An electricity meter is a measuring device for recording the consumption of electricity consumed. Depending on the modification, the device can operate in DC or AC networks. The unit of consumption is kW/h or A/h.
Classification of meters
Counters are usually divided according to three criteria:
- Type of measured quantity.
- Connection method.
- Constructions.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to all three criteria, selecting the optimal device for the required parameters of the electrical network and the level of energy consumption.
Varieties by type of measured quantity
The classification of meters by type of measured value is the easiest to understand even for a person who is far from knowledge of the principle of operation of electrical networks. All devices are divided into single-phase and three-phase. The single-phase electricity meter is designed for connection to AC networks 220 V, 50 Hz. Three-phase devices operate with electrical networks of 380 V, 50 Hz. At the same time, they can carry out measurements when connected to a single-phase network.
Single-phase devices can be found in any apartment or house. They are designed for household use. Three-phase devices are in most cases used at industrial facilities where a three-phase electrical network is installed, required for the operation of powerful equipment. Depending on the modification, three-phase meters may have a three or four wire connection.
Classification by connection method
Based on the connection method, the meters are divided into only two groups. There are direct connection and transformer connected devices. The former are directly connected to the network, while the latter need to be connected to a special transformer, which is connected to the circuit in front of the meter itself.
Varieties by design
Modern meters come in 3 design options:
- Induction.
- Electronic.
- Hybrid.
Induction counter
An induction (mechanical) electricity meter has fixed current-carrying coils inside, creating a magnetic field. The field received from them affects the movable element, which is a disk that works on the principle of a conductor for electric currents. When electricity passes through the disk, it begins to turn around under the influence of the magnetic field of the coils, thereby starting the mechanism with the counting board. The more intense the current passing, the faster the disk rotates. The counting mechanism of the device is designed in such a way that a certain number of revolutions corresponds to a change in one indicator on the dial.
Mechanical devices are losing their relevance because their design is far from perfect against more modern electronic meters.
The disadvantages of induction meters include:
- Inability to take readings remotely.
- Single tariff measurement.
- Low sensitivity.
- Insufficient protection against electricity theft.
Often, induction meters are unable to correctly calculate the level of energy consumed. Quite often, if there is low consumption, for example, when the indicator is on in the charger unit of a telephone or household appliance in standby mode, the meter does not respond at all, although minimal energy consumption occurs. In addition, some modifications of meters have completely opposite problems. When a powerful consumer is turned on, their disk turns over much faster than the actual level of energy consumption.
The advantages of mechanical meters include their truly long service life and complete independence from power surges. They are cheap and quite reliable. But their accuracy class corresponds to a level of 2-2.5%, which is quite low compared to electronic devices.
Electronic electricity meter
The electronic meter works on a different principle. In it, currents act on special electronic elements that convert them into impulses. The number of pulses is proportional to the actual amount of transmitted energy. The reading mechanism can be an electronic or electromechanical device that displays data on an LCD display. Electronic counting elements are suitable for devices that are installed inside apartments and houses. The electromechanical mechanism is used on meters mounted on building facades.
The main advantage of such devices is their high accuracy. They correctly display the amount of energy that was missed for consumers. In addition, their electronic components allow energy accounting at several tariffs. That is, they are able to remember information about how much energy was consumed during the daytime and how much at night. This allows you to pay for consumed electricity at several tariffs, if this is provided for in an agreement with the supplier company.
These devices have a long verification period. Depending on the manufacturer, the meter needs to be verified every 4-16 years.
The electronic meter has in its design a non-volatile clock and counting elements that save data in the event of a power failure. Thanks to this, when turned on after an emergency blackout, all information about the level of electricity used will not be reset to zero. Moreover, such devices have their own software, which automatically adjusts the time, which is important in the case of calculations in several tariffs. Also, such devices have protection against unauthorized access, which records such attempts in the event log.
Electronic meters have a high accuracy class, which is at least 1%. Such devices allow you to remotely check indicators without the need for access to the house. Thanks to this, the inspector does not have to enter the apartment, which is especially convenient if residents are not at home on weekdays. However, an electronic electricity meter also has a drawback, which is expressed in high cost. Repairing such devices is much more expensive than mechanical ones. These devices are very sensitive to voltage changes. In the event of an emergency, it is likely that the device will burn out, which will require its replacement.
