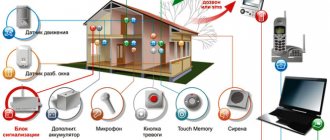
DC servo drive design
Typically, DC servo drives are used in low-power positioning applications. Their classic area of application is robotics.
The design of modern servos is quite simple, but at the same time very effective, as it allows for the most accurate motion control. The servo drive consists of:
- dc motor
- reducer gears
- output shaft
- potentiometer
- control board to which the control signal is supplied
The motor and gearbox form the drive. The gearbox is used to reduce the rotation speed of the motor, which must be adapted for practical use. The required load is attached to the output shaft of the gearbox. This could be a rocking chair, a rotating shaft, pulling or pushing mechanisms.
In order to turn the angle of rotation into an electrical signal, a sensor is needed. Its functions in a DC servo drive are successfully performed by a potentiometer. It produces an analog signal (typically 0 to 10 V) with a resolution limited by the ADC (analog-to-digital converter) that receives the signal.
The most important part of the servo drive is, perhaps, the electronic servo amplifier board, which receives and analyzes control pulses, correlates them with potentiometer data, and is responsible for starting and stopping the engine.
Application area
At the moment, servos have become quite widespread. They can be found in precision instruments, machines that produce various circuit boards, programmable machines, industrial robots and other mechanisms. Drives of this type have gained great popularity in the aircraft modeling industry due to their efficient energy consumption and uniform movement.
The ability to achieve high precision is often the deciding factor for servo drive applications. In addition, thanks to new digital developments that allow for various ways to communicate with objects, the system uses a computer for control and configuration, which greatly simplifies operation.
Servo motors are also used in various fields. They can move the output shaft to a predetermined position and hold it automatically. They will also help to give movement to any mechanism coordinated by shaft rotations. For a motor, important parameters are the uniformity and tone of movement, the efficiency of energy expended.
Servo drives, where the driving mechanism is a piston with a cylinder, have high speed. It is used in a car to change gears in an automatic transmission. Mounted in robots that move loads of more than one hundred kilograms. In industrial installations, for switching dampers in packaging machines, where compressed air is used as an energy carrier.
Principle of operation
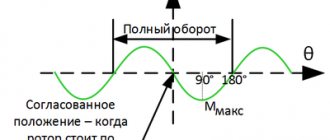
The operating principle of the devices is based on the use of a pulse signal, which has three important characteristics - repetition frequency, minimum and maximum duration. It is the duration of the pulse that determines the angle of rotation of the engine.
The pulse signals received by the servo drive have a standard frequency, but their duration, depending on the model, can range from 0.8 to 2.2 ms. In parallel with the arrival of the control pulse, the operation of the reference pulse generator, which is connected to the potentiometer, is activated. That, in turn, is mechanically coupled to the output shaft and is responsible for correcting its position.
The electronic circuit analyzes the pulses taking into account their duration and, based on the difference value, determines the difference between the expected (set) position of the shaft and the actual one (measured using a potentiometer). Then an adjustment is made by applying voltage to the motor power supply.
Popular manufacturers of servo drives for water heated floors
You can purchase servomotors in different ways, such as: the Internet, building stores, or the market. They are produced by different manufacturers and have their own characteristics. According to consumer reviews, the best companies are considered.
"VALTEC"
This company employs highly qualified Russian and Italian employees to produce basic heating systems and their additional equipment. The best servos produced by them are:
"Watts"
"Watts" is considered one of the leading companies in the production of additional thermoelements for heated floors. The distinctive feature of the company is the quality of its products at an affordable price. The following are considered effective series of servo drives from these manufacturers:
"Rehau"
Servomotors from this German company are considered the best additional equipment for heated floors. Recommended, innovative series are considered:
- UNI for 230.24 V. Using an adapter, servos of this series are attached to the commutator . Visual monitoring of system operation is carried out through a built-in indicator. Cable cross-section - 0.5 sq. mm.
- UNI 230, 24. This servo drive is produced with a built-in monitor, in a “normally” closed form. The product is attached to both the supply and return coolant.
Having examined the types of servomotors and familiarized yourself with their operating principles, you can independently verify that their use increases the functionality of the water system. The devices are reliable, have full temperature control and are easy to use. Having performed the correct installation, servo drives for a heated water floor collector can last quite a long time, which will allow saving on the family budget in the desired microclimate.
