How does it work
The engine chambers contain compressed fuel that can ignite. During the combustion process, gases are formed that begin to rotate the crankshaft. Because of this, the alternator rotor begins to work. A magnetic field is generated in the stator.
Electric generator
The result of the processes described earlier is the appearance of an inductive electric current in the winding. It is available for consumption immediately at the device output by any other devices. Trips to nature, backup power supply - situations when such solutions become relevant. In this case, an electric generator is indispensable.
Gas power generators
In industry, not only diesel electricity generators are used, but also gas generators. Their popularity is due to the prevalence and low cost of gas fuel. Almost all gas industrial electric generators, the price of which is not so high, can produce electricity using fuels such as mine associated gases, oil gases, and gases obtained from the processing of organic matter.
Industrial gas electric generators have a simple internal structure. They are made from elements such as a combustion chamber, turbine, compressor and electric motor. The operating principle is as follows:
- The compressor forces atmospheric air under high pressure into the combustion chamber.
- Gaseous fuel is pumped into the combustion chamber, where it is mixed with air.
- The fuel burns, producing flue gas, which is pumped into the turbine and spins it.
- Thermal energy is transformed at the turbine into mechanical energy of shaft rotation.
- Mechanical energy is supplied through the shaft to the rotor, where electrical energy is generated.
A gas-powered electric generator has many advantages, which is why such equipment can be found in many industries. Among the advantages are economical consumption, high environmental friendliness and safety for humans, fairly high productivity and power. Such generators also have a drawback - high requirements for the qualifications of operating personnel, because gas is potentially dangerous.
Generator types
One classification of generators is based on the source from which the energy comes. The current generated as a result of the operation of internal components is also different, which helps to distinguish other groups. Each variety has its own characteristics, positive and negative sides.
Petrol
In most cases, the power of such devices does not exceed 20 kW. The scope of use of the devices is quite wide:
- Country houses.
- Dachas.
- Power supply for hand-held power tools.
- Small machines, and so on.
Lighting of local areas, retail areas, car parks - work that is not a hassle for these types of electric current generators.
Interesting! AI-92 is a brand of gasoline that serves as a standard fuel source for most models. 76 and 95 are types of fuel that are also allowed to be used, but for a short time.
Gasoline generators for alternating current are either mobile or stationary. The wheelset is equipped with units characterized by increased power. Manual start or starter is used equally, depending on the main characteristics of the model. A sound-absorbing casing is used to make the operation of the device less noisy.
Diesel
The power of devices of this class can reach 3 mW. For country houses and dachas these are good sources of constant energy. Powerful woodworking equipment is also often powered by autonomous diesel sources of alternating electric current. The same applies to machines with other purposes. Diesel generators are sometimes used to provide electricity to entire villages.
Internal organization
The installations in this case also differ in stationary or mobile design. A distinctive feature is noisy operation. Therefore, in some cases it is impossible to do without special casings that absorb sounds from electric generators .
Diesel generators differ from their gasoline counterparts in their reduced fuel consumption. And the raw materials themselves are cheaper. Expensive models support additional functions:
- Control of the energy generation process.
- Automatic activation in case of emergency situations.
Gas
When choosing, the main thing is to decide in what mode the equipment will operate on an ongoing basis. Here experts give several recommendations:
- When organizing a complete autonomous power supply to your home, it is recommended to give preference to models with liquid-cooled internal combustion engines, designed for uninterrupted operation.
- Backup models are relevant if the power is often turned off on the site. Usually they cannot work longer than 10-20 hours. After this, a break is required, and routine maintenance cannot be avoided.
You might be interested in the principle of operation and design of a magnetically controlled reed switch
Launch
The devices can operate on liquefied or natural gas. The latter option is more suitable for devices configured for basic energy saving. Reserve options are best used in conjunction with liquefied gas cylinders. Models are now being produced that support both types of fuel at once.
Some allow operation with gasoline. Therefore, there is no need to worry that the owners will be left without electricity.
How does a mixed signal generator work?
The principle of operation of the mixed pulse generator is aimed at accelerating the formation of signals and reproducing them with maximum accuracy. The front panel of the device is equipped with controls for monitoring the most important and frequently changed parameters. Less popular and rarely used functions can be found in the menu on the main screen.