Hybrid meters
A hybrid electricity meter coexists, which is a device that combines elements of an induction and an electronic device. The permeability of the energy consumed is read by rotating the disk, and the readings are displayed on an electronic dial. Such meters, unlike purely induction ones, are capable of counting according to tariffs.
Technical parameters of electricity meters
Many meter models, designed to operate under the same conditions, differ in accuracy and other characteristics. The main technical parameter of an electric meter is accuracy. Until 1995, all instruments had a maximum permissible error level of 2.5%. After 1996, the requirements for meter manufacturers were tightened, after which devices with an error of 2% began to be installed for the private sector. At the same time, old-style meters are not uncommon and are still in use, subject to verification. All metering devices currently produced have an error of no more than 2%. You can usually find meters with accuracy classes of 0.5, 1 and 2%.
In addition to error, an important parameter is throughput. Household meters are designed for a maximum consumption level of 5A and should be used only in cases where powerful electrical appliances that consume more energy are not used. If the electricity meter is overloaded, a short circuit may occur. Especially for this purpose, it is equipped with electrical circuit breakers that disconnect the circuit to prevent such consequences. It has become common to install more powerful circuit breakers to prevent emergency shutdowns in order to be able to power more energy-intensive consumers. Such techniques are prohibited and are contrary to safety regulations. If intensive energy consumption is necessary, you need to contact the electricity supply company with a request to install a more powerful meter designed for a current of up to 20A or more if 380V is supplied.
Features of filling
The electricity meter, like any other metering device, is equipped with seals that cannot be broken, as there are fines for this. Single-phase meters have two seals installed. One is tightened on the housing fastening to prevent it from being disassembled, and the second is on the clamping cover. In addition, if the device was removed for verification, additional seals may be installed on it, confirming its suitability and the absence of outside interference after testing its functionality.
Metrological aspects of electric power industry
Electrical energy has long and firmly entered our lives. Nowadays, the lack of access to electricity is considered an emergency.
Ensuring the uniformity of measurements for a huge fleet of measuring equipment is a complex task, the solution of which is carried out by tens of thousands of specialists working in various sectors of the national economy.
If we consider electricity as a product that is produced, transported, sold and consumed, then it should, by analogy with other products, be characterized by a set of parameters that most fully reflect its quality and allow its quantity to be determined quite reliably.
In Kazakhstan, these parameters are defined by GOST 13109-97 “Electric energy. Electromagnetic compatibility of technical equipment. Standards for the quality of electrical energy in general-purpose power supply systems", which establishes the following indicators of the quality of electrical energy:
— steady-state voltage deviation;
— amplitude of voltage change;
— flicker dose;
— distortion coefficient of the sinusoidal voltage curve;
— coefficient of the nth harmonic component of voltage;
— negative sequence voltage asymmetry coefficient;
— zero-sequence voltage asymmetry coefficient;
— frequency deviation;
— duration of voltage dip;
— impulse voltage;
— temporary overvoltage coefficient.
Currently, the fleet of instruments for measuring power quality indicators is just being formed; there are difficulties in gaining access to the necessary measuring equipment.
Today, when a huge amount of electricity is produced and consumed, even a small error in the accuracy of measuring its parameters, especially quantitative ones, entails significant economic losses.
The accuracy of measurements is determined by the technical capabilities of the measuring instruments used. Currently, a large number of different means for measuring electrical energy have been registered, especially electricity meters. On the one hand, this is good, since it is possible to select the desired device. On the other hand, there is a problem with their maintenance and reliability.
Another pressing problem, literally a “modern problem,” is the regulatory and metrological support of automated commercial electricity metering systems (ASKUE), which are currently being actively implemented. At the same time, there is no unified system of regulatory and metrological support for this activity.
According to the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On Ensuring the Uniformity of Measurements”, measuring instruments intended for serial production or import into the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan in batches and which are subject to state metrological supervision are subject to testing with subsequent approval of the type of these measuring instruments. The decision to approve the type of funds is certified by a certificate, the validity period of which is established upon its issuance. The approved type of measuring instruments is entered into the register of the state system for ensuring the uniformity of measurements.
The production, verification and repair of measuring instruments can be carried out by individuals and legal entities after receiving the appropriate license issued by the authorized state body for standardization, metrology and certification.
