A microwave works in almost every modern apartment. This convenient household appliance can heat, defrost, and bake. Some models are capable of grilling and executing complex programs to create finished dishes inside. The operating principle of a microwave oven has not changed since its invention. But thanks to technological progress, the safety of the equipment has increased, and the electrical circuit is capable of complex control and precise control of operating parameters.
Microwave design
One of the most important parts that turns a compact chamber into a microwave oven is the magnetron. This is the name given to a vacuum tube capable of reproducing ultra-high-frequency waves. It is microwave waves that heat food. Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 2.45 gigahertz affect water molecules in food, causing them to move faster and increasing friction between them. This heats the food from the inside. The device circuit is closely related to the principle of operation of a microwave oven.
In a microwave oven, one of the largest elements is the metal chamber in which food is placed. The door is equipped with special glass that reflects high-frequency waves. A rotating platform is used to heat food more evenly. It is driven by an electric gear motor.
The microwave oven circuit also includes the following elements:
- ventilation holes;
- frame;
- metal chamber;
- door;
- door latches;
- duct openings;
- glass stand;
- guide roller;
- a heating element;
- clutch;
- control Panel;
- display.
Any microwave oven has door latches blocking holes, because direct exposure to high-frequency waves has a negative effect on any organism.
Microwave radiation is reproduced by a magnetron and enters the chamber through a rectangular waveguide. This causes the device to heat up. For cooling, there is a fan in the case that blows cold air to the magnetron. After heating, it enters the chamber with food. Excess air and water vapor escape through the holes. They are also equipped so as not to emit radiation.
Some models from the line of any leading manufacturer are equipped with a dissector. It is installed inside the camera from above. Although the device looks more like a fan, it is necessary for uniform heating of food. This is achieved through the correct distribution of microwave waves.
Microwave wave distribution schemes
First, it’s worth focusing on the operation of the microwave generation unit. The structure of the magnetron consists of a radiating element and a winding that generates a magnetic field. This lamp, roughly speaking, is constantly wearing out. Everyone has encountered a situation where, as use progresses, the microwave heats up less and less. This is a normal phenomenon; every model sooner or later requires replacement of the magnetron.
Furnaces from different manufacturers (or levels of complexity) may use different microwave wave distribution schemes. In the standard solution used by LG and many other manufacturers, only one waveguide goes from the magnetron to the product area. It is covered with a mica plate to prevent debris and steam from entering.
Important! Models with a single waveguide, which emits a fairly localized stream of waves, use a reflector on the opposite side of the product compartment. This is the concave zone of the wall. It helps distribute microwave radiation more evenly throughout the working volume.
Some Samsung microwaves use a different principle: a main waveguide and several slot antennas are installed. This allows you to evenly distribute the energy flow, forming so-called 3D radiation. In addition, the oven, by varying the power of the magnetron, achieves smooth heating of the products throughout the entire volume.
But the most important thing in generating microwave waves is their parameters. The radiation frequency of the magnetron in the microwave is 2.45 GHz - this is the value that is resonant for water molecules, causing them to vibrate with a large amplitude. The product is heated. Heat from the surface layers gradually spreads throughout the entire volume of the product.
There are some solutions to speed up the heating of food in the oven work area. These are the so-called dissectors. In appearance, such a structural element is similar to a fan on the ceiling of a microwave oven. However, it does another job, namely, it scatters microwave waves.
Other functional elements of the furnace have a completely understandable purpose. For example, a microwave oven with a grill affects food not only with microwave radiation, but also with infrared radiation. It allows you to achieve a beautiful baked crust on your food. Some stove models can be equipped with additional fans to remove heat.
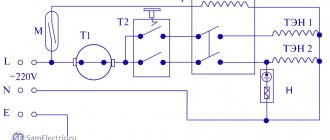
Electrical diagram
Microwave ovens use different electrical circuits, but the general layout is the same. Electronics parts can be divided into control and executive. The first includes the following elements:
- microcontroller;
- control Panel;
- display;
- electromagnetic relays;
- buzzers.
