Stray currents
Stray currents are currents that appear in the soil when it is used as a conducting medium. The reasons for the appearance of such currents in the heating system and water supply systems are varied:
- incorrectly created or missing grounding of electrical installations connected to the dryer;
- close location of live mains (for example, railways, tram tracks);
- short circuits.
In theory, short circuits should not occur if the system is properly constructed. However, it happens that instead of welding they use ordinary bends or install a metal-plastic pipe instead of a metal pipe. As a result of this, stray currents arise, leading to corrosion processes of the electrical or electrochemical type.
Stray currents occur if the riser is made of metal and grounded, and plastic pipes are installed in apartments. In new buildings, grounding is carried out through a potential equalization system, and in old buildings - along a ground loop. If the pipes are plastic, the metal connection between them and the dryer is lost, which leads to the emergence of stray currents: the existing potential is broken. Because of this, there is one potential on the riser, and a completely different one on the “towel”.
Another common cause of stray currents is different potentials of two different metals that are in close contact. Currents are especially active when ordinary steel and stainless steel are adjacent.
The most common causes of current leakage on a heated towel rail:
- Incorrect use of the power supply system when pipes are used as working zeros.
- Unprofessional connection of hydromassage baths, showers, washing machines, dishwashers, sterilizers. In such cases, the pipes are connected to the building's electrical supply.
- Violation of the integrity of cable networks and electrical installations.
- Weakening, burning, physical damage to wiring.
Indications for grounding
In fact, all engineering systems are grounded at the construction stage of the building. A grounding system is created. In old houses, a potential equalization system was used. This system implied the connection of the metal parts of the system. Today, the widespread use of plastic pipes calls this method into question. As a result of the use of plastic inserts, the metal connection of the system breaks, which leads to the occurrence of stray currents.
It seems that the problem can be solved by using metal-plastic pipes, since such pipes contain aluminum film. However, we must not forget that metal-plastic pipes are connected mainly by soldering. To ensure the tightness of the soldering of metal-plastic pipes, it is necessary to clean the joint from aluminum foil, that is, that same metal connection disappears.
New houses are equipped with a special grounding circuit in the electrical panel. This greatly simplifies the grounding of the heated towel rail. In addition, the use of such a circuit is the only possible method to ensure grounding of all systems with parallel use of plastic pipes.
Grounding of the heated towel rail is necessary:
- In a new house with a metal-plastic heating riser. The main pipeline is always made of metal, so there is a high probability that stray currents on the way to the main will get into your heated towel rail.
- After renovation in an old house using metal-plastic pipes. In old houses, as already mentioned, the potential equalization method was used. The result of such repairs is a violation of the grounding system, which means it needs to be provided with a new one.
- Connecting the heated towel rail to the network using metal pipes.
Grounding a heated towel rail is necessary if a metal-plastic heating riser is used.
In general, in order not to be mistaken about the need for grounding, it is better to simply do it regardless of the presence of indications for grounding. This will save time and money for the apartment owner, and will also increase the service life of not only the heated towel rail, but also all metal equipment in the bathroom.
Why ground a water heated towel rail?
After plastic pipes began to replace ordinary metal pipes, they began to ignore their grounding, mistakenly believing that a metal pipe and a metal-plastic pipe have the same conductivity. This is wrong. There is no contact between the metal-plastic pipe and the aluminum: they are not connected.
Practice shows that 90 percent of heated towel rails begin to leak precisely when metal hot water supply systems are replaced with their plastic counterparts (for example, polypropylene). Old metal pipes are replaced with modern plastic ones in order to reduce eddy currents. However, corrosion continues to manifest itself.
The first symptoms of electrical corrosion are the appearance of rust spots on the heated towel rail , and rust appears even on devices made of stainless steel. In general, all metal electrical products in contact with water are subject to both electrochemical and galvanic corrosion. Electrocorrosion occurs in the presence of stray currents. As a result, the metal is simultaneously exposed to electric current and water, after which metal breakdowns appear, and from there corrosion begins to spread.
When two different metals come into contact, one of which is more chemically active than the other, both metals undergo a chemical reaction. Pure water is a very poor conductor of electric current (dielectric), but due to the high concentration of various impurities, water turns into a kind of electrolyte.
Do not forget that temperature has a great influence on electrical conductivity: the higher the temperature of the water, the better it conducts electric current. This phenomenon is known as “galvanic corrosion”, which is what systematically renders the heated towel rail unusable.
Types of Stainless Steel Corrosion
Owners of stainless steel dryers often complain that the device has become covered with rust. Gradually, more and more spots with a diameter of a couple of match heads appear on the surface of the heated towel rail. If you wipe the area of rust, a barely noticeable mark will remain, which over time covers an increasingly larger surface.
Being affected by corrosion, the water heated towel rail begins to leak. The root cause of the destructive process is stray currents. Metal structures that are constantly in contact with water are subject to two types of corrosion: electrochemical and galvanic.
Electrocorrosion occurs when metal through which electricity passes comes into contact with water. Due to high load, so-called metal breakdowns occur, which leads to the development of corrosion processes.
Galvanic corrosion occurs due to the interaction of dissimilar metals, one of which is characterized by higher chemical activity. In this case, the electrolyte is water along with the minerals and salts it contains. Hot water especially enhances electrical conductivity. In this case, the metal deteriorates much faster.