Measuring instruments subject to state metrological supervision are subject to verification upon release from production or repair. The list and frequency of verification of measuring instruments, as well as the procedure for its implementation, are determined by the authorized state body for standardization, metrology and certification. Positive verification results are certified by a verification stamp and a verification certificate.
How to change electricity meters in an apartment: features of the procedure
Replacing metering equipment, as well as its maintenance, is among the responsibilities of the owner of the premises where the meter is located:
It is prohibited to carry out work on replacing the electric meter yourself.
How to replace electricity meters in an apartment: list of documentation
For residents of apartment buildings, there is a certain procedure for replacing electric meters:
All documents are drawn up in accordance with the standards prescribed for them by law.
Please fill out all required documents carefully.
Information that is displayed in the application:
To submit an application, you will need a standard package of documents provided for by the procedure:
Replacement of meters is carried out after the decision of the authorized bodies
Data recorded in the act:
After repairing, checking or replacing the old meter, a representative of the energy sales company is invited
The specialist fills out all fields of the document in two copies, one of which is given to the applicant.
Mercury electricity meters: prices and reviews
The most popular manufacturer of electricity metering equipment on the market is Incotex. Mercury 201 electricity meters are the most popular and optimal single-phase devices. This category of devices is aimed at metering active energy.
Price of single-phase electricity meters Mercury 201 (single-tariff devices):
| Device model | price, rub. |
| Mercury 201.5 63289 | 863 |
| Mercury 201.6 83665 | 1577 |
| Mercury 201.6 83665 | 1180 |
| Price of single-phase electricity meters Mercury 200 (two-tariff devices) | |
| Mercury 200.02 (R) | 1394 |
| Mercury 200.04 (M) | 3089 |
| Mercury 200.05 | 1771 |
Below are reviews left by buyers of Mercury 201 electricity meters, reviews from forums:
“My meter is located in the entrance. The device worked properly and did not cause problems until receipts with large amounts began to arrive. It turns out that the device should have been replaced a long time ago. As I was told, the readings of outdated equipment are calculated according to the standards for electricity consumption per person without a meter. Most of my neighbors had Incotex devices, and I decided to go with the Mercury counter. Upon closer examination, it turned out that the case is made entirely of plastic. This means that the device is completely safe. The numeric data on the dial is clearly visible. In general, I am pleased with my purchase, although the old meter suited me quite well.”
Victoria Bendas, Moscow
Mercury electricity meters
“When it came time to change the meter, on the advice of experts, I bought a single-phase one - Mercury 201. The device is safe and reliable. During six months of operation, I did not identify any shortcomings.”
Evgeny Doroshenko, Ekaterinburg
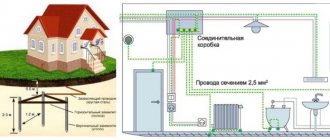
Features of connecting a single-phase electricity meter
For most models of devices, the connection diagram for single-phase electric meters is directly the same. Single-phase equipment is equipped with 4 terminals, which is typical for devices in this category. Electrical cables are connected to them.
Rules for installing single-phase electricity meters:
Connection diagram for a single-phase electric meter
If you study in detail the diagram explaining how to connect single-phase electric meters, even the owner of the apartment can cope with this procedure. Most often, device manufacturers place instructions on the inside of the box.
To securely fix the email. wires at the terminals of the device, it is recommended to use a screw fastening method. The terminals, which serve as outputs, pass current to distributors and protective elements. The general purpose terminal for the neutral wire supplies the “phase” to the RCDs (protective elements) and fuses. For this reason, it would be more rational to install all used devices in one panel.
Special protective shields increase the reliability of fixation of the device and additional devices. The optimal mounting level for the shield is 170 cm from the floor. To make the meter convenient to use, this indicator is calculated based on the height of the apartment owner.
After studying the instructions, you can connect the electricity meter yourself
Recommendations for installing accounting equipment
To install electricity meters seamlessly, experts recommend using the appropriate tool:
- forceps;
- pliers;
- pliers for removing insulating protective coating from wires.
Before carrying out work, you need to make sure that the input wire is accessible. It must be turned off for the period when all work will be carried out, so this operation must be safe and painless.
Be sure to adhere to all safety rules, properly insulate all wire sections and be extremely careful when performing each action. You also need to take care of obtaining the appropriate permission from the control authorities and have the necessary documents available.
