device. The tension force is regulated by technical documentation and is controlled using a dynamometer.
Laying warning tape or bricks
To protect against a person with a shovel, as well as to mark the route, signal tape is used.
Mistake #9
Make no mistake, it should be laid at a distance of 250mm from the cable line itself, and not from the surface of the earth.
That is, when excavating, you must first hit the tape with the bayonet of a shovel, but not reach the shell. When mechanized trench digging, after detection of the warning tape, only manual excavation of the soil is allowed.
If you don’t have tape, use any available materials at home in the country.
The main thing is to lay something that will warn and “scream” - there’s a cable underneath me! Don't dig!
It is also recommended to protect the cable with bricks or asbestos-cement slabs.
Mistake #10
They must protrude at least 50mm beyond the boundary of the cable sheath in cross section.
By the way, the same applies to the tape.
Especially if several cables lie in one trench at the same time.
Mistake #11
You can’t just lay one narrow strip in the middle.
It should protrude beyond the outermost cable in the row. One is missing, use two, three, etc.
Bricks should be used as protection when it comes to the input from a substation or transformer substation to a multi-storey building, factory or other large facility.
Mistake #12
In this case, it is prohibited to use silicate or perforated bricks.
In private construction, with underground entry into a small cottage, no one will complicate their life and increase the cost of repairs by laying red bricks. Therefore, in our case, one tape will be enough.
Cable laid over the air
The main type of installation of the input cable is its installation by air. Air input has its advantages:
- Minimum labor costs.
- It takes a short amount of time to connect your home. It is rare that such work takes more than two hours.
- Low cost of consumables: anchor bolts or clamps, special brackets, insulators.
- Possibility of quick troubleshooting, even if the entire cable needs to be replaced.
The following types of cables are used for aerial installation:
- SIP cable is a self-supporting insulated wire.
- Non-insulated, material - aluminum.
- Bare aluminum with steel core.
Perfectly buried cable
After all the above work, you finally fill the trench with earth. To summarize the above, we can derive the formula for a perfectly buried cable. Here's what we get:
- trench depth 900mm
- sand cushion at the bottom 100-150mm
- the cable itself
- sand cushion over cable 100-150mm
- Red brick
- soil layer 200-250mm without coarse rocks
- warning tape
- residual soil layer
Each layer after laying is compacted manually or mechanically.
As a result, you get a technologically correct and “permanently” laid cable.
Specifics and standards
The distance from the cable to the gas pipeline, as well as other parameters that relate to the transportation of electricity through an electric cable and gas fuel through a gas pipeline, are provided for by special instructions for construction, operation and safety.
Electric cable
The rules for the design of electrical installations provide for a variety of difficulties and subtleties that may arise when placing electrical power panels. They can be group, external or internal.
It is impossible to answer the question of what distance should be maintained between the gas pipeline and the electric cable without taking into account the specific features of the engineering project, because the standards depend on several parameters in each specific case.
Laying high voltage cables underground
Recommendations have been made to the prescribed standards several times. This happened as isolation methods improved, transportation changed, and networks developed and branched out.
Electric cable in the ground
In the case of a pipeline, the distance is regulated according to separate principles. It all depends on the type and variety of the special structure, its technical equipment, the required level of pressure in the gas main, as well as the place and method of its installation:
- In SP 62.13330.2011 “Gas distribution systems”, supplemented and revised SNiP 42-01-2002 (attached to it is a table of minimum distances from gas pipelines, which organically follow from the safety standards and regulations specified in the code).
- The PB (FNiP) approved in 2013 provides for industrial safety features for those facilities that use hydrocarbon fuel in a liquefied state.
- The Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, adopted on November 20, 2000 (No. 878), specifies the distances required to be maintained in public and residential buildings. The main function of this regulation is to prevent dangerous situations. They can arise due to incorrect placement of gas pipes in relation to other systems.
