General data required for calculations
The more powerful the electric heater, the faster it heats a given amount of water. Therefore, devices for this parameter are selected in accordance with the tasks, the required volume and the allowable waiting time. So, for example, heating 15 liters to 60°C with a 1.5 kW heater will take about an hour and a half. However, for large volumes (for example, to fill a 100-liter bath) with a reasonable waiting time (up to 3 hours), a device 3 kW more powerful will be needed to bring the liquid to a comfortable temperature.
To fully calculate the design power, it is necessary to take into account a number of parameters:
Storage water heaters (boilers)
Without physical and mathematical formulas, a household calculation is described as follows: in 1 hour, 1 kW heats 860 liters per 1 K. To more accurately determine the heating time, power characteristics, and volume, a universal formula is used, from which the remaining results are then derived:
This formula consists of several and reflects a number of parameters, taking into account the heat loss factor. (With low power characteristics and large volume, this factor becomes more significant, however, in household heaters this accounting value is often neglected):
N full – power characteristics of the heating element,
Q c – heat loss of the water heating tank.
- c= Q/m*(tк-tн)
- C – specific heat capacity,
- Q – amount of heat,
- m – mass in kilograms (or volume in liters),
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures.
- N=Q/t
- N – heating power characteristics.
- t—heating time in seconds.
- N = N full — (1000/24)*Q c
Simplified formulas with a constant coefficient:
- Calculation of the power of the heating element for heating water at the desired temperature: W= 0.00117*V*(tk-tn)/T
- Determination of the time required to heat water in a water heater: T= 0.00117*V*(tк-tн)/W
Formula components:
- W (in kW) – power characteristic of heating elements (heating element),
- T (in hours) – water heating time,
- V (in liters) – tank volume,
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures (final – usually 60°C).
Volume is often equated to mass (m). Then the power of the heating element will be determined using the formula: W= 0.00117*m*(tk-tn)/T. The formulas are considered simplified, also because they do not take into account:
- actual power of the electrical network,
- ambient temperature,
- design features and potential heat loss of the tank,
- recommendations of some manufacturers regarding temperature (about 5-8 °C in summer and 15-18 °C in winter).
When purchasing a device, you must take into account that the relatively low power characteristics of storage water heaters compared to instantaneous water heaters do not yet guarantee financial savings. Savings ones “take away” less, but due to the fact that they work longer, they spend more. For financial savings, a more reliable strategy would be a general reduction in water consumption through the installation of various types of savers (https://water-save.com/) and strict accounting of water consumption.
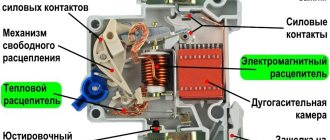
Electric heating element device
The design of heating elements includes the following components:
- metal tube;
- spiral;
- filler;
- ceramic insulator;
- contact rod.
The spiral is completely sealed in a metal tube and connected to a contact rod, the outer edge of which has the necessary projections for connection with the element that supplies the electric current. This design of heating elements eliminates the possibility of short circuits and ensures uniform distribution of heat over the entire surface of the metal tube.
The insulating filler of the spiral from the heating element tube is periclase, a mineral consisting of magnesium oxide sometimes with admixtures of iron oxide, manganese oxide and zinc oxide.
The metal tube of the heater is made of alloys:
- pure brass (Fig. 1) and copper (Fig. 2). These heating element tube materials are necessarily used with coatings;
- become. The steel can be either stainless (Fig. 3) or carbon (Fig. 4), it depends on the design features and operation of the heating element;
- aluminum (Fig. 5)
It can have different diameters, from 6 to 19 mm. The design of the block heating element can be equipped with a temperature sensor and an overheating fuse.
The choice of metals and their alloys depends on the working environment of the heating element. These can be alkalis and acids, air with low and high concentrations of active gases, various metal surfaces that will come into contact with the heating element, fatty compounds and aqueous solutions.
A conductive fechral or nichrome spiral acts as a heating element. Fechral spiral is an iron alloy with additions of copper, manganese, aluminum, titanium and other metals. The main advantages of a spiral made of fechral or its varieties (eurofechral, superfechral) are low price, high resistivity and heat resistance.
