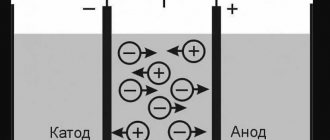
Various electrical appliances and devices are widely used in production and at home. The electricity needed for their operation is delivered through electrical wiring. The source of electricity has high power, which in normal operation of the network is spent to ensure the functioning of the load (power receiver).
A short circuit of both the cable line and the internal circuits of electrical equipment is not always monitored by automatic devices. In this situation, power is released on the current transmission circuits, which is accompanied by their rapid heating with melting of the polymer insulation and ignition of electrical equipment in severe cases.
What does the set of rules 9.13130.2009 regulate?
The most effective means of extinguishing electrical equipment, the fire of which occurs due to a faulty electrical network, is various fire extinguishers. The provisions for their operation are specified by the set of rules 9.13130.2009. This document:
- establishes basic provisions for the selection of stationary and mobile equipment, incl. automatic fire extinguishing;
- sets the provisions for its placement;
- determines the technical parameters of pressure sources for ejecting fire extinguishing mixtures;
- records the frequency of maintenance and other similar properties.
The provisions of the code are mandatory for compliance exclusively with reusable automatic fire extinguishing installations.
It has been established that extinguishing fires in de-energized electrical installations can be carried out using fire extinguishers of any type.
The document is recommended for use in the design and construction of real estate for various purposes.
How to extinguish an electrical panel
Let's start with the fact that a switchboard is a small room in which areas for supplying, monitoring and managing all electrical networks within the facility are grouped. In apartment buildings, an analogue is the distribution board located on the staircase. Everyone knows what it includes. Industrial switchboards are not much different from this one, it’s just that this room is more saturated with various devices and electrical devices. By the way, entry into it for persons who do not have access is prohibited.
So, what kind of fire extinguishers should be in the electrical room. Everything will again depend on the voltage that powers the object, and which is distributed through the panel compartment. If it is no more than 1000 volts, then powder models are suitable; if it is over 1000V, then carbon dioxide models must be used.
Review of existing fire extinguishers
The industry produces a wide range of stationary and mobile fire extinguishers designed to extinguish fires in electrical equipment.
Carbon dioxide
The principle of operation of a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher (CO) is based on supplying a low-temperature composition to the area of the flame, which, due to the high speed of the gas jet, knocks down the flame and also suppresses the fire due to cooling. Using carbon dioxide technology, you can extinguish electrical wiring without leaving traces, which is attractive when operating computer, television and telecommunications equipment. Fires in electrical installations can be extinguished using carbon dioxide devices in case of class E fires, i.e. electrical equipment under voltage up to 10 thousand volts.
Carbon Dioxide Fire Extinguisher Series
The main disadvantage is the rapid drop in oxygen concentration in the room, which prevents the use of carbon dioxide technology in confined spaces.
Powder
Powder fire extinguishers, in accordance with current fire safety regulations, are compatible with installations with operating voltages up to 1 kV. It is permissible to use them even on live equipment.
The principle of operation of such devices is based on suppressing the flame by stopping the access of oxygen after supplying a neutral fire extinguishing powder to the source of fire, which covers the surface with a thin layer. It has been established that extinguishing with a special powder provides the greatest effectiveness when insulation is burning.
In addition to switchboards and electrical appliances, powder technology can be used in electric modes of transport (trolleybuses, trams), as well as in production.
The expiration date, fire extinguishing ability, as well as other data must be indicated on the body of the fire extinguisher in the form shown in Figure 1.
Rice. 1. Marking of powder fire extinguisher
Air foam
Air-foam fire extinguishers, which are represented by the ORP series, belong to rechargeable fire-fighting equipment. Designed as a portable fire extinguisher, often performed as a mobile or stationary installation. Contains a steel cylinder of various capacities filled with water-based foaming material. The functions of the expelling charge are performed by carbon dioxide, which, under high pressure, pushes the fire extinguishing agent out.
