A comb (bus) for circuit breakers is a device for assembling and installing distribution boards. It consists of a solid copper plate, which is placed in a plastic insulator.
According to the type of connected devices, combs are divided into:
- single-pole;
- bipolar;
- three-pole;
- four-pole.
The number of poles is equal to the number of plates that are in the comb bus.
The type of connecting busbars is selected depending on the task at hand. The most rarely used are three-pole combs. To connect single-phase machines, single-pole ones are most often used, and for three-phase machines, four-pole ones are used.
The size range of comb pitches ranges from 18 mm to 27 mm. Possible number of modules (teeth): twelve, twenty-four, thirty-six, forty-eight, sixty.
Design
The combs (tires) consist of a plate placed in a plastic housing and pins, which are called teeth. The body is solid. The pins are bare, that is, they do not have any protective plastic shell, since they are inserted into contacts for the purpose of connecting a protective modular structure.
They can be L-shaped or V-shaped, but the first option is most common.
A standard single-pole comb is presented in the form of a rectangular reddish-yellow plate located in a housing made of refractory plastic.
In the two-pole type there are two bars. The distance between the pins is greater than that of a single-pole one. The reason is that this type of comb has several power cables for connection: phase-zero (L+N) or phase-phase (L1+ L2). The pins in this case go through one another.
Design features
Upon closer examination of the design, you will notice that it consists of a conductive core and a base made of plastic, which is designed for installation on a DIN rail.
The photo shows the appearance of the NS:
The current-carrying core contains holes and clamping bolts for fixing the conductors in it, as well as for neat and safe wiring of conductors N inside the switchgear. NS differ from each other in both the installation method (housing) and the number of mounting holes, respectively, in length.
To ensure a high-quality connection, as well as simplify further maintenance, the bus is made of a single conductive element of sufficient size made of electrical copper or brass. With a different number of bolt terminals to which neutral (N) conductors are connected.
A distinction is made between ground buses in a housing and grounding buses without a housing; the externally conductive elements are identical. The neutral bus is made in a housing or an insulator is installed. For the correct functioning of differential protection devices, it is necessary to connect them correctly, and to separate the conductors N from PE in the distribution board. In the case of a metal shield, this can only be done by isolating the neutral conductor from the housing.
Types of bends
There are two types of outlet of connecting combs:
- Pin type (marked “pin”) - suitable for almost all types of safety units, regardless of the manufacturer.
- Fork ones (marked “fork”) are extremely rarely used, since connection requires a special clamp, which is not present on all devices. Used by branded companies.
Connecting single-phase devices
Single-phase connection is the simplest. It is used for single-pole machines. The procedure is as follows:
- All protection devices are installed in a row. This requires a DIN rail.
- For each individual device, the screws in the terminal blocks are loosened to a certain point. This is done from the top side.
- One single-pole bus is inserted into the terminal blocks of circuit breakers. The pitch of its teeth should be 17.5 mm.
- The screws are tightened. The tightening is tight enough to securely fix the tire pins.
Algorithm for connecting automatic tires
To connect automatic tires you need:
- take a comb and remove the reddish-yellow tire from it;
- if the connection requires fewer circuit breakers than there are taps on the comb mounting rail, then you should cut off the required number of teeth (three, five or seven teeth - depending on your case). This operation can be performed with any tool suitable for the situation, for example, a hacksaw. It is better to cut the parts separately: the insulator separately, the tires separately;
- then, you should cut the plastic block body according to the length of the copper plate, preferably a little more than necessary, so that parts do not stick out from the edges of the comb. This will also help prevent short circuits. Specialized plugs should be placed on the cut sides of the insulator, which, as a rule, are sold complete with the connecting busbar. But if there are none, then you can use electrical tape;
- the bus should be inserted on top of the connected devices (each tap should be connected to the corresponding contact socket). Next, you should screw the comb under the entire row of required machines and connect the power. It is at this point that the wire is connected together with the bus in the machine.
Types of connecting busbars for electrical wiring at home
If you want to choose the right connecting busbar for wiring your home, knowledge of the parameters alone will not be enough. You should also understand the types of these devices. The connecting bars differ in terms of design, contact distribution, and application in the selected conditions. For example:
- Comb wire busbar - used for horizontal and vertical connection of residual current and overcurrent circuit breakers. On the market you can find devices with 1, 2, 3 and even four poles. It should be noted that this type of connecting bars also exists in two- and three-row versions, as well as in the form of pins - they are distinguished by their easy and quick installation and reinforced design;
- Terminal bars are special plug connections that are usually made of copper. They are installed with a branched connection to the main circuit. This type of busbar can be sold in single, two and three phase form - when it comes to the number of modules, the product is sold in a short model (from 4 to 12 modules) and a long model (the number of modules often exceeds 50). Blade busbars usually have a protective insulating coating, so they can be successfully used as part of an electrical installation in the home, as well as in industry or even in construction;
- Rod busbars - in which the contacts are shaped like rods (shaped like rods), these types of connecting busbars usually have a large number of modules, and they are also relatively long. That is why they are often used in industry, metallurgy and construction. Pin splicing is available in the market in vertical, horizontal, single and multiple rows and also has multiple phases. Please note that some models are not suitable for use with devices that have additional contacts and track types.
Installation
Installation of a conventional comb bus takes place within the boundaries of the input or distribution panels. Usually this process does not raise any questions.