A nichrome spiral is an alloy of nickel and chromium and has the same characteristics as fechral, but the main difference between fechral and nichrome spirals is the specific operating temperature when open: a fechral spiral can withstand maximum heating up to +1400 °C, and nichrome spirals up to 1200 °C.
The contact rod can have a cartridge or single-end shape. Depending on the area of operation, air, water or oil heating elements are often distinguished. Heating elements that are used in various gaseous spheres are also classified as air.
Instantaneous water heaters
When calculating the amount of heat for heating running water, it is necessary to take into account the difference in voltage standards in Russia (220 V) and Europe (230 V), since a significant part of electric water heaters are manufactured by Western European companies. Thanks to this difference, the nominal value of 10 kW in such a device when connected to a Russian 220V network will be 8.5% less - 9.15.
The maximum hydraulic flow V (in liters per minute) with given power characteristics W (in kilowatts) is calculated by the formula: V = 14.3 * (W/t 2 -t 1), in which t 1 and t 2 are the inlet temperatures heater and as a result of heating, respectively.
Approximate power characteristics of electric water heaters in relation to domestic needs (in kilowatts):
- 4−6 – only for washing hands and dishes,
- 6−8 – for taking a shower,
- 10−15 – for washing and showering,
- 15−20 – for complete water supply to an apartment or private house.
The choice is complicated by the fact that the heaters are available in two connection options: to a single-phase (220 V) and three-phase (380 V) network. However, heaters for single-phase networks, as a rule, are not produced above 10 kilowatts.
Swimming pool calculations
The calculation of heating water in a pool consists of calculating the parameters of the electric heater and the volume that needs to be heated. The table shows the approximate time in hours during which the temperature rises from 10 °C to 28 °C. In this case, the area of the water “mirror”, the ambient temperature, and the degree of openness/closeness of the pool location play a significant role in the final calculations.
Determining the technical parameters of devices and calculating water heating - the power of the heater, coil, amount of heat and energy consumption for heating water - depends on the type of electric water heater, which can be storage or instantaneous.
Calculation of parameters for heating automation cabinets
Every year, technology development occurs more and more rapidly and very few processes in production can already be done without automation. It is very important to keep equipment that automates production processes in working order for as long as possible, so solutions for its protection are constantly being improved.
The most optimal way to preserve electrical appliances is to place them in special protective electrical cabinets, called automation and control cabinets. Such electrical panels are metal cabinets that can protect equipment from humidity, dust, water droplets and other negative factors.
However, even inside the automation cabinet itself there are a number of conditions that can also negatively affect the operation of electrical components located inside. In this article we will look at some of them in detail.
High cabinet temperature
When almost any electrical equipment operates, a certain amount of heat is generated. This is especially noticeable in the hot season, when heating of equipment can lead to overheating and failure. To avoid this situation, forced air cooling in the control cabinet is necessary. Fans for the control room can help with cooling.
Low ambient temperature
Cold can cause no less damage to electrical equipment than overheating. Most devices are not designed to operate at low air temperatures, and negative air temperatures in winter do not allow them to start at all.
Therefore, for automation cabinets located outdoors or in poorly heated rooms, it is necessary to ensure proper heating in the winter.
Not only does low air temperature itself have a bad effect on equipment, it also causes condensation to form on the interior surfaces of the cabinet when the air temperature inside reaches the dew point.
The dew point is the extreme air temperature at a certain humidity, below which water vapor begins to condense. In the table you can see dew point data for a certain humidity and ambient temperature.
| Relative humidity, % | Ambient temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | |
| 40 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 19 | 24 | 28 | 33 | 37 |
| 50 | 9 | 14 | 19 | 23 | 28 | 32 | 37 | 41 |
| 60 | 12 | 17 | 21 | 26 | 31 | 36 | 40 | 45 |
| 70 | 14 | 19 | 24 | 29 | 34 | 38 | 43 | 48 |
| 80 | 16 | 21 | 26 | 31 | 36 | 41 | 46 | 51 |
| 90 | 18 | 23 | 28 | 33 | 38 | 43 | 48 | 53 |
| 100 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 |
In order to neutralize all the negative conditions for the operation of electrical appliances in automation cabinets, it is necessary to calculate the exact power of the heating elements, which is necessary to heat the air to the optimal temperature. The calculation formula is based on many different parameters, which in turn also need to be correctly calculated and taken into account. Based on the received power, the most suitable heating equipment is selected: OSHA heaters, fans, thermostats.
