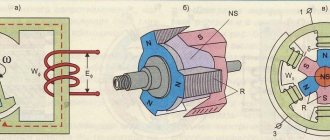
Even though we live in the 21st century, periodic water outages still haunt us. These days, an electric water heater or boiler is becoming an indispensable assistant. This product is also very popular among summer residents if there is no centralized hot water supply in the house. The undoubted leaders in the Russian water heater market are 2 companies Thermex and Ariston.
Any water heater has several consumables, the periodic need for replacement of which is prescribed by the manufacturer. This is a heating element and an anode.
Infrared heating elements
They are used in various devices, primarily infrared heaters for space heating.
Simply put, these are heating devices that create comfort in a house, apartment, office or workshop. A wide variety of heater designs are used for different conditions. Infrared heaters can also be used in various technological equipment where heating of some objects is required. A striking example of such technological equipment are infrared soldering stations and modern laboratory heating cabinets and furnaces. IR heating is widely used in group soldering of printed circuit boards with SMD components.
A description of this process was published in the journal “Technologies in the Electronic Industry No. 3, 2007.” The article is called “Infrared heating in surface mount soldering technology”, the author of the article is V. Lanin. The article provides very interesting facts, both those that have already become history and those that are taking place. The installation diagram for infrared soldering is shown in Fig. below.
Installation of group soldering with IR heating: 1 - exhaust ventilation, 2 - IR lamp matrix, 3 - board, 4 - IR lamp, 5 - reflector, 6 - cooling device, 7 - conveyor
Safety precautions during production
The production of heating elements, like any industrial product, involves the use of technological equipment, which can be a source of industrial injuries. This includes: pipe cutting, countersinking, thread rolling, coiling, cutting, sandblasting machines, lathes and scoring machines, pressing and crimping equipment, high-voltage equipment: punching machines and megohmmeters, thermal, welding equipment, washing baths, etc.
When working with this equipment, you must follow safety rules in accordance with the labor protection instructions in force at the enterprise.
- All workplaces must be certified.
- Production personnel must periodically undergo training in safe work practices and medical examination.
- The enterprise must carry out certification and testing of safety knowledge within the established time limits.
- All workers must know the rules of first aid in case of accidents and be able to provide it.
IR radiation, what it is and how it works
Infrared radiation is one of the components of the solar spectrum. IR rays are found in the lowest frequency zone of sunlight. They are the ones who bring warmth to us on Earth. In this case, infrared rays pass unhindered through the air without heating it at all. The earth's surface heats up, and everything that comes in the way of the sun's rays. And only then, from warm objects, the air warms up. This is why the air is cool in the morning until the sun rises. Infrared heaters, which are the basis of industrial and household heaters, also work exactly the same way.
Of course, the spectrum of man-made IR heaters is not as wide as that of sunlight, and is located in the long-wave region of the IR range with a wavelength λ = 50-2000 microns. Moreover, the lower the temperature of the heated body, the longer the wavelength. In general, the range of IR radiation is much wider and is divided into three subranges:
- short-wave region: λ = 0.74-2.5 µm
- mid-wave region: λ = 2.5-50 µm
- long-wave region: λ = 50-2000 µm
But infrared heating elements only work in the long-wavelength part of the IR spectrum. Various IR heating elements are the basis for creating infrared heaters. Since heat from infrared heating elements is transmitted mainly by thermal radiation, they are often called infrared emitters.
Types of heating elements for heating devices
The simplicity of manufacturing heating elements does not always translate into convenience for users. Many manufacturers produce electric heaters with a specific shape and mounting. If they break, they are quite difficult to buy in a store. Therefore, to make the right choice, it is necessary to study all possible design options.
Tubular models for domestic heating
The tubular design of electric heaters is the most common in mobile oil heaters, portable and wall-mounted electric radiators. Heat transfer in them can occur using: convection, infrared radiation or thermal conductivity.
Ready-made heating elements with a regulator and their own power cord can only be purchased if you are sure that the wire length will be sufficient
The shape and length of the tube in such devices can be any and is dictated only by design features. For example, the heating element of a micatremic heater is a coil located behind a mineral plate. When heated, the plate emits infrared heat.
Its most common characteristics are:
- diameter – 5-18 mm;
- length – 200-6000 mm;
- shell material – steel, stainless steel, ceramics, copper;
- power – 0.3-2.5 kW.
Heating elements with a power of more than 2.5 kW are not used in household heating devices, because apartment wiring simply cannot withstand the greater load.
Finned version of electric heaters
Finned devices are a modification of a tubular heating element. Their feature is the presence of many thin steel plates located along the entire length of the device. This design dramatically increases the area of contact with the environment, ensuring a high heating rate.
