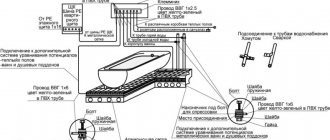
A washing machine, an electric heated towel rail and a water heater are often installed in the bathroom. Often, many apartment owners also install an electric floor heating system in the room, purchase hydromassage bathtubs and shower panels, and sometimes even special audio and video systems.
Low-power devices (for example, lighting), in principle, can be connected via a step-down transformer, but in practice, household appliances are always powered from a 220 V network. Such equipment poses a potential danger, especially during water procedures, when the humidity in the room increases sharply, Condensation will form and water may splash onto sockets and switches.
To protect yourself from negative consequences, including electric shock and a short circuit that can lead to a fire, a separate, necessarily grounded electrical line should be laid in the bathroom.
Practical advice for installing difavtomats
New houses are equipped with grounded sockets and a panel with protective devices.
All that remains is to select an outlet and find out which machine it is connected to. If there is an RCD there, it needs to be dismantled and a circuit breaker installed. In old houses everything is much more complicated. There is no grounding, there is no automatic protection either. They start with installing the ground loop. Three galvanized pipes are installed near the house or in the basement. Their length is from 50 cm. The pipes are positioned so that they are the vertices of a triangle. If it doesn’t work out, you can do it on one straight line. A wire is screwed to one pipe using a bolt - it is pulled into the apartment, to the panel.
The European socket for the washing machine is connected to the automatic machine installed in the panel specifically for this purpose. The device is selected taking into account the current consumed by the equipment. It is determined based on the rated power. Power, kW, is divided by voltage, V. Then 20% is added - this will be the average current. Take the option with a current equal to the calculated value or slightly greater.
Rules for choosing ouzo
The most frequently asked question when installing and connecting washing machines: is it necessary to install an RCD for a washing machine? The answer is simple - yes, it is necessary. After all, the washing machine itself is a fairly energy-consuming device, and also operates in an environment with high humidity, due to which it belongs to the category of increased danger. That is why the installation of an RCD is necessary when connecting washing machines to the power supply network.
In order for the washing machine to serve for many years, and its operation to be safe, it is important to choose the right residual current device. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- Device power. The choice of RCD for a washing machine based on power is based on the rated power of the electrical network. There are single-phase and three-phase devices.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase RCDs are designed for 220 V, and three-phase RCDs are designed for 380 V.
- Current strength. The most common RCDs, which are recommended by experts, have 30 mA protection. It can be set to 10 mA, but a similar degree of protection is not required for household electrical equipment.
- Design features of the RCD. Since the washing machine has a high level of power consumption, it is better to choose a class A residual current device. It is also possible to install class AC, but this type does not always perform its function well.
- Features of the release and marking of the machine. An RCD marked “C” is suitable for the electrical network in an apartment or private house. There are also devices with digital markings; in this case, the correct choice would be a device with a C16 marker or, more rarely, a C25.
- Additional levels of protection. Some RCD models do not have a protection system in case of a break in the neutral conductor, which leads to the device ignoring current leaks.
Electrical safety of the bathroom based on RCD
Let us remind you once again that the task of the RCD is to monitor the condition of the power line, and if leakage currents are detected, to automatically disconnect the power line. Two types of RCDs are offered for sale:
- RCD type A (for example, RCD ID 2p 25A 10mA A 23353);
- RCD type AC (for example, RCD ID 2p 100A 300mA village 23035).
For electrical protection of the bathroom, of particular interest are, of course, type A RCDs, which are capable of responding to both AC and DC leakage currents. This efficiency of type A RCDs also led to an order of magnitude more complex electrical circuit, which in turn was reflected in the price, which is significantly higher than AC type RCDs.
The need to use RCD A is almost always indicated in the operating instructions for the washing machine.
In addition to standard RCDs, which are located inside electrical distribution panels, it is quite possible to come across another type of protective devices in everyday life, namely RCD electrical sockets. Taking into account the installation features, this type of RCD is divided into two classes:
- sockets with RCD, which are installed instead of a standard electrical outlet;
- sockets with RCDs, which are installed in an existing socket, and plugs of household electrical equipment are already connected to them (adapter with protective shutdown RCD-DPA16).
