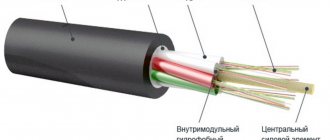
Welding inverter is an established common name for welding machines that use an inverter converter as a current source. Such devices are used for various electric arc welding technologies: MMA (manual covered electrodes), TIG (argon arc) and MIG/MAG (in an inert or active gas atmosphere). Generally, all MIG/MAG and TIG welding inverters can also perform MMA welding. In addition, leading manufacturers produce combined units that combine all three types.
All these technologies have been developed for different types of welding and joining of various metals and their alloys. Before you start choosing a welding machine, you need to answer two questions: what types of welding are supposed to be performed and under what conditions it will work. Nowadays the market offers a huge number of models of both household and industrial welding equipment with the widest range of technical characteristics. It is very difficult to understand which one is better and which manufacturer to give preference to. The only way out in this situation is to independently understand the basics of welding technologies and the operating principles of modern equipment.
Features and principle of operation of the welding inverter
In recent decades, inverter welding has increasingly replaced traditional transformers and rectifiers, not only in industrial production, but also in domestic use. This became possible thanks to the creation of a reliable element base for frequency converters, as well as a significant reduction in the cost of power electronic components. The rising cost of energy and copper, which is used in inverters by orders of magnitude less than in other welding machines, also played a role.
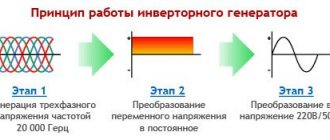
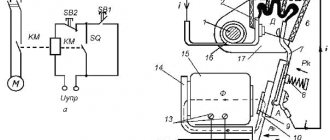
The operating principle of a modern welding inverter is based on the conversion of low-frequency mains current into high-frequency pulses with the subsequent formation of various types of welding currents with adjustable parameters (see figure below).
Figure 2 - Operating principle of the welding machine
Single-phase or three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 or 380 V is supplied to the input rectifier, after which it is smoothed out by large capacitors.
The rectified current with a significant level of ripple is supplied to the input of the inverter, which converts it into high-frequency alternating current. This current is then supplied to the high-frequency transformer, where its voltage is reduced to the no-load value. Then it passes through a rectifier, after which, due to the high frequency, ripple smoothing is no longer required. The rectified current is supplied directly to the welding electrode. Its characteristics are monitored by current and voltage sensors connected to the inverter control unit, so the frequency and duty cycle of the pulses can be changed in real time. The number of turns of the primary winding is inversely proportional to the frequency of the current, so in high-frequency transformers there is orders of magnitude less copper than in conventional ones. This dependence is nonlinear: at a frequency of 10 kHz, the mass and size decrease by 3 times, and at a frequency of 50 kHz - by approximately 15 times (see the transformer in the figure below).
Types of inverter welding machines
Welding inverters differ in the length of continuous operation and are divided into the following types:
- Appliances for household use. Able to work continuously for 5-10 minutes with a further long break. Models produce welding current in the range of 120-200 A. Designed for small volumes of work;
- Semi-professional types. They appear to be the average between the previous and next devices. Work without a break for 15-30 minutes with a break of up to 1 hour;
- Professional type. Can be used for 8 hours with a current of 200-300 A. Used for the manufacture of metal structures and frames, in various repair work;
- Industrial models. They can work throughout the day at industrial facilities with short breaks. The current for welding is 200-500 A.
Other characteristics of these types of devices are no different.
Types of inverters
An inverter welding machine is a complex electronic device that is characterized by a wide range of welding and technological characteristics. Therefore, inverters are classified simultaneously according to several criteria:
- According to the type of element base of the frequency converter, on which the maximum conversion frequency of the input direct current directly depends. Usually we are talking about three varieties: thyristor - up to 5 kHz; on insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) - up to 20 kHz; on MOSFETs - up to 100 kHz or more.
- According to the circuit type of inverter converter (various types of bridges) and the method of regulating high-frequency alternating current (PWM, PWM).
- By type of welding technology. There are inverters for MMA, MIG/MAG, TIG, pulse inverter welding and their varieties. A separate type of such equipment is plasma cutters (CUT), which also use inverters.
- In terms of weight and dimensions. These include mini-devices, as well as portable, mobile and stationary inverters.
