The main problem that craftsmen and designers face when working with strips is the selection of a power supply for the LED strip, since it cannot simply be plugged into an outlet. To connect it to the network, you need to select and purchase a power supply for the LED strip - this is a device that stabilizes and transforms the input voltage of 220 V into a constant 12, 24 V. Miniature dimensions and unremarkable design allow you to discreetly install this device in any convenient place without changing attractiveness of the LED design.
Types of power supplies
The following types of power supplies are available:
- Ordinary
- Pulse
Regular power supply for LED strip
It is carried out in the form of a standard transformer device, which includes:
- step-down transformer - to reduce the input voltage from 220V to 12V;
- a smoothing filter is used to smooth out alternating voltage;
- A rectifier that performs the task of rectifying alternating current.
The transformer power supply has the following advantages: simplicity of design, ability to operate without load, and relative reliability. The disadvantages of such devices include: decent dimensions, significant weight, significant metal consumption, low efficiency of the entire structure.
Switching power supply for LED strip
These devices differ from transformer devices in that they operate at ultra-high frequencies (10 - 100 kHz). Therefore, their operation requires an ultra-high frequency generator and a converter. The switching power supply for LEDs also has a transformer in its circuit, but its dimensions and weight are significantly smaller, since it operates at extremely high frequencies.
The advantages of pulse devices include:
- low cost;
- high efficiency (90 - 98%);
- possibility of supplying voltage with a large spread.
The switching power supply for the tape also has its drawbacks: difficulty in repair, supply of output noise to the power supply network.
Main types
Power supplies can be divided into two main types: transformer and switching. The first are simple and less technologically advanced, the second are a modern version of the power source. Let's consider each of them separately:
Transformer power supplies
A transformer power supply is a device with a step-down transformer and a rectifier using diodes and capacitors. This simple device steps down the voltage and converts it from AC to DC, but incurs large losses. Sometimes the efficiency of such a power supply is only 50%.
The transformer LED power supply is simple and reliable, it does not create interference. But its design is bulky, and during the voltage conversion process most of the current is lost, so it is not economical. To increase the stability of the output voltage, a stabilizer is used, but the efficiency becomes even lower.
Switching power supplies
Switching LED power supplies operate on the principle of initially rectifying alternating voltage, and then generating the necessary pulses. This is compact and high-performance equipment, since its efficiency is higher than that of transformer models and reaches 98%. There are fewer losses here. Such devices operate silently.
Protection circuits against short circuits and overloads contribute to the reliability of switching power supplies. And due to the unified design, this relatively complex LED display equipment is inexpensive. A failed power supply is not repaired, but replaced with a new one.
This equipment has a wide operating voltage range. It will work even if the voltage drops to half normal. A linear device designed for a 220 V network will not work in such conditions. The main disadvantage of pulsed power supplies is the creation of strong high-frequency interference.
The difference between a power supply and a driver
A driver is a device similar in its tasks to a power supply, only at the output it stabilizes not the voltage, but the current at the same level. Since current is required to power a strip of LEDs, they have a so-called current-voltage characteristic of voltage drop.
Therefore, if LED lamps are connected from a pulse unit, and not from a driver, then their further operating mode may be unpredictable. They will shine, but with what mode and for how long is unknown. For each driver, a certain number of LEDs should be selected. When one fails, the driver will direct its current to the remaining ones. This may cause overheating and burnout.
Using a computer's power supply as a driver
Instead of a power supply for a diode strip from a store, you can take a unit from a personal computer. You just need to compare its characteristics with the parameters of the LED strip: the power and constant voltage of 12V correspond, then you can safely connect it.
Everything will work, but for high-quality and durable lighting it is better to choose special varieties.
Driver Disadvantages
Of course, drivers also have their undeniable disadvantages:
- firstly, they are designed only for a certain current and power
This means that for each driver you will have to select a certain number of LEDs each time. If one of them accidentally fails during operation, the driver will send all the current to the remaining ones.
Which will lead to their overheating and subsequent burnout. That is, the loss of one LED entails a breakdown of the entire chain.
There are also universal driver models, for them the number of LEDs is not important, the main thing is that their total power does not exceed the permissible limit. But they are much more expensive.
- highly specialized in LEDs
Simple power supplies can be used for various needs, wherever 12V or more is needed, for example for video surveillance systems.
