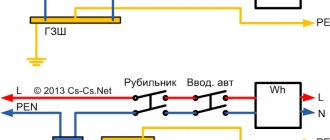
Purpose of the main ground bus (GZSh)
The main grounding bus (GGB) is the most important electrical element of a private home. With a TN-CS power supply system, which is the main one for power supply to the private sector, the necessary separation of the PEN conductor is necessary. And also re-grounding must be done precisely on the main ground bus (GZSh)
In general, on the main ground bus (GZB) with the TN-CS system, all conductors from the protective systems of the house converge. This is a grounding conductor, and conductors from the potential equalization system and a conductor from the arrester (voltage limiter).
GZSH Catalog | Main grounding bars without housing
We manufacture copper ground bars for various applications in the electrical industry.
Copper, known for its conductive qualities, is an ideal material and is often the most popular for busbars that need to be able to conduct electricity as easily as possible thanks to freely moving electrons. Copper is also a particularly strong material with a high threshold for damage from high temperatures, which increases the life of the tire.
Production of main grounding busbars GZSh to order 1-3 days (if copper busbars are available in warehouses)
You can send your application and company card by email
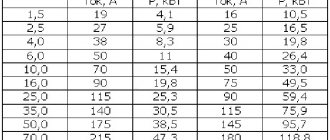
TABLE OF CURRENTS FOR RECTANGULAR COPPER BUS BAR
BUS SECTION, mm DC, A ALTERNATING CURRENT, A
Permissible current copper bus 15×3 210 210 Permissible current copper bus 20×3 275 275 Permissible current copper bus 25×3 340 340 Permissible current copper bus 30×4 475 475 Permissible current copper bus 40×4 625 625 Permissible current copper bus 40 ×5 705 700 Permissible current copper bus 50 × 5 870 860 Permissible current copper bus 50 × 6 960 955 Permissible current copper bus 60 × 6 1145 1125 Permissible current copper bus 60 × 8 1345 1320 Permissible current copper bus 6 0×10 1525 1475 Valid current copper bus 80×6 1510 1480 Permissible current copper bus 80×8 1755 1690 Permissible current copper bus 80×10 1990 1900 Permissible current copper bus 100×6 1875 1810 Permissible current copper bus 100×8 2180 2080 Permissible current copper bus 100× 10 2470 2310 Permissible current copper bus 120×8 2600 2400 Permissible current copper bus 120×10 2950 2650
If you could not find a suitable copper bus model, you can send us a request to manufacture the required configuration. Send your application by email
Indicating the bus dimensions, quantity and connection dimensions.
The good electrical conductivity of copper bars is due to low electrical resistance. Electric current flows through all metals, however they all have some resistance, which means that the current must be pushed (from a voltage source) in order to continue flowing. The greater the resistance, the harder we must press (and the less current). Due to the low electrical resistance, current flows easily through copper without significant energy loss. This is why copper busbars have become widespread in the energy sector. Where size is important and not weight, copper is the best choice. The thick copper strip allows large currents to pass through without melting.
Delivery within Russia - we ship on the day payment is received, if the product is available. Delivery directly from the manufacturer's central warehouse.
Installation of the main grounding bus (GZSh)
The main grounding bus (GZSh) is installed inside the input distribution device (IDU) or separately. When installed separately, the main ground bus (GGB) is installed in a special housing that resembles a small box.
Important! According to the PUE (clause 1.7.119), open installation of a gas shield is possible only in a special room. But even in this case, the installation site of the open gas shield must be protected from accidental contact.
If there are several power supply inputs in the house, then a separate main grounding bus (GZSh) is installed at each input. Also, cables from the potential equalization system are routed separately to each bus.
Main ground bus (GZSh)
To bookmarks
What is the main grounding bus (GGB) and why is it needed?
According to the PUE (clause 1.7.37.): The Main Grounding Bus (GZSh) is a bus that is part of the grounding device of an electrical installation and is intended for connecting several conductors for the purpose of grounding and potential equalization.
As follows from the definition, the GZSh must be grounded by connecting it to a grounding device, and the GZSh, in turn, is connected to grounding conductors, as well as conductors of the potential equalization system.
