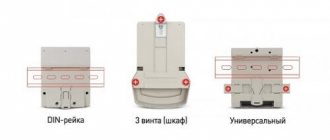
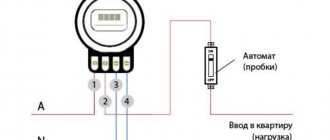
Classification of electric energy meters
The classification of electrical energy metering devices is based on several principles by which they are divided.
Based on the operating principle:
- induction (electromechanical);
- electrodynamic;
- electronic;
- hybrid.
By accuracy class:
- workers;
- reference.
By the number of tariffs applied:
- single-tariff - energy meters without taking into account time intervals;
- two-tariff - used to take into account energy readings in two time periods (for example, during the day and night), while consumption is recorded independently in separate lines;
- multi-tariff - the electric meter works on the same principle as the previous one, but there can be at least three time intervals.
According to the principle of inclusion in electrical networks:
- direct connection - connected to the network without instrument transformers. Such meters are suitable for 0.4/0.23 kV networks at currents up to 100 A;
- transformer connection - needed for connection with established transformation ratios.
By type of network connection:
- single-phase - installed in two-wire networks, with a standard voltage of 220 V;
- three-phase - in three or four-wire networks with a voltage of 380 V.
By type of automation:
- direct (physical) observation counter;
- meter with remote reading.
Advantages and disadvantages of multiple tariffs
Dividing the day into zones to control electricity with multi-tariff meters
New metering devices have their own design features, as well as advantages and disadvantages, which must be familiarized when choosing a device. The advantages include:
- Environmental friendliness. The amount of harmful and poisonous emissions into the atmosphere and people is reduced.
- Tangible savings on the family budget. Experience shows that the device fully pays for itself within one year.
- Facilitating the operation of power plants: saving fuel, reducing the cost of repairs and maintenance.
Among the disadvantages of the devices, it is worth highlighting only the need to adapt to the tariffs of the meter. If you neglect this, the number of expenses will not be reduced.
Main technical characteristics
For the technical characteristics of meters, the following parameters are used:
- Accuracy class — the main technical parameter that estimates the percentage of measurement error of the device. Table of accuracy classes for rated active electricity meters
Consumption category Voltage class Metering device accuracy class Citizens (individuals) Any 2.0 and higher Entries of multi-apartment residential buildings Any 1.0 and higher Consumers with power up to 670 kW Up to 35 kW inclusive 1.0 and higher Over 110 kW 0.5S and above Consumers with power over 670 kW Any 0.5S and higher with the ability to measure hourly consumption volumes and store them for more than 90 days Electricity producers Any All old household electricity meters had an accuracy class of 2.5. Today, more accurate devices with an accuracy class of 2.0 are used.
- Multiple tariffs — the ability of modern devices to keep separate records of electricity consumption by time intervals and by seasons, which is economically beneficial to consumers and makes it possible to relieve urban energy systems during peak hours.
A two-tariff system has become widespread, allowing for separate accounting of electricity consumed at certain times of the day.
- Calibration interval - a characteristic of an electric energy meter that determines the duration of the interval between verifications, which is entered in the passport and guarantees the accuracy of the readings.
Each type and model of meter has its own calibration interval. Its duration can be from four to sixteen years.
The meter parts deteriorate over time, so the accuracy of the readings decreases. Under such circumstances, the appliance becomes unusable and the utility bill becomes invalid.
The longer the interval the manufacturer promises, the longer the electric meter will last.
How to choose a price category
In order to select a price category, you need to calculate the cost of your electricity in the main price categories 1 – 4.
The cost of electricity in price categories 5–6 will be 5% lower than in price categories 3–4 with good planning and 5% higher with poor planning.
Now let's take an example to see how the cost of electricity changes depending on the price category of electricity.
We will do all the calculations for a medium-sized enterprise per month.
Initial data:
| Metered consumption | kWh | 100 000 |
| Tariff for the 1st price category | rub/kWh | 4,2 |
| Tariff for the 2nd price category day | rub/kWh | 6 |
| Tariff for the 2nd price category night | rub/kWh | 3 |
| Power | kW | 150 |
| One-part transmission tariff | rub/kWh | 2 |
| Two-part tariff - payment of losses | rub/kWh | 0,35 |
| Two-part tariff - rate for content | RUR/kW | 600 |
| Price for electrical energy on the wholesale market | rub/kWh | 1,5 |
| Price per capacity on the wholesale market | RUR/kW | 700 |
We will describe further where and how to find the data necessary to calculate price categories for electricity, following the examples.
Types of electricity meters
Induction meters
A familiar device with a transparent plastic window through which a rotating disk is visible. The higher the number of disk revolutions, the higher the energy consumption.
Induction electricity meters, despite their low accuracy, are considered very reliable. Their warranty period is 15 years.
