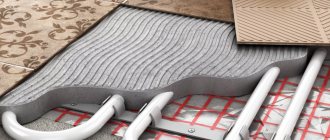
Features of the operation of water heated floors
Water heated floors are used as the main or additional source of heat in private homes. The idea of this system is based on laying thermal circuits and pipelines with coolant circulating through them in the screed. The liquid is heated in a boiler and then distributed through floor loops in different rooms. The main feature of the operation of such a system is the need to maintain a low, uniform temperature across a large number of consumers. The coolant comes from the boiler heated to 60 - 70 degrees, such heat from the floors will be uncomfortable for residents. To reduce the temperature, a mixing unit is included in the system or RTL valves (reverse flow regulator) are installed.
The second feature of heated floors is associated with the uneven distribution of coolant throughout the system. The rooms have different areas, which means the contours will be of different lengths. Redistribution occurs at the collector.
Materials and tools
The work will require tools and materials. You should also calculate the required amount of materials, and in addition, take care of purchasing the necessary system components.
- boiler;
- collector;
- pump;
- valve for adjustment;
- air vent;
- valves;
- fitting;
- screws;
- screwdriver;
- cement;
- sand.
In addition to them, the main components of the system . The main element of the heating system is the heating boiler. When performing installation work, you cannot do without a pressure pump, which can be connected directly to the boiler.
The valves are installed at the inlet of the device. You should also prepare the pipes that will be used to create the wiring. After this, the collector is prepared. This device contains elements used to set the system temperature and regulate it.
The owner must also purchase pipes for laying on the floor surface. In addition to them, fittings are purchased, which during operation are used to lay the main line. These elements are also used to connect laid pipes to the underfloor heating system.
Pipes intended for heated floors can be made of polypropylene . The best choice is products with a fiberglass reinforcing layer. Their advantage is that at high temperatures they expand less. In addition to them, you can use polyethylene pipes, since when heated they expand to a minimum.
When installing surface heating systems, polyethylene pipes are most often used. You should choose products with a diameter from 18 to 22 mm. The pipe must be designed for operating pressures up to 10 bar and temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius. Some pipe models are equipped with oxygen protection and have additional layers in their structure. However, most often owners opt for polyethylene pipes, since their cost is quite low. If the most important thing for the owner when installing a heated floor is to reduce the cost of installing the system, then polyethylene pipes .
In appearance, the collector is a device that has taps. In another way it is called a splitter. It is used mainly for connecting different circuits of the system.
The main line connects different circuits that provide the delivery of heated water and the removal of cold water.
When installing a “warm” floor, two collectors are installed. The first acts as a splitter and is designed to distribute heated water. The second is used to collect cooled coolant.
The devices used to configure the system are located in the splitter structure:
- valves;
- drain control device;
- spare drain;
- air from water.
What does the collector group consist of?
The collector has the form of a metal or plastic tube in which the coolant is collected and redistributed along the circuits. The collector group usually consists of two combs: supply and return, a pumping and mixing unit and additional equipment.
On the left is a pumping and mixing unit with a thermal head, on the right is a manifold comb with rotameters and a drain valve.
Collecting combs
The main differences between the supply and return combs are only in the shut-off valves. The heated coolant from the boiler comes to the supply, then the liquid is redistributed between the heating devices. The substance (water, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol) passes through the circuit, gives off heat and returns to the return comb, from where it goes back to the boiler.
Read more about choosing a coolant for a heating system in a separate article.
How it works?
The collector combs have a larger diameter compared to the pipes, because of this the coolant in the distribution block slows down its movement. Distribution occurs through pipes with a smaller flow. One comb can have up to 14 pipes, depending on the number of heating devices. Typically, the supply is equipped with adjusting devices to change the flow of underfloor heating circuits. More coolant will flow into a pipe with a higher throughput, and accordingly the heating devices will heat up more.
Shut-off valve options
To regulate the amount of coolant on the collector, ball valves, valves, flow meters (rotameters), thermostatic push-action valves or servos are used.