The level control sets the amplitude of movement of the output signal. Amplitude and offset can be adjusted without entering a multi-level menu system.
A separate control also allows you to change the sampling rate by changing the periodicity of the output signal. However, this customizer will not be able to change the form of the latter. This function is only available in the menu on the main editing screen. The shape is selected using the touch panel or mouse. The user opens the desired page and simply fills out the form using the numeric keypad or rotary knob.
Generator classification
There are several signs on the basis of which an electric generator can be classified as one of the varieties:
- Scope of application.
- Operating modes.
- Phasing.
- Autonomy.
For each of the characteristics, you need to study the model in advance, then the choice will be easier to make.
Autonomy
Complete independence from centralized energy sources is one of the main advantages that modern generators have. Depending on this indicator, models are divided into mobile or stationary.
Stationary
We are talking about generating stations, the basis of which are diesel engines. Suitable for supplying electrical energy to consumers remote from other similar facilities. They provide power supply in those areas where even the slightest interruption of production processes will lead to serious negative consequences.
Mobile
Most often, these units are the most compact. Allows movement in the installation space. Mobile stations have a fairly wide range of applications:
- Electric welding.
- Local lighting.
- Supply of current to household electrical appliances, and so on.
An internal combustion engine is installed inside the equipment, which can run on diesel fuel or gasoline. The units differ from each other in size. One person is enough to move only the smallest devices. But there are mobile options, which are installed on car trailers.
Phasing
The units are divided into three- and single-phase depending on the internal structure of the devices.
Single-phase
They are distinguished by their ability to produce single-phase current. Powering household appliances is the main purpose of the devices. Typically, devices are produced as mobile ones to make them easier to handle. Private households are objects within which single-phase units can be found most often. For example, to meet various needs at the household level.
Three-phase
Powering power electrical equipment is the main function. Sometimes such energy is divided into several phases. For powering electrical wiring, this is a very convenient solution that allows you to split the line into several parts.
Interesting! The main thing is that the power consumption of all lines remains approximately the same. The generator quickly fails if there is a serious difference between the values.
Operating modes
Primary and backup are the two main types of operating modes according to this classification.
Basic
Such devices are designed to work on an ongoing basis. The group of industrial installations consists of powerful electric generators equipped with diesel engines. Relevant for facilities that require constant electrical energy.
Reserve
From the name it is easy to understand that such electric generators are used only in some, exceptional cases. For example, if the centralized power supply is turned off for some time. Such devices can turn on if a relay that responds to a decrease in voltage is activated. Continuous operation is only permissible for several hours.
Scope of application
Generators are produced with two main areas in mind: domestic conditions or industrial facilities.
At home
The choice of household generators on the modern market will please any consumer, regardless of scale and requirements. Typically, single-phase installations are chosen that are capable of establishing an uninterrupted supply of electric current in emergency situations. Powering remote electrical equipment is another area of application. The quality of current becomes a particularly important indicator when it comes to household electrical appliances that use a digital element base. In this case, the energy should have the following parameters: 220 V, 1 A, 50 GHz.
You might be interested in Automatic switch ABB 16A
In the country
When performing electric welding work, installations with increased power are used. The advantage is that a serious current is generated to form an electromechanical arc.
Note! If the instructions do not immediately describe the use for electric welding, then you should abandon such an idea. Otherwise, generators quickly deteriorate.
Industrial facilities
More often we are talking about independent powerful stationary installations. They are relevant for industrial enterprises and entire residential areas, hospitals, public institutions with high traffic. Then such mechanical devices are relevant.
Application of alternating current generators in practice
Such generators are used in almost all areas of human activity where electrical energy is required. Moreover, the principle of its extraction differs only in the method of driving the device shaft. This is how hydro, heat and even nuclear power plants work.
These stations power public networks via wires, to which the end consumer, that is, all of us, connects. However, there are many objects to which it is impossible to deliver electrical energy in this way, for example, transport, construction sites far from power lines, very distant villages, shifts, drilling rigs, etc.
This means only one thing - you need your own generator and engine to drive it. Let's look at several small and common devices in our lives.