To increase the intensity of foam formation, use a metal or polymer diffuser of various shapes with a fine mesh that covers the outlet of the diffuser as shown in Fig. 2.
Rice. 2. Typical design of the sprayer of an air-foam fire extinguisher and its connection to the cylinder
To extinguish a fire, the generated powder stream is directed to the combustion site. The greatest efficiency of foam fire extinguishers is achieved when the space around the installation is completely filled.
Foam fire extinguishers are capable of extinguishing flammable liquids.
A serious drawback of this technology is that it only works at positive temperatures.
Water
Water fire extinguishers work on the principle of flooding the fire area with water. Can be used to extinguish only de-energized electrical installations. They require mandatory shutdown of the electrical installation, i.e. They are used only when there is a visible break in the power supply cable. In manufacturing, due to the risk of electrical shock, their use usually requires permission from the dispatcher.
Freon
Portable fire extinguishers with liquid hydrocarbon filler (freon) visually differ little from carbon dioxide ones. The chemical formula of refrigerant differs little from liquid fillers used in refrigeration units.
When leaving the cylinder of a freon fire extinguisher, the composition takes on the appearance of snow, covers the burning surface, cools it and at the same time cuts off the access of oxygen. Combustion stops due to the combined action of these factors.
Due to the chemical neutrality of the freon, there is no damage to the structure of electrical appliances and cables.
Modern refrigerant compounds are corrosion-neutral at room temperatures and do not destroy the ozone layer. Under the influence of a flame, freon decomposes, releasing bromine and fluorine, which are toxic to the respiratory system. Domestic and imported devices of various capacities are available for use, Fig. 3, which allows you to select the desired option.
Figure 3. Series of freon fire extinguishers of various capacities
Aerosol
Aerosol devices have two varieties, which differ in the type of filler: solid and fine powder. The extinguishing effect of these compounds is based on the fact that under the influence of high temperature an aerosol is released, which blocks the access of oxygen, for example, to burning insulation.
Examples of aerosol fire extinguishers
Aerosol fire extinguishers are characterized by:
- simplicity of design;
- operability in a wide temperature range;
- Possibility of use for extinguishing fires of all classes.
The main disadvantage is the toxicity of the aerosol, which precludes the use of this technique in enclosed spaces.
Why do fires occur in electrical wiring?
What can cause electrical wire insulation to catch fire? There are several reasons for this:
- non-compliance of the wire with fire safety standards;
- poor electrical connection;
- incorrectly selected wire or machine.
The latest GOST requirements provide for the use of cable in residential premises with the index “ng”. That is, such an index must be present in the cable marking. The sheath of such a cable is made of flame retardant plastic.
If the cable has conventional insulation, then if it overheats or shorts, it can ignite and cause a fire. Or a wire that has expired is used. Then its insulation may be damaged and lead to a short circuit.
Another option is that the cable or wire was laid in violation of safety regulations, for example, it could be laid over flammable materials without fire-resistant gaskets, when necessary.
The connection of cores in the wire must be carried out in a reliable way. When the cores are made of different materials, such as aluminum and copper, and are connected directly, without intermediate material, this leads to oxidation of the surface.
Oxides have a high resistance to electric current and will heat up. This will start a chain reaction: when heated, oxidation will occur even faster, resistance will increase, and heating will increase.
If the cross-section of the cable does not correspond to the power consumption of electrical appliances, then it will also heat up, and over time the insulation will begin to melt. This will cause the wires to become exposed and a short circuit will occur. The situation will also be aggravated by an incorrectly selected machine that does not turn off the emergency section.
Features of extinguishing fires in electrical installations
The complexity of an electrical installation from a fire hazard point of view is that:
- fire often occurs when the electrical supply is not disconnected from the installation;
- Some traditional fire extinguishing agents have a side effect and, in addition to suppressing the flame and smoldering, damage the insulation and structure;
- not all extinguishing agent options are acceptable for use in enclosed spaces.