- Ball valves are shut-off valves with two positions: (open and closed), allowing you to stop the movement of the coolant through a separate pipe of the comb. Ball valves do not allow you to regulate the flow, so it makes sense to use them in heated floors, where the loops are approximately equal in length. They are also placed in front of collectors.
An example of a manifold with ball valves.
- The valves allow for stepwise changes in the flow diameter and require manual control of the system.
There are flow meters on the top of the supply comb, and thermostatic valves on the bottom of the return.
- Flow meter (rotameter) is a device that measures fluid flow per unit of time. It is a transparent flask with a stem inside; the mechanism of operation of the valves is similar to a regular valve.
The coolant flows along a shorter line with less hydraulic resistance - the flow meter on such loops narrows the passage, and on longer ones it widens it, due to this the floor in different rooms heats up equally.
- Thermostatic pressure valves are installed on the return comb of the underfloor heating manifold. They can close or open depending on the return temperature. The TSG valve is equipped with a Eurocone, which allows you to measure the temperature of the liquid in the pipe.
- Thermoelectric servo drive is a thermostatic head that can remotely control the operation of the comb valves. Servo drives are divided into normally closed and normally open. In the first case, in the normal position the valve is closed and opens when voltage is applied. The servo drive is connected to a thermostat, which is located in the room and responds to changes in air temperature.
The thermoelectric servo drive should not be confused with RTL valves. The first reacts to changes in room temperature, the second is adjusted to the temperature of the coolant.
Thermoelectric head with servo drive.
Typical connection diagrams
Water heated floors are rarely used as the only source of heating. Heating only due to underfloor heating is permissible only in regions with a mild climate, or in rooms with a large area, where heat removal is not limited by furniture, interior items or the low thermal conductivity of the floor covering. Almost always it is necessary to combine radiator circuits, hot water preparation devices and underfloor heating loops in one heating system.
Typical diagram of a combined heating system with connection of radiators and underfloor heating circuits. This is the most technologically advanced and easily customizable option, but it also requires significant initial investment. 1 - heating boiler; 2 — safety group, circulation pump, expansion tank; 3 - manifold for separate two-pipe connection of radiators in a star configuration; 4 — heating radiators; 5 - underfloor heating manifold, includes: bypass, three-way valve, thermostatic head, circulation pump, combs for connecting underfloor heating circuits with gearboxes and flow meters; 6 - heated floor contours
There are quite a large number of variations in the design of the boiler room piping, and each individual case has its own principles of operation of the hydraulic system. However, if you do not take into account very specific options, then there are only five ways to coordinate the operation of heating devices of various types:
- Parallel connection of the underfloor heating collector to the main line of the heating unit. The insertion point into the main line must be made up to the connection point of the radiator network; the coolant supply is provided by an additional circulation pump.
- Association according to the type of primary and secondary rings. The line, wrapped in a ring, has several supply connections in the supply part; the coolant flow in the connected circuits decreases with distance from the heating source. Flow balancing is performed by selecting the pump supply and limiting the flow with regulators.
- Connection to the extreme point of a coplanar manifold. The movement of the coolant in the heated floor loops is ensured by a common pump located in the generator part, while the system is balanced according to the principle of priority flow.
- Connection through a hydraulic separator is optimal when there are a large number of heating devices, a significant difference in flow rates in the circuits and a significant length of underfloor heating loops. This option also uses a coplanar manifold, but the hydraulic arrow is necessary to eliminate the pressure drop that interferes with the correct operation of the circulation pumps.
- Local parallel loop connection via unibox. This option is well suited for connecting a short-length heated floor loop, for example, if you need to heat the floor only in the bathroom.
The simplest option is to connect a heated floor circuit to a radiator heating system with a coolant temperature of 70-80 °C. 1 - line with supply and return of the high-temperature circuit; 2 - heated floor contour; 3 - unibox.
It must be remembered that the nature of the operation of a heated floor may also change depending on the installation pattern of the coil. The “snail” scheme is considered optimal, in which the tubes are laid in pairs, which means that the entire area is heated almost evenly. If the warm floor is arranged as a “snake” or “labyrinth”, then the formation of colder and warmer zones is practically guaranteed. This drawback can be eliminated, including through proper configuration.