- By scope. In this case, inverters are divided into household, professional, industrial, designed for robotic systems and specialized.
- According to the level of mechanization and automation. New to this type of inverter performance is Synergic Control. This intelligent system allows you to adaptively alternate between different modes and completely controls the entire welding process.
In addition, inverters are often classified according to various operational characteristics: protection class, maximum tilt level, ability to operate at reduced input voltage, etc.
Technical parameters of devices
Welding inverters have a number of specific characteristics by which one can judge its technological properties. These include the following parameters:
Welding inverter design
- The type of current that is generated at the output of the rectifier.
- The amount of voltage that is used to supply electricity. Manufacturers produce products that operate on 380 and 220 V. The former are used for professional welding, the latter for work at home.
- Current size, this parameter has a direct impact on the size of the electrode that will be used to perform the weld.
Technical parameters of welding inverter
- Unit power, this parameter provides information about the current and strength that will form the welding arc.
- Open circuit voltage, this parameter shows how quickly the welding arc will be produced.
- The range of electrode sizes that will be used for welding.
- Dimensional and weight characteristics of the inverter welding machine and the size of the welding current at the output. The lower the last indicator, the smaller the device, but accordingly such a device has lower performance characteristics.
Characteristics and criteria for choosing an inverter
When choosing a welding machine with an inverter, first of all you need to decide on the expected maximum thickness and types of material to be welded. The power and welding current of the future purchase, as well as its price, directly depend on these parameters. The table below shows the approximate values of the minimum and maximum currents for various thicknesses of structural steel parts. For other types of steel and non-ferrous metals, these values will be different, therefore, if you intend to weld stainless steel or aluminum alloys, it is necessary to clarify the current parameters for these materials.
| Metal thickness (mm) | 1÷2 | 2÷3 | 2÷3 | 3÷4 | 4÷6 | 6÷8 |
| Electrode diameter (mm) | 1,6 | 2 | 2,5 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Welding current (A) | 25÷50 | 40÷80 | 60÷100 | 80÷160 | 120÷200 | 180÷250 |
The main characteristics of the welding inverter, which are indicated in their catalogs by all manufacturers of this equipment:
- input voltage parameters;
- power;
- ON duration (DS);
- welding current limit values (min./max.);
- open circuit voltage;
- recommended electrode diameter;
- operating temperature range;
- protection class;
- weight and size.
When purchasing a welding inverter, you must take into account that it, like any production equipment, does not last forever. Even with high-quality manufacturing and reliable components, the service life of such a device before complete write-off is 7–10 years, and the mean time between failures is several thousand hours.
Input voltage
Welding inverters are powered by single-phase or three-phase voltages of 220 and 380 V. As a rule, the electrical network serves as the source, but there are also mobile devices powered by a gas generator.
When choosing a device for use in domestic conditions or in small workshops, one of the key criteria is the maximum current consumption, which must correspond to the capabilities of the electrical network of the apartment, cottage, garage or industrial premises. But the purchase of a welding inverter, the current consumption of which complies with the standards of the electrical network, does not at all guarantee that during its operation there will be no problems with the supply voltage. The power of sources of such objects as garages and dacha cooperatives is limited by the capabilities of their substations, therefore, when a high load is switched on collectively, the voltage can “sag” to 150÷180 V. In this case, it is necessary to choose a device with the ability to operate at a reduced voltage.
Welding current
Manufacturers indicate the maximum and rated welding current based on the maximum permissible heating temperature of the electronic components of the inverter.
But the real temperature regime differs from the standard one, since it largely depends on operating conditions: air temperature, humidity, dust. Therefore, it is better to choose the operating current with a reserve: at least 15÷20% higher than required. To avoid overheating, welding of thin sheet metal, as well as a number of metals and alloys, must be performed at low currents. Therefore, if you plan to work with such materials, you need to pay attention to the minimum welding current. Another important indicator of the technological qualities of the inverter is the multiplicity of welding current regulation (ratio of max/min values). For MMA mode, this parameter usually lies in the range 3÷5. The higher its value, the wider the possibilities when performing welding.
Open circuit voltage
By increasing the no-load voltage, the process of igniting the arc is greatly facilitated, and the arc itself becomes more elastic and stable. However, at the same time, the dimensions of the equipment increase and the power factor decreases. Another negative consequence of this option is an increased risk of electric shock.