Finned heating elements are more expensive and require more work space, but provide higher consumer characteristics of heating equipment
Finned models are used mainly in heaters for air heating. They provide a quick increase in room temperature, especially with a built-in fan.
Block designs of heating elements
The block version consists of several tubular heaters combined on the basis of a single mounting.
When choosing block heating elements, special attention must be paid to their power and the ability of the boiler with a pump to provide heat removal
This design is used by a combination of two factors:
- The need for increased device power and high heating rate of the working environment.
- The impossibility of rapid transfer of thermal energy from the spiral to the environment due to the small area of the outer shell.
In fact, in a block heating element, the load on each heating tube is reduced and the heat transfer rate is increased. Such devices are part of household heating boilers and industrial electric heating installations.
The power of block models can be 5-10 kW, so when placing them in an apartment, it is necessary to extend an additional electrical cable into the room.
Cartridge-type devices
Cartridge heating elements have the form of a tube with one free end, which is due to the peculiarity of their installation. The outer shell is usually made of polished steel to provide maximum contact with the surrounding material. Such tubes are tightly inserted into the corresponding hole in the heating device.
The main disadvantage of cartridge heating elements is the small area of the heat-transferring surface, which requires the use of specific methods for removing thermal energy
Fixation of cartridge models is carried out mainly using a flange connection. They are usually used in industry to heat the working parts of extruders.
There are other structural types of heating elements, but they are used mainly in industrial production and do not affect the topic under consideration.
How IR heaters work
In essence, the design of an IR heater is simple and unpretentious: the heating element - the emitter is placed in a housing of one design or another, inside the housing there is a reflector - a reflector, terminals for connecting the emitter, and outside there are terminals for external wires. The figure shows just such a simple version of the heater.
IR heater design: 1 - reflector (reflector), 2 - protective grid, 3 - switch, 4 - mounting bracket, 5 - infrared carbon lamp, 6 - cover, 7 - terminal box, 8 - power cord, 9 - plug.
It is immediately noticeable that the heater of this design is very similar to a spotlight for halogen lamps, used to illuminate advertisements, building facades, porch steps, and part of the yard near the house. In general, some relatively small area, so-called local lighting.
Therefore, with the help of IR heaters, it is also possible to heat not the entire area of the room, but only some part of it. Energy savings are noticeable to the naked eye: why heat the entire room if you can heat the required corner? An example of spot heating is shown in the figure.
Spot IR heating
If you need to provide heating, for example in production, then you will need heaters of a slightly different design that can be installed in the ceiling, like lamps with fluorescent lamps. This option is shown in the figure below.
Heating of large rooms
You can find many similar heating schemes, because IR heaters are used to heat fairly large rooms: workshops, warehouses, workshops, and even small outdoor areas. For example, this could be a gazebo near the house or a veranda of a restaurant with tables.
Tubular electric heaters for heating water in baths
These heating elements are intended for heating and boiling water, weak alkalis and acids, and other liquids. Made from various metals:
Stainless steel
- Diameter, mm – 8.5-13;
- The maximum temperature on the heating element shell is 100°C;
- Maximum power, kW/m – 3.7-5.6;
- Specific power, W/cm2 – 15.
Carbon steel
- Diameter, mm – 8.5-13;
- Maximum power, kW/m – 3.7-5.6;
- Specific power, W/cm2 – 15.
From copper, brass
- Diameter, mm – 8.5-13;
- Maximum power, kW/m – 2.2-3.4;
- Specific power, W/cm2 – 9.
Heating elements on carbon lamps
A carbon lamp is a vacuum tube made of quartz glass, inside of which there is a radiating element made of carbon (carbon) fiber, more precisely from several fibers twisted into a bundle. Sometimes this radiating element is called a carbon spiral, although this is not entirely correct.
Carbon fiber appeared relatively recently, but has gained great popularity in various technologies. Not only carbon emitters are made from it. Using special technologies, carbon fibers are made from carbon fibers.
The range of applications of carbon fiber reinforced plastics is very wide, about twenty areas: from aircraft construction and rocketry to strings for musical instruments. Carbon fiber reinforced plastics are widely used in the automotive industry, mainly in sports cars. Those who are interested in amateur and sport fishing appreciate all the delights of carbon rods.
Carbon fiber has a fibrous structure, which significantly increases the radiation area. This area is tens and hundreds of times greater than the area of a spiral made of nichrome, tungsten, ceramics, flamentin or other materials. Such a developed area leads to the fact that the heat transfer of carbon fiber is 30...40% higher than that of conventional heating elements.