Location and dimensions of the automation cabinet body
First, you need to calculate the area of the walls of the automation cabinet body based on its dimensions. Then, depending on the location of the control cabinet, you need to determine which walls of the control cabinet will dissipate heat. Obviously, the dissipation area will be larger in free-standing electrical cabinets, and control panels in the middle of a row of similar panels will not be in contact with the environment on all sides of the housing, therefore, the dissipation surface area will be smaller.
To organize cooling of the automation cabinet, it would be better if the heat dissipation area is as large as possible. For example, if you have the same set of electrical appliances, then cooling them in a larger control cabinet will be much easier than in a compact electrical panel. But for cooling it’s quite the opposite: it’s easier to heat the air in a small cabinet.
For each control cabinet placement option, you can use ready-made formulas that will help you easily and quickly calculate the dissipation area of the cabinet body surface.
| Cabinet location | Calculation formula |
| Separate accommodation | A = 1.8 H (W + D) + 1.4 W D |
| Wall location | A = 1.4 W (H + D) + 1.8 D H |
| Last place in a row of cabinets | A = 1.4 D (H + D) + 1.8 W H |
| The last place in a row on the wall | A = 1.4 H (W + D) + 1.4 W D |
| Position in the middle of the row | A = 1.8 W H + 1.4 W D + D H |
| In the middle of the row on the wall | A = 1.4 W (H + D) + D H |
| Location on the wall in the middle of the row under the canopy | A = 1.4 W H + 0.7 W D + D H |
Heat flux density
Heat flux density is an indicator of the rate of heat dissipation inside the electrical control panel. This parameter directly depends on atmospheric pressure, so it is very easy to calculate it from the table, knowing the altitude above sea level for the area.
The higher the pressure, the better the heat will dissipate, therefore, cabinets located higher above sea level in an area with lower pressure will dissipate less heat.
For the central zone of the Russian Federation, the heat flux density is 3.2 at an average height above sea level of 170 m.
Thermal conductivity of electrical cabinet housing materials
When calculating the heating power of automation cabinets, the material from which it is made is also important. A parameter such as the heat transfer coefficient depends on the type of metal.
The heat transfer coefficient is a certain amount of heat transferred per unit time through 1 m2 of effective heat exchange surface from a more heated zone to a less heated one.
Let's take as an example the three most common types of metals for control cabinets: painted sheet steel, stainless steel and aluminum. Aluminum has the highest heat transfer coefficient (12), followed by painted steel (5.5), and stainless steel has the lowest (4.5). Based on this, we see that if cooling is necessary, it is better to use aluminum cabinets, as they will dissipate heat well. Due to its good heat transfer, aluminum is used in most types of radiators, in particular in OSHA heaters from the manufacturer The thermoelement radiator is also made of aluminum.
Heat generation by equipment in the automation cabinet
The composition of the set of electrical appliances located in the control cabinet is also an important indicator in power calculations. After all, many types of electrical equipment are capable of generating large amounts of heat when heated and even require additional cooling during the hot season. Among the electrical appliances placed in automation cabinets there are many power supplies, solid-state relays, transformers, frequency converters and other elements. Each of them generates a certain amount of thermal energy and this must also be taken into account when calculating.
Calculation of temperature inside the control room
The formula for calculating the temperature inside the control cabinet is as follows:
Tvnut = Qv * k * A + Tnar
Tvnut – air temperature inside the automation panel,
Tnar – outside air temperature,
Qv – heat release from electrical appliances installed in the control room
k – heat transfer coefficient of the metal from which the automation cabinet body is made
A – effective heat exchange surface area
You can quickly calculate heat generation using the formulas presented in this table:
| Device | Formula for calculation |
| Frequency converters | Qpch = total power * 0.05 |
| Power supplies | Qbp = total power * 0.1 |
| Slot machines | Qa = total current * 0.2 |
| Starters | Qп = total current * 0.4 |
| Transformers | Qt = total power * 0.1 |
| Solid State Relays | Qр = total load current for each phase * 1.2 |
The total heat release of the components Qv is then calculated as the total value of the heat release of all electrical appliances.
Based on the results of calculating the internal temperature of the control cabinet, we can compare the calculated value with the optimal temperature for the equipment placed in it. If the temperature inside the cabinet is higher than recommended, you need to cool the air using fans.