As the welding current decreases, the arc becomes unstable, so modern inverters automatically increase the no-load voltage at low currents and lower it when approaching maximum values. The optimal value for MMA welding is 60÷85 V (depending on the maximum current).
Maximum current operating mode
In the passports of all inverters, the operating mode is always indicated as one of the main characteristics, which is expressed in the form of a standard ratio of the welding time to the total duration of the technological operation. At the same time, manufacturers use different names for this parameter: loading duration (LO) and on-time (ON). The difference between PV and PN is that in the first case it is meant that the inverter is completely disconnected from the network during a pause between welding operations, and in the second - that the inverter continues to produce no-load voltage.
Most often, the PV is given, which is equal to the ratio of the operating time at the rated current to the total duration of the welding cycle. According to international standards, a cycle is considered to be an interval of 10 minutes, i.e. if duty cycle = 40%, then every 4 minutes of welding the inverter should be idling for 6 minutes. Some manufacturers indicate PV for several load values in equipment data sheets. Here is one such example for an inverter with a maximum current of 160 A: 40% - 160 A, 60% - 135 A, 100% - 105 A. At first glance, it may seem that 40% is a very small value. But in fact, the technological process, in addition to the welding itself, includes a number of preparatory, final and auxiliary operations, which take up most of the time of the welding cycle.
Useful additional features
Most modern welding inverters are equipped with additional operating functions, many of which have already become standard for this type of equipment. The most common among them are:
- Open circuit voltage limitation. This mode is aimed at increasing labor safety and is mandatory when working in conditions of high humidity, precipitation and inside metal containers. Before welding begins, the open circuit voltage is no more than 12 V, and when the electrode touches the metal it instantly increases to the nominal value. At the end of welding, the voltage drops again to 12 V.
- Hot start. To facilitate arc ignition, at the start of welding, the inverter for a short period (0.5÷3 s) produces a current pulse that exceeds the value set on the machine by one and a half to two times. This function also helps to improve the quality of the initial part of the weld.
- Anti-stick protection. If a short circuit occurs, after 0.5÷1 second the arc current is reduced for a short period and then restored again.
- Arc Force. Using this function, the mode of droplet transfer of electrode metal into the weld pool is restored. A continuous flow of metal is destroyed by a sequence of short pulses of increased power.
The pinnacle of the functional development of inverter technologies is the synergistic control system, which is capable of independently selecting the desired program according to specified parameters and adaptively controlling the welding process throughout the entire production cycle.
Inverter welding technology
What inverter welding is can be understood by considering its technology.
The whole process is carried out in stages:
- At the initial stage, the arc is ignited. This can be done in several ways - by scratching, tapping or touching;
- then we begin to melt the metal, a weld pool should form;
- the electrode can be carried out at a right angle of 900 or obliquely at an angle of 30-600;
- When carrying out the welding process, it is imperative to hold the welding arc. During this process, it is necessary to maintain a uniform distance between the metal and the electrode. The most suitable level should be 2-3 mm.
It is worth noting! Some inverter models have an automatic arc hold function. If you cannot do this manually, then it is advisable to use this option.
If you look at the detailed instructions, you can understand what inverter welding means. This is a unique process that allows you to join different metal workpieces. Convenient welding machines provide maximum convenience when working in difficult production conditions, which often require welding at heights.
Which inverter to choose for home use
To choose a suitable welding inverter, you must first decide what it is supposed to do and under what conditions it will be used.
Based on these data, it is already possible to select power, operating modes and other technical characteristics of the future device. A home craftsman for household needs is unlikely to require such types of welding as MIG/MAG and TIG, so further we will talk only about manual MMA electric arc welding. In order to qualitatively weld angles, channels, strips and pipes up to 5 mm thick, theoretically, a welding inverter with the following characteristics is sufficient:
- mains voltage - 220 V;
- maximum welding current - 120÷150 A;
- PV - 40÷50%;
- electrode thickness - up to 4÷5 mm.