2. Requirements for the main grounding bus (GZSh) (clause 1.7.119. PUE):
1) Material and cross-section of GZSh:
- The main grounding bus should, as a rule, be copper. It is allowed to use a main grounding bus made of steel. The use of aluminum tires is not permitted .
- The cross-section of the main grounding bus must be no less than the cross-section of the PE (pen) conductor of the supply line.
2) GZSh design:
- The design of the bus must allow individual disconnection of the conductors connected to it. In this case, disconnection should only be possible using a tool.
3) Place of installation of the main gearbox
- The main grounding bus can be made inside the voltage input device of the electrical installation or separately from it.
- Inside the input device, a PE bus should be used as the main grounding bus. ( See an example of a GZSh inside the input device of a residential building here ).
- When installed separately, the main grounding bus must be located in an accessible, convenient place for maintenance near the input device.
- In places accessible only to qualified personnel (for example, switchboard rooms of residential buildings), the main grounding bus should be installed openly. In places accessible to unauthorized persons (for example, entrances or basements of houses), it must have a protective shell - a cabinet or drawer with a door that can be locked with a key. There must be a sign on the door or wall above the tire:
An example of an openly installed GZSh:
An example of a GZSh installed in a separate box (panel):
Note: If the building has several separate inputs, the main grounding bus must be made for each input device. These buses must be connected by a potential equalization conductor, the cross-section of which must be at least half the cross-section of the PE (pen) conductor of the line among the substations extending from the low-voltage switchboards that has the largest cross-section. To connect several main grounding buses, third-party conductive parts can be used if they comply with the requirements of clause 1.7.122 of the PUE. (clause 1.7.120. PUE)
Was this article useful to you? Or maybe you still have questions ? Write in the comments!
Didn’t find an article on the website on a topic that interests you regarding electrical engineering? Write to us here. We will definitely answer you.
↑ Up
5
https://elektroshkola.ru/zazemlenie/glavnaya-zazemlyayushhaya-shina-gzsh/
Connections on the main ground bus (GZSh)
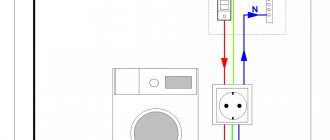
The main purpose, so to speak, of the main grounding bus (GZB) is to separate the PEN conductor of the power cable. The PEN conductor, after cutting, is connected to a pre-installed GZB.
Connection is made using bolts, washers, and nuts. It is advisable to use a locking washer to fix the bolted connection of the main frame (see photo). All connections on the GZSh must be made with bolted fastenings. Each cable connected to the GZSh must have a separate connection.
Note: Bolted connections are needed so that at any time you can disconnect any protective cable separately and make the necessary control measurements (insulation resistance, current flow resistance, etc.)
When installed inside an input distribution device (IDU), the main grounding bus (GGB) is installed directly on the IDU body and has electrically conductive contact with it. (Read in detail about the configuration of the ASU).
A working zero bus (N) is installed next to the main ground bus. The N bus is connected to the main ground bus (GZSh) on which the PEN conductor is separated.
Box of main grounding bars GZSH-21
The PromElectroService NKU company is a certified manufacturer of electrical panel equipment 10/6/0.4 kV. We have at our disposal 3 production sites in St. Petersburg (more than 1600 m2), a large staff of engineers and installers. We offer you competitive prices, high quality electrical panels and prompt delivery times.
Contacts
The most important requirement in the electric power industry is human safety. For these purposes, thousands of engineers and designers around the world are coming up with ways to protect people from electric shock - creating new types of RCDs and diffs. automatic machines, voltage relays, surge suppressors, produce new types of electrical insulating materials, etc.
But all this does not matter if all electrical installations in the building are not properly grounded, including metal sewer and heating pipes, lightning protection systems, metal housings, and air ducts of ventilation systems. For these purposes, boxes of the main grounding bus GZSh .
Material for making GZSh
The preferred material for GZSh is copper. It is possible to manufacture the GZSh from steel. It is prohibited to use aluminum tires for main guns. The ban on aluminum for busbars logically leads to a ban on the use of aluminum lugs for electrical cables connected to the main bus.
