To automate many production processes, it is necessary to monitor the water level in the tank; the measurement is carried out using a special sensor that gives a signal when the process medium reaches a certain level. It is impossible to do without level meters in everyday life; a striking example of this is the shut-off valve of a toilet cistern or an automatic system for shutting off a well pump. Let's look at the different types of level sensors, their design and operating principle. This information will be useful when choosing a device for a specific task or making a sensor yourself.
Various types of level sensors
Design and principle of operation
The design of measuring devices of this type is determined by the following parameters:
- Functionality, depending on this device, is usually divided into alarms and level meters. The former monitor a specific tank filling point (minimum or maximum), while the latter continuously monitor the level.
- The operating principle can be based on: hydrostatics, electrical conductivity, magnetism, optics, acoustics, etc. Actually, this is the main parameter that determines the scope of application.
- Measuring method (contact or non-contact).
In addition, the design features are determined by the nature of the technological environment. It is one thing to measure the height of drinking water in a tank, another to check the filling of industrial wastewater tanks. In the latter case, appropriate protection is necessary.
Design features and operating principle
The design of liquid level meters in a tank is determined by the following characteristics:
- Functionality. Based on this parameter, all measuring devices of this class are classified into level meters and liquid level alarms. The latter determine the specific filling point of the container (maximum and minimum), while the former constantly monitor the liquid level.
- Operating principle. This parameter is based on acoustics, optics, magnetism, electrical conductivity, and so on. The scope of its application depends on the principle of operation of the device.
- Measurement technique (non-contact or contact).
In addition, the design features of the device determine the type of process environment. For example, level gauges in drinking water tanks are different from devices that are designed to measure the fullness of tanks with industrial wastewater.
Types of level sensors
Depending on the principle of operation, alarms are usually divided into the following types:
- float type;
- using ultrasonic waves;
- devices with a capacitive level detection principle;
- electrode;
- radar type;
- working on the hydrostatic principle.
Since these types are the most common, let's look at each of them separately.
Float
This is the simplest, but nevertheless effective and reliable way to measure liquid in a tank or other container. An example implementation can be found in Figure 2.
Rice. 2. Float sensor for pump control
The design consists of a float with a magnet and two reed switches installed at control points. Let us briefly describe the principle of operation:
- The container is emptied to a critical minimum (A in Fig. 2), while the float drops to the level where reed switch 2 is located, it turns on the relay that supplies power to the pump pumping water from the well.
- The water reaches the maximum level, the float rises to the location of reed switch 1, it is triggered and the relay is turned off, accordingly, the pump motor stops working.
It’s quite easy to make such a reed switch yourself, and setting it up comes down to setting on-off levels.
Note that if you choose the right material for the float, the water level sensor will work even if there is a layer of foam in the tank.
Ultrasonic
This type of meter can be used for both liquid and dry media and may have an analogue or discrete output. That is, the sensor can limit the filling upon reaching a certain point or monitor it continuously. The device includes an ultrasonic emitter, receiver and signal processing controller. The operating principle of the alarm is demonstrated in Figure 3.
Rice. 3. Operating principle of ultrasonic level sensor
The system works as follows:
- an ultrasonic pulse is emitted;
- the reflected signal is received;
- The duration of signal attenuation is analyzed. If the tank is full, it will be short (A Fig. 3), and as it becomes empty it will begin to increase (B Fig. 3).
The ultrasonic alarm is non-contact and wireless, so it can be used even in aggressive and explosive environments. After initial setup, such a sensor does not require any specialized maintenance, and the absence of moving parts significantly extends its service life.
Electrode
Electrode (conductometric) alarms allow you to monitor one or more levels of an electrically conductive medium (that is, they are not suitable for measuring the filling of a tank with distilled water). An example of using the device is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Liquid level measurement with conductometric sensors
In the example given, a three-level alarm is used, in which two electrodes control the filling of the container, and the third is an emergency one to turn on the intensive pumping mode.
Capacitive
Using these alarms, it is possible to determine the maximum filling of the container, and both liquid and bulk solids of mixed composition can act as the process medium (see Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Capacitive level sensor
The operating principle of the alarm is the same as that of a capacitor: the capacitance is measured between the plates of the sensitive element. When it reaches the threshold value, a signal is sent to the controller. In some cases, a “dry contact” design is used, that is, the level gauge operates through the tank wall in isolation from the process medium.
These devices can operate over a wide temperature range, are not affected by electromagnetic fields, and can operate over a long distance. Such characteristics significantly expand the scope of application up to severe operating conditions.