If the temperature is not high enough, it is necessary to heat the control room using OSHA heaters. To select the most suitable heater models, you need to determine what total power of the heating elements is needed to maintain the most suitable air temperature in the cabinet.
General data required for calculations
The more powerful the electric heater, the faster it heats a given amount of water. Therefore, devices for this parameter are selected in accordance with the tasks, the required volume and the allowable waiting time. So, for example, heating 15 liters to 60°C with a 1.5 kW heater will take about an hour and a half. However, for large volumes (for example, to fill a 100-liter bath) with a reasonable waiting time (up to 3 hours), a device 3 kW more powerful will be needed to bring the liquid to a comfortable temperature.
To fully calculate the design power, it is necessary to take into account a number of parameters:
Storage water heaters (boilers)
Without physical and mathematical formulas, a household calculation is described as follows: in 1 hour, 1 kW heats 860 liters per 1 K. To more accurately determine the heating time, power characteristics, and volume, a universal formula is used, from which the remaining results are then derived:
This formula consists of several and reflects a number of parameters, taking into account the heat loss factor. (With low power characteristics and large volume, this factor becomes more significant, however, in household heaters this accounting value is often neglected):
N full – power characteristics of the heating element,
Q c – heat loss of the water heating tank.
- c= Q/m*(tк-tн)
- C – specific heat capacity,
- Q – amount of heat,
- m – mass in kilograms (or volume in liters),
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures.
- N=Q/t
- N – heating power characteristics.
- t—heating time in seconds.
- N = N full — (1000/24)*Q c
Simplified formulas with a constant coefficient:
- Calculation of the power of the heating element for heating water at the desired temperature: W= 0.00117*V*(tk-tn)/T
- Determination of the time required to heat water in a water heater: T= 0.00117*V*(tк-tн)/W
Formula components:
- W (in kW) – power characteristic of heating elements (heating element),
- T (in hours) – water heating time,
- V (in liters) – tank volume,
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures (final – usually 60°C).
Volume is often equated to mass (m). Then the power of the heating element will be determined using the formula: W= 0.00117*m*(tk-tn)/T. The formulas are considered simplified, also because they do not take into account:
- actual power of the electrical network,
- ambient temperature,
- design features and potential heat loss of the tank,
- recommendations of some manufacturers regarding temperature (about 5-8 °C in summer and 15-18 °C in winter).
When purchasing a device, you must take into account that the relatively low power characteristics of storage water heaters compared to instantaneous water heaters do not yet guarantee financial savings. Savings ones “take away” less, but due to the fact that they work longer, they spend more. For financial savings, a more reliable strategy would be a general reduction in water consumption through the installation of various types of savers (https://water-save.com/) and strict accounting of water consumption.
Features of choice
Electric heaters designed for radiators may differ in several parameters. Therefore, you should approach the choice wisely
Below we will consider what you should pay attention to when choosing a heating element
Power is one of the most important parameters, since the heat transfer of the device depends on it. Therefore, first of all, you need to calculate the required power for comfortable heating of the room.
On average, 1 kW of power is required for every 10 m2. For a more accurate calculation, it is necessary to take into account the region and heat loss of the room. However, if the heaters are used as an additional heating element, then half the power is sufficient.
Note! It makes no sense to use a heater more powerful than 75 percent of the heat output of the radiator itself, since its capabilities will not be fully used
Bimetallic radiator with electric heating element
Radiator type
Heating elements for aluminum heating radiators and bimetallic batteries are structurally no different from heating elements for cast iron appliances.
However, the differences are in the following points:
- The shape of the outer part of the body.
- Plug material.
The heating element for an aluminum radiator has a plug with a diameter of one inch. The diameter of the plug for standard cast iron batteries is 1¼ inches.
Therefore, before purchasing a heater, you should pay attention to what types of batteries it is intended for. This information is usually contained in the instructions that come with the kit.
Heating element length
An important selection parameter is the length of the heating element. As you might guess, the uniform heating of the battery and the circulation of liquid depend on this. Accordingly, the length is selected depending on the number of sections of the device.
Ideally, the heating element should be 10 cm shorter than the battery. In this case, the liquid will be heated as evenly as possible.
Automation
Automation can be built-in or external. It should be noted that a radiator heating element with a built-in thermostat is cheaper than the components separately. However, outdoor electronics tend to be more functional.