Types of electricity meters
The classification of electrical energy metering devices is carried out depending on the following parameters:
- connection type;
- measured quantity;
- design features.
Let's consider each of the points separately. Based on the type of connection, meters are divided into two main types:
- devices with direct connection to the power circuit;
- meters connected to the power circuit via instrument transformers (the so-called “transformer connection”).
The first type of devices is intended for household metering, while transformers are needed for large buildings and enterprises that consume high current (more than 100 amperes).
Depending on the measured value, electricity metering devices are divided into the following types:
- single-phase (for current 220V with a frequency of 50Hz);
- three-phase (for current 380V with a frequency of 50Hz).
It is worth noting that modern three-phase meters, which have an electronic design, are capable of producing single-phase metering.
Depending on the design features, there are three groups of devices for metering electrical energy:
- Induction (electromechanical electricity meters). Devices whose operation is based on the action of an electromagnetic field. Fixed conductors in the form of coils through which current passes create magnetic impulses. They set in motion a special mechanism, which is a movable rotating disk. The amount of electrical energy consumed in induction devices is calculated by the number of revolutions of this disk.
- Electronic (static electricity meters). The operating principle of these devices is as follows: a solid-state measuring element converts incoming analog signals of alternating current and voltage into counting pulses, the number of which indicates the value of the measured active energy. The counting mechanism has an electromechanical or electronic design and, in addition to the measuring element, includes a device for storing the obtained values and a display for displaying the results.
- Hybrid devices. Models of this group represent an intermediate option. They are equipped with a digital interface, but measurements are made using an electromechanical method. Currently, these devices are rare, as they are inferior to electronic electricity meters in price and functionality.
The catalog of the MosEnergoSbyt online store contains a wide selection of single- and three-phase electronic meters from the following: NEVA, Matrix and others. You can find a complete list of devices on the company's website.
Tips for choosing meters
The selection of metering devices in stores is quite large.
When analyzing which electricity meter is better, it is recommended to pay attention to the following aspects:
- the cost of the meter (but you can’t rush for too cheap products, since low-quality components could be used in their manufacture, which reduce the service life of the equipment);
- device manufacturer, choosing trusted companies;
- warranty period of the device;
- electricity consumption by the meters themselves;
- device noise level;
- the ability to provide service.
There is no need to immediately refuse to buy slightly outdated induction models. They, like electronic devices, have their advantages. There is also no need to purchase devices that have many functions that will not be used. In addition, a large number of microcircuits in meters increases the risk of its failure.
Also, when purchasing, you should make sure that there are clearly readable seals, initial indications and factory stamps in the passport, and a warranty card. It is recommended to purchase recorders in specialized stores.
Passport for an electric meter
It is important to carefully check the date of the meter verification.
According to the PUE, newly installed devices must have state verification seals with the following date:
- for three-phase models: up to one year;
- for single-phase: up to two years.
Thus, if the verification date has expired, the device will not be registered without a new one.
Important! Recommendations on which electricity meter to choose are available on the electricity supplier’s website. In different regions, different brands of meters may be recommended for installation.
In addition to well-known foreign manufacturers, whose products have long been popular (ABB, GE), models of domestic companies are also presented on the market (Energomera - a manufacturer of devices of the same name, Incotex, which produces Mercury meters, Taypit, which offers Neva recorders). Moreover, their quality is sometimes not inferior to imported ones, and the price is much lower.
Basic parameters of electricity meters
The main parameters of electrical energy metering devices include:
- Accuracy class. Technical characteristics showing the maximum possible error in measurements. Until 1996 inclusive, all measuring instruments with which residential premises were equipped had an accuracy class of 2.5 (in other words, the measurement error was 2.5%). In the MosEnergoSbyt online store you can find electricity meters that meet the modern standard in the household sector (with a deviation of no more than 2%).
- Intervalidation interval. During continuous operation, individual elements of the device naturally wear out and cease to perform their functions correctly. As a result, the accuracy class of the measuring device inevitably decreases. Therefore, devices must be periodically checked for accuracy of readings. The time interval from the moment of initial verification (during the production process) to the next is called the inter-verification interval (abbreviated as MPI). This characteristic is calculated in years and indicated in the passport of the measuring device.
- "Tariff". This parameter determines the ability of the electric meter to make measurements at various tariffs (or modes). All electricity meters based on the induction calculation method operate at only one tariff. In contrast, electronic meters are capable of operating according to two (the so-called “day/night” mode) or more tariffs (for example, taking separate readings by season or day of the week).