Should I assemble a collector or buy a ready-made one?
Collectors can be prefabricated, ready-welded or homemade. Let's consider their advantages and disadvantages.
Ready welded
They are usually produced in the form of supply and return combs welded together with a specified number of pipes.
Advantages
- Fast installation - no need to assemble fasteners.
- Minimum qualification requirements for an installer
Flaws
- Difficult to configure for a specific system.
- The number of pipes may not meet the needs, in which case they will have to be blocked off with plugs and not used.
- The collector can be equipped with elements that are unnecessary for a particular heating system. For example, it may have a hydraulic distributor (hydraulic arrow), which is only useful in networks with a large number of pumps.
- The return and feed combs may be welded together, making it difficult to attach separate loops to them. The pipes on factory mixers are usually located at the same distance from each other, but this is not always convenient.
Homemade
You can make a collector with your own hands from available materials: steel pipes with a round or square cross-section. To do this, holes are cut in them and pipes are welded. Couplings are made from round sections of smaller diameter.
Advantages
- Making a collector with your own hands is profitable from a financial point of view.
- You can make a drawing and manufacture an individual manifold for a specific system.
Flaws
- To perform this job, you will need skills in working with a welding machine.
- It will take more time.
- The non-separable design makes it difficult to repair and replace individual elements.
Prefabricated
Such distribution units are assembled from factory parts, which are purchased separately or as a kit. They will be discussed further.
Advantages
- There is variability when designing a collector unit for a specific heating system.
- Does not require special skills or equipment for installation.
- Possibility of separate dismantling of feed and return combs.
- High installation speed.
Flaws
- Components from different manufacturers may not fit together.
- This option usually costs more.
Manifold made of polypropylene pipes
If polypropylene pipes are used for production, you should pay attention to the presence of a reinforcing layer in them. In its absence, the plastic structure may be subject to deformation due to the current temperature conditions.
Detailed technical process for assembling the collector group:
Assembling a collector comb from polypropylene pipes
Mixing units made of polypropylene have an important advantage over their metal “counterparts” - low cost. Otherwise, you will have to come to terms with a number of shortcomings:
- Polypropylene manifolds are installed in systems with a small number of outlets (no more than 5 pieces);
- Flow meters cannot be installed;
- A larger protective box is required due to the massive structure;
- Be sure to have a set of specialized tools and soldering skills.
Assembling a distribution manifold from individual elements
For those who do not have special tools, you can assemble a comb from separate ready-made elements. It is better to select components from one manufacturer.
The circuits are connected according to the chosen scheme, adhering to the main rule - pipes with warm coolant are fixed at the top. Pipes with cooled coolant are secured from below.
At the final stage, it is necessary to carry out pressure testing and a control start-up of the heating in order to timely identify hidden or obvious deficiencies in the structure made.
How to install a rotameter on a manifold comb
Rotameters are often used on underfloor heating manifolds; they are necessary to control flow. Depending on the model, the device can be adjusted to different flow rates from 0 to 5 l/min. The setting is made only when the pump is turned on. It is necessary to remove the decorative protective cap and tighten the fixing nut into the desired position. After setting up the flow meter, the plug is installed in place.
Rotameters differ for the return comb and the feed comb. Inside the glass flask of the device there is a rod with a plate. In the non-working state, the rod plate is pressed to the zero value by a spring. The coolant is always supplied under the valve seat, since the flow opens the valve. On reverse rotameters the rod is at the bottom, and on feed rotameters it is at the top (the numbers will increase from above).
Differences between the rotameter on the feed and return combs.
If you confuse the supply and return rotameter, the coolant flow will press the rod against the seat, and the system will not work. Some devices do not allow you to record the required flow rate, but only measure its value; to distribute flows along the contours of heated floors, it is advisable to use the first option.