When they are combined, a kind of “brain” of the microwave oven is obtained - the power and control board. A small step-down transformer is used to supply power to the control part. The microcontroller uses transistors to control three electromagnetic relays. Turning them on and off directly controls the operating algorithm of the device.
The magnetron of a microwave oven belongs to the executive part. It also includes a glass stand motor, a cooling fan, a backlight and other elements. One of the most important participants in the circuit is the high-voltage transformer. This is the largest element of a microwave oven, which is capable of receiving a power of 1.5–2 thousand watts. Of these, about 500−850 are the useful part. The magnetron consists of the following parts:
- antenna;
- braid;
- chassis;
- radiator;
- connector
An alternating current with a voltage of 220 volts is supplied to the primary winding of the transformer, and an outgoing voltage of 3.15 volts is supplied to the filament winding of the magnetron. Because of this, electrons are emitted. The current consumed can reach ten amperes.
There is also a secondary winding. Together with a voltage doubling circuit involving a high-voltage capacitor and diode, it produces a current of 4 kW, which powers the magnetron. Its power is small - approximately 0.3 A.
The electrons produced by the filament winding begin to move in a vacuum along a special trajectory. This creates microwave radiation, which comes from the magnetron into the chamber through an antenna and a rectangular waveguide. The camera itself in this simple circuit plays the role of a resonator. Ultra-high frequency waves are reflected many times from the walls, again passing through the food.
In part, the control elements can be called protective mechanisms. For example, thermal switches prevent possible overheating. Normal operating temperature is from 80 to 100 degrees. One of the thermal switches is installed on the magnetron. Two more control the temperature of the air duct and grill.
If one of the sensors detects a critical value, the thermal switch opens the circuit. Electricity stops flowing to the magnetron. This usually happens at 120-145 degrees - this temperature is still safe.
Three switches are built into the right end of the microwave chamber, opposite which the door is located. The main and secondary contacts close when the furnace is closed, and the control contact opens. If at least one switch fails, the fuse will trip and the device will not turn on.
To reduce interference occurring in the electrical network, there is a surge filter.
Troubleshooting a microwave oven
If the microwave oven has a digital display on which an error code appears in the form of the letter E with a number, then you need to find in the oven’s operating instructions what malfunction this code means. Perhaps, by following the instructions, you will not have to deal with serious repairs.
Attention! When repairing a microwave oven, care should be taken. Touching exposed parts of a circuit connected to an electrical outlet may result in electric shock. Do not forget to remove the plug from the socket and discharge the high-voltage capacitor when checking!
Before you start repairing the microwave oven yourself, you need to unplug the plug from the socket, unscrew several screws securing the cover and remove it by sliding it towards the rear wall of the oven.
Next, all parts and assemblies are carefully inspected for the presence of mechanical or thermal damage in the form of darkening. The tightness of the slip-on terminals is checked. If no visual defects are found, then according to the instructions in the table, troubleshooting is carried out.
