Nichromes
- These are alloys of nickel and chromium. They have high corrosion resistance and melting point, so they are used in electrical appliances and heating elements. Nichrome is wound in coils with a certain electrical resistance, and a current is passed through them, generating heat.
Fehrali
are ferromagnetic alloys whose electrical resistance properties are similar to nickel-chromium alloys. This makes them suitable for use in electrical heating systems. While the lack of nickel makes fechral less expensive than nichrome alloys, it also makes it more susceptible to corrosion. Care should be taken when operating fechral heating elements in dry conditions to minimize corrosion. Exposure to high temperatures can also lead to creep and embrittlement, but with appropriate support elements these problems can be avoided.
Use this online Nichrome and Fechral wire calculator to calculate the resistance, area, current and length of Nichrome and Fechral wire by simply entering the wattage and voltage.
Calculation of weight and length
11.3040
Calculate
Nichrome
Nichrome alloys typically consist of 80% nickel and 20% chromium
(nichrome 80/20), although other compounds can be found in varying ratios. Nichrome has a silver-gray color and is highly resistant to electrical flow and heat. It is also very resistant to corrosion and wear, very durable and has a very high melting point of around 1400°C.
Oxidation stability
makes nichrome a popular material for use in heating elements. For example, the heating elements in a household toaster are most often made of thick nichrome wire. When used in this manner, nichrome is usually wound in coils to a certain electrical resistance before current is passed to produce the heat generated. When nichrome is heated to high temperatures, it forms an outer layer of chromium oxide, unlike other metals, which can begin to oxidize when heated in air. This means that it is essentially impermeable to oxygen and therefore the heating element is protected from oxidation.
Nichrome alloys are known for their higher mechanical strength
at high temperatures compared to iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) fechral alloys, as well as higher creep strength. Nickel-chromium alloys also remain more ductile than iron-chromium aluminum alloys after long periods of exposure to temperature. Nickel-chromium alloys exhibit good corrosion resistance, except in environments where sulfur is present.
A noticeable increase in electrical resistivity is observed with increasing chromium additions. An addition level of 20% chromium is considered optimal for electrical resistance wires suitable for heating elements.
This composition combines good electrical properties with good strength and ductility, making it suitable for wire drawing.
Fechral
Alloys of iron, chromium, aluminum (FeCrAl)
are high resistance materials that are typically used in applications with maximum operating temperatures of up to 1400°C.
These ferritic alloys are known to have higher surface load capacity, higher resistivity and lower density than the alternative ni-chromium (NiCr)
, which can result in less material to apply and weight savings. Higher maximum operating temperatures can also extend cell life.
Iron Chrome Aluminum alloys form light gray aluminum oxide (Al2O3) at temperatures above 1000°C, which increases corrosion resistance and also acts as an electrical insulator. The formation of the oxide is considered self-insulating and protects against short circuits in the event of metal-to-metal contact. Iron-Chromium Aluminum alloys have lower mechanical strength compared to nickel-chromium materials, as well as lower creep strength.
Application of nichrome wire
The main quality of nichrome is its high resistance to electric current. It determines the applications of the alloy. Nichrome spiral is used in two qualities - as a heating element or as a material for electrical resistance of electrical circuits.
For heaters, an electric spiral made of X20N80-N and X15N60-N alloys is used. Application examples:
- household thermoreflectors and fan heaters;
- Heating elements for household heating devices and electric heating;
- heaters for industrial furnaces and thermal equipment.
Alloys Kh15N60-N-VI and Kh20N80-N-VI, produced in vacuum induction furnaces, are used in industrial equipment of increased reliability.
A spiral made of nichrome grades X15N60, X20N80 , X20N80-VI is distinguished by the fact that its electrical resistance changes little with temperature changes. It is used to make resistors, connectors for electronic circuits, and critical parts of vacuum devices.
Calculation of parameters of nichrome and fechral spirals from resistance
Everything here is very, very simple. You just need to know the initial parameters, which can be found by answering the questions:
- What power should the heating element you want to make have?
- What supply voltage will be supplied to it?
- What wire is available (material, diameter)?
Suppose you need to make a heater with a very small power of 12 Watts, which will operate on a 24 Volt network. Only a coil of nichrome wire with a cross-sectional diameter of 0.2 mm is available.
