- home
- car battery
- …
The topic of internal resistance of a car battery is not so popular. It’s just that before it was quite difficult to measure it (I mean exactly, homemade methods don’t count). Now there are devices that can show this parameter in a matter of seconds. In this article (and of course the video below) we’ll talk about the resistance of popular battery models, such as 60, 75, 90 Ah. I will also tell you what the standard is for new and worn batteries. Well, for convenience there will be a table with indicators...
I want to warn you right away - we will be talking about lead-acid batteries that are used in cars. We won’t talk about other types of lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, etc., they are simply not used in cars
What is the internal resistance of a battery?
This is the sum of the resistances of all the components of the battery (usually polarization and ohmic resistance). By “ohmic” we need to understand the sum of the resistances of the component parts: - separators, plates, electrodes, positive and negative current leads, bridge welded connections between “packages” of plates (and banks), as well as the electrolyte (it is clear that the plastic case has virtually no effect on this value). Measured in Ohms. The “ohmic indicator” is always present (there are no metals or liquids that are completely neutral yet).
In simple words, the normal EMF (electromotive force) of a battery can be 13.5 V, but the internal resistance usually leads this parameter to 12.7 V. Now this is 100% charge for many new batteries, this is exactly the data indicated by many manufacturers (over time these parameters may change as the battery degrades).
Methods for checking the battery with a multimeter
When checking a battery with a tester, two approaches are used: measuring its parameters with the engine running or with the engine turned off. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
How to check the battery while the engine is running
In this case, before checking the battery voltage with a multimeter, it is important to consider the following points:
- You can start the engine only after it is installed on a level surface and put on the handbrake.
- After it starts, the built-in generator and voltage regulator begin to work, recharging the battery.
- The voltage at the terminals when the engine is running reaches a reading of 13.5-14.0 Volts.
- Thanks to the electronic regulator, it is maintained at a level that eliminates the possibility of the electrolyte boiling.
To determine the exact value of the battery voltage with a multimeter, you will need to turn off all “powerful” consumers, including heating devices, headlights and sound-reproducing equipment. If this is not done, then the power of the generator when idling will not be enough to maintain the nominal level.
In this case, its reduced value can be explained by the following reasons:
- Poor contact in the load electrical circuit.
- Faulty built-in generator.
- Failure of the electronic regulator.
If at least one of these malfunctions is detected, it is not recommended to use the battery for a long time. To keep it in working order, you will have to understand the cause of the malfunction and eliminate it.
If the measurement results are satisfactory, you can turn on the energy consumers, and then increase the engine speed and repeat the voltage measurements. In a situation where at high speeds it drops to 13.4 Volts and below, diagnostics of the generating set and control unit is necessary.
When the engine is not running
When the engine is not running, when measuring the battery voltage, the average reading should be in the range of 12.5-13.0 Volts. The upper limit corresponds to 100% charge, and the lower limit corresponds to only 50% charge. These measurements are taken before driving, not after the engine has just been stopped.
Please note: The best option is to use the multimeter in the morning, after the car has sat in the garage overnight.
Only in this case can you get accurate information about how well the battery can hold a charge.
Battery diagnostics
You need to understand that the older the battery is, the higher the internal resistance indicator (or there may be a new battery, but it was stored incorrectly). Impact on everything, for example - on capacitance, voltage, and also current.
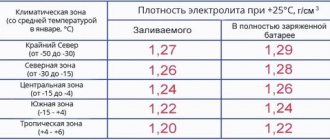
If a new battery with a capacity of 60Ah has a reference internal resistance of only 4-6 mOhm. The voltage rises to 12.7 V without problems. Starting current is approximately 600 A, electrolyte density is approximately 1.27 - 1.29 g/cm3
Then a 5-6 year old battery has an indicator of about 10 - 15 mOhm (much depends on the operation), the capacity is already about 30-40Ah. Voltage (after 3 hours after charging) – 12.3 – 12.5 V. Starting current, God forbid – 300 A, electrolyte density about 1.23 g/cm3
That is, the second battery has almost completely exhausted its resource. The figure rose almost 2.5 times. And how often does this happen due to sulfation of the plates .