Therefore, the choice of fire extinguishing means for electrical equipment must be made taking into account these features.
Up to 400 V
Eliminating the fire of de-energized electrical installations with a rated operating voltage of not more than 400 V according to the set of rules 9.13130.2009 can be done in various ways. To minimize overall risks:
- It is preferable to use halon fire extinguishers;
- Compact jets cannot be used;
- sprayed water is directed towards the fire from a distance of at least 5 meters;
- It is recommended to work with dielectric gloves.
Another extinguishing option is to extinguish with foam, completely filling the space around the installation.
A halon fire extinguisher is used at a distance of at least 1 m.
Features of the use of various types of equipment are shown in graphical form in Figure 4.
Basic rules for using fire extinguishers
Up to 1000 V
The preferred type of fire-fighting equipment for such equipment is a powder fire extinguisher, which is acceptable for use both on de-energized equipment and before the voltage has been removed. It is considered that the required level of personnel safety is achieved with a powder jet length of at least 1 m.
Another means of extinguishing fires at such electrical installations are water spray fire extinguishers. A special feature of such equipment is its mandatory certification according to GOST R 51057 or 51017 in an organization with the appropriate accreditation.
Up to 10,000 V
To extinguish fires of electrical equipment operating at a rated voltage of up to 10 kV, it is permissible to use only carbon dioxide fire extinguishers. Taking into account the danger of high voltage, they are separately rated
- moisture content in gas (not more than 0.006%);
- the length of the jet created by the installation, which should not be less than 3 m.
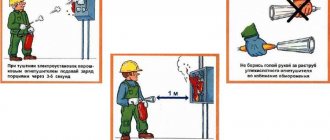
Security measures
Extinguishing live equipment takes place without consequences if the safety rules are followed:
- Electrical voltage must be completely switched off in the entire building (electrical cabinets, equipment, chargers, electrical appliances) if this can be done.
- Two firefighters will be deployed to extinguish the fire. One of them holds the hose and directs it to the source of the fire, the second presses the release button.
- Everyone involved in extinguishing a fire must wear dielectric protective clothing (it is stored in a separate room, high and away from electrical objects and wires).
- Extinguishing electrical equipment with water or water-containing substances is strictly prohibited.
- Fire-fighting operations are carried out with the permission of the administration and the admission of the fire safety chief.
Extinguishing electrical wiring
Electrical wiring fires occur mainly in the event of a short circuit when:
- insulation defects due to aging, lack of maintenance, mechanical damage;
- poor quality of contacts;
- defects in circuit breakers.
If there is no voltage, you can extinguish the electrical wiring with all types of fire extinguishers. It is acceptable to use sand and water.
Fighting fires on 1000-volt wiring without turning off the voltage is possible only with the help of a powder fire extinguisher. On feeders with voltages up to 10 kV, only carbon dioxide fire extinguishers are allowed.
It is prohibited to extinguish electrical wiring with foam due to the high risk of damage to insulation and contact elements by accompanying chemical reactions.
What kind of fire extinguishers can extinguish
It is important to choose the right type of fire extinguisher so as not to create a dangerous situation during the extinguishing process
Foam, water and what you need to know before extinguishing electrical wiring with water
Description of a foam fire extinguisher The series of indicated devices are ORP, OCP and OV. They are allowed to be used to extinguish electrical wiring that is guaranteed to be disconnected from the power supply. Since the substance used in this fire extinguisher is a conductor of electric current, their use on an object connected to the current is dangerous for the person extinguishing the fire.
A foam-forming composition is pumped under pressure into the steel welded body of such a device, which is released through a tube when the shut-off and starting device is activated. The filling must first be removed.
Also read: Switching without excitation - transformer off-circuit switching
Powder
They can be used to extinguish lines with voltages up to 1000 V. Structurally, they are not too different from previous fire extinguishers, but instead of a foam composition, a special powder is used. During the spraying process, air access to the source of fire is stopped, with localization and extinguishing of the fire, and at the same time the flame is knocked out. Considering the short duration of work (from 6 to 15 s.), it should be precisely directed to the place of combustion in order for the application to be as effective as possible. The powder is sprayed from the edge of the fire to the middle, for a vertically located wire - from bottom to top.