Self-assembly of the device
The mounting diagram is most often already present in the kit of any collector device. You can assemble a manifold for a heated floor yourself if you follow the step-by-step instructions. The device is mounted horizontally on the wall or in a pre-prepared niche, leaving free access to the main arrow of the heating pipes. Next, you will need to connect the collector to the boiler so that the heat carrier is supplied from the bottom, and the return flow is from the top. Afterwards, a bypass valve with a temperature limiter is installed, followed by a distribution comb.
Pipes passing inside the floor are fixed from above, coming from the heating system - from below. After installation, the device must be configured according to the rules, check how tight all connections are by connecting the manifold group to the main pump. Using a pump, the pressure inside the system is built up, after which the water circuit must be left in this form for a day. If all indicators are preserved, the installation was carried out according to the rules, the unit can be operated.
Mixing unit
The mixing unit can be used without a collector.
The mixing unit is often included in the collector group. Its operating principle is based on combining the supply and return flows. After passing through the heated floor loop, the medium usually has a temperature of about 30 degrees; at the mixing unit it flows into the supply flow, which allows you to get a comfortable temperature of 40 degrees.
There are many options for implementing this unit: using a three- or two-way valve, using thermostatic valves, etc. Mixers can also be prefabricated or factory-made.
The mixer usually has a thermostatic valve that measures the temperature of the medium. It is equipped with an overhead or cap sleeve. The first is simply glued to the pipe, the second is inserted into the line itself.
A three-way valve with a thermal head is installed in front of the pump. It is also useful to install a coarse filter on the supply before it.
- A three-way valve is installed on the supply side; using a thermostatic head, the element allows you to control two flows. There are mixing valves and distribution valves. The first one receives two streams from different sources, combines them into one and sends them along the required highway. The distribution valve receives one flow, which is distributed through several circuits. These elements are used not only to regulate the temperature of the coolant, but also to protect the boiler to prevent idling and overheating. However, the valve installation and layout will not be the same as when used in combination with a manifold.
A mixer with a two-way valve; on the bypass it is useful to install a hidden valve under a hexagon instead of an element with a handle.
Bypass is a channel between the return and supply combs; it creates a small circle and prevents the pump from working at a dead end when one of the lines is closed.
- The two-way valve is equipped with a thermostatic head and controls the flow in only one direction. When using this element in a mixing unit, an additional bypass valve will be required. In most cases, shut-off valves are placed under the hexagon. Ball valves cannot be used on this unit due to the impossibility of precise adjustment; it is also not recommended to install a valve with a handle, since someone could accidentally mess up the entire system setting.
The mixing unit is installed after the collector. A pump is placed between the collector and the boiler, which ensures movement in a small circle. The three-way mixing valve is installed on the supply line, the distribution valve - on the return line.
Location of two-way and three-way valves in the heating system
| Task | Two way valve | Three-way valve (distribution) | Three-way valve (mixing) |
| Boiler protection | — | Innings | Return |
| Temperature regulation | Innings | Return | Innings |
The mixing unit on a two-way valve can always be distinguished from a three-way valve by the presence of a valve on the bypass.
Adjusting the operation of the mixer using the example of a two-way valve
In a three-way valve, the flow is always open: if one plug closes, the other opens. In a mixer with a two-way shut-off device, only one plug closes; it works as follows: the thermal head determined that the temperature of the medium is lower than necessary, pressed the rod, the valve opened, and a portion passed into the manifold, mixing with the liquid from the return. When the temperature has reached the required values, the thermal head begins to close: the flow from the supply decreases, the flow from the bypass increases.
- The longer the heating circuit of the floor, the more the bypass valve is closed.
The bypass valve has a hidden valve for a hex key. When setting up the system, you need to close the thermostatic valve and open the balancing valve. The rotameters are adjusted, then the valve on the bypass is gradually closed until the rotameter rod begins to show that the coolant is becoming less. Fully open the thermostatic valve and tighten the balancing valve again. As soon as the rotameter plates lower or rise when turning the key on the bypass valve, balancing stops.
Diagram with two-way valve
Install it on the supply from the heating device. A balancing adjustable valve is installed in the place of the jumper between the supply pipeline and the return line. It is adjusted in accordance with the required temperature of the supplied water, usually using a hex key. It is needed to regulate the amount of cold coolant.