Laying electrical cables underground
Norms
The distance between the cable and the gas pipeline is also determined by the specifics of electricity transmission. Gas pipelines can be of underground and above-ground types, electricity can be transmitted through underground cable or overhead overhead lines. The distance from the communication cable in the airspace depends on the security zone of the power line, the power and operating mode of the electrical installation.
Overhead power line
In an underground cable network, everything depends on the voltage class and insulation safety, the proximity of other objects, their size and purpose. A safety zone is provided for power lines, the dimensions of which are marked in the form of a geometrically calculated polygon. The underground cable can be equipped with additional devices that make it possible to reduce the distance.
In addition to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 169, which determines the procedure for installing security zones, rules for the design and provision of electricity transportation and the organization of safety measures, there is GOST 13109-97 “Electric energy”, GOST 14254-2015 “Degrees of protection provided by shells”, technical rules operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP) and SNiP 21-01-97 “Fire safety of buildings and structures”.
Corrugation
The rules for electrical installations have been repeatedly edited and adjusted. They are aimed at preventing possible violations due to non-compliance with distances. The Ministry of Energy regulations, for example, stipulate a minimum distance between sockets for electrical appliances and the gas pipe in the room.
It is set at 50 cm to prevent the possibility of household gas explosion if sparking occurs in the outlet. In other cases there are many nuances
Particular attention is paid to the distance from the cable to the above-ground or underground location of natural gas or energy transportation facilities
Medium pressure gas pipeline
Laying cables in the ground in pipes
All of the above concerns the laying of armored cables. However, due to their high cost, the method most often used is to lay the usual marks in the ground without any armor VVG, AVVG and the like.
Here protection in the form of pipes is used:
- metal
- HDPE
- double-wall corrugated (DKC 121950 or Promsleeve)
The latter can contain both electrical cables and network and telecommunication cables.
Mistake #13
Polypropylene and sewer pipes are strictly prohibited, as well as metal hoses.
For 0.4 kV power cables, a red or black corrugated pipe is used. For low current – blue.
Such corrugation in its properties is much better than asbestos pipes, which were widely used previously.
Pipes are divided according to the degree of compression resistance. And they are able to withstand pressures of several hundred kN.
By wearing special rubber seals, sections of such corrugated tubes can be connected to each other with couplings.
Connection protection degree – IP67!
The cable fill factor in the pipe and corrugation should be 1.4. What does this mean?
Mistake #14
The diameter of the corrugation or pipe should be such that the cable in it occupies no more than 40% of the total space.
Please note that not all HDPE pipes are equally useful for underground installation of cable lines. The vast majority of them are pipes for cold water supply with an operating temperature of up to 40C.
And some cables in normal modes at maximum loads heat up to 90C! Here are the corresponding letters and documents about the ban on HDPE pipes from Rosseti and Rosstandart.
Letters on the use of HDPE pipes
True, this applies primarily to high-voltage cable lines, so for your private house, in principle, little changes, you can use it.
In what cases are pipes still used? For example, in those when it is not physically possible to meet certain requirements and standards for minimum distances:
- when laying in close proximity to or through trees
- approaching or crossing with pipelines or other electrical networks
In such cramped conditions, a reduction in distance is allowed, but with the obligatory use of pipes. They protect:
- from mechanical influences and shocks
- from stray currents
- from aggressive soils
- from rodents
If the route is long (tens of meters), it is best to tighten the cable into the pipe using a special broach with a cable stocking.
And to put this broach inside, use a vacuum cleaner and a strong rope. The rope will be more fun to tighten if you attach a piece of cork or a plastic bag to its end.
Mistake #15
When joining metal sections of pipe, do not use welding under any circumstances if the cable is already pulled inside.
In this case, it is better to use threaded connections, or tighten the input into an initially straight section, and then bend it with a pipe bender.
Obtaining permission for underground input
First, you need to complete the project. It should be developed by a specialist. Technical documentation, plans and drawings must comply with all rules and regulations. The designer determines the brand of cable and calculates the cross-section of the conductors.
To receive a project, a number of technical conditions must be met. To connect a house to a common power line, you will need appropriate permission. For example, an agreement for excavation work is drawn up by the service responsible for facilities and communications.