Car generators
Someone may immediately say: “How? This is a DC generator!” Yes, indeed, it is so, but what makes it so is only the presence of a rectifier, which makes this very current constant. The basic principle of operation is no different - the same rotor, the same electromagnet, etc.
Schematic diagram of a car generator
This device operates in such a way that, regardless of the shaft rotation speed, it produces a voltage of 12V, which is provided by the regulator through which the field winding is powered. The excitation winding starts, powered by a car battery, the rotor of the unit is driven by the car engine through a pulley, after which an EMF begins to be induced.
Several diodes are used to rectify three-phase current.
"Child of Light"
The automobile generator in the modern sense is generated by mankind’s love for electric light. Cars from the dawn of motoring had only a simple unit called a “magneto” - a miniature generator combined with an ignition breaker, integrated into the engine housing and producing exclusively high-voltage impulses for the operation of spark plugs. Neither a lamp nor any other consumer of electricity could be connected to the magneto, so cars of the 19th century illuminated the road with carbide lamps in which acetylene burned - there was no need to expect help from the internal combustion engine...
However, it soon became obvious that the car engine must generate more electricity: not only for its own operation, but also for the operation of external consumers - headlights, horn, front panel meters, battery charging and the like. Therefore, next to the high-voltage “spark” winding of the magneto, an additional winding appeared - a low-voltage one, providing on-board voltage. MAGneto + DYNAMO machine = Magdino. This is how the first generators came to be called.
But since magneto and magdino are traditionally built directly into the engine, their power is limited by their small dimensions. And as soon as it became clear that an increase in generator power was inevitable, the “gene” became external - it moved to a bracket on the cylinder block and began to receive rotation from an external transmission - a belt, and sometimes a chain or gear.
The first generators produced direct current, but after the development of the semiconductor industry in the mid-twentieth century and the advent of powerful rectifier diodes, generators began to produce alternating current, which was then rectified to constant current by diode bridges. Changing the type of current made it possible to stepwise reduce the size and weight of generators several times and increase their power.
Actually, a modern generator is almost identical to what was on machines developed 10, 20, 30, or more years ago. Engines and gearboxes become more complex year after year, but perhaps the main external electrical unit remains virtually unchanged. Its design is not ideal, but it represents a golden balance of properties and cost. However, additional components and improvements appear - for example, instead of a simple pulley for a belt, an overrunning clutch can be installed on the generator, as in a starter bendix, or the number of coils in the stator winding increases and the diode bridge becomes more complicated, but most generators still make do with the classic design.
We recommend reading: How to control a stepper motor without a controller
Basic faults
The manifestation of malfunctions is the voltage in the network leaving the specified limits, as well as extraneous sounds from the operating generator.
The reasons may be different:
- wear of the brush assembly, it is replaced together with the integral relay;
- deep wear of the commutator with brushes, if it can no longer be eliminated by grinding, replace the slip rings or the armature assembly;
- failure of the armature bearings; they can be easily replaced after complete or partial disassembly of the generator;
- burnout of rectifier diodes, currently they are not replaced individually, the entire diode bridge must be replaced;
- short interturn short circuits or breaks in the armature or stator, the corresponding parts are changed;
- burnt or corroded contacts, they can also be replaced or cleaned.
Not directly related to the generator, but a common malfunction is a strong whistle when adding engine speed. This indicates that the belt is slipping on the drive pulleys; the tension can be adjusted, but it is better to replace the belt.
When removing the generator for repair, it is advisable to immediately change the diode bridge, bearings and relay regulator with brushes. This way, the repaired device will gain the highest possible reliability, although only a new generator from a reputable manufacturer can provide a full guarantee.
Rules for operating the generator (according to Oster)
And finally, a few “harmful” tips on how to “burn out” a generator quickly and without problems:
- The best and fastest way is “Reversal”. Swap the wires from the battery terminals, and not only an optical effect is possible (a bright flash inside the generator, a light cloud of smoke), but also an audio effect (from a click to a pop and hiss), an olfactory effect (you will feel the indescribable aroma of burning wires!), and, finally, tactile (1-3 degree burn - selected experimentally!) After using this method, the diode bridge burns out with a probability of 99%, the stator - 60%, the relay regulator - 20%, wires - 10%, the entire car - 0.01% ! The method is very effective when “lighting”. Possible side effects - burnout of on-board computers, alarms, music, etc. A big plus is that it does not require special skills or knowledge and is easy for beginners to master.