Appearance and schematic diagram of an induction meter for metering electrical energy
Advantages of this type of device:
- low cost;
- reliability;
- good quality;
Among the disadvantages are:
- low accuracy class;
- low functionality;
- easy accessibility to use unaccounted for electricity.
Electronic electricity meter
Appearance of an electric meter for electricity consumption
In such a device, pulses are created on electronic elements under the influence of current and voltage, the number of which is proportional to the amount of measured energy. Such counters are programmable and equipped with a liquid crystal display.
The main advantage of the device is the ability to use differentiated tariffs when accounting for consumed energy, since the electronic meter is able to remember how much electricity was used in a predetermined period of time. Each time period corresponding to a specific tariff is equipped with its own counting mechanism.
The interval between verifications for such a meter ranges from 4 to 16 years.
The disadvantage of the electronic device is its rather high cost, but this is quickly compensated by ease of use and measurement accuracy.
Electrodynamic electricity meter
An electrodynamic meter contains a stationary current winding in the form of wire coils. If you turn on an electrical appliance, the current passing through the coils creates a magnetic field. Between the windings there is an armature of three or more coils. A commutator with metal brushes is installed on the anchor. The collector changes the direction of the current in the armature conductors in the magnetic field generated by the stationary coils. The readings of the device are judged by the numbers on the meter scale, appearing in six rectangular windows lined up in a row. The unit of measurement of electrical energy is indicated above them. The first five digits are the whole number of hectowatt-hours or kilowatt-hours of electricity used, the sixth digit is the fractional part of the decimal number.
Advantages of electronic and electrodynamic meters :
- high accuracy class;
- multiple tariffs (from two);
- when metering several types of electrical energy, one meter is sufficient;
- energy accounting is carried out in two directions;
- measure the quality and volume of power;
- save electricity metering data;
- easily accessible data;
- the ability to remotely obtain readings;
- the counter is small in size;
Flaws:
- sensitive to voltage changes;
- more expensive than induction ones;
- complex repair.
Calculation of the third price category of electricity
To calculate the cost of electricity for 3 – 6 price categories of electricity, you will need the following data:
- Hourly metered consumption for each hour of the month.
- The cost of electricity on the wholesale market for each hour (published monthly on the website of your guaranteeing supplier in the section for legal entities).
- Calculation of power per month.
- The cost of capacity on the wholesale market (published monthly on the website of your guaranteeing supplier in the section for legal entities).
- Tariffs for electricity transmission (published on the website of your guaranteeing supplier, as well as on the website of the tariff service).
The cost of consumed electricity in the third price category is calculated separately for each hour.
For example, if on the first day of the month from 8:00 to 9:00 the enterprise consumed 100 kWh, and the tariff from 8:00 to 9:00 was 2 rubles. / kWh, then the cost of electricity for this hour will be 200 rubles.
And so on for every hour of the month.
If you do not have the opportunity or desire to calculate the cost of electricity for your enterprise for each hour, then you can simplify the task and calculate the cost using the average price for electricity on the wholesale market (published monthly on the website of your guaranteeing supplier in the section for legal entities).
Let’s say the weighted average price on the wholesale market is 1.5 rubles/kWh.
Then,
Cost of consumed electricity = consumption * weighted average price per month = 100,000 kWh * 1.5 rubles/kWh = 150,000 rubles
Next, we need to calculate power consumption and cost.
Power consumption is calculated as follows:
We determine the peak load hours in your region for each working day.
Peak load hours are published on the system operator's website.
For example, on the first working day of the month, the peak hour was from 10:00 to 11:00.
Consumption from 10:00 to 11:00 was 140 kWh.
Accordingly, your power for the first working day of the month = 140 kW.
Thus, we find the power for each working day of the month, divide by the number of working days and get the power for the month.
The power in our example is 150 kW.
Power price – 700 rub/kW (we find it on the website of your guaranteeing supplier in the section for legal entities)
Power cost = monthly power * power price = 150 kW * 700 rubles/kW = 105,000 rubles.
A detailed calculation of the cost of power, as well as recommendations on how to reduce it, can be found at the link.
And the last step is calculating the cost of electricity transmission services.
On the website of the guaranteeing supplier or service according to the tariffs of your region, we find a One-part tariff for transmission services for the six months of interest to us.
In our example, the single-rate transmission tariff is 2 rubles/kWh
Cost of transmission services = monthly consumption * single-rate tariff = 100,000 kWh * 2 rubles/kWh = 200,000 rubles
To summarize:
Cost of electricity in the third price category = Cost of consumption + Cost of power + Cost of transmission services = 150,000 rubles + 105,000 rubles + 200,000 rubles = 455,000 rubles
As you can see, the cost of electricity in the third price category was higher than in the first.