Therefore, knowing the internal resistance of a new battery, as well as a used one (or one that was stored incorrectly), you can already understand how much wear the battery has.
Therefore, a simple rule when choosing a new battery:
- If possible, take a battery tester to the store
- Not all even new batteries are “equally useful”
- Measure internal resistance
- If it is within 4 - 7 mOhm (it can be different for different containers, more on that below). You can take it
- If it is 7 - 10 mOhm. This means that the battery has been standing for a long time, or it was stored incorrectly, and sulfation processes have begun inside. It’s not worth taking, or you need to ask for a discount.
Normal indicators
The internal resistance of a car battery should be 5 milliohms. You should focus on this indicator, although there are no standard values that would be considered exemplary. In any case, if the battery has already been used, but is not yet worn out, then the indicator should be in the range from 4 to 6 milliOhms.
A significant influence on the overall loss of physical qualities of the battery is influenced by the indicator that occurs in the working fluid, which is the electrolyte. It depends, in turn, on the ambient temperature and its concentration. As the liquid temperature decreases or the density increases, the current loss rate increases.
The capacity of the battery is to the same extent related to its internal resistance, and knowing this parameter, we can draw a conclusion regarding the capacity of the battery. For example, if it has decreased by 2 times, then experts conclude: the battery has lost up to 50% in capacity. These measurements determine its ability to provide a high starting current to the load. This is an inverse relationship: the smaller it is, the greater the peak current and power will be. The increased resistance causes a sharp drop in voltage at the battery terminals. Even if it is relatively new, it will not be able to produce a good peak current for the load.
Measuring the capacity of a car battery
In the process of general monitoring of battery current loss, this indicator is analyzed for its various components: leads, electrolyte, contacts, etc. If their value differs by more than 10% from the average indicator, then they must be charged separately, and if this does not bring success, then replace with new ones. At the same time, the average user does not own the special equipment required to evaluate this criterion. The most objective method of carrying out such measurements is a control charge for 10 or 20 hours, and then comparison with control data for voltage and discharge current.
In a word, the concept of internal resistance is a conditional value and its value constantly changes under the influence of operational factors. Therefore, when they want to get the most accurate calculations, they take as a basis not the value of internal resistance, but the discharge curves.
Norm for 60 Ah
Ideally, we take a new battery that has not been sitting on the counter for long and is well charged.
In general, there are no exact indicators, there are only averages . But the smaller the battery capacity, the higher the resistance inside it.
This is due to the fact that the size of the plates is smaller - the contact area is smaller, so the indicator increases.
As many manufacturers write, the benchmark for a new battery with a capacity of 60 Ah is 4-7 mOhm. The average data will be in the table below
IMPORTANT - it is advisable to carry out measurements at a temperature of + 20, + 25 degrees Celsius, because in the cold the electrolyte freezes, and this indicator may increase
Battery check
You can learn how to check the voltage on a battery with a multimeter by watching numerous video reviews posted in large quantities on the Internet. In addition, they provide other information of interest to motorists. After watching these videos, anyone can learn how to measure current with a multimeter, as well as how to determine its working capacity and internal resistance. In conclusion, we note that figuring out how to check the battery charge with a multimeter is not difficult at all. To do this, just follow the instructions and recommendations given in this article.
Please click on one of the buttons to find out if the article helped or not.
Indicator for 75Ah
This battery, although almost 25% larger, has almost the same resistance. Again, a lot depends on the manufacturer
If after testing you have from 3 to 7 mOhm on your device, then you can take it. This is an almost 100% battery that will produce an honest 75Ah
Again, we have acid batteries with liquid electrolyte
Norm of indicators
The current in an average-priced battery of an identical product has a current strength of 2.5A. More powerful 12-volt batteries have a current strength of at least 4A. If the indicator is from 1.3-2.9A, this means that the battery life is reduced, but you still shouldn’t throw them away; they are useful for working in remote controls for TVs or household appliances.