Radar
This type of alarm device can truly be called universal, since it can work with any process environment, including aggressive and explosive ones, and pressure and temperature will not affect the readings. An example of how the device works is shown in the figure below.
Level measurement with radar sensor
The device emits radio waves in a narrow range (several gigahertz), the receiver catches the reflected signal and, based on its delay time, determines how full the container is. The measuring sensor is not affected by pressure, temperature or the nature of the process fluid. Dustiness also does not affect the readings, which cannot be said about laser alarms. It is also necessary to note the high accuracy of devices of this type; their error is no more than one millimeter.
Hydrostatic
These alarms can measure both maximum and current filling of tanks. Their operating principle is demonstrated in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Fill measurement with gyrostatic sensor
The device is built on the principle of measuring the level of pressure produced by a column of liquid. Acceptable accuracy and low cost have made this type quite popular.
Within the scope of the article, we cannot examine all types of alarms, for example, rotary-flag ones, for identifying granular substances (a signal is sent when the fan blade gets stuck in a granular medium, after first tearing out the pit). It also makes no sense to consider the principle of operation of radioisotope meters, much less recommend them for checking the level of drinking water.
Liquid level relay
Level control relays are used to regulate the volume of electrically conductive liquid and are used in automation and protection circuits for controlling the draining and filling of tanks. The operating principle is based on monitoring the fluid resistance between immersed unipolar electrodes. For control, alternating voltage is used. These devices control the operation of pump starters and valves to regulate liquid levels, and are also used to protect pumps from dry running or protect tanks from overfilling with liquid. The liquid level switch maintains a given liquid level in industrial tanks, swimming pools, cisterns, etc.
These devices are distinguished by excellent performance characteristics and a high degree of reliability.
The following are level relays from the main domestic and foreign manufacturers:
Level control relay RKU-1M (Relay and Automation, Russia)
RKU-1M relays are designed to control liquid levels and are used in relay protection and automatic control circuits for draining and filling wells or tanks.
- Supply voltage 220V 50Hz
- Power consumption no more than 3.5W
- Sensitivity 50 kOhm
- Number of sensors 3
- The maximum distance from the relay to the sensor is no more than 100m
- Number of contacts 1 changeover
- Rated current 8A
Level sensor-relay ROS-301 (Russia)
Level sensors-relays POS 301 are designed to monitor three levels of electrically conductive liquids through three independent channels in one or in different tanks in stationary and shipboard conditions outside hazardous areas.
Single-level level relay PZ-828 F&F EuroAutomatika (Belarus)
single-level automatic level control with sensitivity adjustment, 16 A, 230 V
The sensor monitors the voltage level in the network and, if it goes beyond the established limits, disconnects the protected equipment from the power supply network. The upper and lower voltage limits are set by a potentiometer on the front panel.
Two-level level relay PZ-829 F&F EuroAutomatika (Belarus)
two-level automatic level control with sensitivity adjustment, 2 x 16 A, 230 V
The machine controls the presence of liquid at two levels. If the liquid level drops below the minimum level, contacts 11 - 12 and 8 - 9 close. When the liquid reaches the upper level, contacts 7 - 8 and 10 - 11 close.
Three-level level relay PZ-830 F&F EuroAutomatika (Belarus)
three-level automatic level control with sensitivity adjustment, 2 x 16 A, 230 V
Designed to control and maintain a given level of conductive liquids and control electric motors of pumping units. The machine controls the presence of liquid at three levels. The third level is emergency.
Three-level (automatic level control) PZ-831 F&F EuroAvtomatika (Belarus)
The operation of the machine is based on measuring the resistance of electrically conductive liquids between a common probe (COM) and probes of 3 levels (R1, R2, R3). When a liquid connects a common probe to any of the remaining probes, the corresponding output relay switches.
For example, if you place probes of three levels (R1, R2, R3) at different heights relative to the bottom of the tank, each of the output relays will signal when the liquid reaches the corresponding level (this signal can turn on some additional equipment).
If you place probes of 3 levels (R1 R2, R3) in 3 different tanks, then you can independently record the achievement of a certain liquid level in each of them. In this case, it is necessary to install a separate common probe (COM) in each of the tanks and connect them to terminal 3 of the relay.
Four-level level relay PZ-832 F&F EuroAutomatika (Belarus)
Designed to control and maintain a given level of conductive liquids in tanks, swimming pools, water towers, etc. and control of electric motors of pumping units.
Liquid level monitoring relay with 3 sensors EBR-1 (Orbis, Spain)
EBR-1 is a modular electronic liquid level control relay with a maximum distance between sensors of 100 meters. Can be used for public water bodies, for example to control the drainage and filling of a well or tank. 3 sensors are connected to the device, which are supplied along with the level switch.
