In order to guarantee a solution to problems with low-quality voltage, it is extremely important to choose the right type and parameters of the voltage stabilizer. Each type has its own characteristics, strengths and weaknesses. Which one is better to choose? Let's find out!
What voltage problems are common?
- Low voltage. Incandescent light bulbs shine dimly, LED light bulbs blink, the microwave does not heat, the pump does not pump well, etc. Let us remind you that according to GOST (29322-2014 clause 3.1) the voltage at the input to the house should not deviate by more than 10%. At the moment there are two standards - 220V (tolerance: 198 - 242V) and 230V (207 - 253V).
- Increased voltage from 250V or more. At values of 265V, household appliances will begin to fail.
- Floating voltage values. When there is a light load on the common transformer, the voltage is increased or normal, and sags are recorded during the load.
Floating voltage
- Short dips and surges of voltage. "Blinking" and "ripple" of the network.
Now let's move on to a brief overview of the types of stabilizers.
Relay stabilizers
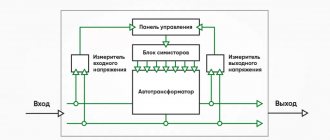
The basis of such a stabilizer is an autotransformer, stepwise taps from which, using electromechanical relays, allow the desired voltage correction to be carried out stepwise. The technology is quite old and, due to its low cost, allows the production of the cheapest stabilizers.
Diagram of operation of a stabilizer on an autotransformer
The advantages of such stabilizers include: + Relatively fast response to voltage sags + Low price
Cons: – Low stabilization accuracy. Usually around 10-8%. For advanced models up to 5% - Service life depends on the frequency of voltage sags and is about 3-5 years - Noise level is average - you will hear the relays switching
The main disadvantage . During voltage sags, which often occur under significant load, electromechanical relays are activated. As a result of step switching, a short-term interruption of power to the connected load occurs, followed by an abrupt switching on. This leads to the formation of a spark inside the relay and, as a consequence, to harmonic interference at the output of the stabilizer. As a result, the relay contacts burn out, its service life decreases, and sensitive household appliances may not work correctly or even fail; the light bulbs will blink noticeably.
Power relays in a voltage stabilizer
Thus, we recommend relay stabilizers only if the voltage values do not fluctuate (for example, stable low values) and you do not have sensitive expensive household appliances and electronics in your home. We do not recommend it in case of constantly floating and “blinking” voltage, as well as if a sag occurs when you turn on powerful equipment in your home.
They are usually made in China or from Chinese components. Popular brands: Energy, Santek, Ruself, Resanta, etc.
Installing a voltage stabilizer by an electrician
The voltage stabilizer must be installed by a qualified electrician. Don't try it yourself! Not knowing basic precautions when working with electricity can lead to dangerous consequences.
Connecting a single-phase stabilizer
This circuit is suitable for any single-phase voltage stabilizers.
Before starting work, turn off the power to the equipment. A phase wire in the distribution board breaks. The wire coming from the input circuit breaker is fed to the input of the voltage stabilizer. The power of this machine must be no less than the power of the stabilizer.
The output wire from the voltage stabilizer is fed to the load. The neutral wire is added to the terminal block or twist. Stabilizers from other manufacturers use four wires for connection. This applies zero to the input of the voltage stabilizer, and zero from the output.
Before turning on, check that the wires are connected correctly. De-energize the load (by turning off the distribution machines, if they are not there, then turn off all devices from the sockets). Turn on the voltage stabilizer. Check the power supply at the stabilizer input and output.
If the voltage is within the voltage stabilizer specifications, then connect the load. After connecting the load, check the load level.
So that the load power does not exceed the power of the voltage stabilizer. Screw and bolt connections must be tightened once a year. Poor contact or poorly tightened contact can lead to failure of the wire insulation or a fire.
Connecting a three-phase stabilizer
Three-phase stabilizers differ from single-phase ones only in the number of stabilization lines.
In fact, you can use three single-phase devices (of the same type and power) by connecting them in parallel to each other (in phases) and in series for the consumer connected to them.
The neutral input terminals are connected to each other. The same is done at the exit. As a result, it turns out that both the network side and the consumer side are connected in a star configuration.
After connecting the three-phase stabilizer to the network, be sure to check the output voltages. They must comply with passport specifications. Be sure to carry out preventive maintenance on screw or bolt connections of wires.
Author: Sergey Vladimirovich, electrical engineer. More about the author.
Electromechanical stabilizers
Here we are again dealing with an autotransformer, but the voltage regulation does not occur stepwise, but smoothly using a brush electric drive. This technology, like relay technology, was one of the first to appear and has a relatively low cost. Pros: + High stabilization accuracy and smooth voltage regulation
Cons: – Since the adjustment is mechanical, during a sudden voltage surge the drive does not have time to make the adjustment and there is a possibility of increased dangerous voltage entering the electrical network of your home – The drive needs regular maintenance
This type of stabilizer can be recommended for rare and smooth voltage deviations from the norm and subject to regular maintenance.
