A microwave transformer is an important link in the chain that generates microwave radiation. This is a converter of the mains voltage to the value supplied to the magnetron input. A high-voltage converter often causes a microwave oven to break down.
Checking the transformer for operability is a mandatory item in the list of technical diagnostic measures to determine the causes of the malfunction. Since we are talking about high voltages, independent intervention is only possible if all safety measures are observed.
Where can I get high voltage?
Food in microwave ovens is heated by the operation of ultra-high-frequency waves. Microwaves are generated by a special emitter - a magnetron. To operate within the specified characteristics, it needs a high voltage - 2,000 V. This is almost an order of magnitude higher than what a household electrical network provides (220 V).
Where do kilovolts come from? They are created at the output of the secondary winding of the high-voltage converter.
Important! A microwave oven, even disconnected from the power supply, can cause an electric shock (U up to 5,000 V).
Types of high voltage converters
Elements of the converter installed in the microwave oven:
- magnetic circuit;
- frame;
- primary winding;
- two secondary windings.
U = 220 V is supplied to the primary winding. The incandescent filament is powered from the secondary windings. The first of the two secondary windings is made of heavy gauge wire. U at the output is approximately 3 V. At the output of the second winding - variable high U = 4 kV.
Microwave ovens of different brands use converting devices from different manufacturers. The converters do not look the same and have different characteristics. They differ:
- power;
- output voltage of secondary windings;
- the number of turns in the coils and the cross-section of the wire;
- dimensions;
- method of fastening.
The secondary coil, like one of the emitter terminals, is connected to the housing.
Electrical circuit diagram
In addition to the converter, the electrical circuit of the microwave oven contains:
- diode;
- high voltage capacitor;
- magnetron;
- fuse;
- electric motor - one or two (for rotating the tray, if provided for in the design, and for the fan);
- Control block.
In expensive microwave ovens, instead of a converter, a pulse unit is used, which has a more complex structure, but weighs less.
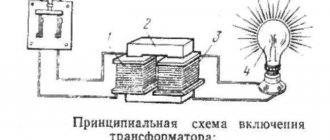
Transformer in an electrical circuit
The simplest circuit involving a high-voltage transformer contains:
- magnetron;
- diode;
- network filter;
- high voltage capacitor;
- door lock switches;
- fuse;
- electric motors for ventilation and rotation of the pallet;
- control module;
- lamp for illumination.
Starting the oven, which is only possible with the door closed, involves moving the tray and cooling the magnetron fan. If the lamp temperature reaches more than 105°C, the thermostat will operate, which will cut off the voltage supply to the primary winding of the transformer.
In expensive models, the circuits are additionally equipped with program-controlled units, LCD displays, dissectors, grills and steamers. And the high-voltage transformer is replaced with a complex pulse unit, which lightens the weight of the entire structure.
What types of malfunctions occur?
You need to check the transformer in two cases: when the stove is not working well and when it is not working at all. You can suspect a malfunction of this particular element based on the following signs:
- The microwave oven makes an unusually loud noise;
- food placed in the chamber is not heated or only slightly heated;
- When working, it smells like burnt insulation and the equipment smokes.
If at least one of the listed symptoms appears, it is better not to turn on the device until the problem is resolved. Turning on a faulty stove can worsen the breakdown.
One of the most common causes of electrical equipment failure is power surges. If there is a suspicion that the device is faulty due to changes in the network, urgent repairs are necessary. However, it is possible that during repair work a manufacturing defect will be discovered.
Electrodes
Installation of electrodes
When choosing electrodes, you need to pay attention to the diameter, which must correspond to the diameter of the wire, because the electrodes will be connected to this wire. To do this, you can use copper rods. If you are creating a low-power device, you can use soldering iron tips.
During operation, the electrodes wear out greatly. Therefore, they need to be sharpened regularly. Of course, over time they will need to be replaced.
So, the wire must be connected to the electrode; this is done using a copper tip. The tip is connected by soldering.
The combination of the tip and the electrode is carried out using a bolted connection. This connection must be reliable, because if the resistance in the area of unreliable contact increases, the device will lose its power. To avoid this problem, it is necessary to make a hole in the electrode and tip. These holes must have the same diameter.
It is better to choose copper bolts because they have minimal electrical resistance.