Such devices are attractive because, first of all, they make it possible to solve the issue of replacing electrical wiring in those houses and apartments of old buildings, which, in terms of its characteristics (or operating condition), does not meet the requirements of the PUE. The disadvantage of RCD sockets is their relatively high cost. Sockets with built-in RCDs, for example, can be found in the range of modern electrical equipment from such well-known manufacturers as
Here I will talk about the most common errors when connecting RCDs (“devices”) in electrical circuits of residential premises. Arising when renovating an apartment, renovating a kitchen, renovating bathrooms and connecting individual electrical appliances (washing machines, dishwashers).
Features of grounding connection in an apartment
If the building is new, and the panel contains N and PE buses, this is where the grounding of the water heater in the apartment ends.
In old buildings, the closest ground loop is at the power substation; there is none in the house, and the wiring contains only two wires. The scheme proposed for a private house will not work, because it will not be possible to make your own ground loop with your own hands. But how can you ground a washing machine or boiler if there is no grounding?
The option of using the floor distribution panel housing is unreliable. All because of the same probability of getting a potential on it when the zero is broken. Therefore, it would be right if you hire an electrician from the management company.
In any case, you can completely protect yourself by installing an RCD on the power line. Leave the grounding conductor in the cable unconnected - it may still be useful.
Grounding purpose
An electrical line using grounding is laid using a three-wire cable. Each cable wire connects the elements of its circuit and is: phase (L), neutral (PE) and ground (PN). The value that appears between the phase wire and the neutral wire is called phase voltage. It is equal to 220 volts or 380 volts, depending on the type of system.
These parts may become live if the equipment itself or the wiring insulation fails. If there is a PN connection, there will actually be a short circuit between the phase wire and ground. The current, choosing the path with the least resistance, will flow into the ground. This current is called leakage current. When touching metal parts, the voltage on them will be less, and, accordingly, the value of the damaging current will be less.
Grounding is also necessary for the operation of devices such as RCDs. If the conductive places of the devices are not connected to the ground, then no leakage current will occur and the RCD will not operate. There are several types of grounding, but for domestic use only two are common:
- TN-C. A type in which the neutral and ground conductors are combined with each other, in other words, grounding. This system was developed in 1913 by the German company AEG. A significant drawback is that when the zero is opened, a voltage appears on the device housings that exceeds the phase voltage by 1.7 times.
- TN-S. The type, developed by French engineers, was introduced in 1930. The neutral and ground wires are independent of each other and are separated from each other at the substation. This approach to organizing a grounding contact made it possible to create differential current (leakage) metering devices that work on the principle of comparing the magnitude of current in different wires.
As often happens, in high-rise buildings only a two-wire line is used, consisting of a phase and a neutral. Therefore, to create optimal protection, it is better to additionally perform grounding. To make the grounding line yourself, a triangle of metal corners is welded. Its recommended side length is 1.2 meters. Vertical posts with a length of at least 1.5 meters are welded to the vertices of the triangle.
Thus, a structure is obtained consisting of a vertical and horizontal grounding strip. Next, the structure itself is buried in the ground with columns down to a depth of at least half a meter from the surface to the base of the triangle. A conductive busbar is screwed to this base with a bolt or welded, serving as the third wire connecting the device housings to the ground.
RCD connection diagram.
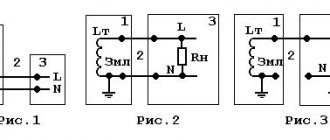
There are several RCD connection schemes. All of them are used quite often in practice, and now we will consider all of these schemes.
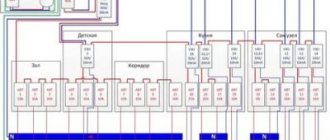
This is the most common RCD connection diagram. In this case, the device will protect a person from electric shock throughout the entire apartment. The current rating of the RCD is one order of magnitude higher than the current rating of the input circuit breaker. If in the RCD it is 40A, then in the circuit breaker it is 32A. The current rating can be increased depending on your current consumption needs. But the rating of the RCD should always be higher.
This scheme is good because it is budget-friendly. Since it only requires one RCD. But it also has its drawbacks. When your residual current device starts tripping, it will be very difficult to determine the cause of the trip. Since one device is responsible for the entire apartment or house.
Therefore, rich people choose the following RCD connection scheme.
From this diagram it can be seen that each group of sockets or lighting is responsible for its own RCD. And in front of it there must be a circuit breaker with a high current rating. And at the input there is a so-called fire protection RCD, where the differential shutdown rating is 100 mA.