| Table of common microwave oven malfunctions and ways to eliminate them | |||
| External manifestation of the malfunction | Possible cause of malfunction | Troubleshooting | Repair method |
| The oven does not turn on | The camera door is not closed tightly | Check the door | Close the door tightly |
| The timer handle rotates on the axis | Remove and check the handle for defects | Replace handle | |
| No voltage at the socket | Check for voltage | Connect any working electrical appliance to the outlet, for example, a table lamp | |
| The power cord is faulty | Visually check the plug and cord for mechanical damage, check the integrity of the cord wires with a multimeter | If faulty, replace the cord | |
| The electrical contact is broken at the connection point of the cord terminals in the surge protector | Check that the cord is securely connected to the filter and that there is no blackening or oxides. | If the contact is weak, tighten the union terminal with pliers; if there are oxides, clean the surfaces with sandpaper. If the terminals are damaged, replace them or solder the wires directly to the contact tracks of the printed circuit board | |
| Fuse F1 on the power filter board has blown | Check the fuse with a multimeter. If it breaks, ring with the door open (resistance should be zero) and closed (resistance should be infinity) contacts of the SWC limit switch | If the SWC is faulty, replace it, if it is not possible to remove the terminals from it and insulate it. Install a new F1 at the same current or repair it. If the new fuse blows, then you need to look for a short circuit in other components of the circuit | |
| Limit switch SWA or SWB faulty | Test the switches with a multimeter. When the door is open, the resistance should be equal to infinity, and when closed - zero) | If the switch malfunctions, replace it; if it is not possible, if only one of the two is faulty, remove the terminals from it and connect them together | |
| Mechanical damage to the movable bar with hooks on the door | Carry out an external inspection of the plank for damage. | Replace or repair depending on damage | |
| Mechanical timer or control unit is faulty | In a mechanical timer, you need to ring the contacts and check the operation of the motor. The electronic unit cannot be repaired independently | Clean the contacts or replace the faulty unit | |
| The display lights up, nothing happens when you press the buttons | The control unit is faulty or the contact pads of the buttons in the touch panel are dirty | Remove the control unit and wash the button contacts with alcohol | If this does not help, replace the control unit |
| The display lights up, the modes are set, but nothing happens when you press Start. | The Start button in the control unit does not work | Clean the touchpad contacts and buttons with alcohol. | In case of malfunction, replace the control unit |
| The switching relay in the control unit is faulty | Ring the relay coil and check the contacts | In case of malfunction, replace the relay | |
| When you press the Start button, the food does not heat up , but the fan and plate rotate, and the chamber lighting turns on | The high-voltage fuse is blown, the power transformer, high-voltage capacitor, diode or magnetron is faulty | Check the fuse, power transformer, high-voltage capacitor, diode and magnetron with a multimeter | Replace the faulty part |
| In modern stoves, the inverter or magnetron has burned out | Identify the faulty unit by replacing it | Replace the inverter or magnetron | |
| Microwave doesn't heat well | The FM fan does not work, the magnetron overheats and the protective thermal relay trips | Check the ease of rotation of the fan impeller with your hand and check the integrity of its windings with a multimeter | Lubricate the fan shaft with machine oil; if the winding breaks, replace the fan |
| Low line voltage or loss of magnetron emission | Measure network voltage | If the voltage is normal, replace the magnetron | |
| The oven does not turn off after the timer runs out | Timer is faulty | Check the timer gear mechanism | Replace timer |
| The food plate does not rotate | The plastic coupling is worn out | Remove the plate and inspect the coupling for damage | If defects are found, replace the coupling |
| The plate rotation motor is faulty or its power supply circuit is broken | Check by hand the free rotation of the shaft and ring the winding | If the rotation is tight, lubricate the shaft bearing; if the winding breaks, replace the motor | |
| Dirt has accumulated under the plate | Remove the plate and inspect | Remove dirt | |
| When heating food, a cracking sound is heard from the chamber and light discharges are observed | The mica plate insulating the magnetron waveguide burned out | Inspect the mica plate for defects (darkened area, hole). The plate is located on the right side of the stove chamber | If defects are found, replace the plate. The mica plate serves to protect electronics from food vapors. If there is no replacement, then you can temporarily reheat food without it |
| The camera stopped lighting | Burnt out light bulb | Check the light bulb and the reliability of fixation of the slip-on terminals on the socket terminals | Replace the light bulb or tighten the terminals with pliers |
Checking the contacts of wires and other parts is standard and does not cause difficulties. Checking the magnetron, high-voltage capacitor and diode has some features.
Checking the high voltage diode (pillar)
The design of a high-voltage pole consists of several low-voltage diodes connected in series, so it is not always possible to test them with a multimeter. The voltage drop on one simple diode is about 0.8 V, and when several are connected in series, the voltage drop is the sum of the drops on each in the chain and the multimeter voltage is not enough.
Therefore, to reliably check a high-voltage column, you need to connect an incandescent lamp of any power in series with it, as shown in the diagram. Using a cord with a plug, apply 220 V mains voltage from the outlet to the chain. The polarity of the diode connection does not matter.
If the lamp flickers and shines at full intensity, then the diode is working. If it is at full heat or does not light up, then the diode is broken or broken and, therefore, faulty.