- Method “Washing”. Wash your car engine. Wash the generator especially thoroughly, making sure that streams of water rinse all the insides of the unit. Under no circumstances should you blow out the generator after washing! Immediately start the car and turn on more loads - all the lights, heating, music. If the effect does not occur, try again. The effect will appear, believe me!!! Plus, the burnt-out generator will be clean.
- The “old-fashioned” method is to pull off the positive terminal of the battery with the engine running, supposedly to check the charging system. The percentage of burnt relays increases to 50-70%. The method requires a certain skill - the main thing is that there are more sparks! High-voltage switching processes occurring in circuits will sooner or later have to burn at least something in your generator, or, in extreme cases, in your car! As always, it is recommended to turn on as many loads as possible - lights, stoves, heating. The method is not very effective on older machines, but the main thing is to believe that it will happen!
- “Puddle” is a method that many car enthusiasts use without even knowing it. At the same time, many sincerely believe that a car and its components, including the generator, should be akin to a submarine in terms of water resistance. Go for it! How many unexplored depths await their discoverers! And another simple piece of advice - you need to drive through the puddle at the maximum possible speed, carefully ensuring that the splashes evenly flood the engine compartment. The absence of protective covers and trays will greatly facilitate your difficult task. A very big plus is that you can use this method almost every day without leaving your car!
- The “Melomaniac” method. For the very cool! Put in your car a super cassette player, a couple of CD changers, a couple of tube amplifiers of 200-300 watts, a subwoofer of 500 watts, well, about a dozen speakers, preferably one and a half. In general, the more, the better! 12-25 thousand bucks! (This is not a lie - the case has been recorded!) Turn it on! If after a couple of minutes the generator is still working, but there is still no characteristic smoke or smell, then you installed too cheap equipment!
- The “battery” method is the most insidious and mysterious of all, since its understanding requires an understanding of chemical and physical processes (well, at least Ohm’s law, which is not given to everyone!) And to put it simply, use a long-expired battery, at least three years old. five years. The older it is, the more likely it is that the battery will contain a short-circuited bank. In this case, the battery can show signs of life - start the car, recharge from the charger, etc., but at the same time it becomes a powerful parasitic load in the generator circuit. It is possible that the current will be enough to operate the injector, but when you turn on the high beams and heating, the generator will heat up so much that it can be used to cook scrambled eggs while camping! The main thing is not to pay attention to it, and the method will work someday!
Quality of operation: what factors does it depend on?
There are some important parameters, without calculating which it is impossible to make the right choice.
- Power.
To do this, you need to calculate in advance how much power all devices installed at home consume. The load from the main consumers can be active and reactive. The main thing is to take into account some margin and apply the appropriate coefficients.
What is inside?
1-1.3 - in this range is the active load factor for household electrical appliances. 3 - the same parameter, but for devices operating with reactive load.
Important! It is necessary to add all types of load to each other in order to understand which unit is required in a particular case. 15% is set aside as a reserve from above. After all, over time, the number of electrical appliances sometimes increases. When starting up, some devices consume much more energy than indicated in the accompanying documentation.
- The type of load the generator operates with.
There are networks with voltages of 220 and 380 V. Many people think that the latter option is universal, which is why it should be preferred in most cases. But it is still better to opt for a single-phase network if there are no plans to connect devices with the appropriate characteristics.
Otherwise, when installing electrical wiring, problems arise that cannot be immediately foreseen.
- Types of fuel used to generate current.
The reliability of most modern installations remains almost the same. The only significant difference is in the cost of devices and energy sources for them.
History[ | ]
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz invented and built a spark generator of electromagnetic waves based on a Ruhmkorff coil.
In 1913, Alexander Meissner (Germany) invented an electronic Meissner oscillator based on a tube stage with a common cathode with an oscillating circuit in the output (anode) circuit with transformer positive feedback to the grid.[5]
In 1914, Edwin Armstrong (USA) patented an electronic generator based on a tube stage with a common cathode with an oscillating circuit in the input (grid) circuit with transformer positive feedback to the grid.