But in practice, the operation of the inverter will most likely occur under conditions different from the standard ones. Therefore, you will almost certainly have to adjust the selected characteristics. First of all, you should analyze the quality and stability of the supply voltage. Typically, welding inverters are designed to operate in conditions of input voltage fluctuations of ±10÷15%, so when connected to an electrical network with such parameters, they will work without any problems. If the deviation reaches 30% (which often happens in dachas, garages and rural areas), then you should choose an inverter model with the ability to operate at reduced voltage.
It must be remembered that the inverter power and welding current will drop in proportion to the decrease in voltage. It should also be taken into account that the use of welding wires longer than five meters (which will certainly be required when welding outdoors) also reduces its power. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a device with a current reserve. In our case, the optimal device would be a maximum current of 160÷180 A.
A home inverter should be lightweight so that it is easy to carry, and compact so that it fits in the trunk of a car. It is advisable to choose an inverter with a shock-resistant and waterproof housing, as well as a transparent protective cover for the control panel. The presence of a digital indicator is desirable, but not necessary, since on inexpensive models they often work with large errors.
Almost all modern inverters (even in the price category up to 10 thousand rubles) are standardly equipped with the Arc Force, Anti stick and Hot start functions. But when choosing a specific model, you should still make sure that these modes are available.
Figure 8 - Welding process
The technical requirements for choosing the best home welding inverter in our version will look something like this:
| № | Name | Household |
| 1 | Input voltage (V) | 220 |
| 2 | Allowable voltage fluctuations (%) | +15 / -40 |
| 3 | Power, kWt) | 4÷5 |
| 4 | Max. and min. operating current values (A) | 10÷180 |
| 5 | Open circuit voltage (V) | 60÷80 |
| 6 | Degree of protection | IP-22 |
| 7 | Electrode diameter (mm) | 1.6÷5.0 |
| 8 | Duration of switching on (duty cycle, %) | 30÷50 |
| 9 | Additional functions | Arc Force, Anti stick, Hot start |
| 10 | Weight, kg) | 4÷5 |
When choosing a specific model, you should focus on well-known brands that have been on the market for at least ten years. It is also necessary to pay attention to the proximity of the service center and the warranty period, which for inverter manufacturers ranges from one to five years.
Additional functions in inverters
Modern inverter devices implement some options that significantly facilitate the welder’s work:
- Hot start - often novice welders, and not only them, have difficulty igniting and maintaining the arc in working condition. At the moment of ignition, the current rises to the required level and immediately after ignition returns to operating parameters. The process of changing the current occurs completely automatically, without the participation of the welder.
- Another problem that plagues beginners is electrode sticking. There are several reasons for this, but there is only one solution - reducing the level of welding current. This operation is also performed automatically.
- Arc forcing allows you to make seams in different spatial positions.
- Reducing the no-load voltage to a level that is safe for the worker and his surrounding people.
Popular inverters for arc welding
The Russian market of welding inverters is represented by several dozen brands, among which four main groups can be distinguished:
- leading Western manufacturers of welding equipment;
- Russian and post-Soviet enterprises that independently produce inverter devices;
- Russian brands representing products manufactured in China;
- Chinese, Japanese and Korean manufacturers of welding inverters.
On the Internet you can find many reviews of welding inverters and reviews of specific models and their manufacturers. All these products are characterized by high quality and satisfy the widest range of needs. Therefore, it is not surprising that various “Top of the Best” reviews present completely different models. The same applies to ratings of brands and manufacturers. The following will be a brief overview of those who, in our opinion, deserve special attention or are rarely mentioned in articles about welding technology.
Aurora
Aurora PRO welding equipment, popular in Russia, is produced by the famous Chinese company Riland Power Source Technology. The inverters of this company have international quality certificates and awards from international exhibitions. The Aurora PRO brand produces all types of welding equipment (MMA, MIG/MAG, TIG and CUT) for industrial, professional and domestic use. According to user reviews, Aurora PRO inverters are reliable and have the best price-quality ratio.
Figure 9 — Aurora welding inverter
BlueWeld
The Italian company BlueWeld is one of the world leaders in the production of welding equipment. It was founded in 1963, and was first introduced to the Russian market in 2002. The quality of BlueWeld inverters complies with Russian GOST and German TUV, and all its production is certified according to the international standard ISO 9001. The company uses a number of its own patented solutions in its equipment and offers a huge selection various models for all types of welding. All BlueWeld inverters are manufactured in European factories and are included in the upper price category on the Russian market.