In cases where the multimeter readings are between 0.7-1.1A, such a voltage source can only work in low-power electrical appliances, and the operating efficiency will deteriorate. This is only possible when there are no other batteries.
The average voltage for a AA battery is 1.5 volts. If the indicator matches the standards, but the battery does not work, the reason for this may be reduced current strength. In this case, you need to buy a new power source.
Resistance for 90Ah
As a rule, such batteries are very large and heavy, 80Ah can also be classified as one, their performance will be almost identical
The norm for 80 - 90Ah is from 3 to 6 mOhm, sometimes I even met batteries that produced about 2 mOhm (but this is extremely rare)
As I wrote above, the larger the battery, the lower its internal resistance indicator due to the more massive and larger components (plates, jumpers, etc.)
What does the parameter depend on?
The internal resistance is dynamic and is influenced by the following parameters: battery capacity, current, load, current charge level, temperature of the electrolyte inside the cans. The higher the load current, the smaller the parameter. The situation is similar with capacity. The higher it is, the lower the internal resistance of the battery.
Battery internal resistance curve.
Why can't you take measurements in cold weather?
As I wrote above, the total resistance is the sum of each component of the battery. And the electrolyte is no exception.
The main indicators of the battery are taken at positive temperatures of + 20, + 25 degrees. Our electrolyte is liquid and works great inside. That is, it reacts with the plates, be it a discharge or a charge
BUT! At negative temperatures, the performance of the electrolyte decreases, because it simply freezes. Its internal resistance increases, the charge-discharge processes decrease (and at -35, the charge will be so minimal that it practically stops).
If – 35, measure the internal resistance of the battery, it will be much higher than + 25 degrees. It’s wrong to measure like that!
What parameters can be checked?
Using a multimeter, you can measure voltage with high accuracy. By the magnitude of the electrical voltage, you can determine whether the battery is charged or the element needs to be charged with direct current.
Using a multimeter, you can check the voltage not only of acid batteries, but also of cell phone batteries. To check the mobile phone's battery charge level, the device is switched to the mode for measuring direct current up to 20 V. In this mode, the digital device allows you to measure voltage with an accuracy of hundredths of a volt.
The screwdriver battery can also be easily checked with a multimeter. The rated voltage of the device, in this case, can be found out from the documentation of the power tool, and if the voltage is less than this value, then the battery must be charged.
The battery capacity can also be checked with a multimeter. For this purpose, you can use several methods.
You can check current leakage using a multimeter. If it is necessary to measure this parameter on a car, then in addition to the current leakage on the body, the leakage in the vehicle’s on-board network is also checked.
In this way, you can prevent rapid discharge of the battery and increase its service life.
How much does resistance increase per year?
That's a very difficult question. Once again, a lot depends on how you use your battery, what your mileage is, what conditions, in what climate (often batteries that are in warm climates last longer).
But if we take the average “hospital temperature”, the increase is approximately 10–15% per year . If a new battery, for example, has a value of 5 mOhm, then a 5-year-old battery will have 6 - 8.75 mOhm.
But after 6 - 7 years, the indicator will exceed 10 - 13 mOhm , and will make the battery practically unusable in cold weather. I will try to summarize the data in the table below.
The increase in resistance occurs only due to the fact that the plates are overgrown with lead sulfates. Part of the surface of the plate is simply packed with them. Of course, you can do the desulfation process , but it doesn’t always help
In real life, if the battery lasted for about 5 – 6 years, this is normal. After all, we don’t always take care of the battery; sometimes we abandon the car if it doesn’t start in the cold (and charge the battery after a few hours, or maybe days).
Experience of car enthusiasts
I never do this on my own. And in general, I rarely take care of the battery the way I should. Therefore, difficulties with ignition often arise. You have to go to car repair shops to get rid of them. I pay money, but I don’t waste my time and energy.