How to ground plumbing and why it needs to be done
Modern apartments are in most cases overcrowded with a variety of household appliances and metal products. The bathroom is no exception. In small toilet rooms you can see a large selection of electrical appliances and plumbing items that are potentially dangerous to humans. Even an acrylic bathtub is included in this list, although it is made of dielectric material. This product is capable of accumulating a powerful charge of static electricity, which can cause significant damage to a person. In addition, the acrylic container is installed on a metal frame, and it conducts electricity well.
All this suggests that grounding in the bathroom must be created, although there are no special requirements in regulatory documents in this regard. For a private house or country house, creating a grounding loop in the bathroom will not be difficult, but in apartments of multi-storey buildings you will have to bring out the grounding wire to the floor distribution board and connect it to a special bus. We will consider below how to protect various plumbing items from the appearance of dangerous electric voltage on them and how to ground a bathtub in an apartment.
Important! The grounding conductor has green-yellow insulation and is designated on the wiring diagrams by the letters PE. This is necessary in order not to confuse the grounding cable with the power lines of the facility's power supply.
Grounding old bathtubs
In Soviet times, cast iron or steel were mainly used to make bathtubs. These products did not provide special structural elements that are necessary to connect the ground wire. But this problem can be solved quite simply! To complete the work, you will need the following tools and materials: an electric drill, a drill with a pobedit tip, a jumper for connecting the ground wire, a set of fasteners (bolt, washers and nuts), as well as a stranded copper cable and a distributor of all ground taps.
A hole of the required diameter is drilled in the bathtub leg and a grounding jumper is installed on the threaded connection. A grounding conductor is attached to the jumper and brought out to the switchgear. The device itself must be secured in a convenient place, since all grounding wires from metal products located in the bathroom will be connected to it. From the distributor, the common grounding wire must be led to the distribution board on the floor landing and connected to the protective grounding bus. All this work is quite simple and can be done with your own hands.
Grounding modern cast iron and steel bathtubs
Grounding cast iron bathtubs manufactured in the last decade will not cause problems even for an inexperienced consumer. All of them are equipped with special petals with a mounting kit for connecting the grounding conductor. Simply tighten the bare end of the wire between the washers and bring it out to the distributor. If for some reason the jumper is missing, a hole will need to be drilled. It is best to perform this operation on special thickenings of the bathtub body, which are designed to wedge the load-bearing legs of the product. This option will create reliable contact between the ground wire and the bathtub.
There will be no special problems with steel bathtubs either. They usually have a petal and do not need to drill a hole. It is enough to strip the enamel coating around the hole on the petal down to the metal and use a crimp screw to secure the grounding conductor. All other operations must be performed by analogy with cast iron baths. Next, we will consider the question of whether it is necessary to ground an acrylic bathtub and how to do this work correctly.
Attention! It is prohibited to connect the ground to the removable legs of steel and cast iron bathtubs. This is due to the fact that there is no normal electrical contact between the supporting elements and the bathtub itself!
Grounding acrylic bathtubs
Acrylic bathtubs are becoming very popular sanitary products. It is they who are gradually ousting steel and cast iron products from the market. The main advantage of acrylic bathtubs is their light weight, but at the same time this is a definite disadvantage. There are two types of such products: cast and extruded. The second type of acrylic plumbing products is installed on steel frames, and as we know, metal is an excellent conductor of electricity. Therefore, acrylic bathtub frames must be grounded. Grounding an acrylic bathtub is carried out by analogy with steel products.
Important! Water getting between the body of an acrylic bathtub and the supporting metal frame can lead to the formation of a conductive layer, so this structure must be grounded!
Jacuzzi grounding
If we can argue about the need to ground various models of bathtubs, then for Jacuzzis (hydromassage baths) this procedure is mandatory! This plumbing product is a complex household appliance that consumes electricity, and any electrical appliance in the bathroom must have protection against the appearance of mains voltage on its body. Hydromassage baths are connected to the grounding bus through special sockets designed for installation in rooms with high humidity. They have special curtains in their design that protect the contacts from water getting on them.
Sockets for connecting a jacuzzi are installed at a distance of 30 cm from the floor of the bathroom and 50 cm from the edge of the whirlpool bath. The cable for supplying electricity and the grounding conductor must be double insulated and placed in a corrugated pipe. For a Jacuzzi, a separate RCD and circuit breaker must be installed in the switchboard; in addition to grounding, this will ensure reliable protection of a person from electric shock. The PUE rules prohibit grounding hydromassage baths through the water supply system. It is advisable to involve an experienced electrician in the installation of a jacuzzi, as this will allow you to avoid errors when connecting.
Attention! When installing electrical wiring and protective grounding cables, the use of twists and other unreliable connections that can lead to a broken contact and electric shock to a person is not allowed!
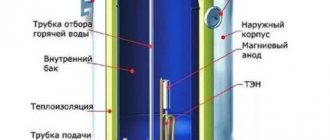
Grounding the heated towel rail
How to ground a stainless steel heated towel rail and is it necessary? The answer to this question can be found in physics textbooks and reference books! There are such concepts as galvanic corrosion and stray currents. These two unpleasant phenomena can reduce the life of the heated towel rail to a minimum! Stray currents occur when electrical energy leaks into the heating system from damaged wiring, household appliances, and for some other reasons. Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals interact with water, which is to some extent an electrolyte.