- Power supply 230V AC, 50-60 Hz
- Load 6(2)A 250V AC
- Power consumption 3.5 VA
- Sensitivity 50KOhm max.
- Number of sensors 3
- Operating temperature -10°С to +45°С
- Protection class IP20
- DIN rail installation
Liquid level control relay with 6 sensors EBR-2 (Orbis, Spain)
The EBR-2 is a modular electronic liquid level relay specifically designed for monitoring liquid levels in tanks and wells. EBR-2 also has many settings, notification when max. or min. level, sensors are sensitive to the electrical conductivity of water, installation on a DIN rail. Supplied complete with 6 sensors. The price makes the EBR-2 an ideal solution for modern liquid level monitoring.
- Power supply 230V AC or 380V AC,50-60 Hz
- Load 6(2)A 250V AC / 8(1)A 400V AC
- Power consumption 4 VA
- Sensitivity 0 to 50KOhm max.
- Number of sensors 6
- Operating temperature -10°С to +45°С
- Protection class IP20
- DIN rail installation
Level control relay E3LM10 (TELE, Austria)
E3LM10 liquid level monitoring relay monitors the level of a conductive liquid using immersed electrodes.
(Two-level/Single-level control)
- Supply voltage 230V AC
- Response delay from 0.5s to 10s
- Number of contacts 1 changeover
- Rated current 5A
Level control relay MRL01 (BMR, Czech Republic)
MRL01 is a two-function liquid level control relay designed to control the maximum and minimum levels of conductive liquid in a container.
- Power consumption max. 1.5 VA
- Sensitivity 5 Ω … 100 kΩ
- Response delay 5 s
- Number of contacts 1 x changeover
- Rated current 8 A
- Peak current 15 A
Level control relay HRH-1 (ELCO, Czech Republic)
HRH-1 liquid level controller is used to control the liquid level in wells, containers, collectors, etc.
The following configurations can be used within one device:
- simple liquid level controller with single level control
- simple liquid level controller with two-level control
- 2 independent level controllers with single level control
Galvanically isolated power supply AC 230 V, AC/DC 24 V or AC 110V Output contact 2x changeover. 16 A / 250 V AC1
Level control relay HRH-5 (ELCO, Czech Republic)
The HRH-5 liquid level controller is used to control the liquid level in wells, tanks, containers, pools, etc.
The following configurations can be selected within one product:
- single level conductive fluid controller(achieved by connecting H and D)
- two-level conductive liquid controller
Galvanically isolated power supply UNI 24.. 240V AC/DC Output contact 1x changeover 8 A / 250 V AC1
Level control relay RKU-10 (ELTIC, Ukraine)
Level control relay RKU-10 is designed to control the liquid level in pools and tanks
The level is maintained by the modes of pumping or pumping out liquid (the mode is selected by a switch).
The sensor can be any conductive material (brass or stainless steel), the sensor is galvanically isolated from the power source. The industrial frequency of 50Hz prevents liquid polarization and increased oxidation of sensors.
- supply voltage 230V 50Hz
- power consumption 8.8W
- measured resistance 5kOhm…10kOhm
- contact group 1NO
- switching current 16A (peak 30A)
Level control relay Telemecanique Zelio Control RM35L (Shneider Electric)
RM35LM33MW RM35LV14MW
Zelio Control level control relays have an operating principle based on measuring liquid resistance, which avoids the problems typical of contact sensors. The level control relay provides the ability to adjust the measurement sensitivity to ensure optimal response levels of the device. In addition, the relays have an adjustable time delay to compensate for liquid sloshing, which avoids false alarms of the device caused by liquid fluctuations. The family also includes relays with digital sensor inputs designed for level measurement of non-conductive materials. Optimized for different power supply networks: from 24 to 240 V AC/DC. current Adjustable time delay from 0.1 to 10 s.
RM35LM33MW :
- 0.25…5 K 5…100 K 0.05…1 M
- 2 perek. rel., 5A
RM35LV14MW:
- Sensor discrete input: contact/closed/opened
- 1 perek. rel., 5 A
Level control relay 72 series Finder (Italy)
72 series level control relay for conductive liquids with fill and drain functions.
72.01 - adjustable sensitivity range (5...150) kOhm, time delay (0.5s or 7s)
72.11 - fixed threshold value 150 kOhm, fixed time delay 1s
- supply voltage 24V DC/AC, 110 AC, 230 AC
- 1 changeover contact
- rated contact current 16A, peak 30A
- +
How to choose?