Then the land plot is traced. If there are any communications in the immediate vicinity of the cable being laid, it is necessary to invite their representative to coordinate the position of the trench and control the work being carried out.
Features of HDPE pipes
Features of using HDPE pipes:
- HDPE pipes have very simple installation;
- Corrugated pipes are suitable for laying electrical network cables;
- If the installation is done correctly, the pipes form a tight connection;
- HDPE pipes return to their previous linear size over time. The use of a probe allows you to simplify cable pulling.
- HDPE pipes have a high elasticity index (more details: “HDPE pipes - application and technical characteristics”). Therefore, they can be used all year round; changes in soil temperature will not affect them.
For laying signal or power cables, double-wall corrugated pipes are optimal. Their use allows you to protect the line from any external influences.
There are two different types of pipes in the manufacture of which low-density polyethylene was used: products that comply with the GOST standard, and other products from the secondary market. The second option is of worse quality. You can choose it if your budget is limited.
Advantages of low pressure polyethylene pipes:
- Long service life (manufacturers claim 50 years);
- No welding is required to connect individual pipes;
- Lightweight design;
- Over time, the product does not lose its performance characteristics;
- External factors do not have a negative impact on HDPE pipes;
- To lay cables in such pipes, no additional grounding is required;
- Wide range of operating temperatures - from -25 oC to +70oC;
- HDPE pipes do not have a negative impact on the environment, as they do not emit toxic waste or condensate;
- Pipes made of low-pressure polyethylene are easily deformed; there is no need to use additional fasteners and connecting parts to lay the pipeline. But you should understand that if the pipe is strongly bent, the cable will not fit into it.
Don't miss: Wire Size Chart. How to collect data yourself
HDPE pipes are gaining increasing popularity in various areas of life. This is due to the abundance of their advantages without harm to the environment. If you approach the installation and installation process correctly, the object will last for several decades without the need for repairs. They also use HDPE pipes for electrical wiring in the house (for more details: “Characteristics of PVC pipes for electrical wiring, advantages and rules of use”).
Pipes used, reasons for their popularity
One of the most popular options for laying wires is to place them in the ground. To implement this method, special pipes are used.
Reasons for popularity:
- When placed above ground, the cable may be damaged by a gust of wind, and the method described above does not have such a drawback.
- The underground wire is much more difficult to damage, and there is also protection from external weather conditions.
- Even if the wire is short-circuited, there will be no fire due to the protection.
There are five types of pipes designed for laying cables:
- Polypropylene . This material is characterized by plasticity and heat resistance. Such pipes are easy to give the desired shape.
- Steel . Such pipes are not used for laying power lines in the ground. As a rule, a steel pipe for cable is used indoors, using corrugation.
- Made from high and low pressure polyethylene . This type of pipe is lightweight, durable and has a long service life, and it also has corrosion protection.
- Asbestos-cement . These are heavy pipes and contain asbestos, which is harmful to the human body.
- PVC pipes.
The greatest demand at the moment is for pipes made of low-density polyethylene (abbreviated as HDPE). There are a huge number of varieties of such products: smooth-walled rigid, double-walled, corrugated pipes and so on.
Corrugated pipes for laying cables in the ground have high elasticity, as well as heavy weight due to the reinforcing mesh inside. In addition to corrugation, double-wall pipes contain a layer of HDPE.
One of the main advantages of laying the cable inside such a product is that it will be completely hidden from the environment. The pipes are durable; the manufacturer claims that they can last up to 50 years. In reality, this period turns out to be higher.
The advantage of this option
Given that there are different installation methods, what are the advantages of this method? Since the pipe is round in shape, it is ideal for laying wire or cable in it. As the conductor is pushed through, it bends less frequently, requiring less effort. Such structures have a smooth turn, unlike the box, which also facilitates installation and protects the wire from breaking.
The round section can withstand more load than any other. Cables laid underground in this way will be more protected from compressive loads and surface deformation, for example, during building subsidence.