Causes of malfunctions
The converter fails most often due to:
- Wire break. The wire of one of the windings may break.
- Short circuit in the windings. This can happen in one coil or both.
- A break or short circuit in the magnetron coil.
The magnetic core of the converter is assembled from steel plates. If the plates peel off, the machine will make noise. It is necessary to find out the power of the transformer and replace it. Such global breakdowns can be easily identified by eye, but they do not happen often. The overwhelming majority of problems are still caused by coils.
Possible transformer malfunctions and their symptoms
Checking the microwave transformer should be done when this household appliance is not functioning well, or when it is not functioning at all. Signs of a malfunction of the transforming device are:
- a fairly strong hum (noise) begins to emanate from the equipment after switching on;
- dishes placed on the platform are not heated at all or only slightly heated;
- During operation there is a smell of burnt insulation.
If such signs appear, it is better not to use the device until it is repaired. In the latter case, it must be disconnected from the network immediately to avoid even greater damage.
It must be remembered that breakdowns with electrical appliances occur during power surges. If this happened, then if the slightest hint of a malfunction appears, repairs should be started, during which a manufacturing defect may also be discovered.
The above manifestations in most cases are caused by a number of reasons:
- a break in the wire of the primary or secondary (boost) windings, in both at the same time (a rare case);
- a short circuit between the turns in one of them, or in two at once;
- a break or short circuit in the winding of the magnetron filament circuit.
Check procedure
To check the serviceability of the high-voltage converter, you need to arm yourself with a multimeter; you will also need:
- screwdrivers with different tips;
- pliers;
- ohmmeter
Sequencing:
- turn off the device - remove the plug from the socket;
- unscrew the screws and remove the casing;
- discharge the capacitor;
- remove the terminals from the transformer;
- check the coils with a tester - if there are no deviations, put them back;
- if damage is detected - the wire has broken or a short circuit has occurred, replace the device;
- assemble the oven and check its operation.
If the device still does not work after taking measures, you should continue troubleshooting or check the device under voltage.
A transformer with traces of melted insulation and a burning smell does not need further inspection: it is broken and cannot be repaired.
Important! To check the transformer, you have to disassemble the microwave oven - this can only be done when it is disconnected from the power supply.
A high-voltage capacitor easily retains a huge electrical charge, so it must be discharged before measurements. How to achieve this? Simply close its contacts to each other - this can be done, for example, with pliers.
Checking explosives. microwave oven transformer
If the microwave oven makes a loud noise, emits a sweetish smell of burnt windings, and does not heat. All these signs indicate that the high-voltage (step-up) transformer may be faulty. In this case, it is necessary to check it and, if necessary, repair the microwave.
In this article we will diagnose the high-voltage transformer of a microwave oven and also consider the reasons for the failure of this component.
Attention! A microwave oven can give you an electric shock (voltage up to 5 kilovolts) even if it is unplugged
We strongly recommend that you seek help from specialists if you are not confident in your knowledge regarding safety precautions when working with electrical appliances.
Transformers in microwave ovens may differ in: mounting configuration to the chassis, size, power, class, output voltage and winding resistance.
Failure of this component can be caused by voltage surges in the 220V network, heavy load, short circuit of the magnetron pass-through capacitor, or manufacturing defects.
So let's get started.
We take a microwave oven with a suspected transformer malfunction (the oven makes a loud noise, smokes, and does not heat food).
Unscrew the screws and remove the casing.
We detect a high-voltage transformer.
It is important to remember that a high-voltage capacitor in a microwave oven can hold about 4000 Volts for several minutes, and if the 10 MΩ resistor in it is broken (which serves for discharging), then a dangerous charge can remain for quite a long time. Therefore, before starting the test, it is advisable to discharge the capacitor, for example, with a screwdriver on the housing or by closing the contacts together with pliers.
We got to the transformer, we will check it, for this we will need a multimeter and pliers.
So, let's check the primary winding. Carefully remove the terminals from the terminals of the primary winding of the transformer.
We set the measurement limit on the multimeter to 200 Ohms.
We make measurements. The winding resistance usually varies from 2 Ohms to 4.5 Ohms (depending on the class of the transformer and the cross-section of the winding wire). If less than two or more than four and a half ohms, most likely the problem is in the primary winding. Also, when taking measurements, do not forget about the error of the multimeter. In order to find out the error, close the multimeter probes for a few seconds at a limit of 200 Ohms.