In this case, you can separately install an RCD in rooms with high levels of humidity, where a differential shutdown rating of 10 mA is recommended. And separately for sockets and lighting in rooms with a shutdown rating of 30 mA. And if an RCD trips in a separate group of sockets, then it will be easier for you to establish the reason why it tripped. And you don’t need to turn off the power to the entire apartment.
Many people once lived without an RCD and felt protected. Because we followed basic safety rules. Then they began to use such protection as grounding and life became even better. But in those days, sockets were rarely installed in bathrooms. Now they are being installed more often and the demand for RCDs has increased. Therefore, many people believe that this device must be installed in rooms with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms. And they install it not for the entire apartment, but only for one room.
From this diagram it can be seen that the RCD is installed only for the bathroom. If you have a group of sockets in the bathroom, then install an RCD with a differential shutdown rating of 30 mA, and if you have only one socket, or more, but basically only one is always working, then install an RCD with a rating of 10 mA.
Basic concepts about RCD
Firstly, residual current devices can be electronic or electromechanical. We will talk exclusively about the electromechanical type of protective devices, because electronic ones are inferior to their electromechanical ones and additionally require power supply at the input of work.
Secondly, the operating principle of electromechanical protective devices is based on a comparison of currents in phase and neutral (zero). If their amplitude (leakage) is higher than the value in the characteristics of the “device” indicated on the facade of the device, then the device relay is activated and turns off both phase and zero.
You must understand that in three-phase protective devices, the current amplitudes in individual phases are summed up and compared to “zero”.
It is important to note that the RCD can also operate when the phase is off (the circuit breaker is switched off) if the current is “zero” or “breaks through.”
Thirdly, the total value of the network leakage current, taking into account the connected stationary and portable power receivers in normal operation, should not exceed 1/3 of the rated current of the “device”.
In the absence of data on the leakage current of electrical receivers, it should be taken at the rate of 0.3 mA per 1 A of load current, and the network leakage current at the rate of 10 μA per 1 meter of phase conductor length.
Fourthly, selectivity requirements must be consistently met. In two- and multi-stage circuits, the one located closer to the power source must have a setting and response time no less than three times greater than that of the “device” located closer to the consumer.
More information
It is unacceptable
to use RCDs in group lines that do not have overcurrent protection without an additional device that provides this protection . 6. In residential buildings, as a rule, “devices” of type “A” should be used. They react not only to alternating currents, but also to pulsating damage currents. The source of pulsating current is, for example, washing machines with speed controllers, adjustable light sources, televisions; video recorders, personal computers, etc. The use of RCDs of the “AC” type, which respond only to alternating leakage currents, is allowed in justified cases. 7. RCDs, as a rule, should be installed in group networks that supply power sockets. Installing it in lines supplying permanently installed equipment and lamps (with the exception of bathrooms), as well as in general departmental lighting networks, is usually not required.
Why install a separate protective device?
Modern homes are literally filled with various equipment and household appliances, many of which are highly powerful. In this regard, the load on the electrical wiring increases significantly, and the likelihood of damage and failure of the insulation after a certain period of operation increases. As a result, the wiring through the damaged insulation is connected to the ground, and the flow of current changes its direction, that is, a current leakage occurs. When coming into contact with dangerous places, a person himself becomes a conductor and can receive serious injuries.
Modern washing machines are also among household appliances with increased energy consumption. They gain maximum power in the range of 3-3.5 kW during operation of the heating element and heating of water. If the insulation is damaged, current leakage can also reach a large value that is dangerous to human life. Therefore, experts recommend installing a separate RCD on the line supplying the washing machine. In the event of a leak, the RCD will simply turn off the network and stop supplying voltage.
To connect the RCD with the consumer into a single circuit, a serial connection is used. The principle of operation of the device is based on measuring and comparing the difference in current at the input and output. If the network is healthy, it will have a zero value. And in the event of a leak, the output current will differ downward by exactly the amount that went along the other path. When the current leakage value for which the device is installed is reached, it will instantly react and turn off the network.
Malfunctions
There are often cases when the RCD turns off when the water heater or washing machine is turned on. There are a number of reasons for this:
- the water heater or machine itself is faulty;
- the installed RCD or automatic circuit breaker does not correspond to the parameters of the electrical network;
- there is a short circuit in the power cord;
- the motor, power supply or heating element is damaged;
- the installation of the RCD for the washing machine or water heater was carried out with errors;
- Voltage surges or current leaks have occurred in the electrical network.