Sources
Source - https://informatikaiikt.narod.ru/computeriustroystvo2.html Source - https://works.doklad.ru/view/ceYjfgwDJ5A.html Source - https://principraboty.ru/programmnyy-princip-raboty-kompyutera/ Source - https://csaa.ru/programmnyj-princip-raboty-kompjutera/ Source - https://znanija.com/task/4005550 Source - https://studopedia.su/1_15411_programmniy-printsip-raboti-kompyutera-sostoit -v-tom-chto-kompyuter-vipolnyaet-deystviya-po-zaranee-zadannoy-programme.html Source - https://studopedia.ru/4_14185_programmniy-printsip-raboti-kompyutera-klassicheskaya-arhitektura-evm-printsipi-fon- neymana.html Source - https://mega-talant.com/biblioteka/prakticheskaya-rabota-programmnyy-princip-raboty-kompyutera-101876.html Source - https://www.asutpp.ru/chto-takoe-servoprivod. html Source - https://academy.evolvector.ru/index.php?route=product/product&product_id=73 Source - https://electrik.info/device/1583-kak-ustroen-i-rabotaet-servoprivod.html Source — https://techtrends.ru/resources/articles/servoprivod/ Source — https://samelectrik.ru/chto-takoe-servoprivod.html Source — https://modelistam.com.ua/kakustroen-servoprivod-printsip- raboty-a-164/ Source - https://tehprivod.su/poleznaya-informatsiya/printsipy-raboty-i-vidy-servoprivodov.html Source - https://principraboty.ru/servodvigatel-princip-raboty/ Source - https ://www.servotechnica.ru/catalog/type/index.pl?id=104 Source - https://tepliepol.ru/voprosy-i-rekomendatsii/kollektor/servoprivod-dlya-teplogo-pola
Basic provisions of the device
If the duration of the reference and control pulses coincides, the so-called zero torque occurs. At this time, the servo drive motor does not work, the drive shaft is in its original (stationary) position.
As the duration of the control pulse increases, the board records the difference in the indicators, the motor receives voltage and starts moving. In turn, the gearbox begins to influence the output shaft, which rotates in such a way as to achieve an increase in the duration of the reference pulse. As soon as it becomes equal to the control pulse, the engine will stop working.
When the duration of the control pulse decreases, the same thing happens, only exactly the opposite, since the engine begins to rotate in the opposite direction. As soon as the pulses are equal, the engine stops.
Servo drives MG995 and MG996 tower pro
The MG995 servo is the second most popular servo model most often connected to Arduino projects. These are relatively inexpensive servo motors with much better performance than the SG90.
Specifications MG995
The output shaft on the MG995 rotates 120 degrees (60 in each direction), although many sellers indicate 180 degrees. The device is housed in a plastic case.
- Weight 55 g;
- Torque 8.5 kg x cm;
- Speed 0.2s/60 degrees (at 4.8V);
- Working power 4.8 – 7.2V;
- Operating temperatures – from 0C to -55C.
Description MG995
The connection to the Arduino also occurs via three wires. In principle, for amateur projects it is possible to connect the MG995 directly to the Arduino, but the motor current will always create a dangerous load on the board inputs, so it is still recommended to power the servo separately, not forgetting to connect the ground of both power circuits. Another option that makes life easier would be to use ready-made servo controllers and shields, which we will review in a separate article.
MG996R is similar to MG995 in its characteristics, only it comes in a metal case.
AC servo drive
AC servo drives use a synchronous motor with powerful permanent magnets. In such motors, the rotor speed coincides with the speed of the magnetic field induced in the stator winding.
The operating principle of a servo drive based on a three-phase synchronous electric motor is as follows. A three-phase voltage is supplied to the stator windings, which creates a rotating magnetic field inside it. This field interacts with permanent magnets located in the rotor. As a result, the rotor rotates at the frequency of the magnetic field.
An encoder with high resolution is mounted on the rotor shaft. The signal from it is sent via a separate cable to a special input of the servo amplifier. At the same time, a control signal is supplied to the control input of the servo amplifier. As a result of comparing these two signals, a mismatch signal is isolated, the magnitude of which is directly proportional to the difference between the target and actual engine rotation rates. Based on this signal, a three-phase voltage is generated with parameters that ensure the fastest possible reduction of the mismatch to zero.
Torque.
One of two main characteristics. Torque (force on the shaft) is a factor responsible for the measure of rotational force applied to the physical body (how much weight the drive can hold in a horizontal position on a lever with a given length parameter). Torque can be nominal (the servo drive can operate with such a torque applied to the shaft for any amount of time) and peak (short-term increased, which is achieved by additionally pumping current into the motor windings). When operating with a torque exceeding the rated one, the motor and driver keys heat up, and prolonged operation (more than a few seconds) can damage the drive. It is by the moment that they look at whether the servo drive is suitable for the task being performed, whether it can rotate what it is supposed to rotate. Different servos produce torque differently; it can be approximately constant over the entire range of revolutions, or drop at low speeds, or vice versa, at high speeds. Torque is provided by the current in the windings, and most servos can briefly supply a torque to the shaft greater than the nominal one specified in the data sheet, but very briefly, so as not to overheat the stator windings.
Control Modes
There are three main operating modes of an AC servo drive.
Position control mode.