Rating of electric meters based on customer reviews
Review of the most popular electricity metering devices, compiled based on the opinions of real users:
| Place | Name | Points |
| Single-phase single-tariff | ||
| 1 | "Neva 102 1SO" | 10 |
| "Puma - 103.3M" | 10 | |
| "Leine Electro-01" | 10 | |
| 2 | "Enron Topaz 101-5 (60) -Ш2Р1М" | 9 |
| "Mercury 201.7 (8)" | 9 | |
| 3 | "MZEP Agat 1-1" | 8 |
| 4 | "KommunarSchetMash" SO-EA09 | 2 |
| Single-phase multi-tariff | ||
| 1 | Iskra ME162 | 10 |
| Matrix AMM MTX 1A10.DF.2Z0-CO4 | 10 | |
| "Neva MT 124 AS OP" | 10 | |
| 2 | "Cascade-1MT-W1-OV3" | 9 |
| "MZEP Agat 2-32" | 9 | |
| "Neva MT124 OR 5" | 9 | |
| 3 | "Energomera SE 208" | 8 |
| 4 | "LENELEKTRO 221 RO" | 6 |
| 5 | "EnergoUchet EU20-33" | 4 |
| 6 | "LENELEKTRO LE2" | 2 |
| "Neva MT 1" | 2 | |
| Three-phase | ||
| 1 | Echelon EM-1023 | 10 |
| "Neva 306 1SO" | 10 | |
| 2 | "Matrix np545" | 8 |
| 3 | "Mercury 230 AM-01" | 7 |
| 4 | "Mercury 231 AT-01I" | 5 |
| 5 | "Scat EKF 301m/1-10 (100) w" | 4 |
Classification and types of electricity meters
Electric energy meters can be classified according to the following principles:
1. Based on the operating principle:
- induction
- electronic (static)
2. According to the accuracy class of meters:
- workers
- exemplary
The meter's accuracy class is its greatest permissible relative error, expressed as a percentage.
In accordance with GOST R 52320-2005, GOST R 52321-2005, GOST R 52322-2005, GOST R 52323-2005, active energy meters must be manufactured with accuracy classes of 0.2S; 0.2; 0.5S; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 reactive energy meters - accuracy classes 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 (GOST R 5242520-05).
3. For connection to electrical networks:
- single-phase (1ph 2Pr single-phase two-wire)
- three-phase – three-wire (3ph 3Pr three-phase three-wire)
- three-phase – four-wire (3ph 4Pr three-phase four-wire)
4. By the number of measuring elements:
- single-element (for single-phase networks (1ph 2Pr))
- two-element (for 3-phase networks with uniform heating (3ph 3Pr))
- three-element (for three-phase networks (3ph 4Pr))
5. According to the principle of inclusion in electrical circuits:
- direct connection of the meter
- transformer connection of the meter:
- connecting the meter to a three-phase 4-wire network using three voltage transformers and three current transformers
- connecting the meter to a three-phase 3-wire network using three voltage transformers and two current transformers
- connecting the meter to a three-phase 3-wire network using two voltage transformers and two current transformers
Energy survey • Energy saving program • Consultation
6. By design:
- simple
- multifunctional
7. By the number of tariffs:
- single tariff
- multi-tariff
8. By type of measured energy and power:
- active electricity (power)
- reactive electricity (power)
- active-reactive electricity (power)
Active power for a 1-phase meter, W: PA1ph2 = UфICosφ
Active power for a 3-phase two-element meter connected to a 3-wire network, W: PA3f3Pr = UAVIACosφ1(UAVIA)+ UСВICCosφ2(UСВIC)
Active power for a 3-phase three-element meter connected to a 4-wire network, W: P3ph4Pr = UАIАCosφ1(UАIА) + UвIвCosφ2(UвIв) + UсIсCosφ3(UсIс)
Counter types:
An electromechanical meter is a meter in which currents flowing in fixed coils interact with currents induced in a moving element, causing it to move at a rate in which the number of revolutions is proportional to the energy being measured.
For example:
Single-phase electric meter SO-505, accuracy class 2.0. Single-phase electric meter SO-1, accuracy class 2.5. Three-phase electric meter SA3U-I670, accuracy class 2.0. Electric meter SR4U-I673, accuracy class 2.0.