The main purpose of the drivers is LEDs.
Are there driverless factory lamps? Eat. Not long ago, many such LED lamps and spotlights appeared on the market.
However, their energy efficiency is not very high, at the level of conventional fluorescent lamps. And how it will behave in the event of possible changes in parameters in our networks is a big question.
Criteria for choosing a power supply
Conversion method
As described above, the power supply for LED strips can be transformer or pulsed. To select a device of relatively low power, it is recommended to choose pulsed models.
Cooling
The power supply for LED can have a passive or active cooling system. In the first option, cooling is realized naturally, and in the second, a fan is used. When the power supply has low power, it is better not to use a device with forced cooling. It requires frequent maintenance, most importantly, it is not protected from moisture.
Execution
All power supplies, depending on the design, are divided into the following types:
- Block in a plastic case. The advantages of such devices are compact size, tightness, light weight, and aesthetic appearance. The disadvantages include difficult heat exchange, fairly high cost, and low maximum power (devices with a power of more than 75 W are not produced).
- Power supply in a compact perforated aluminum case. The metal body ensures good heat transfer. This block is resistant to negative factors: moisture, temperature changes, solar radiation. Their power varies up to 100 W.
- Blocks are open type. The most common and inexpensive type. Typically used when installing LED lighting in the home. The main disadvantages are the dimensions, which are several times larger than previous varieties, and the lack of protection from moisture and dust.
- Network power supply. The power of such devices usually does not exceed 60 W. Typically, their scope of application is limited to organizing power supply for LED strip structures with a length of no more than 5 m.
Output voltage
The tape voltage is indicated on the packaging or tape. At the output, the unit must have the appropriate voltage value: 12 or 24 V.
Power
The power of the LED power supply should have a reserve and be 15-20% more than that consumed by the strip. Sometimes power supplies do not indicate the rated power, but only the permissible current. To convert it into power, you need to multiply the operating voltage (12 or 24 V) by the maximum permissible current in A.
Additional functions
Some block models may have additional built-in devices, such as a dimmer, remote control boards and programming for switching off and on times.
Application
Drivers are used both when powering the LED from a 220V network, and from DC voltage sources of 9-36 V. The former are used when lighting rooms with LED lamps and strips, the latter are more often found in cars, bicycle headlights, portable lanterns, etc.
As already mentioned, the driver is a current source. Its differences from a voltage source are illustrated below.
The voltage source produces a certain voltage at its output, ideally independent of the load.
For example, if you connect a 40 Ohm resistor to a 12 V source, a current of 300 mA will flow through it.
If you connect two resistors in parallel, the total current will be 600 mA at the same voltage.
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
The driver maintains the specified current at its output. The voltage may change in this case.
The driver will create a 12V voltage drop across the resistor.
If you connect two resistors in parallel, the current will still be 300 mA, but the voltage will drop to 6 V:
Thus, an ideal driver is capable of delivering the rated current to the load regardless of voltage drop. That is, an LED with a voltage drop of 2 V and a current of 300 mA will burn as brightly as an LED with a voltage of 3 V and a current of 300 mA.
Driver for LEDs
A stabilized DC power supply is well suited for powering:
That is, when the rated voltage of the LED load is known exactly, and it is enough just to select a power supply for the rated voltage at the corresponding maximum power.
Stabilized DC power supply
Usually this does not cause problems, for example: 10 LEDs at 12 volts, 10 watts each, will require a 100 watt 12 volt power supply, rated for a maximum current of 8.3 amperes. All that remains is to adjust the output voltage using the adjusting resistor on the side, and you’re done.
For an even glow of the LED assembly, it is necessary to ensure the rated current through all crystals. However, the voltage drop across the crystals may differ for different LEDs (since the I-V characteristics of each LED in the assembly are slightly different), so the voltage will not be the same on each LED, but the current should be the same.
Driver for LEDs
LED drivers are produced mainly for power supply from a 220 volt network or from a 12 volt vehicle on-board network. The driver output parameters are specified in the form of voltage range and rated current.
For example, a driver with an output of 40-50 volts, 600 mA will allow you to connect four 12-volt LEDs with a power of 5-7 watts in series. Each LED will drop approximately 12 volts, the current through the series chain will be exactly 600 mA, while the voltage of 48 volts falls within the operating range of the driver.