Checking the high voltage capacitor
To check, you need to disconnect the capacitor from the microwave oven circuit and test them with a multimeter. Before checking, be sure to discharge it, so as not to damage the device, by shorting its terminals with a piece of wire with stripped ends.
Often a high-resistance resistor of 1-10 MOhm is installed inside the capacitor to discharge the capacitor. Therefore, the resistance when checking should be more than 1 MOhm. If less than or equal to zero, then the capacitor is faulty.
You can check the capacitor without a device and in a more reliable way, described above for a high-voltage diode. Instead of a diode, a capacitor is switched on. The power of the incandescent light bulb is selected from 60-150 W.
If the capacitor is working properly, depending on the power of the lamp, its brightness will be lower than usual. The more powerful the lamp, the lower the brightness of its glow will be. The capacitor in this circuit acts as a current limiter. If the brightness of the lamp does not decrease or the lamp does not light up, it means that the capacitor is broken or broken.
Checking the magnetron and thermal fuse
Testing a magnetron is no more difficult than testing a diode or capacitor. First, the resistance of the filament is measured with a multimeter, the value of which should be 3-10 ohms.
The resistance between the anode and cathode of the magnetron is then measured. To do this, just touch the ohmmeter probes between any filament terminal (cathode) and the magnetron housing (anode). Resistance must be endless.
If the resistance of the filament is infinity, or zero between the anode and cathode, then the magnetron is faulty and must be replaced.
The resistance of the thermal fuse must be zero; if it is greater, then it is faulty and must also be replaced, since it cannot be repaired.
If you don’t have an ohmmeter, you can check the magnetron, like the diode, using a light bulb. When you turn on the magnetron filament instead of the diode, the light bulb should glow at full intensity, the anode and cathode should not glow. Thermal fuse - lights up.
Additional items
There are several complementary parts to a microwave. Often, a microwave oven is equipped with a grill in the form of heating arcs or infrared quartz lamps. A convector works in tandem with it. These elements are quite reliable and break down in exceptional cases.
An infrared heater is usually made in the form of two quartz lamps connected in series. With a power of 500-600 watts, they consume a current of 115 volts. Unlike the microwave heating option, the grill does this from the top layers to the inside. Although this takes more time, otherwise you won’t be able to fry the crust.
A convector is necessary for proper air circulation. This helps the food heat evenly.
What types of microwave ovens are there?
Before you dive into the device, you need to determine which microwave ovens are currently on the market. The functionality of such equipment has expanded significantly; now it is not just an oven for heating food, but also a steamer, grill, and programs for automatically cooking food. Some models can even replace an oven, because they are not inferior to it in heating power.
The first microwave oven was invented back in 1947; it was huge, human-sized. Of course, it was not used for homes, only for industrial enterprises and hospitals. The main problem was its overheating, especially at high frequencies of microwave oscillations, and after some time a water cooling system was invented for it. Further, the installation became smaller and smaller, acquiring a more compact appearance. The demand was small, but even then the manufacturers knew that in the future this equipment would find its place in the kitchens of millions of housewives.
In 1966, the microwave was already compact, but the food was heated unevenly, so a special turntable was invented that helped correct this unpleasant feature of the equipment. Nowadays, installations have been invented that do not require such an addition, but previously this invention was considered a breakthrough.
Nowadays there are enough kitchen appliances to choose your own model and buy a good option even at a low price. Therefore, manufacturers are constantly trying to modernize it in order to make it more in demand in the household market, and to sell out as much product as possible.
The operating principle of a microwave oven may also differ. Of course, in each technique, heating is carried out using microwave radiation, but additional details make its functionality more diverse.
Types of microwave ovens.
| Microwave | Functional | Power | |
| Solo | Reheating food Cooking simple meals Defrosting | 800 W | |
| With grill | With heating element | Uniform heating of food thanks to a movable heating tube. | 900–1500 W |
| Quartz | Cooking with the "Open Fire" effect | ||
| Solo with convection | Oven cooking effect | 800–900 W | |
| Grill with convection | |||
These are the standard models currently available on the market. But in order to choose the ideal option for yourself, you need to familiarize yourself with other components that affect the type of equipment. They can be small in size of the chamber, which will reduce energy consumption, but will significantly reduce the capabilities of the oven. Up to 19 liters will be enough to warm up food and put food on defrost. But in such models there will be neither grill nor convection, because the design does not allow additional parts to be placed in it.