These two factors can damage a stainless steel heated towel rail, so it should be grounded. Heating systems consisting of metal pipes are initially grounded and additional grounding is not required to equalize potentials on the heated towel rail. But if the heating pipes are plastic, then it is better to connect it to a common ground bus on the distribution board. This operation will not cause any difficulties; it is enough to secure the grounding conductor to the heated towel rail using a metal clamp and remove its zero bus.
Stainless steel heated towel rails: grounding, problems, connection
Metal corrosion corrodes the surface of various products that we use in everyday life. Water heated towel rails are no exception; stainless steel is susceptible to corrosion and begins to become covered with rust spots. The reasons for this phenomenon in the bathroom may be stray currents or galvanic corrosion.
Grounding the heated towel rail
The bathroom can have hidden dangers and become a source of electrical voltage. Water contributes to the accumulation of an electrical charge, which can cause significant harm to human health. Grounding of a stainless steel heated towel rail must be carried out without fail in order to avoid unforeseen situations. A neighboring apartment along the riser can also become a source of danger when the neighbors have not eliminated the source of electric current accumulation. Microfriction of various media: water and metal creates a potential difference, between which an electric current appears. This is a law of physics. Grounding will eliminate this potential difference.
If your stainless steel heated towel rail is leaking, it is quite possible that this was caused by stray currents. You definitely need to know how to ground a stainless steel heated towel rail to metal pipes and ensure reliable connection between the metal device and the riser pipes. This will equalize the voltage potential and eliminate the source of stray current.
Modern manufacturers make heated towel rails from high quality steel; the product must be grounded.
Features of heated towel rails with side connection
Residents of apartments located in high-rise buildings must install stainless steel water heated towel rails with a side connection. Such recommendations are related to the peculiarity of the geometry of the water main in a residential building and will provide compensation that occurs due to a change in the direction of water movement in heated towel rails. This will prevent the water pipe from bursting in the riser and eliminate unwanted leaks. In order to figure out how to ground a stainless steel heated towel rail, you should contact a specialist. The temperature of the water interacting with the metal also influences the processes occurring inside the water supply. It is temperature changes that can lead to leaks in certain places.
Installation of a stainless steel water heated towel rail with a side connection is possible from any convenient side to the main line; the ball valve is installed on top. There are some tips to keep in mind when installing your device:
- You cannot dry things on a heated towel rail.
- A stainless steel heated towel rail can be installed on a water main made of metal-plastic pipes.
- You should always take into account the difference in pipe diameters to avoid problems with the coolant.
- Remember that the water supply system is under pressure.
Stainless steel water heated towel rails with side connections can be mounted on a hot water riser, after first making sure that there are no valves shutting off the water.
By installing a heated towel rail in your bathroom, you will receive an additional device for heating the room. A multifunctional device has become a mandatory attribute of modern bathrooms. Manufacturers have taken care of the external design of water heated towel rails.
Inexpensive heated towel rails can be bought in the online store by visiting the required section of the catalog, which presents models of various sizes and shapes of the popular device. The cost of the product depends on the manufacturer, material of manufacture and other parameters. For domestic use in bathrooms in residential apartments, stainless steel is more suitable than other materials. Heated towel rails can be finished in bronze or copper, sometimes the color of gold is used. Installing a heated towel rail with a side connection will not take much time; the fasteners are included in the product kit.
First signs of corrosion
You can determine that your heated towel rail has become a “victim” of corrosion processes by the appearance of the equipment. The first signs of metal destruction are:
- swelling of the decorative layer (paint) - first this occurs at joints and on sharp edges of the structure;
- the appearance on the affected surface of a noticeable whitish coating, reminiscent of fine powder;
- the formation of small dents and depressions in the damaged areas - it seems that the metal has been eaten by a bug.
Minor damage is usually the result of galvanic corrosion caused by the difference in electrical potential of dissimilar metals, one of which acts as a cathode and the other as an anode. And if you add stray currents to this, the destruction will be much more serious.
Typical situations in which problems are possible
The main cause of problems is the interruption of electrical communication between different parts of the plumbing system. This should be given special attention in the following cases:
- If the house is old, but it has recently been renovated. If plastic inserts were used as a result, then measures must be taken to combat stray currents.
- When a tenant moves into a new apartment, he must check what material the pipes are made of. If it is plastic, measures will need to be taken to equalize the potential.
- If there is a direct connection of different metals in the plumbing system.
- When a plastic structure is connected using metal inserts.
In an apartment building, plastic inserts can be made by other residents. In most cases, it is almost impossible to know for sure.
What are stray currents?
Stray currents are currents that arise in the ground, which is used as a conductive medium. But this is too general a definition. In the case of heated towel rails, stray currents appear as a result of electricity leakage from the wiring as a result of a wire breakdown. The lost current tends to places with low potential, that is, to any metal structures.
Stray currents are dangerous because they cause metal corrosion, which leads to leaks and wear of the heated towel rail. Another dangerous factor is that a device with stray currents is unsafe for humans. Because there is a high risk of getting an electric shock.
To protect yourself from these two factors, you need to do the following:
- Grounding, that is, to ensure a strong connection between the water supply or heating pipes with the heated towel rail. Then the stray currents will disappear and the corrosion process will stop.
- Create a system that will balance the potentials of all pipes.
Grounding can protect the heated towel rail from corrosion
Stray currents are a common phenomenon and, moreover, dangerous for humans. Therefore, as soon as you notice this feature in your heated towel rail, you need to fix it: by calling a specialist or yourself
Why does a stainless steel heated towel rail need grounding?