A driver for LEDs with stabilized current is a universal power supply for LED assemblies, and its efficiency is quite high and here's why.
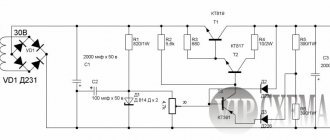
Drivers from different manufacturers differ in output power, protection class and used element base. As a rule, it is based on a pulse PWM converter on a specialized microcircuit, with current output stabilization and protection against short circuit and overload.
Powered by 220 volt AC or 12 volt DC. The simplest compact drivers with low-voltage power supply can be implemented on a single universal chip, but their reliability, due to simplification, is lower. Nevertheless, such solutions are popular in auto tuning.
Driver for LEDs: purpose, selection, connection, circuits
It is possible to use low-power light-emitting diodes without a driver; in this case, its role is played by a resistor.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Drivers for LEDs: types, principles of operation, models, prices In order for them to be guaranteed to work for the stated number of hours, a driver is needed; it stabilizes the current flowing through the LED circuit. Ask, I'm in touch!
Calculation of power supply power for LED strip
The minimum permissible power for the power supply is calculated based on the total power consumption. For example, if the power consumption per linear meter is 4.8 W. Then, to calculate the power of the power source, you need to multiply the required number of meters (16 meters) by the power of the meter:
16 x 4.8 = 76.8 (W)
Power reserve factor
It should be remembered that the power supply is selected based on a 20% power reserve (this is the so-called safety factor). Therefore, to calculate the required minimum power of the unit, the total power consumption of the tape must be multiplied by 1.2.
It turns out that the power of the power supply is 92.162 W
. It is recommended to choose 100 W units.
Kinds
By device type, drivers are divided into linear and pulsed:
- Linear - based on a current generator with a p-channel transistor. They provide smooth current stabilization at unstable voltage. A simple configuration, low efficiency = 85%, low cost and high heat dissipation suggest the use of LEDs in low-power circuits. Plus - a smooth operating mode that does not create electromagnetic high-frequency interference.
- Pulse – generate high-frequency pulses at the output. The operating principle is PWM (pulse width modulation). The average output current is provided by the duty cycle (the ratio of the pulse duration to the number of repetitions). The change in the value of the average output current occurs due to a variation in the filling value from 10 to 80% at a constant pulse frequency. They are widely used due to their high efficiency (95%), long service life and small size. The disadvantages include a high level of interference.
Due to the presence of galvanic isolation, which provides increased efficiency, reliability and safety, preference should be given to drivers with this property. If there is no galvanic isolation, the driver is cheaper, but there is a danger of electric shock (no protection).
Calculation of LED strip per power supply
To provide power to several LED strips with one adapter, the power consumption of each is calculated, and the resulting values are summed up. The tapes are connected in parallel.
Calculation of a transformer for LED strip
When choosing a power transformer for connecting an LED strip, it is advisable to leave 20 - 30% reserve. In other words, if you choose a transformer with a power of 150 W, then it is better not to connect more than 100 W of LED load to it.
Overheating of the power supply: main causes and options for eliminating them
Modern TVs from all well-known manufacturers are equipped with switching power supplies. The devices are compact in size, allowing them to be built directly into the receiver body. Each manufacturer has its own power adapter circuit, but the internal components are the same - capacitors, diodes, transformers. All semiconductor elements are made on the basis of silicon, which begins to self-destruct at temperatures above 150 degrees. Therefore, overheating of the power supply can lead to failure of various TV receiver modules: processor, control board, external interfaces (antenna input, USB and HDMI connectors).
Visually, the malfunction can be determined as follows:
- The power light on the case does not light up;
- the TV turns on late or turns off after several minutes of operation;
- The back cover in the area where the power cord enters is very hot.
During operation, any power supply unit generates heat, which is considered absolutely normal. But if you can’t touch it with your hand, this is a clear indicator of a breakdown.
The reasons why the power supply gets very hot may be the following:
- heat exchange is disrupted;
- electrolytic capacitors have dried out;
- the network cable is damaged;
- unstable voltage;
- The power transistor has failed.