The most popular are the medium models - 20-25 liters. This is a good option for the whole family; the functionality can be significantly expanded with additional modes. If desired, you can replace the oven with a microwave oven if it is large - 26-32 liters. Owners of restaurants and industrial kitchens have larger equipment, but there is no need to buy it for their home.
The type of control in microwave ovens is also very diverse:
- mechanical;
- sensory;
- button;
- mixed.
The touch type will be the most accurate and convenient, but models with other controls are much cheaper, so this is not a necessary condition for the normal operation of the equipment. In addition, mechanical control is considered the most durable and reliable. The lever does not wear out over time and can be easily replaced. Mixed types are used in ovens with wide functionality for more precise control.
Microwave with grill
This is a microwave oven that has an additional heating element added to brown food. This can be a tubular electric heater or a quartz lamp, depending on the model. Most often this is a wavy curved tube, which is located on the top inner panel. This microwave oven ensures uniform heating of food and baking on top, so the food turns out golden brown but juicy. The only drawback of such models is their high power consumption.
Despite the fact that the heating element of a quartz microwave grill is a glass tube, this system allows you to get a smoky dish, as if it had been cooked over an open fire. The lamp can be installed both at the top and in the side and bottom panels; it is not energy-consuming, but the cost of such devices is high.
Convection microwave oven
The operating principle of a microwave oven with a fan is the distribution of heat with air movement. In them you can not only heat and defrost food, but also fully cook it, using the oven as an oven. Thanks to the air flow, the high temperature does not rise, but circulates, enveloping the food, which speeds up the cooking process.
This system does not affect microwave waves in a microwave oven, only warm air, so it does not change their direction. It can already be used for meat, casseroles, and roasting vegetables. It is better not to cook dough products in it, because the specific heating in this technique still differs from a standard oven.
Microwave with inverter
The main difference between this model and a regular household microwave is the absence of a transformer. It is replaced with an electronic control unit. Its dimensions are somewhat smaller, so devices with the same chamber volume will still differ from each other. The operating principle will also be slightly different. Of course, it is based on the generation of waves in a microwave by a magnetron, but its propagation and regulation are different.
Inverter mode allows you to regulate power rather than select a separate temperature range. A standard microwave oven cannot do this. As a result of this process, the structure of the food is less damaged and it does not dry out due to excessive microwave radiation.
Because of this change, food cooked in an inverter oven will taste slightly better, as the manufacturer of this device explains. But the price of such equipment is much higher, so when choosing budget models, you will not be able to try its functionality.
With even microwave distribution
This is another new model that is actively advertised in the household microwave market. Its advantage is the location of the magnetron. If in standard models it is located on the side, here it has been moved down so that the microwaves distribute throughout the chamber more evenly. There is a rotating wave splitter located above the magnetron, but it is not visible when examining the camera. This design does away with the standard turntable that was previously found in every microwave oven.
Mini microwaves
These are solo models that cannot have a grill or convector due to their small dimensions. Of course, its performance depends on the frequency at which the equipment operates, but it cannot boast of a large selection of cooking modes. Most often, they do not have rich functionality and are only suitable for heating food.
Their main advantage is their compactness, thanks to which the equipment does not take up much space in the kitchen. The principle of operation is no different; it is entirely based on the operation of a microwave emitter. The efficiency of a microwave oven with small dimensions is much lower, because it uses a less powerful magnetron.
Special parts
There are special elements in the magnetron power circuit, the properties of which must be taken into account when making independent repairs. This primarily concerns the high-voltage capacitor. It has a built-in resistor necessary for the discharge. The capacitor is under voltage up to 2 kV during operation. However, after finishing work, it may not discharge. This will happen if the internal resistor has burned out. Therefore, there is an important safety measure: before starting repairs on the microwave oven, the capacitor must be forcibly discharged.