In 1915, an American engineer from the Western Electric Company, Ralph Hartley, developed a tube circuit known as the Hartley oscillator, also known as an inductive three-point circuit (“inductive three-point”). Unlike A. Meissner’s scheme, it uses an autotransformer connection of the circuit. The operating frequency of such a generator is usually higher than the resonant frequency of the circuit.
In 1919, Edwin Colpitz invented a Colpitts oscillator using a vacuum tube connected to an oscillating circuit through a capacitive voltage divider, often called a “three-point capacitor.”
In 1932, the American Harry Nyquist developed a theory of amplifier stability, which is also applicable to describe the stability of generators. (Nyquist-Mikhailov stability criterion).
Many other electronic oscillators were later invented.
Unit selection
When purchasing a generator, it is recommended to immediately decide for what purpose the installation is needed. If this is a backup power source, a minimum set of devices must be taken into account. To organize a completely autonomous system, you need to count all the devices and add at least 20% to them.
Work in winter
When choosing between gasoline and diesel units, the buyer must answer several questions:
- Number of phases.
- A type of engine starting for a particular situation.
- Acceptable noise level.
- Required power indicator.
- Expenses for purchasing the unit.
- Which manufacturer did you decide to trust? This is also important for non-electrical installations.
Application[ | ]
This is not a complete list of devices that use signal generators:
- Communication devices - radio receivers (heterodyne in superheterodyne radio receivers), television receivers, mobile phones, transceivers, data transmission equipment, etc.
- Digital and computer technology necessarily contains a clock generator.
- Switching power supplies, inverters, uninterruptible power supplies.
- Measuring instruments - oscilloscopes, measuring voltmeters, ammeters, etc.
- Medical equipment - electrocardiographs, tomographs, x-rays, electronic tonometers, ultrasound machines, physiotherapeutic devices, etc.
- Echo sounders.
- Household appliances - programmable washing machines, microwave ovens, dishwashers, etc.
Which companies to trust?
Not only well-known companies, but also those that have appeared quite recently are engaged in the production of electric generators. It’s easy to get confused in the available assortment without some preparation.
Stationary installation
The following several names are well known to the domestic buyer:
- "Boar". It is in greatest demand among Russian companies engaged in this area. Power ranges from 2 to 230 kW. The generators are suitable for both domestic and industrial use. WAY - models suitable for use at home.
- SDMO. Another manufacturer whose models are found in large quantities. Units in this case also have motors operating on 1 or 3 phases. Power and external design are the main differences between different models. The noise-absorbing housing is perfect for those who use household types of generators. Air cooling, power up to 10 kVA - characteristics of a separate class of devices. They are often equipped with additional outputs for AC or DC current. An electric starter complements the stationary varieties of models. They are installed on a frame or inside containers with sound insulation function.
- Geko. Manufacturer with a wide range of products for any conditions. He creates not only household models, but also options with a narrower specialization. A single- or three-phase motor is installed inside the models, depending on what goals the consumer is pursuing. Starting is manual or it is replaced by an electric starter. Some models have noise-absorbing covers. The built-in automatic start panel is also a good addition to standard power plants.
You may be interested in Single-phase automatic machine c16
Amplifiers: main technical indicators, structure and classification
Definition 2
An amplifier is a device that amplifies electrical power.
The main characteristics of the amplifiers include:
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Rectifiers, amplifiers, electronic generators 440 ₽ Abstract Rectifiers, amplifiers, electronic generators 280 ₽ Test work Rectifiers, amplifiers, electronic generators 210 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
- Nonlinear distortions.
- Output and input data.
- Dynamic range.
- Amplitude characteristic.
- Gain.
- Transition characteristic.
- Efficiency.
- Frequency characteristics (phase-frequency and amplitude-frequency).
An example of a feedback amplifier circuit is shown in the figure below.