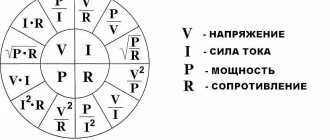
The formulas that we will use in calculations using this method are familiar to everyone from a school physics course. Power is equal to the product of current and voltage:
P (power) = U (voltage) * I (current)
From this formula we can find the current strength in our heater. It will be equal
I = P/ U = 12/24 = 0.5 Ampere
Ohm's law goes like this: "voltage equals resistance times current"
U (voltage) = I (current)* R (resistance)
From here:
R (resistance) = U (voltage) * I (current) = 24 : 0.5 = 48 ohms
We can determine the length of the wire using the formula:
L (conductor length) = S (sectional area) R (resistance) : ρ (conductor density)
Determination of material resistance
In order to find out the resistance value of the conductor from which we will make the heater, you can use the formula and table of values. First you need to find out the cross-sectional area. If we have a wire with a circular cross-section with a diameter of 0.2 mm, then according to the formula for the area of a circle, its cross-section will be equal to 0.0314 mm2. Now let's look at the table with resistance values and look for a correspondence with the calculated cross-section. In our case it is 1300 mm.
We are done with theoretical calculations. Now we need to find out whether the diameter of our wire is sufficient to withstand this level of current. In the table below you can determine the maximum current value for each wire diameter. According to the table, for a wire with a diameter of 0.2, the maximum current is 0.65, which means that the 0.5 A indicator we calculated has an acceptable value.
Please note that the heating environment is also of great importance! To heat the liquid, you can increase the maximum permissible current, but for a closed circuit, on the contrary, you need to reduce it.
Basic Concepts
In general, it is necessary to calculate a heating element made of nichrome using four calculations: hydraulic, mechanical, thermal and electrical. But usually calculations are carried out only in two stages: based on thermal and electrical indicators.
Thermal characteristics include:
- thermal insulation;
- heat efficiency;
- required heat transfer surface.
The main purpose of calculating nichrome is to determine the geometric dimensions of the heating resistance.
The electrical parameters of heaters are:
- supply voltage;
- power control method;
- power factor and electrical efficiency.
When choosing the supply voltage for heating devices, preference is given to that which poses minimal threat to animals and service personnel. The network voltage in agricultural installations is 380/200 volts with a current frequency of 50 Hertz. If electrical installations are used in particularly damp areas, or if there is an increased electrical hazard, the voltage should be reduced. Its value should not exceed 12, 24, 36 volts.
regulate the temperature and power of the heater in two ways:
- changing the voltage;
- changing the resistance value.
The most common way to change power is to turn on a certain number of sections of a three-phase installation. In modern heating installations, power is changed by adjusting the voltage using thyristors.
The calculation of the operating current is based on a tabular relationship that relates the current load on a nichrome conductor, its cross-sectional area and temperature.
Tabular data were compiled for nichrome wire, which was stretched in air without taking into account oscillations and vibrations at a temperature of 20 °C.
In order to move to real conditions, it is necessary to use correction factors in the calculations.
Lookup tables
Electrical resistance is one of the most important characteristics of nichrome.
It is determined by many factors, in particular the electrical resistance of nichrome depends on the size of the wire or tape, and the grade of the alloy.
The general formula for active resistance is:
R = ρ l/S