Grounding is a connection between the metal body of the device and a wire connected to the ground .
If there is such a connection, the charge on the case (including the charge of static electricity ) “drains” to the ground.
If is severely damaged, a short circuit occurs a large current flows through the grounding conductor , which should lead to the switching off of the circuit breakers and de-energization of the line.
Problems arising with a water heated towel rail
A heated towel rail is a necessary element of modern life.
a warm and cozy bathroom without it .
Typically, such a device is part of a general heating system , as a result of which it interacts with the liquid inside it, which is a conductor , which causes problems such as electrochemical corrosion and stray currents .
Attention! It is believed that stray currents are not dangerous for people and central heating and water supply systems , but it is the heated towel rail that they cause significant harm . Therefore, the role of grounding steel water heated towel rails connected to the system by plastic pipes is very important .
Electrochemical corrosion
Modern devices are made from high quality stainless steel . Despite this, they are subject to corrosion , in this case electrochemical . Such damage causes destruction of the metal in contact with the electrolyte, which is the water inside the heated towel rail. In places where there is a potential difference due to the metal being heterogeneous in composition and structure under the influence of hot moving water, occur and rust appears . This, in turn, leads to leaks and failure of the heated towel rail .
Photo 1. Traces of electrocorrosion that appeared on the seam at the junction of the heated towel rail pipes.
A little about the nature of stray currents and their danger
The reason for the appearance of stray currents acting on your heated towel rail is the difference in potential of grounded structures. And in order to equalize the potentials, it is necessary to create a system in which all metal elements will be in contact with the neutral conductor in the existing input distribution device.
Such a system will ensure maximum safety for the user (if you put your hand on a pipe and grounded equipment, you will not receive a fatal discharge). And this is very important, because the greater the potential difference, the more serious the danger threatens a person. For example:
- If this value is 4 or 6B, you may receive a 5 mA shock. It will be sensitive but not fatal.
- If its strength is 50 mA, cardiac fibrillation may develop.
- And when a human body is exposed to a current of 100 mA, death occurs.
But there are cases where even a small potential difference of 4B became the cause of death.
Potential difference: causes of occurrence
But where does the potential difference come from if the house is built taking into account all current standards? In theory, if building rules are observed, there should be no potential difference. But in practice, it often happens that when assembling structures and engineering systems, welded joints are replaced with bends. Another common option is to integrate additional resistances or metal parts into the circuit. Both can cause a potential difference to occur at opposite ends of the pipe and, accordingly, initiate metal corrosion.
We should not forget about the “conflict” between metal and plastic, which also plays an important role in the destruction of various peripheral devices (including heated towel rails). Due to the fact that plastic pipes are often placed between stainless steel plumbing equipment and a metal riser (they are used for wiring throughout the apartment), the connection between these parts of the system is broken. And although the riser will be grounded in any case (in new high-rise buildings this is done through an equalization system, and in older buildings - through a grounding loop located in the basement of the building), a potential difference will still form. And when water moves through pipes, which demonstrates excellent conductivity, microfriction also arises, which is guaranteed to lead to the appearance of stray currents. And they, in turn, provoke corrosion. The circle is closed!
Measurement methods
To check for the presence of BT, devices are used to determine their presence and size. The set of measurements includes:
- testing the voltage and direction of current along the sheaths of main cables;
- finding the potential difference between points: underground communications - rails;
- measurements in individual sections of the railway of the insulation value of the rails from the bedding;
- analysis of the degree of energy leakage from cable sheaths into the ground.
Important! Measurements at railway facilities are carried out during hours of highest train traffic density.
BT measurement kit
The use of a BT protection complex and correct calculation of the potential will minimize the negative impact of currents. An important role is played by the precise determination of BT localization sites. Electrocorrosion protection of objects reduces the cost of repair and replacement of deteriorated pipelines and other underground communications.
The need for anti-corrosion protection
Protecting metal from influences that have a destructive effect on its surface is one of the main tasks facing those people who work with mechanisms, units and machines, ships and construction processes.
The more actively a device or part is used, the more likely it is to be subject to the destructive effects of atmospheric conditions and liquids that are encountered during operation. Many branches of science and industrial production are working to protect metal from corrosion, but the main methods remain unchanged and consist of creating protective coatings:
- metal;
- non-metallic;
- chemical
Non-metallic coatings are created using organic and inorganic compounds; their operating principle is quite effective and differs from other types of protection. To create non-metallic protection in industrial and construction production, paint and varnish compositions, concrete and bitumen and high-molecular compounds are used, especially actively adopted in recent years, when polymer chemistry has reached great heights.
Chemistry has contributed to the creation of protective coatings using methods:
- oxidation (creating a protective film on metal using oxide films);
- phosphating (phosphate films);
- nitriding (saturation of the steel surface with nitrogen);
- cementation (combination with carbon);
- bluing (compounds with organic substances);
- changing the composition of the metal by introducing anti-corrosion additives into it);
- modification of the surrounding corrosive environment by introducing inhibitors that affect it.
Electrochemical corrosion protection is the reverse process of electrochemical corrosion. Depending on the shift of the metal potential to the positive or negative side, anodic and cathodic protection are distinguished. By connecting a protector or a direct current source to a metal product, cathodic polarization is created on the metal surface, which prevents the destruction of the metal through the anode.