A large high-voltage diode consists of many small ones. Thanks to their series connection, the combined element can operate with high voltage. However, this excludes the possibility of testing the diode using the standard method, because the device has high resistance both when connected directly and in reverse.
For many diodes, the highest possible forward voltage is 11 volts, achieved by connecting a dozen smaller parts in series. With this combination, the maximum constant reverse voltage reaches 12 kilovolts.
Bidirectional high-voltage suppressor - a protective diode installed in parallel with the high-voltage capacitor. It is necessary for protection against overvoltage, but often fails. However, the microwave will work even without it - during repairs, the protective diode can simply be removed. If possible, it is better to replace it with a new one - this way the high-voltage capacitor will last longer.
It is better to look for a detailed diagram of a microwave oven from a specific manufacturer in the original instructions. You can find it on the manufacturer's website. The manual should contain recommendations for checking elements, a list of incoming parts, diagrams and disassembly procedures.
Power Features of Low Voltage Turntable Motor
If the microwave oven uses a turntable motor designed for an operating voltage of 220V, then there are no special problems with powering such a motor. Traditionally, it is connected in parallel to the fan motor winding and both motors are simultaneously supplied with mains voltage through the corresponding relay on the control panel.
But what to do if the manufacturer, in a specific oven model, decided to use a low-voltage motor designed, say, 30V? Where to get or how to generate such voltage in the furnace circuit, in which the mains voltage of 220V predominates everywhere? You can, of course, build for this purpose a separate power source that lowers the mains voltage to the required value, but this will complicate the design of the furnace and thereby make it more expensive. Manufacturers have solved this problem by upgrading the fan motor windings. They simply tapped from the middle of the winding and added a third lead. Thus, the winding of the fan motor began to perform two functions: the first is the function of the motor winding and the second is the function of the autotransformer, through which the turntable motor is powered. An autotransformer is a kind of voltage divider. If we make a tap exactly from the middle of the winding powered by a voltage of 220V, then relative to the lower terminal we will remove exactly half of the supply voltage, i.e. 110V. By going down the turns closer to the lower terminal of the winding, you can get any voltage in the range from 220V. to 0V. Figure 2 shows a circuit diagram for switching on a low-voltage turntable motor. One of the terminals of its winding is connected to the lower terminal of the fan motor winding according to the diagram, and the second is connected to the tap - its middle terminal, from which a voltage of 30V is removed relative to the lower one.
In my opinion, there are no particular advantages in using a low-voltage motor in the design of a turntable over using a conventional motor (220V). Yes, on the one hand, the winding of a low-voltage motor is wound with a wire of a larger cross-section than the winding of a 220V motor. Accordingly, such a winding is less susceptible to current overloads that occur when the rotary table is loaded. Such an engine is more reliable and will fail less often. But on the other hand, a low-voltage motor creates additional load on the fan motor winding, which reduces its reliability.
When replacing a faulty fan motor with an auxiliary lead, be very careful. In practice, the middle winding terminal is located not in the middle of the terminal block, but on the right (Figure 3). The middle terminal terminal is shaped differently from the power terminals - it is somewhat narrower, which eliminates confusion with the connectors when replacing the motor.
But the main power terminals are the same in shape, and if, when replacing the motor, you accidentally swap the connectors on the terminals, then instead of the required 30 volts, 220 - 30 = 190V will be supplied to the turntable motor. In this case, both the turntable motor and the fan motor will fail. Once again, be careful! Before replacing the motor, remember, write down or photograph the location of the connectors on the motor winding terminals.
If, for whatever reason, you are confused by these three conclusions, do not be discouraged. The problem is solvable. Connect one of the three connectors, the one that is narrower (different in shape from the others), to the corresponding terminal. It remains to deal with the remaining two. Connect them to the winding terminals in any order. Then, to gain access to the turntable motor, open the access window in the bottom of the furnace, as shown in Figure 5, in the article “Turntable Motor.” Remove the power connectors from the motor terminals and use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance between the connector wires going into the oven. If you guessed the location of the connectors on the terminals of the fan motor winding, then the ohmmeter will show approximately 50 Ohms. If you didn’t guess right, the readings will be higher, approximately 240 Ohms. In this case, you should swap the connectors on the fan motor. Then measure the resistance again and if the ohmmeter reading corresponds to 50 Ohms (approximately), then everything is in order, everything should work.