The choice of a water level sensor in a tank depends on many factors, the main ones:
- Composition of the liquid. Depending on the content of foreign impurities in the water, the density and electrical conductivity of the solution may change, which is likely to affect the readings.
- The volume of the tank and the material from which it is made.
- The functional purpose of the container is to accumulate liquid.
- The need to control the minimum and maximum level, or monitoring of the current state is required.
- Admissibility of integration into an automated control system.
- Switching capabilities of the device.
This is not a complete list for selecting measuring instruments of this type. Naturally, for domestic use it is possible to significantly reduce the selection criteria, limiting them to the volume of the tank, the type of operation and the control circuit. A significant reduction in requirements makes it possible to independently manufacture such a device.
Water pressure sensor
Hydrostatic pressure is determined under conditions where a flow or a certain volume of water is at rest. Most often, a hydrostatic sensor is used in heating and heating devices - boilers, heating boilers.
Water pressure sensor device
Such devices most often operate in trigger mode:
- When water pressure is high, the sensor closes the relay contacts and allows the pump or heater to operate;
- When the pressure in the sensor is low, even the physical ability to turn on the actuator is blocked, that is, no shocks or temporary surges in pressure will make the device work.
If the water pressure sensor is working properly, the sensor will give a signal to start the motor only if the load on the bellows remains for more than three seconds.
A typical smart sensor device is shown in the diagram.
The sensitive element of the system is a diaphragm connected to a bellows; the central rod can rise and fall depending on the pressure, and thereby change the capacity of the built-in capacitor.
Connecting the water pressure sensor
A simplified model of the sensor is used in home systems “hydraulic accumulator - well pump”. Inside the device there is a box with a membrane connected to a swing arm and two balancing springs.
The design is screwed onto the outlet fitting of the hydraulic accumulator. With an increase in internal pressure, the membrane rises and opens the main pair of contacts, so that the system responds properly to water pressure, the moment of turning off and turning on must be adjusted by the settling of the small and large springs in accordance with the readings of the dial pressure gauge.
Making a water level sensor in a tank with your own hands
Let's say there is a task to automate the operation of a submersible pump for water supply to a dacha. As a rule, water flows into a storage tank, therefore, we need to make sure that the pump automatically turns off when it is filled. It is not at all necessary to buy a laser or radar level indicator for this purpose; in fact, you don’t need to purchase any. A simple problem requires a simple solution, it is shown in Figure 8.
Water pump control circuit
To solve the problem, you will need a magnetic starter with a 220-volt coil and two reed switches: a minimum level for closing, a maximum level for opening. The pump connection diagram is simple and, importantly, safe. The principle of operation was described above, but let’s repeat it:
- As the water collects, the float with the magnet gradually rises until it reaches the maximum level reed switch.
- The magnetic field opens the reed switch, turning off the starter coil, which leads to de-energization of the engine.
- As the water flows, the float drops until it reaches the minimum mark opposite the lower reed switch, its contacts close, and voltage is supplied to the starter coil, which supplies voltage to the pump. Such a water level sensor in a tank can work for decades, unlike an electronic control system.
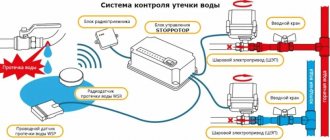
Water leakage sensor
Already from the name it becomes clear that we are talking about a device that detects the presence of water leaks from water supply lines. The operating principle of the device resembles an electrode system. Inside the plastic box, one or more pairs of electrodes are installed in a special pocket. In the event of an accident, water accumulating on the floor flows into the pocket and closes the contacts. The electronic circuit is activated, and based on the sensor signal, the electrically driven ball valves come into operation.
It is clear that the sensor itself is useless if it is used without a control system and automatic water shutoffs installed at the entrance to the house or on one of the water supply branches.
As an example, one of the most popular protection systems is the Neptune water leak sensor. The system includes three main blocks:
- The Neptune leak sensor itself is available in a wired or wireless version; the kit usually includes three separate sensors;
- Ball valve with electric drive, made in Italy, two pieces;
- Control unit "Neptune Base".
The most valuable part of the kit is the automatic taps; they are produced for installation on half-inch and inch pipe threads. The design can withstand pressure up to 40 Atm., and the Italian quality of the drive guarantees at least 100 thousand opening-closing cycles.
The sensor itself looks like two brass plates in a box, to which a low voltage voltage is applied with a very high input resistance; when the sensor is shorted, the current is limited to 50 mA. The design itself is made according to the IP67 protocol, therefore it is absolutely safe for humans.