In our case, everything is in order with the primary winding.
We move on to the next phase of measurements. We measure the secondary winding, the device limit is 2 kOhm
We remove the terminals from one terminal of the secondary winding, the second terminal is the transformer housing (since the housing is bolted to the microwave chassis, you can call the oven housing). The resistance of the secondary winding can vary from 140 Ohms to 350 Ohms (again, as mentioned earlier, it depends on the class and cross-section of the winding) if the readings exceed 350 Ohms or less than 140 Ohms, this indicates that there is most likely an interturn short circuit of the secondary winding.
Now let's check the filament winding, the measurement limit is 200 Ohms. We disconnect the terminals from the magnetron and measure the terminals with the device. The resistance of the filament winding ranges from 3.5 to 8 Ohms.
It happens that the device shows the resistance of all windings within normal limits, but the transformer still does not work well, this happens when the winding is only slightly burnt and only shows itself under load, in this case it is best to throw in a known-good high-voltage transformer.
Diagnostic options
Let's look at common options for finding the causes of a breakdown.
Secure Checkout
The safest test is carried out by a tester and involves examining the coils for damage. Procedure:
- The multimeter is adjusted to the required limits and with its help the resistance of all windings is determined - the primary and two secondary ones. The study is carried out on a removed transformer.
- If the tester displays one, it means a break has occurred.
- When the circuit is closed, a value in the range of 2–4.5 Ohms will appear on the primary coil (the tester is set to 200 Ohms). On the filament - 3.5–8 Ohms, on the high-voltage secondary (2,000 Ohms) - 140–350 Ohms.
If the resistance value is outside the specified ranges, an inter-turn short circuit has probably occurred.
When taking measurements, it is necessary to take into account the multimeter’s own error. It can be determined by short-circuiting the probes within the set limit. The resulting value is the error.
You can perform a secure check yourself or invite a specialist from the service. To ring the windings, the user only needs to know the basics of electrical engineering and have the skills to work with a tester.
Test under voltage
If measurements have been taken, the measurements obtained are normal, but the stove still does not work, it is necessary to examine a number of characteristics. Measuring the output voltage on the secondary windings is a rather dangerous business. Procedure:
- 220 V is supplied to the microwave.
- The tester measures U at the outputs of both secondary windings. High voltage - 2 kV, filament - 3 V.
This method requires equipment that can measure AC voltages greater than 2 kV.
Reverse check
This option is less problematic. 220 V is supplied to the secondary winding, about 24 V is removed from the primary winding. The coefficient is 9.1. If 12 V is applied to the primary winding, the secondary will be about 109 V.
If the transformer heats up when idling, an interturn short circuit has probably occurred. If the device heats up under load, and when it is turned off, it stops heating, you should continue to look for the problem.
High voltage microwave transformer.
A high-voltage transformer provides power to the microwave magnetron. If the step-up transformer malfunctions, power is not supplied to the high-voltage part of the device, the microwave oven stops generating microwaves and, accordingly, heating food.
What are the signs of a faulty transformer:
- The microwave hums and vibrates during operation
- There is a pungent smell of burning or smoke
- The microwave works, but does not heat
Causes of transformer failure
- Interturn short circuit of windings
- Burnt contact on the connector
- Broken contact at the junction of the terminal with the winding
Interturn closure.
The most common cause of transformer failure is an interturn short circuit, resulting from insulation failure due to overheating. Visual signs of an interturn short circuit of a transformer are severe darkening of the high-voltage winding of the transformer and traces of carbon deposits.
The operation of the microwave is accompanied by a loud hum and a burning smell, while the transformer winding gets very hot.
Visible signs of a faulty transformer
Burnt transformer winding
Burnt out transformer
To prevent such malfunctions, it is recommended not to overheat the microwave; after long-term operation, let it “rest” for about 15-20 minutes. so she can cool down.
Burnt contact on the connector.
A common cause of a faulty transformer is a lack of contact at the junction of the terminals and connectors of the transformer. This happens as a result of poor crimping of the connectors. The place of bad contact begins to spark, the contact surface of the connector gets very hot and burns out, and eventually the contact disappears altogether. The consequences of poor crimping of connectors are shown in the photo.
A break at the junction of the terminals and the winding.