Igor Slabkin
Of course, you need to measure. But do not rely on absolute indicators taken from the Internet. It is much more relevant to compare new results with old ones, because they will greatly depend not only on the model, but also on natural conditions. Of course, certain frameworks and standards still exist, but they should only be taken from the official specifications presented on the device body or in its original packaging.
Kirill Semenov
I measure this parameter regularly. One day it got too big. It took me a long time to figure out the reason, and then I realized that something had happened to the coating. I didn’t understand why, but I quickly corrected it. I just replaced the element. The ignition is still fine, so you can do this.
Alexander Rasskazov
I constantly take care of my car’s battery, because I’m afraid that it won’t start in the most inappropriate situation. I measure all parameters, including this one. This is the only way to fully understand the situation and track changes. This is important for diagnosing possible problems and malfunctions.
Victor Kuznetsov
Previously, I didn’t understand how to find out what the internal resistance of a battery is.
As it turned out, the procedure is very simple - certainly no more difficult than measuring the full capacity. The procedure takes only a few minutes. Only the lamps you need are not LED, but ordinary ones. Andrey Kazakov
A few words about AGM and EFB
These batteries are made using different technologies. As many manufacturers write, the lead used is different – more purified. So the electrolyte is in a different state (especially for AGM).
All this allows you to reduce the internal resistance of the battery:
So the 60Ah version, AGM , has an indicator of approximately 3 - 4 mOhm,
Version 60Ah, EFB - indicator approximately 4 - 5 mOhm
This is better than a regular battery (4 - 7 mOhm). Moreover, AGM can have such resistance for a very long time, the whole point is that there the electrolyte is in special mats that come into direct contact with the plates and the sulfation process there is not so obvious.
How to take measurements
Purchasing an industrial meter to check the internal resistance of batteries is not a very rational decision for a car enthusiast.
To make the most accurate measurements, you will need to use discharge curve graphs. And this is impossible to implement in a garage environment. The impedance will be influenced by the degree of charge of the battery, the applied load, temperature indicators, etc.
Therefore, a simplified internal resistance tester is used, with which the motorist can find out for himself about the condition of his battery.
In this case, you can use a car headlight (not LED) of about 60 W and a multimeter.
- the light bulb and multimeter are connected in series with the battery;
- values are read from a voltmeter with a connected load;
- the load is disconnected and the voltage is checked without it;
- values are compared.
Calculations are performed based on Ohm's law. If the voltage difference is up to 0.02 V, then the condition of the battery can be described as good. That is, here the internal resistance does not exceed 0.01 Ohm.
When checking, it is most convenient to use a digital multimeter or voltmeter, since pointer meters cannot give an accurate result.
If such a check does not suit you for one reason or another, or you are not sure of the correctness of the measurements taken, you can always contact a specialist. For a fee, using special equipment, they will conduct a comprehensive diagnostics of the battery, draw conclusions about its current condition, and indicate the exact values of internal resistance.
In specialized auto repair shops, several testers are used.
- Load fork. Used to check voltage parameters. With their help, you can set a certain load and read the operating parameters of the battery.
- Devices that allow you to establish a relationship between the internal resistance parameter and the battery condition.
- Spectrum meters. With their help, conductivity is determined under direct and alternating current conditions.
All these measuring devices, to one degree or another, help to measure the internal resistance in batteries. The task of the testers is to determine the performance of the battery, its current capacity, the time spent on charging and discharging. All these meanings are related to each other. But some to a greater extent, and some to a lesser extent.
Battery resistance table
| Capacity (Ah) | Normal (new) battery (mOhm) | After 5 years, average data, (mOhm) |
| 60 | 4 — 7 | 6 – 13 |
| 75 | 3 — 7 | 4,5 – 13 |
| 80 | 3 — 6 | 4,5 – 12 |
| 90 | 3 — 6 | 4,5 – 12 |
The table is made for ordinary batteries with liquid electrolyte inside. The second column is an estimate of what your batteries may have. A large spread, for example from 6 to 13 mOhm, only because the initial data is different. One battery is ideal, it has 4 mOhm, you have looked after it well, so the degradation rate is only 10% per year. This means that after five years we should expect resistance from sulfation of only 6 mOhm.