Features of connecting the bus under the comb:
- during installation, the conductive portion of the comb comes between the lower pressure plate and the comb itself, which is why the plastic insulating stage on it is directed towards the screw-shaped fastening;
- if this requirement is violated, it will not be possible to obtain an aesthetic connection that will not bend the plate;
- when installing a three-phase type comb, it is necessary to monitor the accuracy of the position of the insulators in order to eliminate the possibility of an interphase short circuit;
- When installing connecting busbars for automatic machines instead of typical cable jumpers, it is important to adhere to the generally accepted markings, which are located on the housings of the mounted products, and also meet the conditions of the existing standards.
Comb Manufacturers
There are many comb tires on sale from different manufacturers. As a rule, these products are produced by the same companies that produce circuit breakers. The most famous brands include the following:
- ABB;
- Schneider Electric;
- EKF;
- Legrand;
- WAGO;
- domestic IEK.
Comb connectors significantly simplify electrical installation. At the same time, the overall shield assembly time is reduced. However, you have to pay for such pleasure. Here everyone decides for himself whether he needs it or not.
If the choice is made in favor of combs, then you need to think about their technical characteristics. The comb must correspond to the total power of all consumers that will be fed through it
It is equally important to understand the design features. After all, there are models for 1, 2, 3 and 4 poles, and each is appropriate in its own situation
Advantages and disadvantages
The disadvantages of copper-based connecting combs include:
- the constant need to turn off the power when necessary to repair or service the device, which creates certain inconveniences;
- difficulties in implementing the modernization of the shield. If you need to install an auxiliary device, you will need to change the connecting comb or install an adapter jumper. But this may have a negative impact on the properties of the contacts;
- changing the first blown circuit breaker will require unfastening each contact on each device, but dismantling the bus may not work any other way;
- Due to the fact that different manufacturing companies in most cases can allow discrepancies in dimensions and instruction volumes, there is a need to install connecting busbars from only one manufacturing company together with the device that is planned to be connected. Choosing different companies may lead to the fact that the electrical connection will be impossible, because the pin may simply not reach the clamping contact;
- using homemade jumpers consisting of wire and electrical tape when connecting machines can be much cheaper than using a connecting bus. But this drawback applies to products from well-known brand manufacturers;
- using a connecting comb is pointless when connecting 1 or several machines. The reason for this is that it is designed for more than six modules.
One of the most popular combs on the Russian market are combs from ABB (abb or abb). This is a Swedish-Swiss company located in Zurich.
The advantages of copper-based connecting combs include:
- ease of use and high assembly speed;
- guarantees a high-quality and also safe galvanic connection, since the terminal can only clamp one contact (the exception is the first terminal, into which power is supplied from the line of the used pin bus, and the fork bus is free from this drawback).
- reduces the total number of contacts by 2 times, and due to this, the reliability of the resulting connections increases, eliminating the possibility of excessive heating of the contact points;
- An inherent advantage is the switching property; contact with a branch core is many times better than using a single-core cable as a jumper. Using a comb almost eliminates overheating of the contact pad;
- most often, the busbars of a connecting comb for six modules are designed for a load of 63 A. In order for the wire to withstand this load, it must have a cross-section of at least 16 square millimeters, and this significantly makes working with it more difficult;
- thanks to the comb in the shield, the number of wires is reduced, which affects the neatness of the wiring, as well as its indicativeness. This makes it easier to understand it if the need arises. The use of a comb allows you to independently carry out high-quality wiring.
Using a comb for automatic machines makes installation in the switchboard much easier and faster, and this fact is the main advantage.
Connecting RCDs and differential circuit breakers
Using a two-pole comb, designated as (L+N), as well as its 3-pole analogue, it is convenient to combine not only ordinary circuit breakers, but also to add residual current devices (RCDs) to them. When simple disconnecting circuit breakers and RCDs are installed in a cabinet in one line, the installation of a combination of protective devices becomes noticeably more complicated. The difficulties that have arisen are explained by the peculiarities of supplying power buses to various types of devices, which manifest themselves differently in the following two options:
- One or more RCDs are installed together with a line of several machines.
- Instead of automatic machines and RCDs, differential devices that completely replace them are lined up.
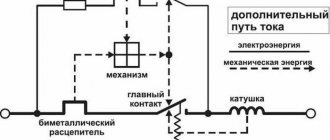
A difavtomat is a RCD and a conventional circuit breaker combined in one housing.
The first case, in turn, involves two installation options: the comb is used in a single-phase circuit or installed in a three-phase power line.
Single-phase connection
The peculiarity of this connection is that for automatic machines you will need a single-pole line, and for an RCD - a two-pole line. The condition for operation of the latter is the joint switching of phase and zero. In this case, they proceed from the principle of maximum capabilities, that is, they choose a two-pole bus, and the earth bends attached to the machines are simply bent.
3-phase connection
In this case, you will have to use a 4-pole copper comb, the three phase contacts of which are used on both the machines and the RCD. The fourth “zero” row is used for connection to an RCD, and in the area of the “ground” contacts of conventional disconnecting devices it is simply bent. When installing some automatic devices in any situation, the comb taps are connected to all contacts involved in the circuit.
A connecting comb for circuit breakers and RCDs is a convenient way to combine them into a single structural unit. It can be used both in standard closed-type distribution cabinets and in any other place reserved for the installation of switching devices.