Installation of wireless water leakage sensors
In the Neptune system, the sensor can be removed from the control unit at a distance of more than 50 m. In more advanced NEPTUN PROW+ wireless systems, instead of a wire system, water leakage sensors equipped with a WF module are used.
The control unit is equipped with a channel protected from interference and moisture, and an on/off system for ball valves. It is believed that no interference or random drops of moisture or condensation affect the operation of the sensors.
Boxes with a leakage sensor are installed no more than 2 m away from the pipes; the sensors cannot be shielded by metal plumbing fixtures or furniture.
Wireless water leak sensor
The design of a wireless meter is more complex than a conventional two-electrode version with a wired connection. There is a controller installed inside that continuously compares the current flowing between the electrodes with a reference value stored in memory. In this case, the reference value “dry floor” can be adjusted according to your own choice.
A very convenient solution, considering that the humidity level in the bathroom can be very high, and regularly occurring condensation can lead to false alarms.
As soon as the controller determines the level corresponding to flooding, the water control device sends an alarm signal to the base unit. The most advanced models are capable of duplicating a command via SMS message via GSM channel.
Level switch with float sensor
Sensors of this type are usually used to monitor the level of non-aggressive liquids.
If we are talking about an open container, then the float is immersed directly into it. Moreover, it is suspended using a flexible cable. And for balancing they use a special weight.
The cable of this system is equipped with two switching supports. They serve to rotate the rocker arm located in the contact device. Moreover, this happens at those moments when the water surface reaches maximum levels. As a result, the rocker closes certain contact pairs. Which turn on the electric motor of the pump or turn it off.
If the container is closed, then the float is mounted on a lever. The second end of the lever is located in a housing containing the contact part of the sensor. That is, the node from which the signal goes to the level relay.
But users do not need special knowledge about the sensor design. Because, as a rule, each level relay is sold together with the sensor that is best suited for it. After purchase, the user only needs to connect the kit and configure it. But, of course, this must be done correctly.
Water flow sensor
In many cases, for stable and trouble-free operation of equipment, a water presence sensor is not enough; information is required about whether the flow is moving through the pipeline, what its speed and pressure are. For these purposes, water flow sensors are used.
Types of water flow sensors
In household and most simple industrial equipment, four main types of flow sensors are used:
- Pressure meter;
- Petal type sensor;
- Blade measurement scheme;
- Ultrasound system.
An outdated pitot tube design is sometimes used, but for reliable operation it requires at a minimum the absence of contamination and laminar water flow. The first three sensors are mechanical, so they are often subject to clogging or water erosion of the sensing element. The latest type of sensor, ultrasonic, is capable of operating in almost any environment.
The operating principle of an ultrasonic meter can be understood from the diagram. Inside the tube there is a wave emitter and a receiver. Depending on the flow speed, the sound wave may deviate from its original direction, which serves as the basis for measuring the flow characteristics.
Design and principle of operation
The simplest petal flow sensors work on the principle of a rowing oar. A petal suspended on a hinge is immersed in the flow. The higher the flow speed, the more the sensor lobe deflects.
More accurate vane sensors use an impeller or turbine made of polyamide or aluminum alloy. In this case, it is possible to measure the flow speed by the rotation frequency of the moving element. The only drawback is the increased resistance created by the petals and blades in the water flow.
The pressure sensor operates using dynamic flow pressure. Under the pressure of water, the movable element with a magnetic liner is squeezed upward, thereby freeing up space for the movement of liquid. The reed switch installed in the head instantly reacts to the magnetic field of the liner and closes the circuit.
Float-type level sensors and alarms
Float sensors and level switches are the simplest element of a level control automation system. Due to the simplicity of the device, float devices are highly reliable, low cost and can be used with various types of liquids, from distilled water to aggressive liquids. Operating principle of sensors
and signaling devices of this type is based on the effect of buoyant force on a float, the mass and volumetric density of which is less than the density of the controlled liquid. Float level sensors consist of a housing with a built-in microswitch and a connecting cable. Hollow polypropylene balls or spherocylinders are most often used as floats. Sometimes the float material is indicated in the name of the device, for example, polypropylene float switch. The connecting cable is made of polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride. Such materials are used to make sensors resistant to aggressive media, such as weakly concentrated solutions of acids and alkalis, inorganic solvents, gasoline, diesel fuel, and wastewater. The switching element is a liquid metal switch without mercury. Switching occurs when the sensor deviates from the horizontal plane by an angle from 3 to 18 degrees. The switching voltages used in float sensors range from 20 to 265 VAC or from 6 to 60 VDC. Operating temperature up to 120 degrees Celsius. Float switches can be equipped with additional weights or secured to the guide using locking rings.