©Elesant.ru
Normative references
- PUE, Electrical Installation Rules, edition 7
- GOST 121.030-81, Electrical safety. Protective grounding. Zeroing
Other articles in the section: House electrical wiring
- 26 Rules for power supply and wiring of a wooden house. part 1, rules 1-7
- 26 Rules for power supply and wiring of a wooden house. part 2, rules 8-13
- 26 Rules for power supply and wiring of a wooden house. part 3, rules 14-26
- Anchor clamps and brackets
- Fittings for SIP 2
- Inserting cables from the trench into the house
- Input device. VU for a private house
- VRU. House input and distribution device
- GZSH. Main Grounding Bus
- Deep ground electrode
What is GZSH?
The main grounding bus (GZSh) is a part of the grounding device of an electrical installation up to 1 kV, intended for connecting several conductors for the purpose of grounding and potential equalization in the TN-CS and TN-S grounding systems. The GZSh bus can be installed in the input electrical panel (MSB, ASU) or in a separate housing of the GZSh cabinet. The cross-section of the GZSh bus should not be less than the cross-section of the neutral working or protective conductor of the input supply line.
The main task of the GZSh is to provide zero protective potential relative to the ground at the entrance to the building or electrical installation. The presence of main switchboards is one of the key requirements for main distribution boards.
PUE requirements
In the rules for the arrangement of electrical installations, paragraph 1.7.119 defines all the basic requirements regarding the arrangement of the main grounding bus of the main power supply system in networks with a power of up to 1 kW. The system is located in the control cabinet of a specific device. In case of a large number of grounding conductors, installation in a separate additional cabinet is allowed.
For systems implemented on the basis of TN-C, the PE bus is used as a main bus. But it should be taken into account that the PE cross-section must be larger than the wires themselves. It is recommended to use copper for arranging the main building. Steel is installed less often. But aluminum is the biggest mistake. This material is strictly prohibited for use in these conditions.
All connections must be removable. They are usually bolted on. The wires are crimped to the lugs and then screwed onto the busbar. A symbol indicating the grounding bus must be placed on the wall next to the latter.
Paragraph 1.7.120 determines that for rooms with two or more inputs a separate bus must be equipped. It is necessarily connected by conductors at various distribution devices. Metal structures can be used to connect buses from various devices. But only on condition that they are non-removable and have constant electrical contact. At the same time, it is prohibited to use oil/gas/water pipelines, heating systems, cable sheaths, cables and supporting structures of cables as grounding conductors. It is worth paying attention to an important nuance.
This is a common mistake when arranging the main grounding bus of the GZSh - the rules for electrical installations (clause 1.7.20) allow these structures to be grounded to the main bus. However, connecting them directly from different cabinets using these structures is strictly prohibited. This is stated in paragraph 1.7.123 of the electrical installation rules.
Expand catalog and diagrams
| type | diagram (drawing) | Nom. current A | elements on the diagram | Dimensions HxLxB mm | |
| Designation | Name | ||||
| Box GZSH-10 -1-10 | 340 | P.E. | Ground bus; 3×25 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-10 -3-10 | 625 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4×40 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-10 -3-20 | 625 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4×40 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-10 -4-10 | 860/870 | P.E. | Ground bus; 5×50 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-10 -5-10 | 1475/1525 | P.E. | Ground bus; 50×10 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-10-2-10 | 475 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4×30 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-21 -1-20 | 340 | P.E. | Grounding bus: 3×25 20 connections | 395x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-21 -2-20 | 475 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4×30 10 connections | 395x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-21 -4-20 | 860/870 | P.E. | Ground bus; 5×50 20 connections | 395x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-21 -5-20 | 1475/1525 | P.E. | Ground bus; 50×10 10 connections | 395x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-8 -01-8 | 340 | P.E. | Ground bus; 3×25 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-8 -02-8 | 475 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4×30 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |
| Box GZSH-8 -03-8 | 625 | P.E. | Ground bus; 4x 40 10 connections | 265x310x120 | |