Figure 1. Feedback amplifier circuit. Author24 - online exchange of student work
An amplifier is a sequence of amplification stages that are connected to each other by direct connections. Some amplifiers have feedback (between and within stages). Negative feedback can improve the stability of the amplifier, as well as reduce nonlinear and frequency distortion of signals. Feedback may include temperature-dependent elements, such as thermistors and posistors, which are designed to equalize the frequency response. In the input and output circuits of amplifiers, as well as between its stages, potentiometers or attenuators can be included to control the gain and filters that form a given frequency response.
About welding generators
Users often ask whether welding equipment can be connected to generators. Manufacturers say that this is possible, but only for welding inverters. The main thing is to operate the equipment without overloading. This directly affects the service life.
Connection
For cooking, it is recommended to use an electrode no larger than 2 mm. It is not advisable to choose a larger diameter; this will negatively affect welding.
Voltage controlled oscillator (VCO)[edit]
Main article: Voltage controlled oscillator
The generator can be designed so that the oscillation frequency can be changed over a certain range by the input voltage or current. These voltage-controlled oscillators are widely used in phase-locked loops, in which the frequency of an oscillator can be synchronized with the frequency of another oscillator. They are ubiquitous in modern communications circuits, used in filters, modulators, demodulators, and form the basis of frequency synthesizer circuits that are used to tune radios and televisions.
RF VCOs are typically made by adding a varactor diode to a tuned loop or resonator in the oscillator circuit. Changing the DC voltage across a varactor changes its capacitance, which changes the resonant frequency of the tuned circuit. Voltage-controlled relaxers can be built by charging and discharging an energy storage capacitor with a voltage-controlled current source. Increasing the input voltage increases the charging rate of the capacitor, reducing the time between switching.
Ensuring security requirements
Generators are usually installed outside closed areas. The main thing is that they are located where complete protection from precipitation and other environmental influences is guaranteed. The toxicity of exhaust products is the main reason why generators are prohibited from operating in enclosed spaces.
Note! A solid, stationary horizontal surface without elevations is the optimal support for installation. During installation, you must ensure that there is a free space of at least 1 square meter. This distance should remain on each side of the generator. This is necessary to organize free air circulation and eliminate heat transfer from the generator to surrounding objects.
There should be no foreign objects on the side of the outlet. They can damage the structure or become a source of additional danger to it. The ventilation openings should also be free of any contamination.
Children and other unauthorized persons must not have access to the generator. The same applies to other people who are not familiar with the principle of safe operation.
Self-repair of generators is prohibited; for this you need to invite specialists.
Finding sources of flame or smoldering combustion near the unit is unacceptable. Otherwise, it will not be possible to convert energy safely.
Compact devices
Description of circuits
To obtain a connected three-phase system, the windings of the electric generator must be connected to each other in one of two ways:
"Star"
A star connection involves electrically connecting the ends of all windings at one point. The connection point is called “zero”. With this connection, the load can be connected to the generator with 3 or 4 wires.
The wires coming from the beginning of the windings are called linear, and the wire coming from the zero point is called zero. The voltage between linear wires is called linear.
Line voltage is 1.73 times greater than phase voltage.
The voltage between neutral and any of the linear wires is called phase. The phase voltages are equal to each other and shifted relative to each other by an angle of 120 degrees.
A feature of the circuit is also the equality of linear and phase currents.
The most common 4-wire circuit is a star connection with a neutral wire. It allows you to avoid phase imbalance in the case of connecting an asymmetrical load, for example, on one phase there is an active load, and on the other there is a capacitive or reactive load. At the same time, the safety of switched on electrical appliances is ensured.
"Triangle"
A delta connection is a series connection of the windings of a three-phase generator: the end of the first winding is connected to the beginning of the second, its end to the beginning of the third, and the end of the last to the beginning of the first.
In this case, the linear wires are diverted from the connection points of the windings. In this case, the linear voltage is equal to the phase voltage, and the magnitude of the linear current is 1.73 times greater than the phase current.
All mentioned dependencies are valid only for a uniform phase load. If the load of the phases is uneven, they must be recalculated using analytical or graphical methods.
Additional information about connection and operation
It is also better to entrust the installation to specialists so that the device can continue to operate without interruptions. In this case, he will not become a source of danger to others. Connecting the device involves connecting its electrical wiring to a centralized network. Therefore, additional safety regulations must be observed.