Electrochemical protection methods consist of two options:
- the metal coating is protected by another metal that has a more negative potential (that is, the protecting metal is less stable than the protected one), and this is called an anodic coating;
- the coating is applied from a less active metal, and then it is called cathode.
Anodic corrosion protection is, for example, galvanized iron. Until all the zinc from the protective layer is used up, the iron will be relatively safe.
Cathodic protection is nickel plating or copper plating. In this case, the destruction of the protective layer also leads to the destruction of the layer that it protects. Attaching a protector to protect a metal product is no different from the reaction in other cases. The protector acts as an anode, and what is under its protectorate remains safe, using the conditions created for it.
Selecting components for bath grounding
Typically, in apartments and private houses, a stranded wire with a cross-sectional area of at least 6 square meters is used for grounding and grounding. mm. This cross-sectional area of the grounding conductor is quite sufficient to provide protection against electric shock to a person in residential premises. It is better to choose a copper cable, but in extreme cases you can use aluminum wire or copper-sheathed steel wire. The grounding conductor should be masked. This is necessary not only from an aesthetic point of view, but also to protect the grounding from accidental damage. Usually the cable is hidden in bathroom furnishings, behind screens and plastic panels. To connect the grounding of all items in the bathroom to a common bus, use a special distributor.
How to solve a problem
In order to protect against stray currents, it is necessary to ground the heated towel rail and connect it to other metal parts of the water supply system. To do this:
- It is necessary to connect the structure with the pipes of the water supply system. To do this, you must use a wire with a cross-section of at least 4 square meters. mm. If the heated towel rail is installed in the bathroom, you need to connect all the elements of the system together in this way.
- It is necessary to make a connection between this wire and grounding in the power supply panel.
- It is necessary to attach a grounding wire to the heated towel rail. For this purpose, you can use a special clamp.
If the metal riser has contact with the ground for grounding, you can make a connection to it. However, sometimes there is no reliable information about what actually happens. Therefore, a more reliable solution would be to connect the ground wire to the corresponding contact on the distribution panel.
The wire must be cleaned before connecting. The paint must first be removed from the area where it is connected to the pipe. If these conditions are met, you can be confident in the reliability of the contact. If there are other parts of pipes in the house separated by plastic inserts, you need to connect them all using this wire.
Depending on the design features, connection diagrams may differ. In cases where the metal of the heated towel rail is in direct contact with steel or cast iron pipes, and there are no plastic inserts in them, the problem described here does not arise.
If the structure is made of plastic, and for insertion the master placed a section of pipe made of this material, then the connection must be made between the previous metal part, the next one and grounding.
In the case when not only the heated towel rail, but also the pipes of the water supply system are polymer, when connecting the structure, a metal insert is made in one of the two connecting pipes, which will need to be connected to the ground loop.
Mechanism of formation of stray currents
In the table we have given several sources as examples; now we will consider in detail how the process of interest to us is formed in them. As mentioned above, for it to appear, a potential difference must occur between two points on the ground. Such conditions are created by the circuits of the charger systems with a solidly insulated neutral.
The neutral wire (PEN) is connected at one end to the electrical substation charger, and at the other end it is connected to the consumer’s PEN bus, which is connected to the facility’s grounding device. Accordingly, the difference in electrical potential between the terminals of the neutral conductor will be transferred to the memory, which will create conditions for the formation of a circuit. The amount of leakage will be insignificant, since the main load will follow the path of least resistance (neutral conductor), but, nevertheless, part of it will go along the ground.
Formation of stray currents between the neutral wire charger
Almost similar conditions arise when problems arise with the insulation of wires (destruction of the sheaths) of cable mains or overhead lines. When a short circuit to ground occurs, at this point the potential is equal or close to phase. This causes the formation of a leakage current to the nearest charger at the potential of the PEN wire.
In the above example, we are not talking about a constant leakage of alternating currents, since according to current standards, two hours are allocated for searching and eliminating damage. In this case, in most cases, disconnecting a damaged line or localizing a section with a short circuit is carried out automatically. The process can be significantly delayed if the short-circuit current is below the emergency threshold.
As practice shows, the largest share of sources of constant leakage currents comes from urban and suburban rail electric transport. The mechanism of their formation is demonstrated below.
Electric rail transport as a source of stray currents
Designations:
- The contact wire from which the power plant of an electric vehicle receives power.
- Power feeder (connected to the contact wire).
- One of the traction substations that supplies the tram network.
- Drainage feeder (connected to rails).
- Rails.
- Pipeline in the path of stray currents.
- Anode zone (positive potentials).
- Cathode zone (negative potentials).
As can be seen from the figure, constant voltage enters the traction network from the substation and returns along the rails. If the resistance of the rail tracks relative to the ground is insufficient, electric stray currents arise in the ground. If there is a pipeline or other metal structure in the path of the leakage of stray currents, then it becomes a conductor of electricity.
This is due to the fact that current travels along the path of least resistance. Accordingly, as soon as a conductor appears, the current will spread through the metal, since its electrical resistance is less than that of the ground. As a result, the section of the pipeline through which the electric current passes will be more susceptible to metal corrosion. The reasons for this are discussed below.