Source
Safety regulations
When using and repairing any household appliances, you must follow safety rules. Violating them can not only damage the device, but also harm human health or life.
Using a microwave oven correctly is easy:
- If the door is open, the oven cannot be turned on. This may occur if the waveguide or door locking system is damaged.
- You cannot connect a removed magnetron, it is dangerous to life.
- Do not operate the oven with a broken fan, otherwise it will lead to damage to the magnetron.
- Any actions with microwave parts are permissible only after disconnecting from the network and completely forcibly discharging the high-voltage capacitor.
- When the repair is completed, all objects must be removed from the waveguide, regardless of their size.
- Do not turn on the oven without load. If you need to run it in idle mode, then you must supply some food. It can be replaced with a container of water.
When disassembling, you should take photographs of each step. If problems arise with assembly, you can use the existing photographs. It is advisable to capture the original position and fastening of all parts using mobile phones or digital cameras.
Repair features
One of the most common malfunctions is due to the fact that the microwave does not respond in any way to opening the door and operating the equation panel. It happens no less often that the oven does not heat, although it shows signs of operability: the lights are on, the glass table is rotating.
If there is no response to launch
First you need to check whether current is flowing to the surge protector. To do this, the casing is removed, and the high-voltage capacitor is forcibly discharged. Check the power cord with a multimeter. All wires running from the socket to the terminals must be connected. The grounding terminal must be connected to the housing.
If the wire is intact, then you need to check the condition of the mains fuse. It can be found on the filter board. In case of malfunction, you will have to install the same one. It is important to take into account that a more serious malfunction caused the fuse to burn out - it would not be superfluous to inspect the microwave.
When performing a visual inspection, it is better to use a flashlight and a magnifying glass. The following factors indicate a problem:
- breakdowns and abnormal holes in elements;
- darkening similar to burning;
- swollen capacitors or deformation of other elements.
The sense of smell will help diagnose the problem. The smells of burnt insulation, failed printed circuit boards or transformer oil are quite strong and therefore easy to detect. If you understand where the smell is coming from, you can localize the problem.
Light without heating
Often this situation is caused by faults with the high-voltage circuit or magnetron. But before checking these components, you need to inspect the camera. You need to make sure that there are no burnt holes, dirt or worn out enamel anywhere. The rectangular plate of radiotransparent dielectric located on the left must be removed and examined especially carefully. To do this, you will have to wash it with alcohol.
If there are through holes or dark spots on the plate, it will have to be replaced. Most likely, this happened due to the fact that metal utensils were placed inside the oven or they forgot about timely cleaning.
You need to check the safety diode in the magnetron circuit. If it burns out, then just install a new one. The part must have original parameters.
A burnt-out antenna cap indicates the need to replace the magnetron. The same applies to breakdowns in the housing. If the microwave oven has been in service for more than five years, then repair may not be advisable - it is more economical to buy new equipment.
Typical problems
Let's look at typical breakdowns of Samsung microwave ovens:
- Sparking. A similar phenomenon can occur if the magnetron cap is damaged or if the enamel on the door is damaged. Continued operation of the device is dangerous and requires immediate repair.
- Not warm. If a Samsung device does not heat up, there may be several reasons. The magnetron may have broken. Voltage surges may also be the cause. But still, most often the problem lies in a blown fuse that powers the relay or the primary transformer winding.
- Increased heating time. This is not yet a problem, but it is a harbinger of one, which indicates the need to probably replace the magnetron soon.
- The device does not turn on. First, the cable is checked: either it is not connected to the network or it is damaged. It is possible that the door switches are faulty, causing the device to be blocked by the security system. The temperature sensor may also fail.
- The tray does not rotate. Most likely the problem is in the engine.
- Strong hum. The cause may be the operation of a fan or transformer.
- If control problems occur, the problem may be with the electronic board.