"Fast and Furious"
Welding inverters "Forsazh" are produced by the Ryazan instrument-making plant. These devices do not have an outstanding design, but their high reliability and excellent technical characteristics are recognized by everyone. Forsazh machines are presented in versions for three- and single-phase networks, and their model range covers the range of welding currents from 160 to 500 amperes. A special feature of this equipment is a three-year warranty period.
"Resanta"
The Latvian enterprise SIA Resanta, which produces electrical products, voltage stabilizers and power equipment, has been operating on the Russian market since the mid-nineties of the last century. The line of welding inverters from this company is represented by twelve models with maximum currents from 140 to 315 amperes, in a price range from 4.8 to 31 thousand rubles. This product is popular in Russia, and the overwhelming majority of reviews about it are positive.
Patriot
The owner of the famous American brand Patriot is an international corporation specializing in the production of power tools, power equipment, gardening and construction equipment. Patriot is produced at seventy enterprises located in Russia, China, Italy, Belarus and Korea. Patriot welding inverters are designed for domestic use and small industries. There are twelve models available for MMA welding, ranging from 150 to 250 amps, and four models for TIG welding.
"Interskol"
Interskol is one of the leaders in the Russian market of power tools, machine tools and power equipment. The company has its own production, which is located in Khimki. Interskol produces only inexpensive welding inverters for manual welding with stick electrodes, and its model range is represented by seven devices with maximum currents from 160 to 250 amperes and prices from 5.2 to 10.5 thousand rubles.
Figure 10 — Welding inverter Interskol
Fubag
The Fubag trademark belongs to the famous German manufacturer of welding equipment Fubag GmbH. The equipment of this brand is produced in different countries of the world according to uniform standards, and it is supplied to Russia from China and France. The Fubag inverter range includes three lines: for professional use (IN index, seven models), for use in small industries and households (IR index, six models) and small-sized mobile (IQ index, three models).
Elitech
The international brand Elitech belongs to the Russian group, which supplies the Russian market with power and hand tools, machine tools, power equipment, as well as gardening tools. Welding inverters of this brand are produced in China and Belarus. The product line includes dozens of machine models for all types of welding and applications. All production of this brand is certified according to the ISO 9001 standard. Elitech has more than a hundred service centers and according to this indicator is among the leaders of the Russian market.
Daewoo
Korean Daewoo brand welding inverters attract users with their low price, European quality and the authority of the manufacturer. Manual welding machines of twelve varieties with a maximum current range from 150 to 260 A are supplied to Russia. All Daewoo inverters are designed to operate at reduced voltage, and the duty cycle is 60÷80%. These devices are lightweight and equipped with all standard inverter functions.
Popular universal inverters
Universal inverters are devices that combine several welding technologies. Typically, this kit includes manual alternating and direct current (MMA) welding, semi-automatic gas welding (MIG/MAG) and tungsten arc welding (TIG). Combined devices are always more difficult to operate, more demanding in terms of workmanship and are much more expensive than conventional ones. When purchasing such a device, the user is always faced with the question of choosing the golden mean between price and quality. Therefore, the most popular on the market are not the best models from world leaders, but devices from manufacturers with good traditions and an established reputation. Among inverters of this type, some of the most popular are:
- Svarog Pro MIG 200. Its features include the ability to weld with flux-cored wire and welding of aluminum alloys. It is also necessary to note the warranty period of 60 months.
- Elitech AIS 200 PNS. This inverter has a synergic control system and is able to operate when the input voltage drops to 160 V.
- Wester Combi 250P. The device is equipped with an improved overheating protection system, operates at an input voltage of 180÷250 V and has the ability to connect an external 36 V power source for the gas mixture heater.
Figure 11 — Welding inverter
On the websites of welding equipment sellers, universal inverters are usually designated by the word “combi” or a combination of abbreviations “MIG/MAG/MMA/TIG”.
On specialized forums they often write that in universal welding inverters, TIG (argon arc welding) technology is implemented only for direct current (TIG DC). While for welding aluminum and its alloys it is necessary to have a TIG AC/DC (variable/constant) with an oscillator. Therefore, some experts advise not to buy a combi, but to purchase two devices: MIGMAGMMA and TIG AC/DC. What do you think about this? We will be very grateful if you express your opinion in the comments to this article.