Here are the main recommendations:
- When the installation work is completed, the unit is prepared for operation.
- To do this, check the oil level in the crankcase.
- This procedure is carried out while the unit is on a flat horizontal surface.
- As it is consumed, it is refueled.
- If the unit is indoors, be sure to ventilate it during maintenance.
- The gas station does not allow smoking or the use of open flames.
- Gasoline is poured as carefully as possible, avoiding leaks.
When the preparatory work is completed, the engine is started. This is achieved by a manual or electric starter, depending on the model.
Alternating current generators on the modern market are presented in a large number of models. Everyone makes the final choice depending on their needs and purposes of use. Various power systems and power range are determined by the object within which the installation is installed. Sometimes the availability of specific types of fuel in a particular region is assessed. It is recommended to choose models that require the least maintenance costs.
Design and principle of operation
Device
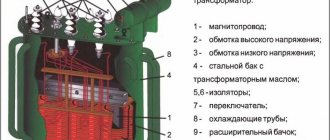
Any alternating current generator consists of:
- Direct current or electromagnet that creates a magnetic field. In order to obtain a powerful magnetic flux, special magnetic systems of two cores, which are made of electrical steel, are installed in generators.
- The winding in which an alternating EMF occurs. The windings that create the magnetic field are placed in special slots of one core, and the windings in which the EMF occurs are placed in the slots of the other.
- To supply the supply voltage and remove the resulting alternating current, slip rings and brushes are used. These parts are made of conductive materials. The current strength in the windings of the electromagnet that creates the magnetic field is much less than that which the generator supplies to the external circuit, so it is more convenient to remove the generated voltage from the stationary windings, and apply a low-power supply voltage through the sliding contacts.
In low-power devices, brushes and rings are used much less frequently, since their designs can use rotating permanent magnets, which do not require a supply voltage.
Usually:
- The inner core (rotor) together with the winding rotates around its axis.
- The outer core (stator) is stationary.
- The gap between the rotor and stator must be minimal - only then the power of the magnetic induction flux is maximum. In this case, the magnetic field is created by a stationary magnet, and the windings in which the EMF is created rotate.
However, in large industrial generators, the outer core, which creates the magnetic field, rotates around the inner one, and the windings in which the emf is induced remain stationary.
During operation, an EMF arises in the rotor winding, the amplitude of which is proportional to the number of turns. In addition, it is proportional to the amplitude of the alternating magnetic flux (through the coil).
Operating principle of a synchronous generator:
Rotor
A rotor (from the English rotation) is the moving part of a self-generator. It consists of a shaft with an excitation winding located on it, located between two pole halves. The latter are made by stamping, each of them has six beak-shaped protrusions located on top of the winding. These halves form a pole system and slip rings. The purpose of the rings is to supply electric current to the winding through its terminals.
The excitation winding is designed to create a magnetic field. To solve this problem, a weak electric current must be applied to it. Before starting the power unit, the battery supplies current to form a magnetic field. When the internal combustion engine is running and the speed reaches the required value, the generator will supply current to the excitation winding
In addition, the rotor contains:
- Drive pulley.
- Rolling bearings.
- Cooling device (fan).
The rotor is located inside the stator, sandwiched between the housing covers. The covers are equipped with seats in which rotor bearings are placed. In addition, the cover located on the drive pulley side has holes for ventilation.
Generator ventilation diagram
Stator
This element, unlike the one described above, is motionless (static), which is why it got its name. Its task is to obtain an electric current of variable magnitude arising under the influence of the magnetic field of the rotor. The stator consists of windings and a core. The latter is made of sheet steel and has grooves for laying three windings (according to the number of phases). Windings can be laid in one of two ways: loop or wave. The pattern of their connection can also be different - in the shape of a star or a triangle.
1 - core; 2 - winding; 3 - groove wedge; 4 - groove; 5 - terminal for connection to the rectifier.
In a star connection, all the windings are connected together at one end at a common point. Their second ends serve as conclusions. The “triangle” circuit involves connecting the windings according to a different principle: the 1st to the 2nd, the 2nd to the 3rd, and the 3rd, in turn, to the 1st. In this case, the function of the terminals is performed by the connection points. Both diagrams are clearly shown in the figure.