Features of a stainless heated towel rail
When purchasing a stainless steel heated towel rail, we count on its long-term service. The very word “stainless steel” is associated with something aesthetic, durable, and reliable. But is this really so? How long should a stainless steel heated towel rail last ? This depends on several factors.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel is different from stainless steel. It all shines the same, but resists corrosion differently. Heated towel rails must be manufactured from Group 300 austenitic stainless steel pipes in accordance with AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute) standards. These are mainly AISI 304, AISI 304L. Due to the high content of chromium, nickel (about 8-12%) and low carbon, these steels have high anti-corrosion characteristics, strength, are easy to weld, process, polish, and are intended for food production.
Some manufacturers, especially from Southeast Asian countries, use pipes made from AISI 409, 430 and other 400 group steels to produce stainless heated towel rails. They are cheaper, but less resistant to corrosion. This means they will last less and can leave marks on towels and linen.
Take the time to find out what steel the heated towel rail pipes are made of. If not from the AISI 304, 304L brands, it is better to refuse to buy one. By the way, NAVIN stainless heated towel rails from our range are made from AISI 304L pipes .
Below in the table you can see the ratio of corrosion resistance of commonly used stainless steels:
Welding
The type of pipe welding has a great influence on the durability of the products and their ability to work under pressure. There are several methods of welding stainless steels: TIG (tungsten inert gas), high frequency currents, laser, electron beam, plasma.
The European PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) states that for equipment operating at pressures greater than 0.5 Bar, pipes welded only by TIG . Today, up to 70% of stainless steel welding in Europe is carried out using TIG or TIG combined with plasma. The TIG method produces a wide, dense, homogeneous weld without cavities or inclusions, which is not inferior in strength to the base metal. However, the TIG welding speed is low, so the price of the pipe, and, accordingly, the finished heated towel rail is slightly (5-15%) higher.
Relationship between stray current and corrosion on metal
Due to the presence of water and dissolved salts in the ground, any metal structure in the soil is susceptible to corrosion. But if the metal is also exposed to stray currents, then the process becomes electrolytic in nature. According to Faraday's law, the rate of an electrochemical reaction directly depends on the current flowing between the anode and cathode. Consequently, the rate of corrosion of a metal pipe (laid in the ground) will be influenced by the electrical resistance of the soil, as well as the complex nature of the processes occurring in the cathode and anodic zone.
As a result, the metal structure, in addition to normal corrosion, is exposed to leakage currents. This can cause the formation of a galvanic couple, which will significantly accelerate the corrosion process. In practice, there have been cases when a section of a water supply system pipeline that was subject to galvanic corrosion failed after two years, with an estimated service life of 20 years. An example of such an impact is presented below.
Pipe after exposure to stray currents
Why do you need a heated towel rail?
This equipment is a repeatedly curved pipe or structure in which the horizontal parts are arranged like a ladder. A heated towel rail is sometimes installed in an apartment from the very beginning. As the name implies, it is convenient for drying wet towels or other similar things.
By watching the video, you can learn more about installing and grounding the heated towel rail:
In order for the pipe to heat up, it is connected to hot water, which raises the water temperature to the desired level. Depending on its features, a heated towel rail can be connected to a hot water supply or to a heating system. Its use is very convenient, but if used incorrectly, the device may suffer from corrosion.
Is it possible to secure a heated towel rail?
The advantage of stainless steel heated towel rails is their unlimited service life. Their shine is caused by polishing during manufacturing. Features of heated towel rails:
- they are resistant to mechanical stress, unlike devices made of copper and brass;
- any damage in the form of scratches can be eliminated with mastic and a felt cloth;
- Seamless devices, which are guaranteed for 20 years, can withstand currents.
The heated towel rail is resistant to mechanical stress
However, even such durable devices are subject to electro-corrosion, which can only be determined with the help of professional instruments.
To eliminate stray currents, it is necessary to ensure a reliable metal connection between the riser pipes and the metal end devices. In simple words, the process is called grounding the heated towel rail. All that is required of you is to ground your device to metal pipes. Grounding will get rid of stray currents immediately: potential equalization will occur, and the current will not be able to “leak through.”
When all the pipelines were made of steel, the problem of grounding the batteries never arose. This is explained by the grounding of each pipeline, as an extended element, in two sections of the basement. In addition, previously the bathroom was grounded using separate conductors, which provided an electrical connection to the water supply.
Methods for grounding a heated towel rail
There is actually only one way to ground a heated towel rail: using a grounding wire connected to the grounding circuit in the electrical panel. When using plastic in the installation of a heated towel rail, each metal element of the system is grounded. For this:
- The wire must be stripped and then bent into a loop shape.
- The paint is removed from the pipe, and then the stripped part of the wire is placed against the metal part of the pipe.
- The loop is secured with a metal clamp.
- These loops go around all metal parts of the structure.
- The wire is routed to the electrical panel in the entrance and connected to the ground loop.
There is only one way to ground a heated towel rail. In old houses, where a grounding loop is not provided, you will have to make do with metal pipes so as not to break the loop that equalizes the potentials of metal structures.
Methods of protection against stray currents
To prevent the harmful effects of electrochemical potential, protection methods are used, which may differ depending on the characteristics of the metal structures. Let us consider, as an example, methods for protecting water pipes, heated towel rails and gas pipelines, starting in the order given.
Video about various protections against stray currents
Water pipe protection
For metal structures laid in the ground, in particular water pipes, two protection methods are used: passive and active. We will describe each of them in detail.
Passive protection
This technique involves applying a special insulating layer to the surface of metal structures, forming a protective barrier between the ground and the metal shell. Polymers, various types of epoxy resins, bitumen coating, etc. are used as insulating materials.