Cheap models are made in China, but there is a premium Italian brand of electromechanical stabilizers, Ortea.
How to extend the working life of the stabilizer?
Device required:
- install correctly;
- protect against overloads;
- periodically monitor;
- serve on time.
Let's take a closer look at each of the listed points.
Correct installation
The location chosen for placing the stabilizer must provide acceptable environmental conditions and sufficient ventilation, as well as the ability to place the device in an operational position. It is also important that there are no factors hazardous to the product (they, along with the requirements for temperature, humidity and ventilation, are indicated in the technical documentation).
Typical mistakes when installing a stabilizer, which can significantly reduce its working life:
- the room is too humid or dusty;
- proximity to a source of increased vibration;
- no gap between the ventilation holes and the nearest surface;
- placement and subsequent switching on in a position other than the operational one.
Overload protection
One-time overloads are not dangerous for most modern stabilizers, but constant operation at the limit of their capabilities reduces their reliability and durability. For example, the service life of electronic components of budget stabilizers may be reduced by more than half.
The fight against overloads consists of monitoring the parameters of both the equipment fed through the stabilizer and the input network. In addition, it is recommended to select the device “not end-to-end”, but with a margin of 30% of the power of the equipment planned to be connected.
Note!
If the load power changes during its operation, then the stabilizer allowed for connection must cover the maximum possible value. This is especially true for products that protect equipment whose starting energy consumption is several times higher than the rated one (such loads, in particular, include almost all devices with electric motors).
Important!
Significant deviations in the input voltage lead to a decrease in the actual output power of the stabilizer. Therefore, a device operated under conditions of strong network fluctuations may require additional power reserve (above and above the recommended 30%).
Periodic control
Modern stabilizers operate automatically and do not require constant human presence, which nevertheless does not relieve the owner from the need to check their condition (at least once a month). In most cases, a visual inspection is sufficient to ensure that:
- the indication works correctly;
- there are no alarms;
- the operation of the product and load is not accompanied by extraneous sounds and vibrations.
If any problems are detected, please refer to the documentation corresponding to the stabilizer. If studying it does not help in eliminating the problem, then you need to resort to the services of a specialized service center.
Note!
The absence of a negative impact on the quality of current work is not a reason to delay the elimination of the identified failure. Please note that timely replacement of worn-out components extends the overall service life of the stabilizer!
Important!
Inverter and electronic stabilizers are so complex that not every workshop can handle troubleshooting them. Therefore, it is recommended that repairs of such products be carried out only in service centers authorized by the manufacturer, where they have the necessary technical facilities and personnel with the appropriate level of qualifications.
Service
The lion's share of modern stabilizers does not require specific procedures associated with disassembly or long-term decommissioning. The typical maintenance program consists of:
- visual inspection (see previous paragraph);
- cleaning from dust and other contaminants should affect not only the outer surface of the stabilizer, but also its ventilation holes. It is recommended to use soft, dry rags or a low-power vacuum cleaner;
- checking and, if necessary, tightening all connections - it is necessary to make sure that the cables are securely fixed in their corresponding connectors, as well as that the stabilizer is securely fastened at the site of operation (if the installation method provides for such fastening).
The interval at which it is recommended to repeat these actions is six months. Let us note that it is permissible to reduce it and carry out work as it is actually necessary.
Note!
The technical documentation for a specific stabilizer may contain additional maintenance measures - all of them are mandatory. Strictly according to the instructions and within the time period agreed by the manufacturer!
Important!
Any work that involves contact with the stabilizer body should be carried out only after disconnecting the product from the power supply.
Electronic stabilizers
Electronic stabilizers are similar in principle to relay stabilizers, only the autotransformer windings are switched using high-speed semiconductor switches - thyristors or triacs. This allows correction to be carried out instantly and without noticeable harmonic interference at the output.
The advantages of such stabilizers: + As a rule, high accuracy and speed of stabilization + Silent operation + Long service life up to 10-15 years
Cons : – Noticeably higher price due to the use of expensive electronic components. If the input voltage of extremely low quality, in particular, jumps very sharply and sags, you should pay attention to inverter stabilizers
Summary: electronic stabilizers solve most problems with low-quality voltage and can be safely recommended for most country houses.
Most manufacturers are located in Russia and popular brands include: Energotech, Leader, Voltaire, Shtil and others.
Service life of stabilizers of different types
Inverter and electronic stabilizers have the longest service life (up to 10 years). The durability of simpler relay and electromechanical models usually varies from 5 to 8 years, although there are exceptions with a longer/shorter service life.
Sometimes the service life established for a stabilizer does not apply to individual components of the device, which, due to their specific nature (for example, constant mechanical movement), wear out faster than the rest of the product. We are talking primarily about current-collecting contacts and executive relays of the classical type. The former are present in the design of electromechanical stabilizers, the latter – in the relay circuit. The power part of inverter and electronic models is more balanced and does not have similar components.
Note!
The problem with many modern stabilizers is the accelerated wear of cooling fans. It is provoked by their continuous rotation and leads to the fact that these components have to be replaced long before the end of the service life of the rest of the device. The solution to this situation is an adaptive cooling system. In it, the fans turn on only after the internal temperature of the device reaches the maximum limit.