The other one initially has - 7 mOhm, you didn’t take good care of it, left it (for a long time without a charge) after the motor did not start in the cold. Its sulfation process is much higher, and 13 mOhm is not the limit. This is exactly the run-up that I included in both columns of the table.
Now watch the detailed video
Now I think it’s clear to you why the internal resistance of a battery is a very important indicator that can tell you almost 100% about the condition of both a new and used battery. The main thing is to take measurements correctly.
Similar news
- Can the battery charge itself? Let's say in the warmth or in the summer? T…
- What is an AGM battery? 8 fundamental differences of this technology...
- How much lead is in the battery. We look at car options...
NiMH batteries, how to extend their service life
We use more and more mobile technology. It uses batteries that allow you to increase its use time and work on one set for a long time (more than 500 charge-discharge cycles). Since the actual number of cycles is often much less, the question arises, why? I would like to talk about it briefly and clearly, but to understand the problem you need to understand some basics. For those for whom these basics are too complicated, read immediately the “Conclusion”, which briefly outlines the recommendations.
Like all radio-electronic and electrical components, chemical power sources and batteries in particular have varying characteristics. It is determined by the accumulation of errors at each technological stage of production. And despite the fairly high quality of the technology, ultimately the spread in the characteristics of batteries from the best manufacturers is up to 6.5% (and may be lower than stated) [L.1].
The spread of characteristics is important for the longevity of batteries when working as part of a battery, since poor charging increases it even more.
Internal resistance has the greatest influence on this.
So why?
Because now, to power electronics, batteries are used, usually containing 2, 4, 6 or more elements connected in series. This is required to obtain the voltage required for the electronic device. Moreover, there are now publications on the parallel connection of cells and batteries, which is used to increase the operating time of devices by increasing the capacity of the battery; previously, parallel connection was not allowed at all, due to the large variation in capacity.
I once came across recommendations that read:
“When combining elements of NiCd batteries into batteries, it is necessary to select batteries with the same internal resistance into the group. Parallel connection of batteries is not permitted"
Current recommendations:
“Batteries with increased operating voltage, at high load currents, can be collected by sorting batteries according to the internal resistance parameter”
With the exception of the last instruction for NiCd batteries, both before and now the general recommendation is the same - to select batteries with the same internal resistance for a battery with a series connection. The difference is one thing: previously the spread of internal resistance reached 20%, but now, with the qualitative growth of technology, it is up to 6.5%.
But despite this, with each charge-discharge cycle, the difference (internal resistance and capacity) between the batteries in the battery increases by 1.5 - 3%. And so on every cycle.
Therefore, to reduce this scatter, it is necessary to carry out battery training after 5-8 charge-discharge cycles.
It is the spread of internal resistance that has a significant impact on the longevity of the battery, which is determined by the longevity of any of its worst elements.
Some publications write:
“during the discharge process, Ri changes differently: in the discharge range from 0 to 50-60% it noticeably decreases, in the second half of the discharge it increases”
In reality, the change in Ri during the discharge process has the form shown in Fig. 1.
Picture 1.
A fully charged battery (freshly charged) has a minimum internal resistance, then it grows quickly and, reaching a certain value (at approximately 10% capacity), the growth rate drops and in the range from 10% to 90% capacity Ri changes slightly and is equal to the nominal (average) Ri. Further (when the battery voltage reaches less than 1.05 V) Ri quickly increases. Operating the battery in this area is not recommended.
This characteristic is given for a discharge current equal to 1C.
At other discharge currents, the characteristic has a similar character, but with a tendency for the central section to narrow and its steepness to increase with increasing load current. And vice versa at lower load currents.
