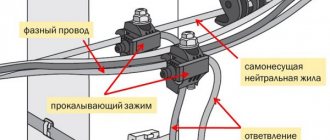
Operating and installation conditions for SIP-4 4x70:
— Type of climatic modification of wires B, placement categories 1, 2 and 3 according to GOST 15150-69; — SIP wires 4 4x70 are resistant to bending at temperatures: up to -40°C; — Laying and installation of SIP 4 4x70 wires must be carried out at an ambient temperature of: not lower than - 20°C; — Allowable forces in the zero load-bearing core during tension and operation should not exceed: 45 N/mm2; — SIP 4 4x70 wires after exposure to water at a temperature of (20+10) °C for at least 10 minutes must withstand an alternating voltage test at a frequency of 50 Hz for at least 5 minutes at the construction length: • self-supporting insulated with cross-linked polyethylene - 4 kV ; • self-supporting insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene and flame retardant polyethylene composition – 2.5 kV; — Operation of SIP 4 4x70 wires at temperatures from - 60°C to + 50°C.
Table 4.5 (ENSTO manual)
Continuous permissible current for SIP 4, SIP 5 (self-supporting insulated wire without a separate supporting conductor) Continuous permissible current is indicated for an ambient temperature of 30C. At design ambient temperatures other than 30C, it is necessary to apply the correction factors specified in Table 4.7
| Number and cross-section of cores, mm2 | Continuous permissible current, A |
| 2x16 | 84 |
| 2x25 | 112 |
| 2x35 | 138 |
| 4x16 | 84 |
| 4x25 | 112 |
| 4x35 | 138 |
| 4x50 | 168 |
| 4x70 | 213 |
| 4x95 | 258 |
| 4x120 | 296 |
| 4x35+25 | 138 |
| 4x50+25 | 168 |
| 4x70+25 | 213 |
| 4х95+25 | 258 |
| 4x120+25 | 296 |
| 4x35+35 | 138 |
| 4x50+35 | 168 |
| 4x70+35 | 213 |
| 4х95+35 | 258 |
| 4x120+35 | 296 |
| 4x50+2x25 | 168 |
| 4x70+2x25 | 213 |
| 4x95+2x25 | 258 |
| 4x120+2x25 | 296 |
| 4x50+2x35 | 168 |
| 4x70+2x35 | 213 |
| 4x95+2x35 | 258 |
| 4x120+2x35 | 296 |
Source:
A manual on the design of overhead power lines with a voltage of 0.38 kV with insulated wires (VLI) using ENSTO fittings. - Almaty, 2011.
Go to the article “Selection and testing of 0.4 kV cables”
Table 4 (PUE RK 2015)
Long-term permissible current for wires and cords with rubber and polyvinyl chloride insulation with
copper
conductors.
Table 5 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for rubber and polyvinyl chloride insulated wires with
aluminum
conductors.
Table 6 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for wires with
copper
conductors with rubber insulation in metal protective sheaths and cables with
copper
conductors with rubber insulation in lead, polyvinyl chloride, nayrite or rubber sheaths, armored and unarmoured.
Table 7 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for cables with
aluminum
conductors with rubber or plastic insulation in lead, polyvinyl chloride and rubber sheaths, armored and non-armored.
Table 8 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for portable light and medium hose cords, portable heavy duty hose cables, mine flexible hose cables, spotlight cables and portable wires with
copper
conductors.
Table 9 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for portable hose cables with
copper
conductors and rubber insulation for peat enterprises.
Table 10 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for hose cables
copper
conductors and rubber insulation for mobile electrical receivers.
Table 11 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for wires with
copper
conductors with rubber insulation for electrified transport is 1.3 and 4 kV.
Table 13 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
copper
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead sheath, laid in the ground.
Table 14 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
copper
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead sheath, laid in water.
Table 15 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
copper
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead sheath, laid in the air.
Table 16 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
aluminum
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead or aluminum sheath, laid in the ground.
Table 17 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
aluminum
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead sheath, laid in water.
Table 18 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with
aluminum
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead or aluminum sheath, laid in the air.
Table 19 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for three-wire cables with a voltage of 6 kV with
copper
conductors with lean insulation in a common lead sheath, laid in the ground and air.
Table 20 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible continuous current for three-wire cables with a voltage of 6 kV with
aluminum
conductors with lean insulation in a common lead sheath, laid in the ground and air.
Table 21 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with separately leaded
copper
conductors with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation, laid in the ground, water, air.
Table 22 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for cables with separately leaded
aluminum
conductors with paper impregnated with oil-rosin and non-drip insulation, laid in the ground, water, air.
Table 24 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for single-core cables with a
copper
conductor with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead sheath, unarmoured, laid in the air.
Table 25 (PUE RK 2015)
Permissible long-term current for single-core cables with
an aluminum
core with paper impregnated with oil rosin and non-drip insulation in a lead or aluminum sheath, unarmoured, laid in the air.
Go to the article “Selection and testing of 0.4 kV cables”
Scope of application of SIP-2 wire:
for use in overhead power lines and lighting networks for alternating voltage up to 0.6/1 kV with a nominal frequency of 50 Hz. The wires comply with the European Committee for Electrical Standardization (CENELES) standard HD 626 S1. Type of climatic modification of UHL wires, placement categories 1, 2 and 3 according to GOST 15150-69.
- The wires ensure high reliability and uninterrupted power supply to consumers (short circuits due to clapping of phase conductors, accidental overlaps, etc. are excluded)
- Allows you to significantly reduce overall operating costs by reducing the volume of emergency recovery work
- Prevents ice formation on wires
SIP-4 4x70
Description
Design
Wire design SIP-4 4x70:
The conductors are aluminum, round, multi-wire, compacted.