An example of finding and eliminating one of the faults in which the RCD of a water heater knocks out is shown in the video:
If you choose and install the RCD correctly on the boiler and washing machine, you will ensure the operation of the equipment for a long time during washing and heating water, and protect against current leaks and fires. And most importantly, protect people from being exposed to electricity. Therefore, think about protection in advance so that you don’t have to deal with the consequences later.
Feel free to install a 10mA RCD with a rated current of at least 16A (that is, your RCD can be installed).
Read why to install a 10mA RCD in the table at the bottom of the post. After reading, you can consciously set it to at least 300mA - no one will forbid you. After 5 years, if the RCD starts to trip, read the table below again and replace the RCD or repair the washer/boiler/wiring. I hope I helped you with your choice)The nature of the effect of electric current on the human body:
0.6-1.5 mA
Alternating current
— Mild itching, tingling of the skin under the electrodes
Direct current
— Not felt2.0-4.0 mA
Alternating current
— The sensation of current spreads to the wrist, slightly cramps the hand
Direct current
— Not felt5.0-7.0 mA
Alternating current
— The pain intensifies in the hand, accompanied by cramps.
Mild pain throughout the arm. It is possible to overcome the convulsive contraction of the muscles and unclench the hand in which the electrode is clamped Direct current
- Weak sensation of heating the skin under the electrode8.0-10 mA
Alternating current
- Severe pain and cramps in the entire arm.
Difficult, but possible to remove your hand from the electrode Direct current
- Increased sensation of skin heating10-15 mA
Alternating current
- Barely bearable pain in the entire arm increases over time.
Can't take your hand off the electrode Constant current
- Even more intense heating sensation both under the electrodes and in surrounding areas of the skin20-25 mA
Alternating current
“Your hands are instantly paralyzed; it is impossible to tear them away from the electrodes.
Severe pain, difficulty breathing Direct current
- Even greater heating of the skin, a sensation of internal heating. Minor contractions of the arm muscles25-50 mA
Alternating current
- Very severe pain in the arms and chest.
Breathing is extremely difficult. If the current flows for a long time, respiratory paralysis or weakening of the heart with loss of consciousness may occur. Direct current
- A feeling of intense heating, pain and cramps in the hands. When you remove your hands from the electrodes, barely bearable pain occurs as a result of convulsive muscle contractions50-80 mA
Alternating current
- Breathing becomes paralyzed within a few seconds.
The work of the heart is disrupted. With prolonged current flow, cardiac fibrillation may occur. Direct current
- A feeling of very strong superficial and internal heating, severe pain in the entire arm and in the chest area. Difficulty breathing. It is impossible to take your hands off the electrodes due to severe pain when contact is broken100 mA
Alternating current
Direct current
- Respiratory paralysis due to prolonged current flow300 mA
Alternating current
- The same effect in less time
Direct current
- Heart fibrillation after 20-30 s; after a few more seconds - respiratory paralysisMore than 5000 mA
Breathing is paralyzed immediately - within a split second. Cardiac fibrillation usually does not occur; temporary cardiac arrest is possible during the flow of current. If the current flows for a long time (several seconds), severe burns and tissue destruction occur. The outcome is usually fatal
The incompatibility of water with electricity, and especially in the presence of a person, raises great concerns. Installation errors or malfunctioning connectors in the bathroom can have tragic consequences. Let's talk about the rules of safe electrical wiring, the nuances and specifics of installation.
Two main elements of protection
The correct choice of materials and the quality of wiring installation are fundamental aspects in any home, and even more so in the bathroom.
There are two main points here that must be observed: a residual current device, briefly called an RCD, and the presence of grounding. You cannot choose just one; during installation you must use both elements together. RCD for the bathroom
An RCD will protect against electrical damage if minor phase damage occurs in live conductors or if contacts or insulation in electrical equipment are broken. This device instantly reacts to the potential difference that occurs when current leaks.
It is advisable to install not only one RCD for the entire flow into the house/apartment, but also separately for the bathroom. The principle of operation is to block the supply of electricity in the event of any violation; the shutdown reaction occurs in milliseconds, even if the neutral wire is shorted with a metal object.
Grounding
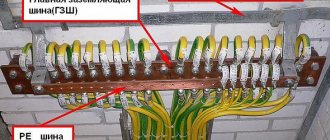
The specificity of the wiring is the use of a three-core cable, which provides for the presence of zero, phase and ground. The wires are different colors, so there is never any confusion in the connections. The earth is in the shield and goes to the metal object.