Dependence of Ri on capacitance?
Battery internal resistance
Internal resistance
The battery characterizes its ability to transfer the energy stored in it to the load, and is determined by the formula:
Ri = E/Isc [1]
where: E - battery emf or open circuit voltage (xx), Is - short circuit current.
The greater the internal resistance of the element Ri, the less energy it can transfer to the load due to the voltage drop across its internal resistance.
Measuring internal resistance using this formula is easy to do, but operating the battery in short circuit mode is not recommended by the manufacturer.
Therefore, in practice, a different measurement method is used. The load current is measured at two load resistance values. The maximum load current I2 and some intermediate value I1.
Ri = (U1 – U2)/(I2 – I1), [2]
where: - U1 is the voltage at current I1, and U2 is the voltage at current I2, and I2 > I1.
From formula 2, one can obtain a practical option, when the EMF of the element (E) and the voltage on the element (U2) and current at rated load (Inom) are measured. After measurement, the internal resistance is calculated using formula 4.
Ri = (E – U2)/I2, [3]
Therefore, the voltage on the battery (U2) at the rated current (Inom = I2) is the best criterion for discharging the battery.
The internal resistance changes as the battery cell discharges. The general trend is an increase in internal resistance as the battery discharges (about 4-8 times). Therefore, the presence of at least one incompletely charged element in the battery leads to a drop in voltage at the battery terminals and premature activation of the discharge alarm when most batteries are not completely discharged.
Figure 2.
Discharge characteristics of batteries.
We must remember that in all electronic devices, be it a camera, a cell phone or a laptop, the criterion for battery discharge is the voltage drop across the load below a certain value, depending on the number of batteries. Based on 1V per battery.
In a series battery of cells, an increase in the internal resistance of one cell results in a proportional increase in the total internal resistance.
Therefore, if a battery of rechargeable cells has at least one cell with high internal resistance or is not fully charged, this leads to its complete discharge, while the remaining cells are not completely discharged. In this case, the electronic device that is powered detects a low voltage and issues a “Charge the battery” signal.
Charging such an element in a standard charger, paired with an under-discharged element, leads to overcharging of the charged element and again to incomplete charging of the element with high internal resistance.
This shortens the life of an incompletely discharged element.
How to charge NiMH cells used in batteries to maintain their longevity?
Main.
Since batteries release charge individually during operation and this difference increases with each cycle, each such element must be serviced individually.
In this case, the charging cycle of each element must include its preliminary discharge to a given level (1.05 V at rated load current). During the discharge process, faulty elements whose voltage is lower than the specified one can be rejected.
Charging is also performed individually for each element, with individual shutdown when it reaches the nominal capacity. Such charging will completely eliminate the recharging of the cells and significantly extend their service life.
This mode is needed even for charging high-quality elements, and even more so for elements with a wide range of characteristics.
Are there chargers that provide this mode?
Of the chargers that I came across while using all my electronic devices, there was not a single one that met these requirements.
In the best chargers, there is no discharge of elements, although practice shows that the usual underdischarge is up to 30%. In all chargers, cells are charged in pairs. I even came across one charger where all 4 elements are charged from one source.
Therefore, almost 4 sets (4 cells each) failed prematurely when using standard (same manufacturer as the cells) chargers.
Each set withstood a maximum of 15 - 20 charges.
In order not to create advertising, I will not talk here about specific models of chargers, I can only say that they exist. There are few of them and their prices are more than 1000 rubles. (please don't choose a charger based on price) but they are worth it. One of the external features of such a charger is a display with complete information about each battery. (Operating mode “charge-discharge”, and the amount of charge on the battery)
Each element must be charged individually. (The instructions do not specify where to include the battery cells when charging 1, 2, 3, 4 cells).
If there is no such charger, then the lot of the battery owner is to train it.
Battery training
What is training?
This is a charge-discharge cycle while monitoring the final voltage on each battery (1V) and charging it to its rated capacity.