The main thing in this mode is control over the angle of rotation of the rotor shaft. Control is carried out by a sequence of pulses that can come, for example, from a controller. This mode is used for precise positioning of various components of process equipment.
The position control pulse combination can convey information not only about position, but also about the speed and direction of rotation of the motor. Three types of signals can be used for this: 1) quadrature pulses (with a phase shift of 90 degrees), 2) clockwise or counterclockwise rotation pulses, acting alternately, and 3) speed pulses and direction potential, applied to two inputs.
As a rule, in all servo amplifiers the control inputs are named as PULSE, SIGN.
Speed control mode.
In this case, control is carried out by an analog signal. Speed values can also be switched to fixed values by applying signals to the corresponding digital inputs. In the case of using a multi-polar analog control signal, it is possible to change the direction of rotation of the servomotor.
The speed control mode is similar to the operation of an asynchronous motor controlled by a frequency converter. Parameters such as acceleration and deceleration times, maximum and minimum speeds, and others are set.
Torque control mode.
In this mode, the engine can rotate or stand still, but the torque on the shaft will be specified. Control can be carried out by a discrete or analog bipolar signal. This mode can be used for machines where it is necessary to change the clamping force, pressure, etc.
The current motor torque required for control is assessed using a built-in current sensor.
Scheme and types of servos
The operating principle of a servo drive is based on feedback from one or more system signals. The output indicator is fed to the input, where its value is compared with the setting action and the necessary actions are performed - for example, the engine is turned off. The simplest implementation option is a variable resistor, which is controlled by the shaft - when the parameters of the resistor change, the parameters of the current supplying the motor change.
In real servos, the control mechanism is much more complex and uses built-in controller chips. Depending on the type of feedback mechanism used, analog and digital servos are distinguished. The former use something similar to a potentiometer, the latter use controllers.
The entire servo control circuit is located inside the housing, control signals and power are supplied, as a rule, through three wires: ground, supply voltage and control signal.
Continuous rotation servo 360, 180 and 270 degrees
There are two main types of servomotors - with continuous rotation and with a fixed angle (most often, 180 or 270 degrees). The difference between servo limited rotation lies in the mechanical elements of the design that can block the movement of the shaft outside the angles specified by the parameters. Having reached an angle of 180, the shaft will affect the limiter, and it will give a command to turn off the motor. Continuous rotation servomotors do not have such limiters.
Servo gear materials
For most servos, the connecting link between the shaft and external elements is a gear, so it is very important what material it is made of. There are two most affordable options: metal or plastic gears. In more expensive models you can find elements made of carbon fiber and even titanium.
Plastic options are naturally cheaper, easier to manufacture, and are often used in inexpensive servos. For educational projects where the servo makes a few movements, this is not a big deal. But in serious projects, the use of plastic is impossible, due to the very rapid wear of such gears under load.
Metal gears are more reliable, but this, of course, affects both the price and the weight of the model. Thrifty manufacturers can make some parts plastic and some metal, this should also be kept in mind. And, naturally, in the cheapest models, even the presence of a metal gear is not a guarantee of quality.
Titanium or carbon gears are the most preferable option if you are not limited by budget. Lightweight and reliable, such servos are widely used to create models of cars, drones and aircraft.
Advantages of servo motors
The widespread use of servo drives is due to the fact that they have stable operation, high resistance to interference, small size and a wide range of speed control. Important features of servos are the ability to increase power and provide information feedback. And it follows that in the forward direction the circuit is a transmitter of energy, and in the reverse direction it is a transmitter of information that is used to improve control accuracy.
Differences between a servo and a conventional motor
By turning a conventional electric motor on or off, we can generate a rotating motion and cause wheels or other objects attached to the shaft to move. This movement will be continuous, but in order to understand at what angle the shaft has turned or how many revolutions it has made, you will need to install additional external elements: encoders. The servo drive already contains everything necessary to obtain information about the current rotation parameters and can turn off independently when the shaft rotates to the required angle.
Differences between servo and stepper motor
An important difference between a servo motor and a stepper motor is the ability to work with high accelerations and under variable loads. Also, servo motors have higher power. Stepper motors do not have feedback, so the effect of loss of steps may be observed; in servomotors, loss of steps is excluded - all violations will be recorded and corrected. With all these obvious advantages, servomotors are more expensive devices than stepper motors, have a more complex connection and control system and require more qualified maintenance. It is important to note that stepper motors and servos are not direct competitors - each of these devices has its own specific area of application.
Recovery process
Regeneration occurs when the direction (sign) of the load torque changes in relation to the torque of the servomotor. If the recovery energy is small, it accumulates on the DC link capacitors, increasing the voltage across them.
If the difference between the absolute torque values of the load and the servomotor is significant, the voltage on the DC bus capacitors may exceed the threshold level. In this case, the regenerative energy is dumped into the braking resistor.
Other useful materials:
Choosing the optimal motor size Servo drive or stepper motor? PLC Programming Principles