Installation principles
There are no particular difficulties in the work, but it is important to maintain consistency.
Firstly, you need to take into account the main rule: do not install any junction boxes or panels in the bathroom - everything is moved outside. Otherwise, no matter how thoroughly the connections are soldered and the contacts are carefully insulated, it is impossible to create complete tightness in the boxes. Over time, condensation and moisture will reach their goal and oxidize the contacts. Accordingly, the current can reach the surface, which is extremely dangerous. All wires must be pulled through the walls and connected directly to the device only in the right place. Secondly, you need to rationally distribute the load. It is clear that the bathtub has great functionality. There are not only water taps, but also sockets for powerful consumption: hair dryer, washing machine, electric shavers, possibly water heaters. Accordingly, the electrical circuit should be built according to the load principle. To do this, a number of circuit breakers are installed and an RCD is installed in front of them without fail. All machines are connected in parallel, and the RCD is included in this circuit in series.
Each group of high consumers (more than 1.5 kW) has its own individual machine. For example, a boiler for heating water, a washing machine, and a socket for a hair dryer must have their own device; a separate one is provided for lighting.
Selection of equipment for electrical installation
When purchasing lamps and other equipment, you should only choose those that have a three-pin connector for installation at the output.
It is not recommended to use two-wire terminals because there is no ground wire. Experts recommend setting the lighting to 12 V in conditions of high humidity; this is not only economical, but also safe, so choose diode devices and lamps. To do this, the distributor will require a step-down transformer. If you prefer lamps powered by 220 V, then be sure to buy ones with a sealed housing that protects against condensation.
Sockets must also have grounding and preferably moisture protection. Therefore, buy those that have “curtains” in the holes for the plug or the case is equipped with a lid with a rubber seal that limits the flow of moisture. Equipment with a lid prevents penetration even from drops of water running down the walls. The perimeter of the outlet is coated with sealant.
If the cable runs behind drywall, or in voids behind panels, then laying in a corrugated sleeve or special mounting boxes is required. This will protect against mechanical stress, and in the event of a fire, even a plastic corrugation will limit the supply of oxygen and protect against fire.
Why should the power supply of the bathroom be especially careful? The answer to the question is obvious - the bathroom, due to its small size and constant high humidity, is a room where electric shock is more likely, and most importantly - more dangerous than in other rooms of the apartment or house.
Therefore, in the presence of such electrical household appliances as electric water heaters, washing machines and others that receive power from a 220-volt network, it is necessary to introduce protective devices and devices. The main measures on this issue are the presence of protective grounding and a residual current device, abbreviated as RCD. And these measures are not just desirable - they are necessary, because... Your health and even your life are at stake. Protection against leakage currents is carried out by RCD devices and automatic circuit breakers with a residual current device. What is the best way to protect your bathroom?
Dangerous area
From the point of view of electrical safety, the bathroom is a room with a high degree of responsibility. This is due to high air humidity and the possibility of uncontrolled splashing of water.
The bathroom space is conventionally divided into zones. There are requirements for the installation of electrical installation devices and lighting by zone, as well as requirements for their design in terms of water resistance:
- in zone 0, directly in the bathtub or shower tray, it is allowed to use devices with a voltage of no more than 12 V, with the highest degree of protection from moisture;
- in zone 1 it is allowed to install water heaters protected from low pressure water jets from all sides;
- in zone 2, within 0.6 m from the edge of the bathtub or shower tray, it is allowed to install lamps with a degree of protection that allows them to be used in the presence of drops and splashes;
- in zone 3, at a distance of more than 0.6 m from a bathtub, sink or tray, it is already allowed to install 220 V sockets protected from drops and splashes.
Due to the increased risk of electrical shock in the bathroom, the requirements for the use of protective devices are quite high.
All electrical devices must be protected by residual current devices (RCDs) or differential circuit breakers, unlike other premises where protection can be organized using circuit breakers of the required rating.
Is it dangerous!
Several reminders and warnings regarding safety precautions when doing electrical wiring yourself.
Attention! Installing sockets, switches, and electrical appliances in the bathroom without using a 10 mA RCD is deadly!
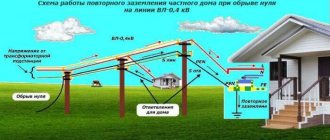
Do not voluntarily connect the neutral wire to your ground. That is, do not re-ground the neutral wire at the input and, accordingly, ground electrical appliances.