The choice depends on the purpose of the heater. If it is to be used as the main heat source, external electronics can be installed to ensure maximum heating comfort. If the device is planned to be used as an additional one, a heating element for heating radiators with a thermostat in one housing is also suitable.
Inexpensive heating element with thermostat for cast iron radiator
Manufacturer
As for the manufacturer, in this case the choice is not so important. The fact is that well-known European companies do not produce this equipment. Therefore, as a rule, you can find products of Polish, Ukrainian and Turkish origin on the market.
All these heating elements are quite similar in quality, so more attention should be paid to their characteristics. The only thing is that it is better to refrain from purchasing Chinese products, since suppliers often import the cheapest, low-quality models. However, even among them sometimes there are decent heaters.
These are, perhaps, all the main points that are important when choosing heating elements for batteries.
The use of heating elements for radiators does not provide any benefits compared to other types of electric heating. However, these heaters are an excellent option for heating all kinds of utility rooms. In addition, they can be used as an additional or emergency heat source.
You can get additional and useful information on this topic from the video in this article.
Instantaneous water heaters
When calculating the amount of heat for heating running water, it is necessary to take into account the difference in voltage standards in Russia (220 V) and Europe (230 V), since a significant part of electric water heaters are manufactured by Western European companies. Thanks to this difference, the nominal value of 10 kW in such a device when connected to a Russian 220V network will be 8.5% less - 9.15.
The maximum hydraulic flow V (in liters per minute) with given power characteristics W (in kilowatts) is calculated by the formula: V = 14.3 * (W/t 2 -t 1), in which t 1 and t 2 are the inlet temperatures heater and as a result of heating, respectively.
Approximate power characteristics of electric water heaters in relation to domestic needs (in kilowatts):
- 4−6 – only for washing hands and dishes,
- 6−8 – for taking a shower,
- 10−15 – for washing and showering,
- 15−20 – for complete water supply to an apartment or private house.
The choice is complicated by the fact that the heaters are available in two connection options: to a single-phase (220 V) and three-phase (380 V) network. However, heaters for single-phase networks, as a rule, are not produced above 10 kilowatts.
Swimming pool calculations
The calculation of heating water in a pool consists of calculating the parameters of the electric heater and the volume that needs to be heated. The table shows the approximate time in hours during which the temperature rises from 10 °C to 28 °C. In this case, the area of the water “mirror”, the ambient temperature, and the degree of openness/closeness of the pool location play a significant role in the final calculations.
When calculating the power of electric heating elements, the following calculation data were used: mass of water, initial and final (desired) water temperature and time spent on heating.
Heating element power P
P=0.0011m(tk-tн)/T
.
in which: m
is the mass of heated water,
tk
and
tн T
The calculation of the power of the heating element is performed by this calculator without taking into account heat losses associated with the design features of the container, ambient temperature, the state of the heating surface of the heating element, etc.
In addition, you should take into account the actual supply voltage, which may differ greatly from the nominal value.
So, at a reduced voltage, the temperature of the working surface will be less than the value declared by the manufacturer, therefore, more time will be required for heating.
Considering the specific gravity of water is 1 g/cm3, the value of its volume can be used in the “Mass of heated water” calculator field when entering data.
When heating cold water from city water supply systems, the recommended initial temperature is 5-8°C in summer and 13-18°C in winter. The result of the calculation (P) can be the power value of either one heating element or several parallel-connected elements.
Electrical calculations online
© Forum220.ru | 2009 – 2015 | Electrical engineering calculations online Placing these materials on other web resources is possible only if there is a hyperlink back to the site Forum220.ru
Water heating time calculator
Operating rules
In order for the heating element installed in the heating radiator to serve you as long as possible, you must follow the following rules:
- Do not use excessive force during the installation process. Do not forcefully tighten the contact nuts and the heating element fastener itself. Brittle material may burst.
- The heater turns on only if there is water in the battery. If liquid gets on the already heated tube of the device, a small thermal explosion may occur. As a result, not only the heating element will fail, but the heating battery may be damaged.
- During operation of the device, scale will form on its surface, which must be cleaned off periodically. The recommended maintenance schedule is once every three months. If the thickness of scale on the heating tube exceeds 2 millimeters, heat transfer will decrease and the device may fail.