R - active electrical resistance (Ohm), ρ - specific electrical resistance (Ohm mm), l - conductor length (m), S - cross-sectional area (mm2)
Electrical resistance values for 1 m of X20N80 nichrome wire
No. Diameter, mm Electrical resistance of nichrome (theory), Ohm
| 1 | Ø 0.1 | 137,00 |
| 2 | Ø 0.2 | 34,60 |
| 3 | Ø 0.3 | 15,71 |
| 4 | Ø 0.4 | 8,75 |
| 5 | Ø 0.5 | 5,60 |
| 6 | Ø 0.6 | 3,93 |
| 7 | Ø 0.7 | 2,89 |
| 8 | Ø 0.8 | 2,2 |
| 9 | Ø 0.9 | 1,70 |
| 10 | Ø 1.0 | 1,40 |
| 11 | Ø 1.2 | 0,97 |
| 12 | Ø 1.5 | 0,62 |
| 13 | Ø 2.0 | 0,35 |
| 14 | Ø 2.2 | 0,31 |
| 15 | Ø 2.5 | 0,22 |
| 16 | Ø 3.0 | 0,16 |
| 17 | Ø 3.5 | 0,11 |
| 18 | Ø 4.0 | 0,087 |
| 19 | Ø 4.5 | 0,069 |
| 20 | Ø 5.0 | 0,056 |
| 21 | Ø 5.5 | 0,046 |
| 22 | Ø 6.0 | 0,039 |
| 23 | Ø 6.5 | 0,0333 |
| 24 | Ø 7.0 | 0,029 |
| 25 | Ø 7.5 | 0,025 |
| 26 | Ø 8.0 | 0,022 |
| 27 | Ø 8.5 | 0,019 |
| 28 | Ø 9.0 | 0,017 |
| 29 | Ø 10.0 | 0,014 |
Electrical resistance values for 1 m of X20N80 nichrome tape
No. Size, mm Area, mm2 Electrical resistance of nichrome, Ohm
| 1 | 0,1×20 | 2 | 0,55 |
| 2 | 0,2×60 | 12 | 0,092 |
| 3 | 0,3×2 | 0,6 | 1,833 |
| 4 | 0,3×250 | 75 | 0,015 |
| 5 | 0,3×400 | 120 | 0,009 |
| 6 | 0,5×6 | 3 | 0,367 |
| 7 | 0,5×8 | 4 | 0,275 |
| 8 | 1,0×6 | 6 | 0,183 |
| 9 | 1,0×10 | 10 | 0,11 |
| 10 | 1,5×10 | 15 | 0,073 |
| 11 | 1,0×15 | 15 | 0,073 |
| 12 | 1,5×15 | 22,5 | 0,049 |
| 13 | 1,0×20 | 20 | 0,055 |
| 14 | 1,2×20 | 24 | 0,046 |
| 15 | 2,0×20 | 40 | 0,028 |
| 16 | 2,0×25 | 50 | 0,022 |
| 17 | 2,0×40 | 80 | 0,014 |
| 18 | 2,5×20 | 50 | 0,022 |
| 19 | 3,0×20 | 60 | 0,018 |
| 20 | 3,0×30 | 90 | 0,012 |
| 21 | 3,0×40 | 120 | 0,009 |
| 22 | 3,2×40 | 128 | 0,009 |
Calculation of nichrome spiral
When winding a nichrome spiral for heating devices, this operation is often performed “by eye”, and then, including the spiral in the network, the required number of turns is selected based on the heating of the nichrome wire. Usually this procedure takes a lot of time, and nichrome is wasted.
To rationalize this work when using a nichrome spiral for a voltage of 220 V, I propose to use the data given in the table, based on the calculation that the resistivity of nichrome = (Ohm mm2 / m) C.
With its help, you can quickly determine the length of winding turn to turn depending on the thickness of the nichrome wire and the diameter of the rod on which the nichrome spiral .
to recalculate the length of a nichrome spiral to a different voltage using a simple mathematical proportion.
The length of the nichrome spiral depending on the diameter of the nichrome and the diameter of the rod
Ø nichrome 0.2 mm Ø nichrome 0.3 mm Ø nichrome 0.4 mm Ø nichrome 0.5 mm Ø nichrome 0.6 mm Ø nichrome 0.7 mm Ø nichrome 0.8 mm Ø nichrome 0.9 mm Ø rod , mm spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm spiral length, cm Rod Ø, mm Spiral length, cm
| 1,5 | 49 | 1,5 | 59 | 1,5 | 77 | 2 | 64 | 2 | 76 | 2 | 84 | 3 | 68 | 3 | 78 |
| 2 | 30 | 2 | 43 | 2 | 68 | 3 | 46 | 3 | 53 | 3 | 64 | 4 | 54 | 4 | 72 |
| 3 | 21 | 3 | 30 | 3 | 40 | 4 | 36 | 4 | 40 | 4 | 49 | 5 | 46 | 6 | 68 |
| 4 | 16 | 4 | 22 | 4 | 28 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 33 | 5 | 40 | 6 | 40 | 8 | 52 |
| 5 | 13 | 5 | 18 | 5 | 24 | 6 | 26 | 6 | 30 | 6 | 34 | 8 | 31 | ||
| 6 | 20 | 8 | 22 | 8 | 26 | 10 | 24 |
For example, you need to determine the length of a nichrome spiral for a voltage of 380 V from a wire 0.3 mm thick, a winding rod Ø 4 mm. The table shows that the length of such a spiral at a voltage of 220 V will be equal to 22 cm. Let’s make a simple ratio:
220 V - 22 cm
380 V - X cm
Then:
X = 380 22 / 220 = 38 cm
Having wound the nichrome spiral , connect it, without cutting it, to a voltage source and make sure that the winding is correct. For closed spirals, the winding length is increased by 1/3 of the value given in the table.
Calculation of the mass of nichrome X20N80 (wire and tape)
This table shows the theoretical weight of 1 meter of nichrome wire and tape. It varies depending on the size of the product.