The temperature sensor is placed after the pump, which in turn moves water in the direction of the comb. Only now the intensity of movement of the heated coolant from the boiler changes. In this way, the temperature of the supply water changes at the pump inlet, while the cold flow is adjusted and stable.
Mixing always occurs and water from the boiler does not enter directly into the circuits, since this is impossible. This scheme can be considered more reliable. But it should be noted that a mixing group equipped with a two-way element is capable of heating 150 - 200 “squares” of area, since there are no valves with greater capacity.
Do you need a hydraulic gun?
A hydraulic separator (hydraulic arrow) is a device that is usually placed between the boiler and the collector; it provides zero resistance in this area. Visually, the element is a hollow pipe with 4 pipes: on one side, two are intended for the boiler, on the other, for the collector. The question of installing a hydraulic separator arises when there is a need to install more than 4 pumps and more than 1 boiler.
The hydraulic arrow can be fixed vertically or horizontally, it does not matter. The first option is often chosen, as it simplifies the installation of the air vent in the upper part. A tap can be attached to the bottom to remove sludge.
Often in articles this device is attributed properties that it does not possess. We list the tasks for which you should not buy a hydraulic gun.
- Does not increase boiler efficiency
- Does not reduce fuel costs
- Does not protect against heat stroke
- You still need to select pumps for each circuit separately.
- Not intended for air bleeding or sludge protection.
The hydraulic arrow can worsen the operation of the system if the pumps are incorrectly selected. For example, a boiler unit is much inferior to the total power of devices on other circuits. As a result, the coolant reaches the comb already cold due to mixing with the reverse flow.
Are a manifold and mixing unit required?
In a small house, a heated floor may not take up so much, in which case the costs of a collector and mixer will not be worth it. The simplest solution would be to install a heated floor with one or two circuits, controlled by a TSG thermal head or an RTL tap. Regulation in this circuit occurs by limiting the temperature on the return flow.
The RTL valve is not intended for installation on a manifold; it has high hydraulic resistance. Due to the large size of the head, it is inconvenient to screw the element onto a distribution unit with a large number of adjacent circuits. This also makes it impossible to use built-in plumbing cabinets. It is not recommended to install RTL cranes on a circuit longer than 70 meters. The thermal head is usually placed in a plastic box that is hung on the wall.
The TSG head also limits the return flow, but has a Eurocone, so it can be installed on the return of the manifold. The actuator acts on the stem, and not on the valve itself. In this case, the head is occupied by the working valve of the manifold, because of this, installation of the servo drive becomes impossible. The absence of resistance makes it possible to install a longer circuit.
Collector, what is this?
A collector is a device for mixing different media from parallel branches for subsequent supply of the mixture further. In our case, two streams of water of different temperatures are mixed to achieve the temperature we need. This mixing is possible due to the large cross-section of the collector pipes and the low water flow rate.
For underfloor heating, the collector consists of two pipes with outlets for heating circuits. On both sides of these pipes there are threads for connection to inlet and outlet pipes, as well as additional equipment. The configuration of collectors varies, and the price depends on this. The collectors are sold assembled, but it is possible to assemble it yourself, you will just need to buy all the components separately, but this way you can save money. There are several types of collectors:
- The simplest one is just a pipe with outlets for attaching heating circuit pipes. For this type you need to buy a lot more.
- Manifolds with simple control valves. Suitable if you have a small number of circuits of the same length, since precise temperature control in the circuits is impossible.
- Collectors with more precise adjustment. It is already possible to install automatic servos on them, which will be regulated by room thermostats, setting the required temperature in each circuit automatically.
- Manifolds for automatic adjustment of circuits of various lengths. Such manifolds have flow meters on the supply manifold, and on the return manifold there are places for installing servo drives.
Read also: Advantages and disadvantages of heated floors
Flow meters set the required flow, as a result, each circuit will have the same coolant flow, regardless of its length. Servo drives are required to open and close circuits automatically. If the circuits are in an open or closed state most of the year, servos can be replaced with simple simple taps.