- To eliminate possible voltage surges, it is recommended to connect the heating element through an uninterruptible power supply or stabilizer. The heater must be grounded during installation.
- Manufacturers recommend using only distilled water as a coolant. In apartment buildings with a common riser, it is unrealistic to comply with this requirement, so it is necessary to clean the heating elements from scale more often.
When you decide to install heating elements in your home heating system, choose products that match the diameter of your radiators
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the power of the devices. This will ensure optimal temperature conditions indoors.
When choosing a heating element, you can be guided by the following diagram:
- 20 W/m3. This power is suitable for new buildings that have excellent thermal insulation.
- 30 W/m3 – suitable for apartments with plastic windows, walls and floors equipped with reliable thermal insulation.
- 40-50 W/m3. Heating elements with such power are recommended for use in old houses.
Installing a heating element is the best option to ensure comfort and coziness in residential areas. In fact, this design can be compared to an oil heater, but heating elements provide faster and more uniform heating of all rooms in the apartment. It is worth noting that if the utilities in your city are working at the proper level, it is not advisable to install heating elements. Electricity bills will be quite impressive.
The amount of electricity kWh and the cost of heating water.
The calculator will calculate the heating time of water in storage water heaters depending on the capacity of the tank, the power of the heating elements, the heating temperature and the temperature of the incoming water.
You can specify the efficiency of the storage water heater (usually 95-99%).
Calculator taken from the site: https://nagrev24.ru/voda
Electricity is converted into heat and the efficiency depends on the material of the heating element (on the loss of electricity in it and on thermal conductivity), on the area of contact of the element with water, the contact resistance of the contacts and losses in the power cord. At each stage some energy is lost. Depending on the type of device, the efficiency is in the range of 95-99%.
The more effective the thermal insulation properties of the material separating the internal tank from the environment, and the thicker its layer, the more economical the water heater. Modern boilers guarantee a decrease in water temperature of no more than 0.25 - 0.5 degrees per hour and electricity consumption of less than 1 kW/h per day in standby mode.
The most optimal operating temperature for the water heater is 55-60°C. This reduces power consumption to maintain the temperature of hot water, reduces the formation of scale, and provides a more gentle regime for the internal tank.
Heated medium – water
Designation of these heating elements according to GOST 13268-88:
- “R” – material of the heating element tube – black steel;
- “J” – heating element tube material – stainless steel.
The permissible specific power (R permissible) on the surface of the heating element is 15 Watt/sq.cm. This indicator determines the maximum permissible power of the heating element. When selecting water heating elements, the following rules must be observed:
- When operating a heating element, it is necessary to take all measures to prevent the formation of “scale” on its surface - these are deposits on the heating element tube of various impurities present in the liquid. Impurities are present, for example, in dirty or hard water; they envelop the heating element tube in the form of a film of varying thickness. The thicker the film, the worse the heat transfer from the heating element to the liquid, and at some point the heating element may overheat and fail. Water extracted from artesian wells is especially dangerous in this sense. Therefore, from the very beginning of the operation of heating elements, it is necessary to take care of installing all kinds of filters and liquid softeners, as well as carry out preventive cleaning of heating elements and tanks.
- The active part of the heating element must be completely immersed in liquid. Let us recall that the active length of the heating element is equal to its full length minus the length of the “non-heating zone” of the heating element (this is the amount by which the contact pin from the end enters inside the heating element). Most water heating elements have cold zones A = 40 mm and B = 65 mm, so such heating elements must be almost completely immersed in the liquid. In the case of using heating elements with other non-heating zones (C=100 mm; D=125 mm; E=160 mm; F=250 mm; G=400 mm, etc.), the liquid level should be 20 - 30 higher than the non-heating zone mm.
- Sometimes, for technological reasons, the heated liquid must be drained from the reservoir at some intervals. In this case, the heating elements are exposed and move from the aquatic environment to the air, i.e. operate in the “water-air” media change mode (of course, when the liquid is drained, the heating elements are turned off). In such cases, it is not recommended to use heating elements made of black steel, because when heated, cooled and changing environments, black steel begins to intensively corrode (rust) and quickly collapses. But, for example, such conditions do not have a detrimental effect on stainless steel.