In most cases, you will not be able to solve the problem yourself, since you will need to open the TV, resolder the power supply, or completely change the module. If you do not have sufficient qualifications or are not sure that you can fix the breakdown on your own, call a specialist. Our service center engineers will perform diagnostics, determine exactly where the problem is, and promptly fix it at your home.
Reasons for LED strip failure
Tapes or their fragments often burn out without producing the declared resource. The reasons for this may be:
- Non-branded LEDs, which fail when heated.
- Incorrect installation causes overheating of the LEDs and damage to the tracks. Gluing the tape tightly causes the entire tape to heat up more. The tape should not be bent more than 5 cm.
- Excess supply voltage. It is better to reduce it from 12 to 11.5 - 11.7 V using a construction resistor installed next to the wire terminals.
BP classification
Based on their location, power supplies are divided into internal (placed inside the luminaire body) and external (placed outside the body). In this case, external power supplies can be included with the lamp or purchased separately.
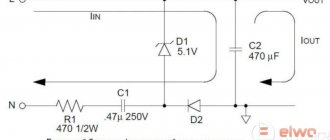
Based on their design, power supplies can be divided into two large categories - isolated and non-isolated. A feature of an isolated power supply is that its output does not have a galvanic connection with the input. Thanks to this, a higher level of electrical safety of the device is achieved. The electric potential at the output of a working insulated power supply will under no circumstances reach a dangerous value. In principle, an isolated type power supply is the same classic transformer-based power supply design that has been used for many decades. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the network through a converter, and the load is connected to the secondary winding through a rectifier. The differences from the classic version are that the transformer does not operate at the mains frequency, but at a higher frequency, and also in the presence of galvanically isolated feedback to stabilize the voltage or current. Isolated power supplies are relatively expensive, but they cope well with voltage surges and impulse noise that exist in Russian electrical networks.
An example of a circuit diagram of an isolated power supply. Source: Macro Group
Non-isolated power supplies have a galvanic connection to the output. Therefore, although the potential difference between the lines at the output of such a power supply is a safe value that does not exceed 60 V DC for LED lamps, nevertheless, the potential between one of the output lines and the ground can be comparable to the mains voltage, i.e. . take on a dangerous value. The advantages of non-isolated power supplies are compactness, low price and slightly higher efficiency than non-isolated power supplies. This is why non-insulated power supplies are so popular among manufacturers of very cheap lamps - in addition to the low cost of the power supply, higher efficiency allows the use of LEDs with lower light output. Non-insulated power supplies are also widely used in LED retrofit lamps, but in some cases they cannot be avoided due to their small size. Due to low electrical safety, non-insulated power supplies can only be internal. The disadvantage of non-isolated power supplies is the penetration of powerful impulse noise into the output, which “walks” through the network. In addition, when a switch is installed in the gap of the neutral wire (which happens when LED lamps are installed to replace pre-existing lighting), the LEDs in the lamp equipped with such a power supply glow faintly when turned off. All this leads to premature failure of LEDs.
An example of a circuit diagram of a non-isolated PFC type power supply. Source: Macro Group
Advanced non-isolated power supplies are often colloquially called PFC from the words Power Factor Correction - power factor correction. They have a higher power factor compared to conventional non-isolated power supplies - about 0.9 versus 0.6. In such power supplies, the problems that cause premature failure of LEDs are partially solved. However, they still lose to isolated power supplies in terms of resistance to voltage surges.
Connecting LED strip
Connecting a power supply to an LED strip is not at all difficult and requires solving the following issues:
Connection polarity
At the output of the power supply, you need to find the “plus” and “minus” markings on the terminals. Additionally, the terminals on the block can be colored: respectively, red is “plus”, black is “minus”. Similarly, on the LED strip you need to find the corresponding symbols.
Selecting wire cross-section
To do this, divide the power of the tape in W by the supply voltage - Volts. If there are several LED strips, then their power needs to be added up. To determine the required wire cross-section, you should use special tables with continuous-permissible currents and required wire cross-sections.
Selecting a connection scheme
When there is only one LED strip, its connection diagram will be as simple as possible: the output terminals of the strip are connected to the supply wires, taking into account the polarity. To connect several tapes, you must use a parallel connection diagram.