In case of emergency situations on the supply line, such as no contact; break of neutral conductor; conductor burnout; erroneous reversal of phase and neutral; overlapping of wires on overhead lines - the only neutral of all houses through your grounding can become your grounded neutral.
If re-grounding is done at home, without following the rules and appropriate qualified tests, the grounding is unlikely to withstand such accidents and may burn out. At best, there will be a fire, and even if it survives, there is no guarantee that it will provide safe touch voltage on open conductive surfaces.
In this connection, it is inevitably fatal and criminally liable for violation of the rules for operating electrical installations, electric shock through electrically connected open conductive surfaces and the risk of fire!
Always remember, when doing any work on electrical wiring, turn off the power supply to the lines, or better yet, the general apartment circuit breaker (this especially applies to old houses). In old houses, the more you work, the more you marvel at the intricacies of the old electrical wiring.
That's all about errors when connecting an RCD! Good luck to you in your endeavors!
Device selection
You should select an RCD for a boiler taking into account the main characteristics of the water heater and the electrical network. Thus, with a properly selected RCD, the operation of the water heater will be safe and reliable. The following requirements for choosing a protective device should be adhered to:
- The power of the device depends on the rated power of the electrical network. They are divided into single-phase and two-phase models.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase RCDs are designed for a boiler operating from a network with a voltage of 220 V, and three-phase ones for a 380-watt network.
- RCD protection degree. It is recommended to use protective devices with a protection level of 30 mA. You can also choose a 10 mA device, but in a domestic situation this level of protection is not always necessary.
- Place of application of the RCD. For a more correct selection of a suitable residual current device, both alphabetic and numerical markings are used. For using an RCD in a private house or apartment, a device with a C16 or C25 marker is suitable.
- Design features of RCD. A water heater is considered an electrical appliance with high energy consumption and therefore it is better to choose class A protective devices. In some cases, you can choose class AC, but such devices do not always cope well with high loads.
Features of the use of difavtomats
In order not to install separately the RCD and the automatic circuit breaker for a washing machine or boiler, you can replace these two switching devices with one device. This is a very popular differential circuit breaker that is widely used in household electrical networks.
The device is combined in one housing and combines the protective effect of both the RCD and the machine.
The difavtomat has one drawback: its high price. That is why many people prefer two switching devices placed in series (an RCD and a conventional circuit breaker).
But you just have to imagine how many automatic devices and RCDs will be needed for the bathroom, if some have a washing machine, a water heater, and an electric boiler there. And in private houses, the room is often adjacent to the bathhouse, where there is a stove. What type of distribution board should there be to accommodate such an amount of automation? It may happen that there is not enough space on the DIN rail for all the devices. Therefore, it is recommended to install a separate automatic switch on the washing machine, boiler and other household appliances in the bathroom.
Pros and cons of RCDs or difavtomats in the following video:
How to ground boilers and washing machines
To power single-phase consumers, two wires are used: phase and neutral. And to connect their bodies to the ground, a third one is added - a grounding one. It connects to the additional, third pin of the plug.
Such a plug also requires a special socket with characteristic antennae - these are the corresponding grounding contacts. Grounding of a washing machine or boiler occurs only through such sockets.
A three-core power cable is laid from the socket to the distribution panel. The yellow-green wire in it serves to connect the ground. In the shield it is connected to the PE bus, used for switching grounding conductors.
Even if the wiring in the apartment is made with three-core cables, you cannot connect to the home electrical wiring locally. The water heater and washing machines still require a personal power cable connected to its own protective device. To protect against leaks, an RCD is additionally installed.
How to choose a protection device
The operating current of the RCD determines the maximum permissible load in the circuit that will pass through it. It must match the power of the water heater.
For example, if a boiler consumes up to 2.3 kW, then the protective device should be rated at 10 A. For heaters of 5.5–7 kW, a 32 A device is needed. But for boilers of 7–8 kW, a 40 A RCD is required.
The two main parameters of a residual current device are the rated “operating” current (in amperes, “A”) and “leakage” (in milliamps, “mA”). In household models they are directly related, but there are also special devices for which this correlation is absent
The leakage current is indicated in mA (milliamps). According to electrical rules, its calculation must be made based on 0.4 mA for each Ampere of operating electric current. Plus, 10 µA per meter of wire to the water heater is added.
It is not for nothing that RCDs are recommended to be installed directly next to the boiler in order to exclude the influence of the second parameter in the calculations.