- To install the heating element in the tank and seal it (sealing gasket), fittings are attached to the ends of the heating element - bushings with threads and a flange for the gasket. The fitting is secured to the end of the heating element in different ways. One of them is crimping the fitting with special press shears. This method creates a strong and fairly tight connection between the fitting and the heating element tube, which allows the heating element to be used when heating liquid in tanks with an internal pressure of no more than 0.25 MPa (2.5 atm.). That is, in conventional heating systems, in conventional heating tanks, heating elements with pressed fittings are used very widely.
If the pressure in the tank exceeds 2.5 atm. (for example, in steam generators), crimping the fitting no longer provides sufficient tightness, and the fitting must either be soldered or welded to the heating element tube. This must be remembered when ordering a heating element, otherwise the fitting will “pass” liquid through the heating element tube, which will ultimately disable it.
Otherwise, choosing a heating element should not cause difficulties: according to the table on the website, select the power, voltage, length and diameter of the heating element tube, its material and shape, the required fitting and contact part.
How much kWh of energy is spent heating water?
This calculator will calculate how much money, electricity and time is spent heating water. You don't need any formulas or coefficients: just enter your data and get the answer.
To calculate the consumed electricity, you must indicate the temperature of cold and hot water, as well as its volume (mass). You can indicate the efficiency of the heating device if you know it. If you set the efficiency to 100%, the calculation will show only the useful power spent on heating water. When indicating the real efficiency, the calculation will give the total power consumed from the network.
To estimate how long it takes to heat up, indicate the power of the electrical appliance you use to heat water, in kilowatts (kW). The power is often indicated on the body of the device, as well as in its instruction manual or passport.
Boiling water in an electric kettle
I usually fill the kettle with water at room temperature 20°C to the 1 liter mark and always bring it to a boil (up to 100 degrees). Kettle power 2 kW. The simplest calculation shows that boiling will cost approximately 0.1 kWh (kilowatt hours) of electricity, 3 minutes of time, and, according to Moscow tariffs, fifty kopecks of money.
This means that each tea drink adds half a ruble to your electricity bill, but this is significantly less than the price of a serving of tea or coffee.
Heating water in a storage water heater
Every time I take a shower, I completely empty all the hot water from the storage heater, because at the end the water turns cold. In winter, the heater heats cold tap water from 5 to 45 degrees. Tank volume 80 liters. With a heating element power of 2 kW, fresh water in the tank will heat up for 2 hours, while approximately 4 kW of electricity and 20 rubles of money will be spent to pay for it. In summer, the water heats up from 18 to 45.
This means that in winter, each shower costs the family treasury 20 rubles, and in summer - 15 rubles, not counting the cost of cold water.
Despite today's wide range and functionality of electric boilers produced by various manufacturers, their homemade analogues have not lost their relevance in our time.
This is primarily due to the lower cost of the latter, therefore, to heat water, say for a summer shower or a washbasin in the country, many often use homemade electric water heaters, which are structurally a container with a heating element - a heating element.
Heating elements for heating radiators
In radiators, heating elements are installed to maintain the temperature of the coolant during a short-term shutdown of the central heating system or for additional heating of the coolant.
Such additional heating at night can be beneficial if the main source of heat is a boiler using expensive liquid fuel, and a two-tariff electric meter is installed in the house. Heating elements for heating radiators are distinguished by a thin flange and a narrow heating element. They are installed on cast iron and aluminum radiators, can be made in different capacities and differ in the length of the heating element. The delivery set includes a protective casing that protects the heating element from moisture.
Since the tube is plated with chromium and nickel during the manufacturing process, heating elements for radiators are durable and reliable. The capillary thermostat allows you to accurately regulate the heating temperature, and two temperature sensors protect the device from overheating. Modern heating elements have additional functions, for example “Turbo”, when the device operates at maximum power for some time to quickly warm up the room, or “Anti-freeze”, designed to maintain a minimum temperature of 10 ° C for a long time.
Installing a heating element into a radiator is quite simple: remove the plug from the bottom flange of the heating device, screw the heating element into the hole, install the thermostat and connect the power supply to grounding. The passport for the device must indicate the requirements for tightness, if not met, the radiator may become energized, and this is life-threatening. Advantages of installing heating elements in a central heating system:
- protection of the premises from freezing;
- protection of the system from damage in severe frosts;
- efficiency, because all energy is converted into heat;
- pulse operation, which saves energy;
- high accuracy of temperature control;
- additional useful functions;
- reasonable price.