Polarity connection errors
Since a diode is a semiconductor, characterized by the ability to pass current in one direction and not in the opposite direction. If the LED strip is connected incorrectly to the power supply, it will not light up. If you change the polarity, the tape will glow. This quality is unique to LEDs.
Using additional adapters
The lighting will be complete only if the appropriate connection diagram is followed. Before connecting the LED strip to the power supply, you should take care of a device that allows you to change the intensity of the lighting device. If any of the circuit elements are connected incorrectly, the operation of the backlight will be disrupted.
A dimmer, or an additional adapter for a 12-volt LED strip, is a device that allows you to control the brightness of the light. The use of this device is the main reason for the popularity of LED strips.
The power supply for the LED strip is connected with a dimmer, which eliminates the difficulties of using it.
The use of this circuit allows you to control the flow of light. The dimmable LED strip is connected simultaneously with the main and additional adapters, that is, a dimmable power supply is needed.
Before calculating the connection diagram, it should be taken into account that 12-volt tapes have different power ratings. Since choosing a power supply for a chandelier differs from choosing a transformer for an LED strip, two indicators should be taken into account:
- power;
- voltage.
The first parameter is determined by the length of the led or rgb strip, and the second is about 12 or 24V. To dim the tape, you will need to correctly connect not only the transformer to it. The circuit must include a dimmable power supply, the power of which is 12 or 24V.
This involves using a certain type of dimmer.
For example, for an RGB tape that has 3 colors, a special adapter is required that allows you to mix colors and turn them on separately. If the dimmable power supply is selected correctly, the backlight adjustment functions.
Connecting Wires and Terminals
You can choose the right block, purchase a high-quality tape, but when connecting, use a thin cable and not achieve the desired cross-section. To correctly select the cross-section and power wires, you can use two methods.
Selection by belt load
Since it is not always possible to use a table of correspondence between current and wire cross-section, you can use the universal dependence. It has been established that every 10A of connected load will require a copper wire of 1 sq. mm.
To determine the amount of current that the backlight consumes, it is necessary to divide the total power by the resistance value. Next, divide the calculated current value by 10A, according to the formula, to obtain the required wire cross-section used for installation.
Selection by block power
It is not the power of the belt that is used, but the power of the block. It is required that the condition be met: the device must withstand 1.35 of the rated current of the power source.
In addition to normal operation of the tape, short circuits may occur. The protection is triggered at overloads of 1.05 - 1.35.
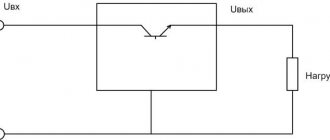
What is a current driver?
LED current driver
is a converter that stabilizes the current. Widely used for connecting LED devices. Ensures energy efficient operation of LED devices. The converter maintains the specified current at the output, but the voltage changes.
Interesting materials:
Why does the pressure in the boiler not rise? Why doesn't current flow through a capacitor connected to a DC circuit? Why doesn't lawn grass sprout? Why doesn't the grass sprout? Why don't irises open? Why doesn't the flower of women's happiness bloom? Why don't my orchids buds bloom? Why can't I hear sound on my iPhone? Why don't apples ripen? Why doesn't the induction cooker work?
What is their difference and what is better to choose: let’s summarize
And so, generally speaking, the power supply, the electronic transformer, and the driver belong to the category of electrical converters. But, each of them has its own purpose in applied electronics. In theory, they are interchangeable, but most equipment they are designed for will not work with similar devices or will not work correctly.
What can each of them be used for:
- Driver – used to connect an LED; it is not practical to use a driver for other devices. The driver is already installed in the LED bulbs as a required component. However, it should be noted that a specific driver is used exclusively for a semiconductor or group of semiconductors that matches its parameters. If one of the LEDs burns out, the driver will no longer match the new current.
- Power supply - suitable for switching on low-voltage equipment with a constant supply voltage of 12 V, 24 V, etc. Often used to connect LED strips, since the strips already have variable resistors and do not need to limit the current. But they need to use a rectifier, which is provided by the power supply, since the LED is sensitive to any fluctuations in the supply quantities.
- Electronic transformer - often used for halogen lamps, which is due to the presence of a minimum load, without which it simply will not start. LED devices for an electronic transformer may not be enough, but halogen ones are more than enough. But the halogen lamps themselves can be turned on either from a transformer or from a power supply, since they operate from actual voltage.