An example of a protective coating for a pipe for underground installation
Unfortunately, modern technology does not allow creating a protective barrier that provides complete insulation. Any coating has a certain diffusion permeability, so with this method only partial isolation from the ground is possible. In addition, it should be taken into account that during transportation and installation the protective layer may be damaged. As a result, various insulation defects form on it in the form of microcracks, scratches, dents and through damage.
Since the considered method is not sufficiently effective, it is used as a supplement to active protection, which will be discussed below.
Active protection
This term refers to the control of the mechanisms of electrochemical processes that occur at the points of contact of metal structures with the electrolyte formed in the soil. For this purpose, cathodic polarization is used, in which the negative potential displaces the natural one.
Such protection can be realized using the galvanic method or using a direct current source. In the first case, the effect of a galvanic couple is applied, in which the anode is destroyed (sacrificial anode), while protecting the metal structure, which has a slightly lower potential (see 1 in Fig. 5). The described method is effective for soils with low resistance (no more than 50.0 Ohm*m); at lower conductivity levels, this method is not used.
The use of a direct current source in cathodic protection makes it possible not to depend on soil resistance. As a rule, the source is made on the basis of a converter powered from an alternating current electrical circuit. The design of the source allows you to set the level of protective currents in accordance with the current conditions.
Figure 5. Options for implementing cathodic protection
Designations:
- Use of a sacrificial anode.
- Polarization method.
- Metal structure laid in the ground.
- Laying a sacrificial anode in the ground.
- DC source.
- Connecting a poorly soluble anode to a source.
Protection of heated towel rails
Towel rails and other metal terminal devices on water pipes (faucets) were not threatened by corrosion caused by stray currents until plastic pipes began to be widely used in everyday life. Even if metal pipes are installed in your riser, it is not a fact that the neighbor below them is not plastic, and plastic is probably used for pipes to the bathroom and kitchen.
To ensure protection against emergency current leaks and prevent electrocorrosion, it is necessary to equalize the potentials by grounding the heated towel rail, water pipes in the riser, and the heating battery.
Gas pipeline protection
Protecting underground gas pipelines from stray currents that cause corrosion is carried out in the same way as for water pipes. That is, one of two options for active cathodic protection is used, the operating principle of which was discussed above.
Ground the heated towel rail
For what? How?
The title of the article will surprise many. Does it need to be grounded? For what? There is no direct answer to the question. But we will try to clearly describe the problem and give ways to solve it. Any questions - call
The fact is that so-called “stray currents” lead to electrochemical corrosion of metal parts of the water supply system. Electrocorrosion affects all water supply systems to one degree or another, but at different rates.
And if the heated towel rail is leaking , this is a signal to check the entire system, because... he suffers first.
Modern stainless steel heated towel rails with welded joints are at risk. Like “ladder”, “snake” and the like. If the heated towel rail is leaking, then, as a rule, that’s where it is.
By the way, for this reason, the most reliable heated towel rails are the classic S-shaped ones , because they do not have welded elements. And air jams do not form in them. There is nothing new - everything ingenious is simple, and the beauty of non-standard forms, alas, requires sacrifice.
Why is my heated towel rail leaking?
There are two main reasons why heated towel rails rust and leak :
- The weld seam is the weak link of any metal structure. Welding stainless steel requires high qualifications and strict adherence to technology. Its violation (overheating, poor treatment of the seam after welding, etc.) leads to a violation of the anti-corrosion properties of the metal.
- The quality of stainless steel and its thickness in modern heated towel rails, unfortunately, leave much to be desired.
Some manufacturers of heated towel rails, in order to protect against electrocorrosion, coat the inside of the pipes with polymer coating to prevent direct contact of water with the metal.
Yes, this slightly increases the service life, but does not completely solve the problem. If stray currents are present, they enter the heated heated dryer not only with the water carrier, but also through the connecting nuts of the water supply. Such heated towel rails can also leak. Hot water acts as a catalyst for oxidation and corrosion affects the weld, and then the pressure of the circulating water damages the polymer coating in this place and a leak forms.
It is not without reason that the well-known Russian company that produces heated towel rails with internal polymer coating strongly recommends grounding them under the threat of denial of warranty (in the first case, a leaking heated towel rail will be replaced, but they will strongly recommend grounding it and will warn that the second time they will refuse to replace it due to electrochemical corrosion) .
Sources of stray currents
In most cases, stray currents arise in the ground (as well as in reinforced concrete structures) due to the peculiarities of the organization of urban electrical networks. However, they often occur due to a malfunction or incorrect connection :
- Household appliances that come into direct contact with the water supply (washing machines, dishwashers, water heaters, etc.);
- Electrical wiring in an apartment or communal electrical panel.
Moreover, even plastic pipes do not guarantee the absence of stray currents. On the contrary, the plastic pipes separating the heated towel rail from the main water supply prevent its natural grounding through the default grounded common riser.
The leak may not be in your apartment, but in your neighbors or in common building communications. But this does not make it any easier - due to stray currents, pipelines, heated towel rails and other metal structures rust.
Why haven’t similar difficulties arisen before?
Strange as it may sound, progress has become the reason for the emergence of such a problem as potential difference in engineering systems. Namely, the widespread replacement of metal pipes with plastic ones. As long as the hot water supply, hot water supply and heating pipelines were completely metal, no difficulties arose. And there was no need to separately ground each radiator, faucet or heated towel rail either - all pipes were grounded centrally in the basement of the house, in two places. And all metal appliances in bathrooms and toilets automatically became safe and protected from stray currents.