Important!
Mistakes made by owners when using a stabilizer reduce its service life. Achieving maximum service life, and this is precisely the value indicated in the technical documentation, will only be achieved if all established operating rules and requirements are unquestioningly observed!
Inverter stabilizers
Made using double conversion technology, which has long been actively used in the production of on-line UPSs. The principle of operation is to convert the incoming alternating voltage into direct current, and then the alternating voltage is again generated from the direct current. This circuit allows you to achieve maximum accuracy and quality of the output voltage.
This leads to the main advantage of such stabilizers: + this is the maximum quality of power supply for household appliances and electronics, regardless of the quality of the input voltage, even if your neighbor likes to weld + They correct the shape of the sine wave. Service life 8-10 years + Maintenance free
However, this technology also has its disadvantages . – First: inverter stabilizers should be selected with a good power reserve, since the double conversion circuit is critical to possible overloads and non-linear loads – Second: many models have forced constant cooling by fans, which means noise – And third: this is a relatively low efficiency – Fourth – this is the price
Summary: inverter stabilizers can be recommended in case of extremely low quality of the electrical network in the presence of equipment that is highly demanding on voltage quality. Sometimes it is advisable to install such stabilizers on individual consumers.
The main market is occupied by two manufacturers: Shtil and Volter.
A few more tips regarding voltage stabilization:
- If you have a very low voltage of less than 160V, pay attention to special models with a stabilization range shifted to the bottom; they are usually designated by the letter index LV (low voltage).
- For three-phase input, we recommend installing three voltage stabilizers, one for each phase. However, if necessary, the entire most important load can be assembled into one or two phases and, accordingly, one or two good stabilizers can be installed.
- We recommend additionally installing lightning protection - SPD to protect stabilizers and household appliances from powerful impulse noise. For air entry, Class 1+2, for underground, class 2. It would also be useful to have grounding, which is necessary for the correct operation of the stabilizers.
- In case of severe voltage sags, as well as network outages or blinking, we recommend installing a double conversion UPS with internal batteries for autonomous operation of up to 60 minutes or external batteries for autonomous operation of up to a day instead of the stabilizer.
All the best voltage stabilizers for the home are in our catalog.
Ask your questions in the comments!
Types of stabilizers and their capabilities for correcting voltage sags
Today, there are several types of voltage stabilizers on the electrical market, among which relay, electromechanical, electronic and inverter models stand out. Each of them has certain technical capabilities for correcting low input voltage.
Let's look at the technical characteristics of each of them in more detail:
| Stabilizer type | Technical capabilities (characteristics of some stabilizers may differ from those shown in the table) |
| Relay | · maximum input voltage range – 120-276 V (for some models 140-260 V); · reaction to a sharp decrease in voltage – from 10 to 20 ms; · Voltage correction accuracy – 5-10%. |
| Electromechanical | · maximum input voltage range – 130-276 V (for some models 150-250 V); · reaction to a sharp decrease in voltage – more than 100 ms; · Voltage correction accuracy – 2-5%. |
| Electronic (triac and thyristor) | · maximum input voltage range – 120-280 V; · reaction to a sharp decrease in voltage – from 10 to 20 ms; · voltage correction accuracy – 4-10%. |
| Inverter | · maximum input voltage range – 90-310 V; · response to a sharp decrease in voltage – 0 ms; · Voltage correction accuracy – up to 2%. |
Comparing the technical characteristics of different types of stabilizers, we can conclude that among the above devices, inverter models have the widest range of input voltage, have a higher accuracy of its correction and are able to instantly respond to sudden drops in the input signal.
These features make it possible to use inverter models in case of very significant network drawdowns, which are often found in holiday villages and villages, to protect the most demanding power consumers, for example, the electronics of gas boilers and circulation pumps.
Network quality and low voltage
If there is a small child in the family, washing clothes and preparing soup on electric burners becomes quite problematic. At this voltage, the microwave does not turn on at all. The tea boils for 20 minutes. Due to constant changes, the refrigerator, electric oven, and TV fail. People are tired of constantly living in the field.
But even a low-voltage stabilizer does not always cope with the situation:
- fans turn off;
- if the voltage is below 90 V, the device knocks out.
Without a normalizer, the filament in the light bulbs is barely visible. In a word, it turns out like in the song: “And twilight has come again...”
What to do if the voltage is less than 100 volts?
This is a terrible question, but unfortunately, we hear it from our customers from time to time. You need to measure the readings of devices in the network, take a video and contact GorElektroSeti in your region and the prosecutor's office, because such voltage goes beyond all limits of decency.
If you still want to get a higher voltage without waiting for a global solution to the issue, then each brand of voltage stabilizers has its own series of reduced voltage. For example, in the SUNTEK line of voltage stabilizers there is a special LV (low voltage) series. By installing such a stabilizer and not loading it above 50-60% of the nominal value, you will get a more or less stable voltage even at 100 volts in the outlet.