Diameter, standard size, mm Density (specific gravity), g/cm3 Sectional area, mm2 Weight 1 m, kg
| Ø 0.4 | 8,4 | 0,126 | 0,001 |
| Ø 0.5 | 8,4 | 0,196 | 0,002 |
| Ø 0.6 | 8,4 | 0,283 | 0,002 |
| Ø 0.7 | 8,4 | 0,385 | 0,003 |
| Ø 0.8 | 8,4 | 0,503 | 0,004 |
| Ø 0.9 | 8,4 | 0,636 | 0,005 |
| Ø 1.0 | 8,4 | 0,785 | 0,007 |
| Ø 1.2 | 8,4 | 1,13 | 0,009 |
| Ø 1.4 | 8,4 | 1,54 | 0,013 |
| Ø 1.5 | 8,4 | 1,77 | 0,015 |
| Ø 1.6 | 8,4 | 2,01 | 0,017 |
| Ø 1.8 | 8,4 | 2,54 | 0,021 |
| Ø 2.0 | 8,4 | 3,14 | 0,026 |
| Ø 2.2 | 8,4 | 3,8 | 0,032 |
| Ø 2.5 | 8,4 | 4,91 | 0,041 |
| Ø 2.6 | 8,4 | 5,31 | 0,045 |
| Ø 3.0 | 8,4 | 7,07 | 0,059 |
| Ø 3.2 | 8,4 | 8,04 | 0,068 |
| Ø 3.5 | 8,4 | 9,62 | 0,081 |
| Ø 3.6 | 8,4 | 10,2 | 0,086 |
| Ø 4.0 | 8,4 | 12,6 | 0,106 |
| Ø 4.5 | 8,4 | 15,9 | 0,134 |
| Ø 5.0 | 8,4 | 19,6 | 0,165 |
| Ø 5.5 | 8,4 | 23,74 | 0,199 |
| Ø 5.6 | 8,4 | 24,6 | 0,207 |
| Ø 6.0 | 8,4 | 28,26 | 0,237 |
| Ø 6.3 | 8,4 | 31,2 | 0,262 |
| Ø 7.0 | 8,4 | 38,5 | 0,323 |
| Ø 8.0 | 8,4 | 50,24 | 0,422 |
| Ø 9.0 | 8,4 | 63,59 | 0,534 |
| Ø 10.0 | 8,4 | 78,5 | 0,659 |
| 1 x 6 | 8,4 | 6 | 0,050 |
| 1 x 10 | 8,4 | 10 | 0,084 |
| 0.5 x 10 | 8,4 | 5 | 0,042 |
| 1 x 15 | 8,4 | 15 | 0,126 |
| 1.2 x 20 | 8,4 | 24 | 0,202 |
| 1.5 x 15 | 8,4 | 22,5 | 0,189 |
| 1.5 x 25 | 8,4 | 37,5 | 0,315 |
| 2 x 15 | 8,4 | 30 | 0,252 |
| 2 x 20 | 8,4 | 40 | 0,336 |
| 2 x 25 | 8,4 | 50 | 0,420 |
| 2 x 32 | 8,4 | 64 | 0,538 |
| 2 x 35 | 8,4 | 70 | 0,588 |
| 2 x 40 | 8,4 | 80 | 0,672 |
| 2.1 x 36 | 8,4 | 75,6 | 0,635 |
| 2.2 x 25 | 8,4 | 55 | 0,462 |
| 2.2 x 30 | 8,4 | 66 | 0,554 |
| 2.5 x 40 | 8,4 | 100 | 0,840 |
| 3 x 25 | 8,4 | 75 | 0,630 |
| 3 x 30 | 8,4 | 90 | 0,756 |
| 1.8 x 25 | 8,4 | 45 | 0,376 |
| 3.2 x 32 | 8,4 | 102,4 | 0,860 |
Temperature accounting
For example, a wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm at a current of 2.7 A will heat up to 700 °C, and a current of 3.4 A will heat it to 900 °C.
There are reference tables for calculating temperature and current. But you still need to take into account the operating conditions of the heater.
When immersed in water, heat transfer increases, then the maximum current can be increased by up to 50% of the calculated one.
A closed tubular heater, on the contrary, impairs heat dissipation. In this case, the permissible current must be reduced by 10-50%.
How much do nichrome or fechral heaters cost?
The cost of a muffle furnace directly depends on the features of its assembly elements. The material of the heater also plays an important role in determining the price. The key difference between fechral and nichrome is that the cost of combining iron, chromium and aluminum is 3-5 times cheaper than that containing nickel.
Don't rush when choosing an alloy. First, calculate:
- Maximum heating temperature.
- Time of uninterrupted operation of equipment.
- Frequency of equipment switching on and off.
Only after this should you make a purchasing decision. Don't chase a lower price. If the heater wears out quickly, its constant replacement and interruptions in the operation of the device will cost much more.
You can always buy muffle furnaces with high-quality heaters at. We will select for you the ideal turnkey solution that will be reliable and durable. Contact us!