Operation of a carbon heater
When voltage is applied, the carbon fiber heats up instantly, and the generation of radiant heat immediately begins, without harmful radiation in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum. The increased heat transfer of carbon fiber leads to more economical energy consumption than conventional heaters made of nichrome spirals.
For the same power consumption, carbon heaters produce more heat. In this case, the heat does not go to the ceiling, as in the case of heating, for example, with an oil radiator or a central heating battery.
The optical radiation of carbon lamps is very small. A slightly visible red glow does not affect vision at all and does not blind, but the glow is still noticeable. The figure above shows a working household heater based on carbon lamps.
At the top of the heater there are switches that set operating modes. The heater base has an electric drive that rotates the heater in different directions, similar to how fans do it. These turns increase the heating area.
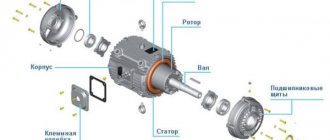
Replacing a water heater heating element
Boilers have a fairly simple design and operate on a basic principle. If you don’t want to overpay the craftsmen for the work, then you can handle this task yourself. If your water heater is under warranty, you must contact the service center if all operating rules are followed.
Visual inspection of parts
A visual inspection allows you to objectively assess the condition of the heating element for the water heater. To do this, you will need to disconnect the boiler from the network, drain the water from it and disassemble it, cleaning the heating element from scale.
Inspect the part for cracks, chips, swelling or damage. If you find them, feel free to throw the item in the trash, as it will no longer be possible to repair it. In this case, the only option is to replace the heating element for the water heater with a new one.
This happens due to untimely replacement of the anode. Since after its destruction, the heating element itself and the walls of the boiler begin to corrode. It is extremely important: damage and leakage of the heating element will lead to damage to the thermostat, which will significantly increase the cost of repairs. If the heating element is damaged at the slightest level, it should be replaced immediately!
Tools for replacing heating elements
If a malfunction is detected, you need to prepare for replacement and purchase tools. Most of them are available in almost every home, so there should be no problems with replacement. So, to replace the heating element you will need the following tools:
- Wrench;
- Pliers or pliers;
- Absorbent fabrics (rags or napkins);
- Straight and Phillips screwdriver;
- Phase meter (screwdriver with indicator);
- New heating element.
Replacing the water heating element
Turn off the water supply by turning off the tap near the boiler. If there is no shut-off valve, turn off the water in the entire apartment by shutting off the riser. In addition to shutting off cold water, hot water also needs to be shut off.
The replacement process is quite simple, just do the work in the following order:
1. Draining water 1.1. Turn off the power supply to the device; 1.2. Make sure the water inside the appliance is at a safe temperature; 1.3. Turn off the cold water supply to the water heater; 1.4. Open the hot water tap on the faucet to relieve pressure inside the tank; 1.5. To allow air to enter the tank, open the shut-off valve on the tee installed at the hot water outlet of the water heater. If it is missing, it is necessary to dismantle the connections at the outlet of the water heater; 1.6. Connect the drainage hose directed to the sewer to the shut-off valve on the tee installed at the cold water inlet of the water heater and open it. If not available, a drainage hose must be installed at the inlet of the water heater. Water will flow out from the cold water supply point, and air will flow through the hot water connection point; 1.7. After draining, make sure there is no water inside the water heater. 2. Replacement of internal elements 2.1. Remove the cover of the device; 2.2. To replace the thermostat, slide it out of the socket and disconnect it from the power supply; 2.3. Remove the thermostat; 2.4. Unscrew the heating element or the heating element mounting using an open-end wrench, an adjustable wrench, or a gas wrench; 2.5. Wash the internal tank of the water heater and replace the heating element (anode and thermostat if necessary); 2.6. Assembly is carried out in reverse order. The main thing is to pay attention to the grounding wire.
Attention:
The magnesium anode is an integral part of the system for protecting the water-containing container and heating element (heating element) from corrosion. It is necessary to check the condition of the magnesium anode annually. If the magnesium anode is severely worn, it must be replaced. It is necessary to replace the magnesium anode at least once every 24 months.
Attention:
A tubular electric heater (TEH) is designed to heat water in an internal tank by converting electrical energy into heat. The formation of limescale (or scale) on its surface can lead to poor heat transfer, overheating or failure. Regularly inspect and, if necessary, remove scale from its surface using a descaling agent.
Ceramic infrared heaters (emitters)
They are a regular heating element, “sharpened” in a ceramic shell – the body. The heat from the heating element heats up the ceramics, and from it heat rays are emitted into the external environment. The ceramic shell has an area several times larger than the area of the heating element, so heat is transferred more actively.