Static meter - a meter in which current and voltage act on solid-state (electronic) elements to create output pulses, the number of which is proportional to the measured energy.
For example, a single-phase electricity meter Mercury 201 or Mercury 200.02, accuracy class - 2.0. Or three-phase electricity meter Mercury 230A, accuracy class 1.0. Three-phase electricity meter ALPHA A1R, accuracy class 0.5S.
Multi-tariff meter is an electric energy meter equipped with a set of counting mechanisms, each of which operates at set time intervals corresponding to different tariffs.
Reference Meter - A meter designed to convey the size of a unit of electrical energy, specifically designed and used to obtain the highest accuracy and stability under controlled conditions.
Basic concepts, terms and definitions
Counting mechanism (reading device): Part of the counter that allows you to determine the measured value of a quantity.
The readout device may be a mechanical, electromechanical, or electronic device containing both a memory and a display that store or display information.
The measuring element is the part of the meter that produces output signals proportional to the measured energy.
Current Circuit: The internal connections of the meter and the part of the measuring element that carries the current of the circuit to which the meter is connected.
Energy audit • Energy passport • Energy saving program
Voltage Circuit: The internal connections of the meter, the measuring element part and, in the case of static meters, the power supply part supplied by the voltage of the circuit to which the meter is connected.
Direct connection electric meter (or direct connection): As a rule, a 3-phase electric meter connected to a 4-wire network, with a voltage of 380/220V, without the use of current and voltage measuring transformers.
Transformer meter is a meter designed to be switched on through voltage (VT) and current (CT) measuring transformers with predetermined transformation ratios.
The meter readings must correspond to the value of the energy passed through the primary circuit of the instrument transformers.
Basic concepts of electricity metering
Commercial metering of electricity – metering of electricity for monetary payment for it
Technical accounting of electricity - accounting for monitoring electricity consumption inside power plants, substations, enterprises, for calculating and analyzing electricity losses in electrical networks, as well as for accounting for electricity consumption for production needs.
Meters installed for settlement accounting are called settlement meters.
Meters installed for technical metering are called technical metering meters.
Meters that take into account active electricity are called active energy meters.
Meters that take into account reactive electricity for an accounting period are called reactive energy meters.
A measuring instrument is a technical device intended for measurements.
Measuring complex of electricity metering means - a set of devices of one connection intended for measuring and metering electricity: current transformers, voltage transformers, electric energy meters, communication lines.
Starting current (sensitivity) - the lowest current value at which continuous recording of readings begins
Base current - the current value that is the initial value for establishing the requirements for a directly connected meter
Rated current - the current value that is the initial value for establishing requirements for a meter operating from a transformer
Maximum current is the highest current value at which the meter meets the accuracy requirements established in the GOST R 52320-2005 standard.
Rated voltage - the voltage value that is the initial value when establishing the requirements for the meter.
Requirements for installing an electric meter
In apartments, distribution boards are installed strictly in accordance with the requirements of the regulatory framework. It clearly states that the device must be installed:
- at a height not higher than 1.7 m;
- the contact area of the meter from the floor should not be located below 0.8 m;
- the device must be firmly mounted in the panel;
- the cable to the terminals must be continuous (without twists or connections);
- free access must be ensured for taking readings, maintenance, prevention and repair.
Despite the apparent complexity, choosing an electric meter is quite simple. You just need to prioritize the technical characteristics of the device. But it is not recommended to install it yourself. If you have any questions regarding the right choice, write in the comments and our editors are ready to answer them.
Vortex water meters and their features
Vortex meters can operate stably only if the water in the pipeline is clean and free of abrasive particles that can distort the readings.
Each vortex counter contains a streamlined body. It is placed in a pipe and acts as an obstacle to the flow of water. Further along the flow direction there is a highly sensitive sensor. It reacts to the slightest pressure fluctuations in the flow.
The sensor that is equipped with the vortex counter is characterized by excellent balancing. Even pipe vibration does not affect the accuracy of its readings
When the speed of a moving fluid reaches a certain value, vortices appear outside the obstacle. They are formed alternately from different sides and move with the flow. In this case, zones of low and high pressure appear. This gives rise to a phenomenon called a “vortex street.”