The shape and size of the protective device under consideration can be mounted on a DIN rail in a switchboard or in the form of a block with a plug in a regular socket.
There are models of water heaters on sale that initially come with RCDs built into the cable. All parameters of such protective devices are already pre-calculated for a specific boiler; they just need to be plugged into a power outlet.
If you don’t have the skills to install electrical wires, then you can use an RCD in the form of an adapter into a socket - there will definitely be no problems connecting the water heater, you just need to choose the right parameters of the protective block
Another point in choosing an RCD is the presence of natural current leaks in almost every electrical appliance. If they exist, they are indicated in the technical data sheet of the water heater.
The nominal parameters of the protection device must exceed these rating data at least three times, otherwise false alarms will constantly occur.
Among the best manufacturers of differential switches are:
- Swedish-Swiss ABB;
- French Legrand and Schneider Electric;
- German Siemens and AEG;
- Russian "KEAZ", IEK and DEKraft.
European manufacturers have slightly higher prices. At the same time, products from Russian companies are often in no way inferior in quality.
What is the difference between a shutdown device and a difavtomat?
Both types of devices are designed to protect against electric shock when a leakage current to ground occurs, and to disconnect the load in this case. That is, they protect us from electric shock in case of damage to the insulation, and in the case of a bathroom, in case of breakdown through moisture. However, the differential circuit breaker has one more, perhaps main, function - disconnecting the consumer when the load current exceeds the rated one for a given circuit breaker and there is a short circuit.
Differences in Features and Settings
The main characteristics of an RCD are sensitivity (minimum leakage current at which it triggers) and rated operating current. For the bathroom, you should choose devices with a sensitivity of 100 to 300 mA and a rated current equal to the current consumption of all connected electrical devices. For example, if you plan to install a washing machine in the bathroom, the operating current of the device is selected equal to 16 amperes.
The main characteristics of an AV with a differential block are the operation (shutdown) current and the differential shutdown current. There are machines with operating currents from 1 to 300 A and settings for shutdown by leakage current of 10 and 30 mA.
So, the main differences between the RCD and the automatic differential switch:
- both devices will protect us from electric shock, but the machine will also turn off the load if the power consumption exceeds the norm; the first one will simply fail during long-term operation in this case.
- the difference in leakage response currents (for AVs is much less) also limits the scope of application of both devices.
- significant difference in cost.
How to distinguish RCD from differential. machine - watch the video:
What to use to protect electrics in the bathroom
In relation to the power supply of powerful devices in the bathroom, it is more advisable to install a separate RCD unit, as a device specially designed and intended for these purposes. In addition, the high sensitivity of differential protection in an AB can provoke false alarms when connecting a washing machine, mainly due to high-frequency interference from its electronic components; by the way, this is why it is not recommended to install differential circuit breakers in the computer’s power supply circuits. The area of application of differential circuit breakers is electrical lighting circuits.
Connection diagram of the residual current device. To connect the protection device, it is necessary to have a third protective conductor in the circuit. When turned on without this wire, the device will not perform its functions.
Which denomination to choose
The minimum dangerous current value for the body is 100 mA. An RCD or difavtomat will allow you to turn off the power supply when the leakage current reaches 30 mA, regardless of what rated current any of these devices are designed for.
The specified value of the differential current - 30 mA, is the minimum in accordance with the requirements of the PUE (electrical installation rules) for use in residential premises. But to ensure greater safety, experts recommend using an RCD for the bathroom with a differential current of 10 mA.
The fact is that a person, having felt the effect of electricity, can instinctively make uncontrolled movements. If you are in a confined space in the bathroom, and even on a wet, slippery floor, this can lead to injury. And when exposed to a current of 10 mA, the reaction may be less intense.
Parameters and characteristics of difavtomats
To decide which RCD to install for a washing machine or water heater, first familiarize yourself with the basic parameters and characteristics of the device:
Depending on the network in which the difavtomat will be installed (single-phase or three-phase), a two-pole device (for an operating voltage of 220 V) or a four-pole device (380 V) is selected.
Please note that the rated operating voltage must be indicated on the device body
- Rated current. This is the amount of current, measured in amperes, that can pass through a switching device over a long period of time. The standard range of rated currents is as follows: 6, 10, 16, 20, 32, 40, 50, 63 A.
- Time-current characteristic (“B”, “C” or “D”), this parameter expresses the dependence of the response time of the machine on the current flowing through it.