Battery training should be carried out:
- For storage or rare use - 2-3 training cycles - once a month,
- During operation - 2-3 at 8 - 10 working cycles Z-R.
- With super fast charging, every 4 - 5 work cycles, 2-3 cycles of training are carried out in nominal mode.
My experience
I bought battery-charger kits from one manufacturer, reasonably hoping that the manufacturer, in order not to lose face, would make a competent charger for its batteries.
GP PowerBank Rapid 2 charger set with 4 GP batteries with a capacity of 2500 mAh
No discharge, charging in pairs of 2 batteries.
DESAY Full-Power Harger charger kit with a set of 4 Duracell 2500 mAh batteries
The manufacturer declares individual charging of each battery, with a training mode. In reality, charging in pairs with individual control of the charging of each element. It failed while charging and damaged a couple of batteries.
Batteries cannot be discharged below 1.05 V; the share of recoverable batteries when they are discharged to 0.9 V is up to 40%. Or batteries discharged to 0.9 V or less can be considered irreparable under normal conditions. Some craftsmen talk about restoring completely discharged (up to 0.4 V) batteries.
Conclusion
There are often recommendations to use chargers and batteries from the same manufacturer, but following this recommendation, as practice shows, does not always solve the problem.
To prevent you from finding yourself with a battery-powered device that suddenly fails, you should adhere to certain rules:
- You must follow the manufacturer's recommendations and instructions and keep your batteries clean and at the temperature recommended by the manufacturer.
- Before use, a new battery must be charged for 14-16 hours in slow (trickle) charging mode to obtain maximum capacity and optimal battery performance in the future. Charging with a current of 1/10 Cn is usually safe for any battery;
- It is advisable to avoid overdischarges (below 1.05 V) and short circuits.
- It is recommended to avoid a combination of used and unused batteries.
- The battery requires periodic training (even in the best charger, in this case, once every 3-4 months).
- When charging a battery installed in a portable device, it is advisable to turn off the device to ensure the most complete charge.
In order not to perform a workout, you need a charger that should provide:
Rejection of faulty batteries – (there must be a specific indication in the description),
Charging mode selection: Fast charging (1-2 hours), Fast charging (3-5 hours), Slow charging (12-18 hours),
Automatic discharge of each battery (up to 20% of the nominal capacity or 1.05 V) - (there must be a specific indication in the description),
Individual charging of each element with automatic termination due to negative dU (ΔU) – (there must be a specific indication in the description). They often write “it is possible to charge 1 battery,” but it is better when it specifically states “individual charging of each element.
If you are not in a hurry, avoid chargers with super fast charging (within an hour or two). Practice shows that such devices are short-lived. There is nothing stopping you from charging your batteries overnight.
These conditions are met by many “smart” chargers that have a higher price. But don’t skimp on the charger; if you save, you’ll lose on batteries.
But a high price is not a guarantee of quality!
Read the descriptions carefully!
The reason for the fragility of chargers with ultra-fast charging mode is that when quickly charging batteries, the charging current is numerically equal to 1-2 C (C is the battery capacity). For example, to charge a battery with a capacity of 2500 mAh, a charging current of 2.5 - 5A is required. This is about 6-13 W per channel and in total about 24-52 W only for charging batteries. The very real figure given in one of the descriptions is the power consumption of 50 W. Up to 80% of this power turns into heat, and this is in a small box often with poor ventilation. Yes, and batteries do not like overheating, and at high charging currents it can happen.
And controlling a charging current of several amperes is a non-trivial task. After all, this means that the charging control circuits for each battery must be designed for this current.
Tested for yourself!
My DESAY Full-Power Harger fast charger of this type failed after 4 charges (after opening it, it turned out that it had already been repaired before being sold in the store). The chip of one of the two charging channels has visually burnt out. As a result, this channel stopped turning off automatically (even the end of charging indication does not work) and as a result, the batteries failed.
Most of the problems with repairs sorted out on the Internet relate specifically to such “fast memory”.