Calculator for calculating the power of heating elements for heating water
The proposed calculator, based on the capacity of the water heater tank, the initial and final (required) water temperature and heating time, allows you to calculate the required electrical power of the heating element with a sufficient degree of accuracy, which is influenced by the design features of the heating element and the actual voltage of the electrical network.
When the network voltage is lower than Uwork of the heater (for example, as a result of a voltage drop in the line), it is obvious that its operation will be less efficient and reducing the temperature of the heating surface will increase the duration of heating the water to the required temperature.
The result of the calculation does not mean that it is mandatory to use a heating element of this rating: the resulting power can be gained by several heating elements connected in parallel.
Please note that the calculation is made without taking into account possible heat losses from electric water heaters to the environment, which arise due to a variety of factors, ranging from the design of the boiler to the state (presence) of thermal insulation.
Operating principle of the heating element
Knowledge of the design of the heating element is necessary to understand the principle of its operation. The spiral located inside the thermal heating element is specially made of a thermoelectric alloy. This property allows it to conduct electric current through itself, heating up greatly, but without melting. The material that surrounds the spiral is a dielectric, and thanks to it, heat is not only perfectly transferred to neighboring environments, but is also distributed throughout it, which ensures uniform heating of the metal shell, and, as a result, the working environment of the heating element.
Heating rate calculation
When calculating the power of electric heating elements, the following calculation data were used: mass of water, initial and final (desired) water temperature and time spent on heating. Heating element power P
is determined by the mathematical expression:
P=0.0011m(tk -t n)/T
.
in which: m
is the mass of heated water,
tk
and
tn
are the initial and final temperatures of the water,
T
is the time spent heating it. The calculation of the power of the heating element is performed by this calculator without taking into account heat losses associated with the design features of the container, ambient temperature, the state of the heating surface of the heating element, etc. In addition, you should take into account the actual voltage of the supply network, which may differ greatly from the nominal value. So, at a reduced voltage, the temperature of the working surface will be less than the value declared by the manufacturer, therefore, more time will be required for heating. Considering the specific gravity of water is 1 g/cm3, in the “Mass of heated water” calculator field, when entering data, the value of its volume can be used. The result of the calculation (P) can be the power value of either one heating element or several parallel-connected elements.
Pros and cons of using heating elements for heating a home
The main disadvantage of this heating method, as in the case of other electrical appliances, is the cost of operating costs. Electricity is still the most expensive source of heat (unless, of course, you have the opportunity to use free solar or wind energy and are connected to the main power grid). Another disadvantage is the impossibility of repair if the spiral fails. However, there are some positive aspects that in some cases may become a priority.
- Environmental friendliness of the heating system. When using electric heating devices, there is no need to stock up and store any fuel, and there are no harmful combustion products that enter the environment;
- Possibility of autonomous installation of a heating system in the absence of access to other thermal resources (for example, gas);
- Small dimensions and a large selection of models in terms of power and functionality;
- Possibility of automating the heating process: installation of heating elements with a thermostat;
- Low purchase and installation costs. There are models whose cost does not exceed 1000 rubles. And you can install heating elements in heating radiators yourself.
And finally, some tips for installing tubular electric heaters yourself. How to properly install a heating element into a heating system? First of all, you need to choose the right model by measuring the diameters of the radiators where the heating element is supposed to be installed and making power calculations. Then carefully read the instructions for the device, which should indicate whether additional sealing is required or not. This is one of the most important points, since contact of the conductor with the heat-conducting liquid will cause your radiators to be energized, and this is dangerous for residents. If the manufacturer indicates the need for additional sealing, then it must be done. In addition, it is unacceptable to use electrical heating devices without grounding.
Location of heating elements in a cast iron heating radiator
Installing heating elements in cast iron heating radiators has a number of features. They are related to the diameter of the pipe and the direction of the thread. In general, the procedure for installing heating heating elements into an existing system is as follows: disconnect the heating system from the heat source, drain the water, install the heating element, fill in the coolant, check the functionality of the system. When using heating elements with thermostats in the heating radiator system, it is also necessary to check their functionality after installation. It is also advisable to install water sensors and check the angles of the radiators. Since air locks can significantly affect the operation of the entire system and damage the heating element.