- Rated differential current. This is the amount of current leakage to which the difavtomat will react and turn off. There is also a standard range of differential current - 10, 30, 100, 300, 500 mA.
- Rated breaking capacity. This parameter represents the maximum value of short circuit current that the differential circuit breaker is capable of switching off and remaining in working condition after that.
- Temperature Range. It usually varies from – 20 degrees to + 45.
All these parameters are indicated on the device body.
There you will find a connection diagram, the nominal frequency of the power supply (50 Hz), the type of built-in RCD (electronic or electromechanical).
Also, differential circuit breakers are of three types depending on the form of current leakage to which they react:
- “A” – for alternating sinusoidal and constant pulsating current forms.
- “AC” – for alternating sinusoidal current leakage.
- “B” – for alternating sinusoidal, constant pulsating and rectified forms of current leakage.
How does an RCD work and why is it needed?
First, you need to understand the difference between RCDs and circuit breakers.
The machine is the main protection of the power supply network. If overcurrents occur during an overload or short circuit, the switching device will react to the excess current and turn off, cutting off the emergency section and saving the entire network from damage.
The main function of the RCD is to protect not the network, but the person and this device reacts to small values of leakage currents. How does this happen?
Our homes now have a huge number of different household appliances, and some devices have quite a lot of power. Electrical wiring does not have a lifetime; the longer it is in use, the greater the likelihood of insulation failure. Damage to the insulating layer entails the connection of the wiring to the ground, as a result, the path of the current changes, and now it flows to the ground. And in some cases, a person can become a conductor for current leakage.
More clearly about the principle of operation of the device in the video:
Modern washing machines and water heaters are considered equipment with a higher energy consumption class. They take maximum power during the period when the heating element is operating and water is being heated (about 3-3.5 kW). This is a very large load for electrical wiring, which can cause premature aging of the insulation.
Let's assume that the insulating layer breaks down in a washing machine, causing the body to become energized. By touching the machine, a person may be exposed to electricity.
To protect yourself from such a situation, you need to install an RCD for the washing machine.
If a current leak occurs to the ground, the device will turn off and stop supplying voltage.
The RCD is connected to the consumer in one circuit in series, and its operating principle is based on measuring the difference between the input and output current values. Ideally, it should be equal to zero, that is, whatever amount of current comes in is what comes out. As soon as a leak occurs, the output will have a different reading, smaller by exactly the amount of current that went along a different path. The measured difference will change accordingly. As soon as the current leakage reaches the value for which the device is designed, it will immediately react and turn off.
There are no particular difficulties in connecting the device. In the circuit, first there is a circuit breaker, after it there is an RCD, from the output contacts of which the wires go to the consumer, that is, the power outlet for the washing machine or boiler.
Main and additional reasons for triggering
If bare wires come into contact with the housing, the RCD will trip constantly
If the boiler knocks out the machine, the reasons most often are as follows:
- Damage to the insulation of electrical models with heating elements-tubes. The protective layer is destroyed when water comes into contact with conductive components. To check the part, you will need to remove it from the tank and inspect it. Cracks indicate that the heater needs to be replaced.
- Current leaks. They occur when connecting the water heater to old wiring, a cable with exposed wires, mechanical damage to the insulation and installation errors.
- Short circuit of the exposed cable to the housing. When a bare wire comes into contact with the body, the machine will turn off permanently. The phenomenon leads to electric shock.
- The RCD does not comply with the voltage and power parameters. The knockout is periodic - the device simply cannot cope with the load.
- Malfunction of the device itself. The main reasons are wear of the trigger mechanism or a stuck test key.
Why does the RCD of Termex boilers trip?
Termex instantaneous and storage type water heaters are popular due to their ease of connection, tank capacity, good power and low cost. When an RCD is triggered during operation, it is possible that the Termex water heater is damaged or the electrical network is faulty:
- Hull breakdown. If there is grounding, the device will work immediately.
- Broken wiring in the room. Most often the neutral is damaged.
- Mechanical damage to the heating element. The heater coil comes into contact with water in the presence of permanent scale.
- Contact between housing and phase. The shutdown occurs after heating the water.
- The riser ground line is connected to the network zero. If the boiler turns on, there is a risk of injury.
- Malfunction of the RCD itself. Chinese complete devices often fail. They need to be changed.
- Exceeding the load rating. When the boiler, stove and iron are turned on at the same time, protection against network overloads is activated.