Therefore, I would recommend smart chargers with an accelerated (4-5 hours) charging mode, or better yet a normal (15 hour) charging mode. Like more reliable. At the same time, there is less heating of the batteries and lower charging currents, which has a positive effect on the reliability of the batteries and charger, and even with slow charging, the batteries accept a more complete charge.
As for the long wait for charging, if you use your electronics intensively, it is better to have a backup set of batteries.
PS
Food for thought.
Typical characteristics of sealed alkaline batteries
| Characteristics | NiMH batteries |
| Specific energy Ah/kg | 40-80 |
| Operating temperature range deg. WITH | -10 -:- +40 |
| Maximum discharge current, fractions C (capacity) | 2C, 3C |
| Self-discharge within 1 month, % of capacity | 20 -:- 40 |
Pay attention to the last line of the table - from 2 to 4 months and the battery is discharged without working for a minute during storage.
Batteries are designed to power actively working devices; if you work with your electronic device periodically (rarely), then it is better to use simple batteries; they can be stored for about a year.
Literature:
- Comparative performance of commercial sealed alkaline batteries. Author Taganova A.A., 09/18/2006, https://www.megaron.su/content/view/16/18/
- About battery recovery. Translation and technical editing by Vladimir Vasiliev, https://infoart.iip.net/tech/battery/recovery.htm
- Method for checking the performance and capacity of batteries https://bbs.radiolink.ru/forum/showthread.php?t=7678
- Computer press, No. 11, 2006, Modern batteries, Oleg Tatarnikov, https://www.compress.ru/Article.aspx?id=16846&iid=781
Checking the actual battery capacity
To measure such an important parameter as the actual capacity of the battery, you only need to have connecting wires and a load of known power (or known resistance) in the multimeter kit. In this capacity, it is very convenient to use 12-volt car bulbs:
- they are sold at any auto store;
- You can dial the battery to any desired power and set any discharge current.
In addition, lamps as a load stabilize the current. As the voltage at the battery terminals decreases, the threads cool down somewhat, their resistance decreases, and the current decreases slightly. This improves measurement accuracy. But LED devices are not suitable for these purposes - they have too little power consumption, and you will need too many of them. We need to look for incandescent lamps.
It should be remembered that the capacity depends on the current with which the battery is discharged. The declared power is declared when the battery is discharged with a current of 5% of the nominal value. It is necessary to select the power of the lamps so as to obtain such a current. For example, for a battery with a capacity of 60 A*h, it is optimal for measurement to discharge with a current of 3 A. To do this, the power of the lamps at a voltage of 12 volts should be P=U*I=12*3=36 watts. You can take three 12-watt lamps or two 18-watt lamps, etc. There is no need to particularly strive for accuracy - the exact capacity is still unknown, it just needs to be found out.
Battery capacity measurement circuit
Before measurement, you must fully charge the battery and assemble the circuit as shown in the figure. The start time of the discharge must be recorded. If you have two multimeters, you can measure current with one, voltage with the other, or you can periodically connect the tester either as a voltmeter or as an ammeter. Results should be recorded every 30-60 minutes, and when the level reaches 11.5 volts - every 10-15 minutes. When the voltage drops to 10.5 volts, the discharge must be stopped and the time of its end recorded. The actual capacity is calculated using the formula C=I*t, where:
- I – average current in amperes;
- t – discharge time in hours.
Battery charge level
Using a tester in voltmeter mode, you can check how charged the battery is. The level of stored energy is uniquely determined by the voltage at the battery terminals at idle:
- if the voltage is 12.6 volts or higher, the battery is charged at 100;
- 12.3... 12.6 volts – charge level 75%;
- 12.1…12.3 volts – 50%;
- 11.8…12.1 volts – 25%;
- 10.5…11.8 volts – the battery is completely discharged;
- less than 10.5 volts – deep discharge.
Before checking without removing it from the car, you must disconnect the positive terminal (or better yet, the negative terminal too).