If there is no visible damage to the transformer, but the transformer does not work, there may have been a loss of contact at the junction of the winding with one of the terminals. This happens quite rarely, mainly due to poor quality factory soldering.
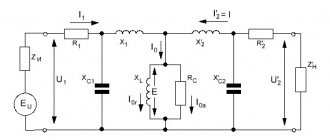
Microwave transformer circuit
The microwave power transformer has a primary winding of 220 Volts and two secondary windings, one of which increases from 220 Volts to
2000 Volts required to power the high-voltage magnetron circuit, the second step-down from 220 V to
3.1 V, the so-called “heat winding”, is necessary to power the magnetron anode.
Diagram of the high-voltage part of the microwave
How to test a high voltage transformer with a multimeter
The presence of contact can be checked with an ohmmeter. To check the connection, it is necessary to “ring” the resistance of its primary and secondary and filament windings. Before taking measurements, you need to disconnect all terminals from the transformer.
Primary winding test: 2 to 4 ohms. At the same time, the terminals of the primary winding should not “ring” to the transformer body. If there is a breakdown of the primary winding on the housing, the transformer is faulty.
Checking the secondary winding: from 120 to 200 Ohms. One of the terminals of the secondary winding is fixed to the transformer body, so when “testing” the secondary winding, we touch the metal body of the transformer with one of the tester probes, and the terminals of the secondary winding with the other.
Checking the filament winding: from 0.1 to 1 Ohm. If the filament winding is in good working order, there should be no breakage.
Microwave transformer winding resistance
| Circuit being measured | Resistance |
| Primary winding | from 2 to 4 ohms |
| Secondary winding | from 120 to 200 Ohm |
| Filament winding | from 0.1 to 1 Ohm |
Replacing a microwave transformer
To replace a faulty high-voltage transformer, you need to select a similar part. Microwave transformers have a general operating principle, but they differ in class (see markings 200, 220, 250 class), power and location of mounting fixtures. The power of the transformer must be matched to the power of the connected magnetron.
If the power of the new transformer is less (100-200 watts), then the oven will be slightly underheated; it is necessary to increase the heating time. If the power is greater, nothing bad will happen, the power reserve will increase slightly and, accordingly, the life of the transformer will increase.
1″ :pagination=pagination :callback=loadData :options=paginationOptions>
Which microwave ovens have problems?
Most often, problems with the converter occur in microwave ovens of the Samsung, Daewoo brands.
Considering the eminence of the brands, it is difficult to assume that they all neglect the quality of the electrical circuit components used. Most likely, this trend is associated with the popularity of these brands. They are bought more often, which is why the breakdown statistics are higher. But when calculating the number of breakdowns per number of units sold, it becomes obvious that they break down no more often than other well-known brands.
Precautionary measures
When carrying out measurements under voltage, electric shock, even death, can occur. Two rules will help you avoid danger:
- It is strictly forbidden to touch the internal parts of the microwave oven while it is operating. To carry out measurements, you need to put crocodile probes on the tester’s terminals and connect them to sections of the circuit.
- If you need to touch high-voltage parts with your hands, you should not only disconnect the stove from the power supply: you can prevent electric shock by shorting the magnetron leads to the housing. Thanks to this precaution you will protect yourself from capacitor discharge. There is a resistor in the microwave electrical circuit to discharge the capacitor, but it does not eliminate the danger 100%. The resistor may burn out or they completely forgot to install it, and such a mistake could cost the life of a do-it-yourselfer.
Repairing any electrical equipment involves the risk of electric shock. When testing a transformer in a microwave, you need to be extra careful due to the high voltage and capacitor. Use safe measurement methods and follow safety regulations.
How does a magnetron work?
A magnetron is a vacuum tube that performs the functions of a diode and consists of several main parts:
- a cylindrical copper anode, which is divided into ten parts;
- in the center there is a cathode in which a filament is built in, and its main function is to create a flow of electrons;
- at the ends there are ring magnets necessary to create a magnetic field, which provides microwave radiation;
- a wire loop connected to the cathode, which is removed from the magnetron using a special emitting antenna and directed along a waveguide into the chamber; its main function is to collect radiation.
During operation, the magnetron heats up greatly, and therefore the case of this device is initially equipped with a special plate radiator and a blown fan. To protect this element from overheating, the power circuit has a thermal fuse.