Star and delta circuit
Brush block
The task of this component of the generator is to transmit electricity to the excitation winding. Structurally, the block is a housing with a pair of spring-loaded graphite brushes located in it. The latter are pressed against the slip rings with the help of springs, but are not rigidly fastened to them.
Voltage regulator
The regulator is needed in order to maintain the output voltage within the established limits. This is necessary because the amount of current, as well as its parameters, depends on the engine speed, and the durability of the battery is directly related to the applied potential difference. Insufficient voltage will lead to a “chronic” undercharging of the battery, and excess voltage will lead to overcharging. In both the first and second cases, the battery life will noticeably decrease. Modern cars are equipped with electronic semiconductor regulators.
Voltage regulator
Current collection unit
In a brush generator, the structure of the current collection unit is as follows:
- the brushes slide along the commutator rings;
- they transmit direct current to the excitation winding.
Electrographite brushes wear out less than copper-graphite modifications, but a voltage drop is observed on the collector half-rings. To reduce electrochemical oxidation of rings, they can be made of stainless steel and brass.
Since the operation of the current collection unit is accompanied by intense friction, brushes and commutator rings wear out more often than other parts and are considered consumables. Therefore, they are quickly accessible for periodic replacement.
Rectifier
Since the stator of an electrical appliance generates alternating voltage, and the on-board network requires direct current, a rectifier is added to the design, to which the stator windings are connected. Depending on the characteristics of the generator, the rectifier unit has a different design:
- the diode bridge is soldered or pressed into horseshoe-shaped heat sink plates;
- The rectifier is assembled on a board, heat sinks with powerful fins are soldered to the diodes.
The main rectifier can be duplicated by an additional diode bridge:
- sealed compact unit;
- dida-pea or cylindrical shape;
- inclusion in the overall scheme by small buses.
The rectifier is the “weak link” of the generator, since any foreign body that conducts current, accidentally falling between the heat sinks of the diodes, automatically leads to a short circuit.
Diode bridge (rectifier block)
The task of this element is to convert the alternating current supplied to it into the direct current necessary to power the on-board network. Structurally, it consists of heat-removing plates, into which 6 diodes are mounted - 2 for each stator winding (on “+” and on “-”).
Impeller
The friction parts inside the generator are cooled by forced air. To do this, one or two impellers are placed on the shaft, sucking air through special slots/holes in the product body.
There are three types of air-cooled car generators:
- if there is a brush/collector ring assembly and the rectifier and voltage regulator are moved out of the housing, these components are protected by a casing, so air intake holes are created in it (position a) of the lower circuit;
- if the arrangement of the mechanisms under the hood is dense, and the air surrounding them is too hot to properly cool the internal space of the generator, a specially designed protective casing is used (position b) in the lower figure;
- in small-sized generators, air intake slots are created in both housing covers (position c) on
We recommend reading: What is galvanic isolation used for?
Overheating of windings and bearings dramatically reduces the characteristics of the generator, and can lead to jamming, short circuit and even fire.
Frame
Traditionally, for most electrical appliances, the generator housing has a protective function for all components located inside it. Unlike a car starter, the generator does not have a tensioner; the sagging of the transmission belt is adjusted by moving the housing of the generator itself. For this purpose, in addition to the mounting tabs, the body has an adjustment eye.
The body is made of aluminum alloy and consists of two covers:
- The stator and armature are hidden inside the front cover;
- Inside the back cover there is a rectifier and a voltage regulator relay.
The correct operation of the generator depends on this part, since a rotor bearing is pressed inside one cover, and the belt is tensioned in the eye of the housing.
Bearings
The front bearing is considered to be on the pulley side, its housing is pressed into the cover, and a sliding fit is used on the shaft. The rear bearing is located near the collector rings; on the contrary, it is mounted on the shaft with interference; a sliding fit is used in the housing.
In the latter case, roller bearings can be used; the front bearing is always a radial ball bearing with a one-time lubricant applied at the factory, which is enough for the entire service life.
The higher the generator power, the greater the load the bearing race experiences, and the more often both consumable parts need to be replaced.