The transition to plastic changed everything: on the one hand, pipelines began to last longer, and on the other hand, there was a need for additional protection of plumbing equipment. And here it’s not only about the pipes themselves, because in terms of conductivity, metal-plastic is close to traditional metal, but also about the fittings - connecting elements. More precisely, in the materials from which they are made and which cannot provide electrical contact with the aluminum “core” of the metal-plastic pipe.
Video
On the YouTube channel, Vyacheslav Yankevich published several good videos on how to ground a heated towel rail. Below we present two of them.
Electrocorrosion of heated towel rail
In April of this year, for the FIRST TIME IN BELARUS, mass production of “Lesenka” type heated towel rails with protection against electrocorrosion will begin.
Why is this topic so acute and relevant? In fact, consumers often ask questions about how to protect a heated towel rail from electrocorrosion . They are also concerned about topics such as:
- What is “electrocorrosion of a heated towel rail”, “stray currents”, or the more general term “electrochemical corrosion”?
- Why does a stainless steel heated towel rail still leak?
- Why don’t almost any manufacturers provide a guarantee if a heated towel rail leaks due to electrochemical corrosion?
- Is it even possible to protect a heated towel rail from stray currents?
Later in the article we will try to answer these questions in more detail.
Stainless steel heated towel rails
One of the popular materials from which heated towel rails are made is stainless steel, or “stainless steel”. The name suggests that this material does not rust.
The presence of oxygen in our tap water has always been the main cause of corrosion in black or galvanized steel heated towel rails. Indeed, a stainless steel heated towel rail is not subject to this type of corrosion for at least 10 years, provided that high-quality stainless steel, for example AISI 304, is used.
However, one circumstance is an exception - stray currents in the heated towel rail. They are the reason for the question “why is the heated towel rail leaking?” .
Polymer processing - a solution to the problem without grounding
But you can solve the problem in another way by treating the inner surface of a stainless steel water heated towel rail with a special polymer composition. It will create an insulating coating that will “work” effectively, preventing the formation of potential differences and the occurrence of corrosion.
Polymer treatment of water heated towel rails is an additional service that is performed by our company at the buyer’s request. And you can order it online on the ZIGZAG website.
Go to
Passive ways of fighting
Manufacturers of the devices in question are aware of the potential problems and therefore take measures to reduce the risk. One popular option is to use an internal coating in pipes. In this way, the contact between the conductive liquid and the walls is broken, preventing the destruction of the latter.
It must be remembered that passive protection is not completely reliable. Over time, it becomes unusable. It is also impossible to exclude the occurrence of diffusion processes, as a result of which the liquid will gradually begin to seep through the coating.
On the other hand, this protection prevents the deposition of substances contained in tap water on the walls, helping to maintain them in normal condition. However, the coating in question will not be able to protect a person from current if it is large enough.
Grounding as protection against electrocorrosion
To prevent the occurrence of stray currents in the system and protect the heated towel rail from electrochemical corrosion, it is necessary to recreate a stable connection between it and the riser pipe. In other words, you just need to ground the peripheral device by connecting the heated towel rail with a wire to a metal riser, or install a potential equalization system.
It is also important to do this because some unscrupulous residents of apartment buildings, wanting to save money, put bugs on their electricity meters and use pipelines from heating or water supply systems as grounding. And then their neighbors are in real danger, because even simply touching a metal battery will give a person a “chance” of receiving a fatal electric shock.
Methods to prevent electrochemical corrosion in heated towel rails
Heated towel rails are made from various metals, and stainless steel products are considered the most resistant to corrosion.
But even this material cannot withstand the onslaught of electrochemical corrosion: small spots of rust appear on the surface of the pipe, which grow over time and “burn through” the metal, creating through holes under water pressure.
The entire surface of the heated towel rail and fittings suffer, but it all starts from the weakest points - from the welds. As a result, fistulas and leaks appear, and a real threat of emergency situations, including flooding, is created.
If this problem affects a heated towel rail made of high-quality stainless steel, then the reason is the presence of electricity in the water, or, as they also say, “stray currents”.
Electrochemical corrosion has faithful assistants who speed up the process itself significantly:
- Oxygen is a strong oxidizing agent;
- Various chemical impurities present in tap water;
- High temperature (up to 70°C).
So, what measures need to be taken to protect the heated towel rail from electrochemical corrosion?
First way
Arrange for proper grounding of the heated towel rail. Three options are possible, depending on the materials of the riser and pipes.
For safety reasons, other conductive objects should also be grounded - for example, a steel or cast iron bathtub.
What is corrosion
The process of destruction of the top layer of a metal material under the influence of external influences is called corrosion in the broad sense.
The term corrosion in this case is only a characteristic of the fact that a metal surface enters into a chemical reaction and loses its original properties under its influence.
There are 4 main signs by which you can determine that this process exists:
- a process that develops on the surface and eventually penetrates into the metal product;
- the reaction occurs spontaneously because the stability of the thermodynamic balance between the environment and the system of atoms in the alloy or monolith is disrupted;
- chemistry perceives this process not simply as a destruction reaction, but as a reduction and oxidation reaction: when entering into a reaction, some atoms replace others;
- the properties and characteristics of the metal undergo significant changes during such a reaction, or are lost where it occurs.