Carbon dioxide
Description of carbon dioxide fire extinguisher A series of op-amps of various capacities are produced. They are distinguished by the greatest efficiency compared to other devices. The fire extinguishing agent is acid, which does not conduct electricity, so these devices can be used to extinguish wiring with voltages up to 10 kV, which is more common in industrial production. Also, this substance is not aggressive, which is safe for the integrity of wires and equipment.
This type of fire extinguisher, in addition to its high efficiency, differs from others in its lighter weight and greater ease of use.
Please note that this acid is dangerous due to the following features:
- vapors of the substance when used in confined spaces can cause poisoning;
- During use, the composition has a low temperature, which can cause damage to the skin of the hands.
Simultaneously with knocking down and extinguishing the flame, during the use of this fire extinguisher, the temperature heating of the surfaces being treated is reduced.
A distinctive design feature of carbon dioxide fire extinguishers is the use of a rigid tube instead of a hose, which can be rotated around its own axis to control the acid stream.
Conclusion
In practice, various types of fire extinguishing installations are used. Selecting a specific type of this equipment is a multi-criteria task. When making the final decision, the following are taken into account:
- operating voltage of the protected network;
- equipment location;
- efficiency of de-energizing equipment in the event of an emergency;
- financial capabilities of the electrical equipment owner.
Regardless of the latter, human safety is always put at the forefront. The main means of achieving this are the correct selection of the type of fire extinguisher, the choice of the distance from which extinguishing is carried out, and the use of protective equipment. Regardless of the current situation, it is advisable, if possible, to first de-energize the equipment that has caught fire.
Fire extinguisher selection criteria
If a fire hazard occurs in rooms with electrical equipment, it is recommended to use primary fire extinguishing means: fire extinguishers that are easily moved from place to place and used to extinguish fires with special substances that stop combustion. The basic rule when choosing a fire extinguisher is the correct monitoring of a number of factors: the distinctive properties of the equipment being protected, the category of the room, the volume of the protected area, the properties and mass of products susceptible to fire. You should also take into account the effectiveness of using a fire extinguisher to eliminate a fire of a particular class.
The use of extinguishing agents, depending on the fire class according to GOST 27331-87 .
| Fire class | Class characteristics | Fire subclass | Subclass characteristics | Recommended extinguishing media |
| A | Combustion of solids | A1 | Combustion of solids accompanied by smoldering (e.g. wood, paper, coal, textiles) | Water with wetting agents, foam, freons, ABCE type powders |
| A2 | Combustion of solids not accompanied by smoldering (rubber, plastics) | All types of fire extinguishing agents | ||
| B | Combustion of liquid substances | IN 1 | Combustion of liquid substances insoluble in water (gasoline, petroleum products), as well as liquefied solids (paraffin) | Foam, finely sprayed water, water with the addition of fluorinated surfactants, freons, CO2, powders like ABCE and VSE |
| AT 2 | Combustion of polar liquid substances soluble in water (alcohols, acetone, glycerin, etc.) | Foam based on special foaming agents, finely sprayed water, freons, powders such as ABSE and VSE | ||
| WITH | Combustion of gaseous substances | — | Household gas, propane, hydrogen, ammonia, etc. | Volumetric extinguishing and phlegmatization with gas compositions, powders such as ABCE and VSE, water for cooling equipment |
| D | Combustion of metals and metal-containing substances | D1 | Combustion of light metals and their alloys (aluminum, magnesium, etc.), except alkali | Special powders |
| D2 | Combustion of alkali metals (sodium, potassium, etc.) | Special powders | ||
| D3 | Combustion of metal-containing compounds (organometallic compounds, metal hydrides) | Special powders |