Work progress
- We install the mixer on the return comb, if an assembled factory element is used, and tighten the union nut (American) with a wrench.
- A mixer is installed on the child’s feed using the same principle.
- We install air vents for return and supply.
- Plugs are installed at the ends opposite from the mixer; they should be tightened with a wrench.
- A drain valve is installed on the comb; it is usually located under the air vent; they are designed to bleed gases from the manifold.
- For convenience, you can screw the fitting into the comb separately and then install the tap on it.
- A pump is attached between the return mixer and the supply comb.
- The fastening element is assembled; all manufacturers have their own in the form of runners or strips. If a homemade manifold is used, then the fasteners are made from improvised materials. The holders are first mounted on the combs and only then on the wall.
- The combs should be at the same distance from each other so that they are parallel on the wall. This is not a technical requirement, but more of an aesthetic consideration. To align the combs, they are first fixed to the fasteners on one side, then the same distance is measured from the other end. This is easy to achieve in short manifolds. Typically, for many manufacturers, the standard distance between combs should be 21.5 cm.
- In practice, from the point of view of system operation, it does not matter which comb is on top. In most cases, a supply distributor is placed there, but nothing will change if you put it below. The main thing is not to confuse the supply and return rotameters.
- The plug is removed from the factory return mixing unit, the thermostatic head is screwed to it, and the measuring sleeve is inserted into the supply comb mixer.
- Two mounting strips are fixed to the wall. Fasteners and hardware are selected depending on the base material. It is advisable to fix the collector at 4 points.
- The connection is made using a Eurocone. A nut is put on the pipe, then a ring, and a thrust bushing is placed in the hole. Fixation is carried out using two keys. One fixes the hexagon, the other tightens the nut. You need to do this carefully so as not to rip off the fitting.
- The contours are drawn in increments of 100 mm.
- Installation of the circuit is completed by connecting the line to the return comb. Pipes must be placed in an insulating casing. The system is filled through drain and fill valves. The ball valves on the manifold are closed.
Nuances of pipe installation
When laying pipes, certain rules must be followed:
Pipe installation work should be carried out from the outer wall of the room, since it is colder than all the others.
If pipes pass into the room from the outside wall, then the part of the pipe from the entrance to the wall should be insulated.
To ensure a gradual reduction in the heating of the floor from the outer wall, a snake installation method for pipe products is used in the room.
If in the room in which the heated floor is installed, all the walls are internal, then to solve the problem of uniform heating of the floor, use spiral installation in the direction from the wall to the center.
The pipe should run in a spiral to the center of the room. When laying, you should adhere to a double step between them, and after that it can be unrolled and unrolled in the opposite direction until you exit the room directly to the splitter.
Manifold cabinet: purpose, types and advantages
Manifold cabinet
The manifold cabinet is a protective structure that protects the mixing unit from outside interference. Essentially, this is a box installed in a horizontal position, equipped with fastening mechanisms and a door.
The use of such a cabinet makes it possible to place the manifold unit in a convenient place without damaging the interior and technical content. Thus, the collector-mixing unit can be placed in any room without fear that children and pets will be interested in the contents.
There are two types of manifold cabinets:
External ones are mounted on the wall surface using special fasteners and legs (if necessary, height adjustments). The outlet slots are covered with removable metal plates. The cabinet itself is coated with powder paint or an anti-corrosion compound on the sides; the door can be white, beige or another color according to the consumer’s taste.
External manifold cabinet
Built-in ones are installed in a niche or covered with clapboard or plasterboard. The side parts, as a rule, are not painted, since they contain fastening and outlet spans. The facade is painted white, but options are also possible.
Built-in manifold cabinet
Both types of structures must have a strong lock and protection against possible thermal burns. Cabinets are not placed below floor level, but are not raised too high. After installing the box, the process of assembling the water floor collector proceeds according to the planned diagram. At the same time, all bends remain easily accessible for laying contours.
You can also place a water supply meter inside the cabinet, combining all the circuits at one point. On the wall, the entire structure will look many times more aesthetically pleasing than a bunch of pipes for the water circuit of a heating system with numerous sensors, valves and taps.