Vortexes appear with a frequency proportional to the speed of the moving flow. The distance between adjacent vortices corresponds to the volume of water flowing during the corresponding period. Therefore, the flow rate can be calculated by multiplying the number of vortices by the volume. The higher the flow speed, the more often vortices occur.
The vortex counter can be improved by adding a temperature controller. In this case, the measurement accuracy will increase when adjusted for temperature.
The average service life of the device is 8 years. The main purpose is to regulate technological processes. It is irrational to use such devices in water distribution in an apartment.
Features of tachometer counters
This type of water meters is the most common. They operate on a simple principle.
Positive and negative characteristics
Mechanical water meters are compact. They can be installed in remote places, so they do not spoil the interior of the room. The simplicity of the design allows these devices to be priced at an acceptable price for most consumers. The error in their readings is insignificant.
Tachometer counters are non-volatile devices. The main element in their design is the impeller placed in the water. The volume of water is calculated by the number of revolutions it makes.
The following characteristics are considered negative:
- blade wear;
- sensitivity to impurities present in water;
- dependence of water meter readings on the magnetic field;
- inability to record instantaneous flow;
- the presence of moving elements in the flow chamber.
Despite the presence of shortcomings, if you follow the verification schedule, the meter can last up to 12 years. The device does not require external power supplies to operate.
Operating principle and design
The main element of the meter is the impeller. It has a perpendicular orientation of its axis relative to the direction of the water supply. The nominal diameter of a device of this type does not exceed 50 mm.
Tachometer meters are installed to measure the flow of both cold and hot water, if we are talking about small volumes. These water meters are not designed for high flow rates.
When an avalanche of water transits through the impeller, it moves in a circle. Each is accompanied by the pouring of a certain amount of liquid through the device. The more pressure the water creates, the faster the impeller rotates.
A sensitive counting mechanism receives information about the number of revolutions through the gearbox, and all changes are shown by the dial.
Devices with an impeller can be single-jet, multi-jet, or combined. First, water is supplied to the input blades in one stream. A magnetic coupling sends a torsional impulse to the counting unit indicator. Experts advise installing such meters on hot water pipelines with a cross-section of 15 to 30 mm.
In multi-jet models, the flow is broken into parts on the way to the impeller. The measurement error decreases because the blades are exposed to the same force. In this case, flow turbulence is completely eliminated.
The device is designed for installation on cold water pipes with a maximum diameter of 50 mm. This water meter is ergonomic and easy to install and dismantle if you need to perform verification.
When the coverage of water use measurements needs to be expanded, a combined type tachometer device is installed. It is understood that with a change in the flow rate, one counter comes into operation. The transition occurs automatically.
A combined meter consists of a main and an additional device. The first is activated by opening the valve when large volumes of water are consumed
There is only one measuring unit, it is highly accurate and sealed, so it works even in flood conditions. For pipe diameters greater than 50 mm, a rotating turbine is installed in the design of the device instead of an impeller. In this case, the water meter is installed along the axis of the main line. The ideal place to install it is at the entrance.
Such meters are installed on pipelines of industrial enterprises with a cross-section of up to 500 mm, where significant volumes of water flow. The direction and angle of the flow is determined by a special fairing.
Dry and wet-propelled devices
Based on the location of the counting device, tachometer water meters are divided into dry and wet running. In the first case, the liquid has no effect on the counting mechanism. The rotational movement from the impeller is transmitted to it through a special magnetic coupling.
The mechanism is protected from corrosion by an impenetrable partition. The model has a fairly high cost, but it can be used even where hot water is supplied, which contains foreign impurities in large quantities.
In addition, the accuracy of the readings of such a device is very high. If there is a need for remote data acquisition, you can include a pulse output device in the system.
Mount the pulse output unit directly at the pipeline inlet. The information transformed into an impulse is sent to the recording device
The module collecting information can be located at any distance from the measurement site.
In a wet-flow device, the counting unit is in constant contact with dirty liquid. This negatively affects the duration of its service. To correct the situation, a filter is installed in front of the meter.
Multi-tariff and single-tariff metering devices
If you are going to buy a multi-tariff meter, then it will definitely be an electronic metering device. The selection criteria in this case are the type of load you have in the apartment and the hours of its use. If you are a “night owl” and not a “lark” or you have powerful electric heating devices that are turned on at night, then your choice will be multi-tariff. The higher price of the meter will be repaid many times in the future.