The appearance of the ceramic heater is shown in the figure. Such heating elements are often called panel infrared heaters. The shape of heating panels is very diverse. The heater can be flat, concave or, conversely, convex.
Appearance of a ceramic heater
On the front surface you can see the configuration of the heating element; on the back surface there are wire leads insulated with ceramic beads. The operating temperature of ceramic heaters is 700...750 degrees, specific surface power is up to 64 kW/m2. The power of ceramic heaters can range from several tens of watts to several kilowatts. As they say, for all occasions.
Some types of ceramic heaters have an open, visible coil, such as the HSR type. The operating temperature of the heater is 900 °C, the heater is designed for rapid heating. The appearance of the HSR heater is shown in the figure.
Heater type HSR
Ceramic IR heaters come in three types: volumetric (solid), hollow, and heaters with a built-in thermocouple. Volumetric elements are quite inertial, take a long time to heat up and cool down slowly. In cases where periodic switching on/off of the heater is required, hollow heaters are used.
They are less inertial, which allows them to be used in various technological processes where it is necessary to maintain the exact temperature of the working medium by periodically turning on/off the emitter. Due to the reduced mass, the heating rate of hollow emitters is 40% higher than that of volumetric emitters.
Unlike volumetric emitters, most of the radiation from hollow emitters is directed forward. Radiation back is prevented by a hollow thermal barrier on the rear side, which provides a gentle temperature regime for the elements of the housing structures, and also increases the efficiency of the emitter. Compared to volumetric emitters of the same power, the reduction in electricity consumption reaches 15%.
When using a volumetric radiator, such heat distribution can only be achieved using a reflector. Some types of IR panel heaters have a built-in K or J type thermocouple, allowing precise temperature control and regulation. Very convenient for use in technological processes.
There are quite a lot of technological processes where IR emitters are used. Here are just a few of them:
- Paint drying (two-component paints, epoxy varnishes),
- Plastics processing (PVC vulcanization, thermoforming of ABS plastics, polyethylene, polystyrene, auto body parts, powder painting)
- Drying of adhesives,
- Food processing (keeping warm, grilling, sterilization and pasteurization),
- Textiles (silk-screen printing, T-shirt decals, carpet latexing),
- Beauty and health (infrared heat cabins, saunas)
Internal structure of electric heaters
It is convenient to consider the device using the example of a tubular model. An electric heater is a ceramic or metal tube filled with a thermal conductor with a spiral located inside. In the place where the tube is fixed to the flange there are insulating bushings that make it impossible for the conductive spiral to contact the heating element body.
Most models of heating elements use similar components, but their durability may vary depending on the build quality
The electric heater is mounted primarily with a flange connection, which allows the internal environment of the heating device to be sealed from the external space. The disadvantage of this design is the impossibility of replacing the spiral if it burns out internally.
Infrared ceramic Edison lamps
They are hollow ceramic emitters, available with an E27 base, like a regular incandescent lamp. This base was invented a long time ago by the great inventor T. Edison. It is the letter “E” in the name of the base that perpetuates the name of the inventor, and 27 is the diameter of the base in millimeters. The design is very convenient: you just screw it into the socket instead of an incandescent lamp, and it immediately becomes warm!
It is believed that these heating elements are most often used in livestock farming. Even on Chinese sites with free shipping, from the clumsy machine translation from English, you can understand that these heaters are intended for cowsheds, poultry houses and pigsties.
Heating elements for heating oil
These double-ended oil heating elements are intended for heating oil, fats, bitumen and other fatty substances in baths and other containers. Heating elements are manufactured bent in different planes with different fastening elements.
- Maximum temperature of the heated medium, °C – 250;
- Maximum permissible surface load, W/cm2 – 3.5;
- Shell diameter, mm – 8.5-16;
- The maximum power (in kW) per 1 meter of active length of the heating element is 0.93-1.75.
Use of copper heating elements
Copper heating elements are no less in demand - special copper alloys that are resistant to aggressive environments are used to produce housings. Their main advantage is higher thermal conductivity, which makes it possible to heat water faster. This allows you to spend less electricity on heating.
Copper products have several advantages:
- High corrosion resistance. Such products last a long time, although corrosion resistance largely depends on the quality of the water used. If there is a large amount of chlorine in tap water, then the corrosion process occurs faster, so it is advisable to install a post-treatment system.
- Natural bactericidal properties. Contact with this metal is detrimental to microorganisms, so it is an additional means of water disinfection.
- High plasticity. Copper heating elements can have a variety of configurations, which expands production possibilities.
- Efficient heat dissipation. The heating element does not deform even with sudden temperature changes.