Insulation is made of light-stabilized polyethylene.
Twisting - insulated strands are twisted together.
Decoding
Explanation of the name of the wire SIP-4 4x70:
- S – Self-supporting.
- I - Isolated.
- P - Wire.
- 4 — SIP construction type: there is no separate load-bearing core.
- 4 - Number of cores.
- 70 — Section of veins.
Characteristics
Technical characteristics of wire SIP-4 4x70:
- permissible load for wires of types 1, 2 and 4 – 0.66/1 kV; for cable 3: up to 35 kV;
- mains frequency: 50 Hz;
- operating conditions: from - 50 degrees to +50;
- in this case, installation and tension are possible only at temperatures down to -20;
- the bending radius during installation of wires installed on supports is at least 10 outer diameters;
- approximate wiring life: 50 years;
- Many manufacturers also provide a warranty for their products, most often for 5 years.
Advantages of SIP-4 4x70 over traditionally used bare wires of grades A and AC:
- High reliability in providing electrical energy.
- A sharp reduction (up to 80%) in operating costs, caused by the high reliability and uninterrupted power supply to consumers, as well as the absence of the need for wide clearings for laying overhead lines in forests and clearing clearings during the operation of the line.
- Absence or slight accumulation of ice and wet snow on the insulated surface of the wires. In wires of grades A and AC, wet snow can be retained in the grooves between the wires, being the root cause of fouling.
- Reduced energy losses in the line due to a more than threefold reduction in the reactance of insulated wires compared to non-insulated ones.
- Simplicity of installation work, the ability to connect new subscribers under voltage, without disconnecting the rest from the power supply and, as a result, reducing repair and installation time.
- Improves the overall aesthetics of urban environments and significantly reduces the incidence of electric shock during line installation, repair and operation.
- The possibility of laying self-supporting insulated wires along the facades of buildings, as well as joint suspension with low and high voltage wires, communication lines, which provides significant savings on supports.
- Simplicity of the design of the supports (no traverses or insulators).
- Low risk of short circuits (short circuits) between the zero carrier and the current-carrying conductors; safe work near overhead power lines up to 1 kV.
- High mechanical strength of the cores and, accordingly, a lower probability of their breakage, increasing the span length to 60 m.
- The use of SIP on overhead lines reduces the likelihood of electricity theft, since insulated, twisted wires prevent unauthorized connection to the line by throwing onto the wires.
- Significant reduction in the number of cases of vandalism and theft.
There are also some disadvantages :
A slight increase in cost (no more than 1.2) of insulated wires compared to traditional non-insulated wires A and AC.
Wire SIP-4 4x70 technical characteristics
| Specifications | |
| Voltage, kV | 0,6/1 |
| Number of current-carrying cores, pcs | 4 |
| Number of load-bearing cores, pcs | 0 |
| Number of auxiliary cores, pcs. | 0 |
| Harness diameter, mm | 31 |
| Outer diameter of current-carrying core, mm | 9,7 |
| Outer diameter of the neutral core, mm | 0 |
| Harness weight, kg/km | 946 |
| Permissible load current of the conductor, A | 240 |
| Permissible one-second short circuit current of the conductor, kA | 6,5 |
| Electrical resistance of TPG, Ohm/km | 0,443 |
| Electrical resistance of the neutral core, Ohm/km | 0,443 |
| Conductor material | Aluminum |
| Material of the supporting zero core | — |
| Insulation material | Light stabilized cross-linked polyethylene |
| Nominal insulation thickness, mm | 1,7 |
| Number of wires in TPG, pcs. | 7 |
| Number of wires in the zero core, pcs. | 7 |
| Core tensile strength | — |
| Service life, years | 40 |
| Permissible operating temperatures, °C | from minus 60 to plus 50 |
| Permissible installation temperatures, °C | minus 20 |
| Permissible operating temperature of core heating, °C | 90 |
| Permissible core heating temperature during a short circuit, °C | 250 |
Operating conditions for SIP-2 wire:
For overhead power lines and branches to inputs into residential buildings, outbuildings in areas with temperate and cold climates, in an air atmosphere of types II and III according to GOST 15150-69.
| Technical and operational characteristics of SIP-2 wire | |
| Operating voltage | 0.6/1 kV |
| Ambient temperature during operation | from -50°С to +50°С |
| Relative air humidity (at temperatures up to +35°C) | up to 98% |
| Minimum cable laying temperature without preheating | -20 °C |
| Limit long-term permissible operating t° of cores: | |
| SIP-1 | +80 °С |
| SIP-2 | +70 °С |
| Maximum permissible heating temperature of cable cores in emergency mode (or overload mode): | |
| SIP-1 | +80 °С |
| SIP-2 | +130 °С |
| Maximum temperature of the cores under the conditions of non-ignition of the cable during a short circuit: | |
| SIP-1 | +80 °С |
| SIP-2 | +250 °С |
| Minimum permissible bending radius when laying | 7.5 outer diameters |
| Life time | 25 years |
| Warranty life of the cable | 3 years |
Wire (cable) SIP-4 4x70 description
Wire SIP-4 4x70 is a high-quality four-core wire that is used for laying overhead power lines. Its technical features made the wire quite popular among buyers. The main purpose of using the SIP 4-4x70 cable is to create subscriber branches and inputs into residential and commercial premises.
Self-supporting insulated wire can be used in a temperature range from minus 60 to plus 50 degrees. Installation is possible down to temperatures of minus 20 degrees. SIP is resistant to most types of external influences, including the influence of sunlight, precipitation and other atmospheric phenomena. Only the highest quality materials are used to make the wire, which allows us to achieve a high quality product.